Department of Management, Sunway University Business School (SUBS), Sunway University, No 5, Jalan Universiti, Bandar Sunway, Selangor Darul Ehsan 47500, Malaysia
Sustainability 2021, 13(9), 5025; https://doi.org/10.3390/su13095025 - 30 Apr 2021
Cited by 40 | Viewed by 5654
Abstract
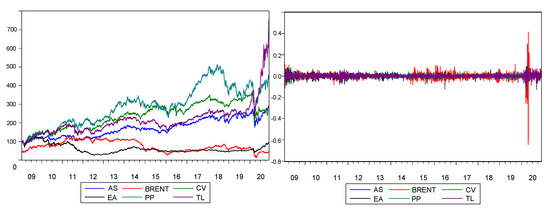
This study investigated the impact of entrepreneurial attitude, perceived desirability, and perceived feasibility on sustainable entrepreneurship intentions under the moderating impact of entrepreneurial passion among undergraduate students of Malaysia. It was a quantitative study that compared two groups of students, i.e., Group A,
[...] Read more.
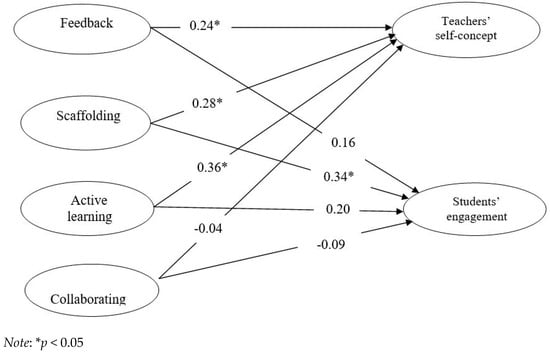
This study investigated the impact of entrepreneurial attitude, perceived desirability, and perceived feasibility on sustainable entrepreneurship intentions under the moderating impact of entrepreneurial passion among undergraduate students of Malaysia. It was a quantitative study that compared two groups of students, i.e., Group A, comprised of students who have studied entrepreneurship modules and whose programmes did not offer any dual/triple award degrees and Group B, made up of students who have studied entrepreneurship modules and whose programmes offered dual/triple award degrees. Data were collected from 542 undergraduate students of universities located in Kuala Lumpur and Selangor through survey questionnaire. WarpPLS Software version 7.0 was used to analyse the data. The findings of this study revealed that Group B students’ entrepreneurial attitude, perceived desirability, and perceived feasibility positively and significantly impacted the sustainable entrepreneurship intentions under the moderating impact of entrepreneurial passion. However, the impact of entrepreneurial attitude was found positive and significant on sustainable entrepreneurship intentions among students of Group A and entrepreneurial passion was found to be significant moderator to improve the impact of only entrepreneurial attitude and perceived desirability on sustainable entrepreneurship intentions but not for the impact of perceived feasibility on sustainable entrepreneurship intentions among these students. Moreover, the direct impacts of perceived desirability and perceived feasibility were also found non-significant on sustainable entrepreneurship intentions among Group A students. The findings reveal that universities having partnership with other overseas’ universities may offer high quality entrepreneurship modules due to which their students have high entrepreneurial passion and develop more entrepreneurial attitudes, and are more willing and capable to start their own businesses as compared to students of other local universities who have no partnership with overseas’ universities.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Entrepreneurial Education Strengthening Resilience, Societal Change and Sustainability)
▼
Show Figures