1
School of Geomatics, Liaoning Technical University, Fuxin 123000, China
2
Chinese Academy of Surveying and Mapping, Beijing 100039, China
Sustainability 2023, 15(7), 5955; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075955 - 29 Mar 2023
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 2939
Abstract
Managing the human–nature relationship is key to facilitating the sustainable development of cities. The coupled coordination relationship between ecological civilization construction and urban green development and influence of spatio-temporal heterogeneity has been insufficiently studied. We used the coupled coordination degree model (CCDM) and
[...] Read more.
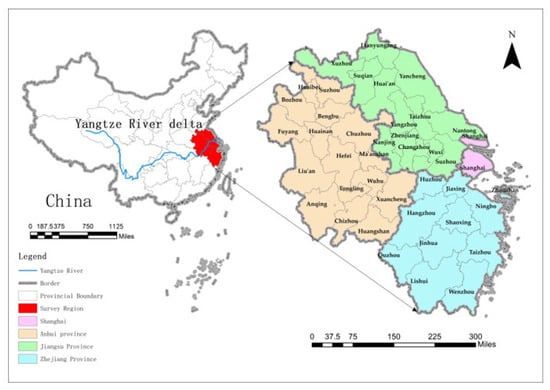
Managing the human–nature relationship is key to facilitating the sustainable development of cities. The coupled coordination relationship between ecological civilization construction and urban green development and influence of spatio-temporal heterogeneity has been insufficiently studied. We used the coupled coordination degree model (CCDM) and spatio-temporal weighted model (GTWR) to analyze the relationship and heterogeneity between ecological civilization construction and UGD and ECC in each city in the Yangtze River Delta region from 2010 to 2019. The results show that: (1) UGD and ECC coordination levels fluctuated more from 2010 until 2019. There was a transition from lagging UGD and ECC to lagging ecological civilization construction and a decreasing degree of coupling coordination in the Yangtze River Delta region from east to west from near imbalance to primary coordination. (2) The Yangtze River Delta’s negative UGD and ECC effect was concentrated in northwest inland cities; the positive UGD and ECC effect was concentrated in southeast coastal cities. Thus, UGD and ECC and ecological civilization construction complement each other. This study provides a scientific basis for analyzing the coordination between ecological civilization construction and UGD and ECC and provides practical guidance for formulating and implementing urban high-quality development countermeasures.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Urban Green Development and Resilient Cities)
▼
Show Figures