Diagnostics 2021, 11(10), 1878; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101878 - 12 Oct 2021
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 2963
Abstract
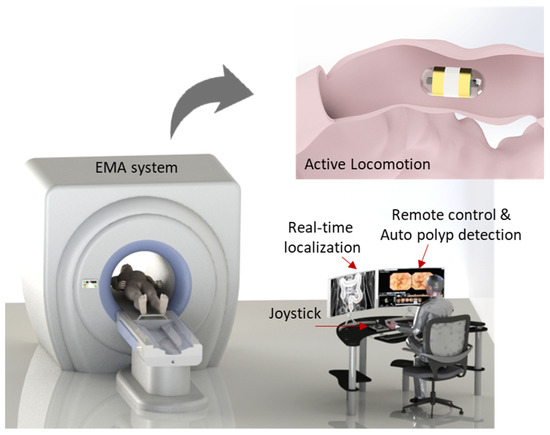
This paper presents an active locomotion capsule endoscope system with 5D position sensing and real-time automated polyp detection for small-bowel and colon applications. An electromagnetic actuation system (EMA) consisting of stationary electromagnets is utilized to remotely control a magnetic capsule endoscope with multi-degree-of-freedom
[...] Read more.
This paper presents an active locomotion capsule endoscope system with 5D position sensing and real-time automated polyp detection for small-bowel and colon applications. An electromagnetic actuation system (EMA) consisting of stationary electromagnets is utilized to remotely control a magnetic capsule endoscope with multi-degree-of-freedom locomotion. For position sensing, an electronic system using a magnetic sensor array is built to track the position and orientation of the magnetic capsule during movement. The system is integrated with a deep learning model, named YOLOv3, which can automatically identify colorectal polyps in real-time with an average precision of 85%. The feasibility of the proposed method concerning active locomotion and localization is validated and demonstrated through in vitro experiments in a phantom duodenum. This study provides a high-potential solution for automatic diagnostics of the bowel and colon using an active locomotion capsule endoscope, which can be applied for a clinical site in the future.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Capsule Endoscopy: Clinical Impacts and Innovation since 2001)
►
Show Figures