1
School of Economics, Hainan University, Haikou 570228, China
2
Management School, Hainan University, Haikou 570228, China
Sustainability 2022, 14(12), 7461; https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127461 - 18 Jun 2022
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2444
Abstract
▼
Show Figures
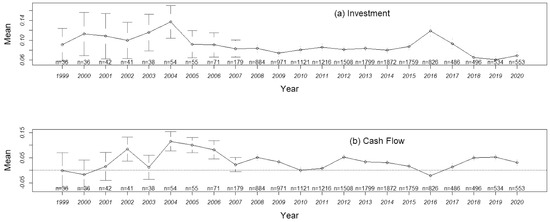
The ability of using internally generated funds to finance investments affects corporate sustainability. We empirically examine trends and gaps in the reliance of company’s investments on internally generated funds. We collect financial data of Chinese listed companies from 1998 to 2020, use corporate
[...] Read more.
The ability of using internally generated funds to finance investments affects corporate sustainability. We empirically examine trends and gaps in the reliance of company’s investments on internally generated funds. We collect financial data of Chinese listed companies from 1998 to 2020, use corporate cash flow as a proxy for internally generated funds, control for corporate investment opportunity Q, and specify a two-way fixed effects model of investment on cash flow. We find that investment-cash flow sensitivity exhibits a decreasing trend over time; firm size, government equity, and the HP and WW indices effectively explain the gaps in the sensitivity of investment to cash flow between two types of firms with tighter and looser financing constraints, but cash dividends do not explain the gaps; and the gaps in the sensitivity of investment to cash flow are narrowing in the long term. These empirical findings indicate that compared to external funding, internal funding is becoming less important in supporting a firm’s investment-induced sustainability.
Full article