1
State Key Laboratory of Robotics, Shenyang Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenyang 110016, China
2
Institutes for Robotics and Intelligent Manufacturing, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenyang 110169, China
3
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
Machines 2022, 10(10), 905; https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10100905 - 8 Oct 2022
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 3584
Abstract
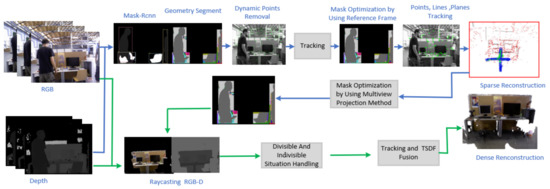
Reverse engineering is an important process of real model digitization. However, the existing methods are limited by the characteristics of the modeling object; the modeling is low efficient, has poor versatility, and unstable accuracy. To complete the reverse engineering of a real workpiece
[...] Read more.
Reverse engineering is an important process of real model digitization. However, the existing methods are limited by the characteristics of the modeling object; the modeling is low efficient, has poor versatility, and unstable accuracy. To complete the reverse engineering of a real workpiece with irregular deformation based on the ideal computer-aided design (CAD) model, a high-precision reverse engineering method of the workpiece based on the CAD model prior was presented. Through the registration of the ideal CAD model and the point cloud model of the real workpiece, the geometric feature position information and feature constraint information contained in the CAD model are transmitted to the modeling process, which helps to improve the accuracy and efficiency of reverse engineering. This method is applied to the reverse engineering process of the engine compartment with slight irregular deformation, the modeling accuracy reaches 0.04 mm, and the high-precision reverse engineering of the engine compartment is successfully realized.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Advanced Manufacturing)
▼
Show Figures