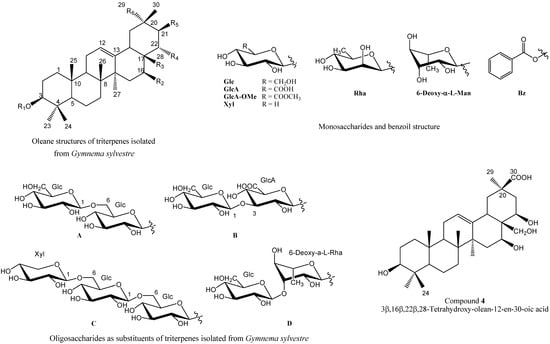
Molecules 2013, 18(12), 15080-15093; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181215080 - 6 Dec 2013
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 6403
Abstract
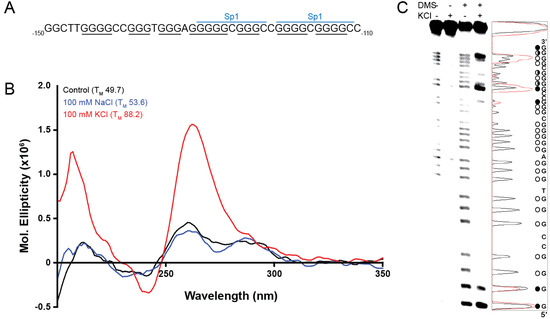
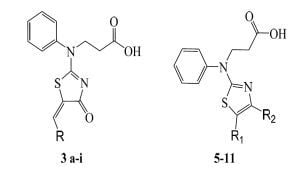
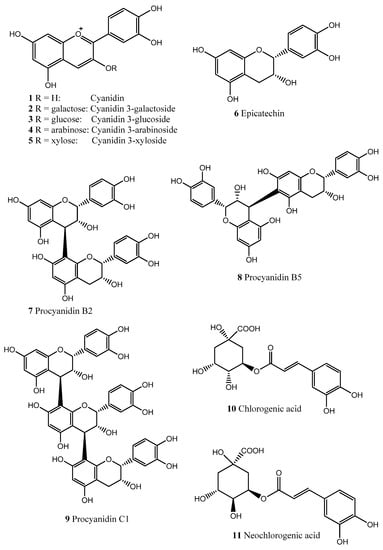
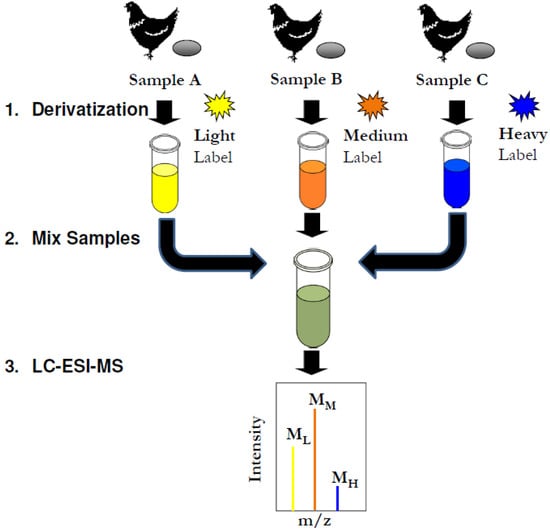
Ethyl 2,3-diendo-3-aminobicyclo[2.2.2]oct-5-ene-2-carboxylate ((±)-1) was resolved with O,O'-dibenzoyltartaric acid via diastereomeric salt formation. The efficient synthesis of the enantiomers of 2,3-diendo-3-aminobicyclo[2.2.2]oct-5-ene-2-carboxylic acid ((+)-7 and (–)-7), 3-endo-aminobicyclo[2.2.2]oct-5-ene-2-exo-carboxylic acid ((+)-
[...] Read more.
Ethyl 2,3-diendo-3-aminobicyclo[2.2.2]oct-5-ene-2-carboxylate ((±)-1) was resolved with O,O'-dibenzoyltartaric acid via diastereomeric salt formation. The efficient synthesis of the enantiomers of 2,3-diendo-3-aminobicyclo[2.2.2]oct-5-ene-2-carboxylic acid ((+)-7 and (–)-7), 3-endo-aminobicyclo[2.2.2]oct-5-ene-2-exo-carboxylic acid ((+)-5 and (–)-5), cis- and trans-3-aminobicyclo[2.2.2]octane-2-carboxylic acid ((+)-6, (–)-6, (+)-8 and (–)-8) was achieved via isomerization, hydrogenation and hydrolysis of the corresponding esters (–)-1 and (+)-1. The stereochemistry and relative configurations of the synthesized compounds were determined by NMR spectroscopy (based on the 3J(H,H) coupling constants) and X-ray crystallography.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Organic Chemistry)
►
Show Figures