Sensors 2021, 21(14), 4661; https://doi.org/10.3390/s21144661 - 7 Jul 2021
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 5000
Abstract
Loss-of-balance (LOB) events, such as trips and slips, are frequent among community-dwelling older adults and are an indicator of increased fall risk. In a preliminary study, eight community-dwelling older adults with a history of falls were asked to perform everyday tasks in the
[...] Read more.
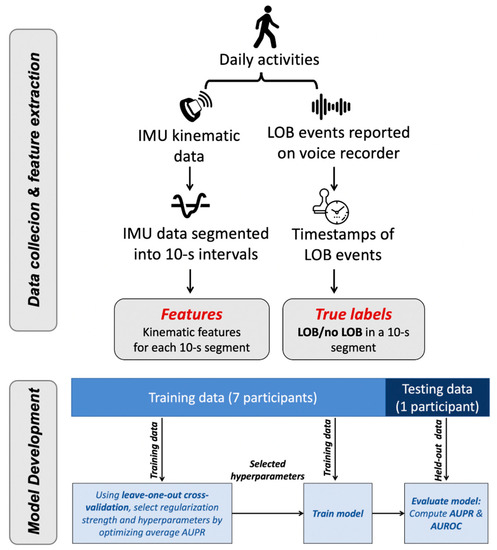
Loss-of-balance (LOB) events, such as trips and slips, are frequent among community-dwelling older adults and are an indicator of increased fall risk. In a preliminary study, eight community-dwelling older adults with a history of falls were asked to perform everyday tasks in the real world while donning a set of three inertial measurement sensors (IMUs) and report LOB events via a voice-recording device. Over 290 h of real-world kinematic data were collected and used to build and evaluate classification models to detect the occurrence of LOB events. Spatiotemporal gait metrics were calculated, and time stamps for when LOB events occurred were identified. Using these data and machine learning approaches, we built classifiers to detect LOB events. Through a leave-one-participant-out validation scheme, performance was assessed in terms of the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) and the area under the precision recall curve (AUPR). The best model achieved an AUROC ≥0.87 for every held-out participant and an AUPR 4-20 times the incidence rate of LOB events. Such models could be used to filter large datasets prior to manual classification by a trained healthcare provider. In this context, the models filtered out at least 65.7% of the data, while detecting ≥87.0% of events on average. Based on the demonstrated discriminative ability to separate LOBs and normal walking segments, such models could be applied retrospectively to track the occurrence of LOBs over an extended period of time.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Wearable Sensors for Gait and Falls Monitoring)
►
Show Figures