Molecules 2011, 16(11), 9340-9356; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16119340 - 7 Nov 2011
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 7796
Abstract
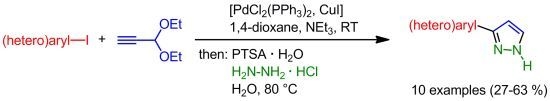
A novel consecutive three-component synthesis of 3-(hetero)aryl-1H-pyrazoles via room temperature Sonogashira arylation of propynal diethylacetal used as a propargyl aldehyde synthetic equivalent has been disclosed. The final acetal cleavage-cyclocondensation with hydrazine hydrochloride at 80 °C rapidly furnishes the title compounds in
[...] Read more.
A novel consecutive three-component synthesis of 3-(hetero)aryl-1H-pyrazoles via room temperature Sonogashira arylation of propynal diethylacetal used as a propargyl aldehyde synthetic equivalent has been disclosed. The final acetal cleavage-cyclocondensation with hydrazine hydrochloride at 80 °C rapidly furnishes the title compounds in a one-pot fashion.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Multicomponent Reaction)
►
Show Figures