Sustainability 2020, 12(11), 4484; https://doi.org/10.3390/su12114484 - 1 Jun 2020
Cited by 48 | Viewed by 7114
Abstract
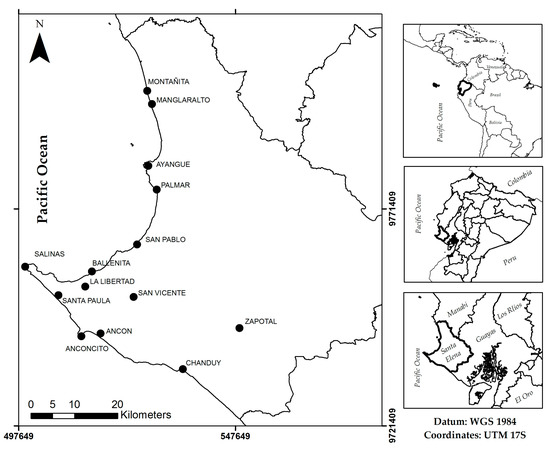
Santa Elena Peninsula is characterized by beautiful geological features, historical geoscientific knowledge, and mineral and tourism resources that could all be combined for the sake of community development. This article provides an overview of the Santa Elena Peninsula Geopark Project through the assessment
[...] Read more.
Santa Elena Peninsula is characterized by beautiful geological features, historical geoscientific knowledge, and mineral and tourism resources that could all be combined for the sake of community development. This article provides an overview of the Santa Elena Peninsula Geopark Project through the assessment of six areas that are considered by inhabitants and researchers possible geosites to foster geotourism. The methodology included: (i) a technical description and assessment of the areas of interest evaluating their geological relevance, representativeness, geotouristic prominence, geotouristic scientific interpretation, and conservation criteria; (ii) an assessment through questionnaires carried out on inhabitants; and (iii) a SWOT Plus analysis to propose strategies for promoting geotourism. Results show that the areas of interest are highly valued as geosites, since they integrate geodiversity, biodiversity, and sociocultural aspects. For example, Ancon is a historical icon of early oil exploitation, Baños de San Vicente is a natural spring of thermal water and mud volcano, and Anconcito has bituminous exudations of natural occurrence together with a spectacular landscape produced by erosion. Overall, 90% of these sites were proved to be of high and very high interest in scientific terms. Geotourism is believed to be beneficial for the inhabitants of the Santa Elena Peninsula with respect to education, valorization of resources, and the strengthening of cultural identity of communities.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Natural Resources of Tourism: Towards Sustainable Exploitation on Regional Scale)
►
Show Figures