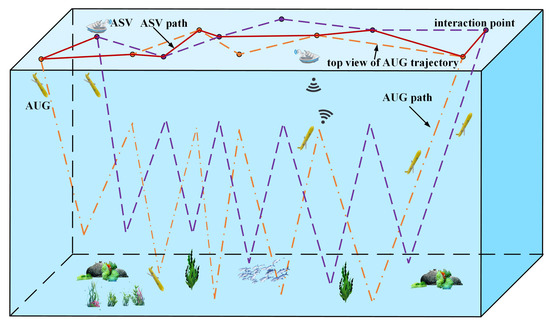
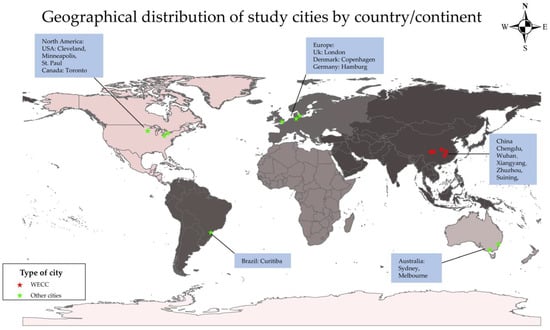
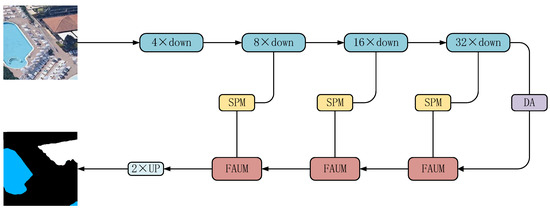
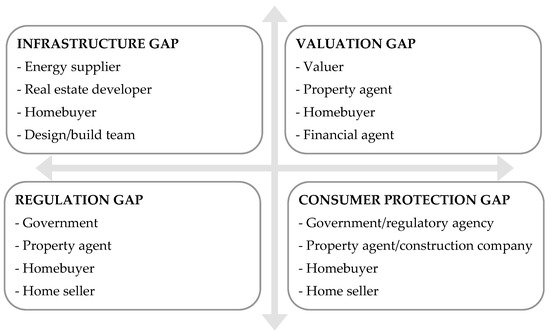
Sustainability 2023, 15(4), 3180; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043180 - 9 Feb 2023
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 3385
Abstract
In the international debate, the relationship between sustainable management in agriculture and the enhancement of landscapes is recent and is discussed in various international agendas. These objectives are connected to a growing demand for sustainable agricultural practices, quality productions, and ecosystem services in
[...] Read more.
In the international debate, the relationship between sustainable management in agriculture and the enhancement of landscapes is recent and is discussed in various international agendas. These objectives are connected to a growing demand for sustainable agricultural practices, quality productions, and ecosystem services in which farmers and institutions play a strategic role. According to the literature and international guidelines, new functions, and territorial connections can produce added value, especially in marginal rural areas. In this study, the aim is to investigate the factors that allow potential spatial concentrations for sustainable rural development to be identified, placing the landscape at the center of the research. Starting from a literature review, we select specific indicators and variables and analyze them combining Principal Component Analysis and cartographic analysis. The method applied to a region of significant importance in Italy, Apulia, has highlighted the importance of specific factors and significant imbalances, especially in marginal municipalities. The method, applicable in different regional contexts, can represent a useful policy tool, especially in marginal rural areas because it allows us to identify the geography of socio-economic spatial concentrations, suggesting interventions and actions in line with international agendas, such as Common Agricultural Policy reform and Green Deal.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Rural Development Practices and Results: Learnings and Results from Policies and Initiatives)
►
Show Figures