Cancers 2021, 13(20), 5131; https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13205131 - 13 Oct 2021
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 9141
Abstract
Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) is defined as the presence of a monoclonal protein (M-protein) produced by a small amount of plasma cells. The majority of patients remain asymptomatic; however, a fraction of them develop clinical manifestations related to the monoclonal gammopathy
[...] Read more.
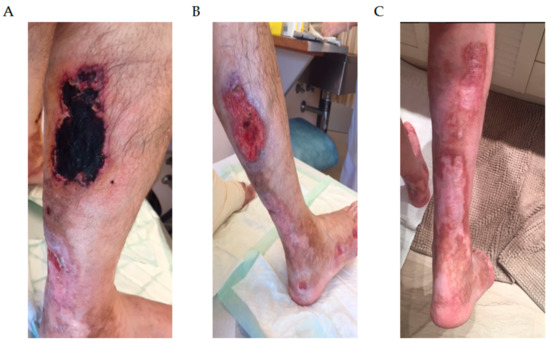
Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) is defined as the presence of a monoclonal protein (M-protein) produced by a small amount of plasma cells. The majority of patients remain asymptomatic; however, a fraction of them develop clinical manifestations related to the monoclonal gammopathy despite not fulfilling criteria of multiple myeloma or other lymphoproliferative disorder. These patients constitute an emerging clinical issue coined as monoclonal gammopathy of clinical significance (MGCS). The mechanisms involved are poorly understood, and literature is scarce regarding management. The clinical spectrum involves symptoms related to renal, neurologic, skin, ocular, or bleeding manifestations, requiring a multidisciplinary approach. Treatment strategies rely on the basis of symptomatic disease and the M-protein isotype. In this review, we focus on MGCS other than renal, as the latter was earliest recognized and better known. We review the literature and discuss management from diagnosis to treatment based on illustrative cases from daily practice.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Emerging Treatment Strategies for Multiple Myeloma)
►
Show Figures