-
 Advancing Energy Management Strategies for Hybrid Fuel Cell Vehicles: A Comparative Study of Deterministic and Fuzzy Logic Approaches
Advancing Energy Management Strategies for Hybrid Fuel Cell Vehicles: A Comparative Study of Deterministic and Fuzzy Logic Approaches -
 Analytical Modelling of Arc Flash Consequences in High-Power Systems with Energy Storage for Electric Vehicle Charging
Analytical Modelling of Arc Flash Consequences in High-Power Systems with Energy Storage for Electric Vehicle Charging -
 One-Dimensional Simulation of Real-World Battery Degradation Using Battery State Estimation and Vehicle System Models
One-Dimensional Simulation of Real-World Battery Degradation Using Battery State Estimation and Vehicle System Models -
 Electromagnetic Analysis and Multi-Objective Design Optimization of a WFSM with Hybrid GOES-NOES Core
Electromagnetic Analysis and Multi-Objective Design Optimization of a WFSM with Hybrid GOES-NOES Core -
 An Optimal Multi-Zone Fast-Charging System Architecture for MW-Scale EV Charging Sites
An Optimal Multi-Zone Fast-Charging System Architecture for MW-Scale EV Charging Sites
Journal Description
World Electric Vehicle Journal
World Electric Vehicle Journal
is the first peer-reviewed, international, scientific journal that comprehensively covers all studies related to battery, hybrid, and fuel cell electric vehicles. The journal is owned by the World Electric Vehicle Association (WEVA) and its members, the E-Mobility Europe, Electric Drive Transportation Association (EDTA), and Electric Vehicle Association of Asia Pacific (EVAAP). It has been published monthly online by MDPI since Volume 9, Issue 1 (2018).
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), Ei Compendex, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Engineering, Electrical and Electronic) / CiteScore - Q2 (Automotive Engineering)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 17.6 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
2.6 (2024)
Latest Articles
Active and Reactive Power Scheduling of Distribution System Based on Two-Stage Stochastic Optimization
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(9), 515; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090515 (registering DOI) - 11 Sep 2025
Abstract
►
Show Figures
With the large-scale integration of distributed resources into the distribution network, such as wind/solar power and electric vehicles (EVs), the uncertainties have rapidly increased in the operation optimization of the distribution network. In this context, it is of great practical interest to ensure
[...] Read more.
With the large-scale integration of distributed resources into the distribution network, such as wind/solar power and electric vehicles (EVs), the uncertainties have rapidly increased in the operation optimization of the distribution network. In this context, it is of great practical interest to ensure the security and economic operation of the distribution network. This paper addresses this issue and makes the following contributions. Firstly, a two-stage stochastic rolling optimization framework for active–reactive power scheduling is established. In the first stage, it dispatches the active power of distributed resources. In the second stage, it optimizes the reactive power compensation based on the first-stage scheduling plan. Secondly, the simulation-based Rollout method is proposed to obtain the improved active power dispatching policy for cost optimization in the first stage. Meanwhile, the aggregated power of EVs can be determined based on the mobility and charging demand of EVs. Thirdly, based on the aggregated power of EVs, a scenario-based second-order cone programming is applied to perform the rolling optimization of reactive power compensation for voltage performance improvement in the second stage. The numerical results demonstrate that this method can effectively improve the economic operation of the distribution network while enhancing its operational security by leveraging the charging elasticity of EVs.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
A Novel Railgun-Based Actuation System for Ultrafast DC Circuit Breakers in EV Fast-Charging Applications
by
Fermín Gómez de León, Ara Bissal, Maurizio Repetto and Fabio Freschi
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(9), 514; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090514 - 11 Sep 2025
Abstract
This paper presents a novel ultrafast DC circuit breaker concept based on a railgun actuator, designed for ultrafast charging stations operating at 800
This paper presents a novel ultrafast DC circuit breaker concept based on a railgun actuator, designed for ultrafast charging stations operating at 800
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Fast-Charging Station for Electric Vehicles: Challenges and Issues)
Open AccessArticle
Railway Fastener Defect Detection Model Based on Dual Attention and MobileNetv3
by
Defang Lv, Jianjun Meng, Gaoyang Meng and Yanni Shen
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(9), 513; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090513 - 11 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Defect detection in rail fasteners constitutes a fundamental requirement for ensuring safe and reliable railway operations. Confronted with increasingly demanding inspection requirements of modern rail networks, traditional manual visual inspection methods have proven inadequate. To achieve accurate, efficient, and intelligent detection of rail
[...] Read more.
Defect detection in rail fasteners constitutes a fundamental requirement for ensuring safe and reliable railway operations. Confronted with increasingly demanding inspection requirements of modern rail networks, traditional manual visual inspection methods have proven inadequate. To achieve accurate, efficient, and intelligent detection of rail fasteners, this paper presents an enhanced YOLOv5m-based defect detection model. Firstly, a dual-attention mechanism comprising Squeeze-and-Excitation and Coordinate Attention modules is employed to enhance the model. Secondly, the network architecture is redesigned by adopting MobileNetv3 as the backbone while incorporating structures with Ghost Shuffle Convolution (GSConv) modules and lightweight upsampling operators to reduce computational overhead. Finally, the original CIoU loss function in YOLOv5 is replaced with SIoU to accelerate convergence rate during training. Experimental results on a custom-built rail fastener dataset comprising 6500 images demonstrate that the enhanced model achieves 96.5% mAP and 17.9 FPS, surpassing the baseline by 3.1% and 2.1 FPS, respectively. Compared to existing detection models, this solution exhibits higher accuracy, faster inference, and lower memory consumption, providing critical technical support for edge deployment of rail fastener defect detection systems.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Modelling, Analysis, and Nonlinear Control of a Dynamic Wireless Power Transfer Charger for Electrical Vehicle
by
Ahmed Hamed, Abdellah Lassioui, Hassan El Fadil, Hafsa Abbade, Sidina El jeilani, Marouane El Ancary, Mohammed Chiheb and Zakariae El Idrissi
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(9), 512; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090512 - 11 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This article presents an in-depth study of a dynamic wireless power transfer (DWPT) system used to charge electric vehicles (EVs), with a focus on modeling and controlling a double-D (DD) coil structure. The chosen DD coil design improves energy transfer efficiency and minimizes
[...] Read more.
This article presents an in-depth study of a dynamic wireless power transfer (DWPT) system used to charge electric vehicles (EVs), with a focus on modeling and controlling a double-D (DD) coil structure. The chosen DD coil design improves energy transfer efficiency and minimizes mutual coupling between adjacent transmit coils, a common problem in dynamic applications. A comprehensive mathematical model is developed to account for the nonlinear dynamics of the system, i.e., when the vehicle is moving and misalignments and coupling variations occur. A robust nonlinear control method based on sliding mode control (SMC) is implemented to ensure stable operation and accurate regulation of the output voltage. The controller is tested in different scenarios where the vehicle speed changes, thus ensuring its robustness and stability under all operating conditions. Particular attention is paid to the critical transition zone, in which the receiver coil is placed between two transmitter coils in order to achieve minimal magnetic coupling. The simulation results demonstrate that the proposed controller offers a fast dynamic response (~0.07 s) and stable voltage tracking, even in the event of significant variations in mutual inductance and different EV movement speeds. These results confirm the effectiveness of the control approach and its potential for real-time charging of electric vehicles in large-scale DWPT applications.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Remaining Useful Life Prediction of PEMFC Based on 2-Layer Bidirectional LSTM Network
by
Wenxu Niu, Xiaokang Li, Haobin Tian and Caiping Liang
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(9), 511; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090511 - 11 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) are considered promising solutions to address global energy and environmental challenges. This is largely due to their high efficiency in energy transformation, low emission of pollutants, quick responsiveness, and suitable operating conditions. However, their widespread application is
[...] Read more.
Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) are considered promising solutions to address global energy and environmental challenges. This is largely due to their high efficiency in energy transformation, low emission of pollutants, quick responsiveness, and suitable operating conditions. However, their widespread application is limited by high cost, limited durability and system complexity. To maintain system reliability and optimize cost-effectiveness, it is essential to predict the remaining operational lifespan of PEMFC systems with precision. This study introduces a prediction framework integrating a dual-layer bidirectional LSTM architecture enhanced by an attention mechanism for accurately predicting the RUL of PEMFCs. Raw data is preprocessed, and important features are selected by the smoothing technique and random forest method to reduce manual intervention. To enhance model adaptability and predictive accuracy, the Optuna optimization framework is employed to automatically fine-tune hyperparameters. The proposed prediction model is benchmarked against several existing approaches using aging datasets from two separate PEMFC stacks. Experimental findings indicate that the proposed two-layer BiLSTM with attention mechanism surpasses other baseline models in performance. Notably, the designed prediction model demonstrates strong performance on both benchmark datasets and real-world data acquired through a custom-built experimental fuel cell platform. This research offers meaningful guidance for prolonging the service life of PEMFCs and enhancing the efficiency of maintenance planning.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Fusing Direct and Indirect Visual Odometry for SLAM: An ICM-Based Framework
by
Jeremias Gaia, Javier Gimenez, Eugenio Orosco, Francisco Rossomando, Carlos Soria and Fernando Ulloa-Vásquez
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(9), 510; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090510 - 10 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The loss of localization in robots navigating GNSS-denied environments poses a critical challenge that can compromise mission success and safe operation. This article presents a method that fuses visual odometry outputs from both direct and feature-based (indirect) methods using Iterated Conditional Modes (ICMs),
[...] Read more.
The loss of localization in robots navigating GNSS-denied environments poses a critical challenge that can compromise mission success and safe operation. This article presents a method that fuses visual odometry outputs from both direct and feature-based (indirect) methods using Iterated Conditional Modes (ICMs), an efficient iterative optimization algorithm that maximizes the posterior probability in Markov random fields, combined with uncertainty-aware gain adjustment to perform pose estimation and mapping. The proposed method enhances the performance of visual localization and mapping algorithms in low-texture or visually degraded scenarios. The method was validated using the TUM RGB-D benchmark dataset and through real-world tests in both indoor and outdoor environments. Outdoor experiments were conducted on an electric vehicle, where the method maintained stable tracking. These initial results suggest that the technique could be transferable to electric vehicle platforms and applicable in a variety of real-world conditions.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Optimization of Prefabricated Building Component Distribution Under Dynamic Charging Strategy for Electric Heavy-Duty Trucks
by
Xinran Qi, Weichen Zheng, Heping Wang and Fuyu Wang
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(9), 509; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090509 - 10 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
To align with the adoption of electric vehicles in the transportation sector, this paper proposes the use of electric heavy-duty trucks for the logistics and distribution of large prefabricated building components. This approach aims to address the problems of high total costs and
[...] Read more.
To align with the adoption of electric vehicles in the transportation sector, this paper proposes the use of electric heavy-duty trucks for the logistics and distribution of large prefabricated building components. This approach aims to address the problems of high total costs and significant energy waste in prefabricated component transportation. Focusing on the multi-to-multi distribution mode, a two-level optimization model is constructed. The upper-level model is responsible for the reasonable allocation of demand points. The lower-level model optimizes the selection of road network nodes and charging stations along the delivery routes. It also dynamically adjusts charging timing and volume according to the real-time power situation. To enhance solution performance, a two-level multi-objective evolutionary algorithm based on Pareto theory is designed. This algorithm simultaneously optimizes distribution costs while coordinating path planning and charging strategies. Comparative experiments across different cases show that, compared with traditional single-level and multi-stage models, the proposed algorithm improves both solution accuracy and quality. Additionally, when compared with the scheduling scheme based on the full-charge capacity strategy, the dynamic charging strategy proposed in this paper reduces the total distribution cost by approximately 15.83%. These findings demonstrate that the constructed model and algorithm can effectively optimize the logistics and distribution of prefabricated components. They also provide a feasible solution for the practical application of electric vehicles in engineering logistics.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Optimal Air Gap Magnetic Flux Density Distribution of an IPM Synchronous Motor Using a PM Rotor Parameter-Stratified Sensitivity Analysis
by
Jun Zhang, Wenjing Hu, Yanhong Gao, Sizhan Hua, Xin Zhou, Huihui Geng and Yixin Liu
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(9), 508; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090508 - 10 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In addressing the challenges posed by the numerous rotor structure parameters and the difficulty in analyzing the air gap magnetic field distribution in interior permanent magnet (IPM) motors, and to enhance the performance of automotive IPM synchronous motors, this paper proposes a multi-objective
[...] Read more.
In addressing the challenges posed by the numerous rotor structure parameters and the difficulty in analyzing the air gap magnetic field distribution in interior permanent magnet (IPM) motors, and to enhance the performance of automotive IPM synchronous motors, this paper proposes a multi-objective optimization method based on sensitivity stratification. Firstly, sensitivity analysis is conducted on the positional and shape parameters of the rotor permanent magnets (PMs), and the parameters are stratified according to their sensitivity levels. Subsequently, distinct analysis and optimization methods are applied to parameters of different strata for dual-objective optimization, which aims to increase the amplitude of the air gap flux density and reduce its total harmonic distortion (THD). Moreover, the waveform of the air gap flux density is analyzed to propose a targeted arrangement of magnetic isolation slots, thereby further optimizing the magnetic field distribution. Meanwhile, the demagnetization conditions and influencing factors of the PMs under overload are analyzed to enhance their demagnetization resistance and determine the final structural parameters. Simulation results indicate that, with the application of the proposed optimization method, the fundamental amplitude of the air gap flux density is increased by 0.035 T and THD is decreased by 9.9% when the proposed optimization method is applied. This verifies the effectiveness and feasibility of the method.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Research on Noise Suppression Strategies for High-Frequency Harmonic Noise in Automotive Electronic Water Pumps
by
Xiaodan Feng, Xipei Ma, Pingqing Fan and Yansong Wang
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(9), 507; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090507 - 9 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In this paper, in order to effectively reduce the electromagnetic noise of automotive electronic water pumps, a Hybrid Random Carrier Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation Hybrid Random Carrier Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation, (HRCSVPWM) technique based on linear congruential generator (LCG) algorithm is
[...] Read more.
In this paper, in order to effectively reduce the electromagnetic noise of automotive electronic water pumps, a Hybrid Random Carrier Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation Hybrid Random Carrier Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation, (HRCSVPWM) technique based on linear congruential generator (LCG) algorithm is proposed to study the suppression effect of current harmonics and acoustic vibration response with an automotive electronic water pump as the research object. Firstly, the HRCSVPWM based technique is proposed on the basis of SVPWM and pulse width modulation strategies. Secondly, the performance of random numbers generated for HRCSVPWM is analyzed, and it is proposed to use an LCG random number generator to generate excellent random numbers combined with a genetic algorithm to quickly determine the optimal values of three random parameters, namely, random number Ri, mixing degree coefficient Ki, and spreading width Ti, which enhances the stochasticity and spatial traversal of random sequences and ensures the effect of the HRSVPWM control method. Finally, simulation analysis is carried out, and a noise experimental platform is built for experimental verification. The results show that using the improved HRCSVPWM control strategy, compared with the SVPWM control strategy, the total harmonic content decreased by close to 21.81%, and the sound pressure level amplitude decreased by an average of approximately 6 dB.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Maximum Power Point Tracking Strategy for Fuel Cells Based on an Adaptive Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm
by
Jing Han, Xinyao Zhou and Chunsheng Wang
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(9), 506; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090506 - 9 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
With the growing global demand for clean energy, fuel cells have been adopted as key components in renewable energy systems. Their high efficiency and environmentally friendly operation make them attractive. However, during maximum power point tracking (MPPT), traditional proportional–integral–derivative (PID) controllers often fail
[...] Read more.
With the growing global demand for clean energy, fuel cells have been adopted as key components in renewable energy systems. Their high efficiency and environmentally friendly operation make them attractive. However, during maximum power point tracking (MPPT), traditional proportional–integral–derivative (PID) controllers often fail to maintain optimal power output. Dynamic load changes and complex operating conditions exacerbate this issue. As a result, system response is slowed, and tracking accuracy is reduced. To address these problems, an online identification method based on recursive least squares (RLS) is employed. A cubic power–current model is identified in real time. Polynomial fitting and the golden section search are then applied to estimate the current at the maximum power point. Following model-based estimation, adaptive particle swarm optimization (APSO) is utilized to tune the PID controller parameters. Precise regulation is thus achieved. The use of RLS enables real-time model identification. The golden section search improves the efficiency of current estimation. APSO enhances global optimization, while PID provides fast dynamic response. By integrating these methods, both tracking accuracy and system responsiveness are significantly improved in fuel cell MPPT applications. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed strategy enhances maximum power output by up to 12.40% compared to conventional P&O, fuzzy logic control, GWO-PID, and PSO-PID methods, as well as maintaining a consistent improvement of 1.50% to 1.90% even when compared to other optimization algorithms.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Assessment of Ejector-Expansion Heat Pump Systems with Low GWP Refrigerants for Electric Vehicles
by
Zhenying Zhang, Yuying Wang, Zhengdao Zhou, Zheng Guan, Li Chang and Meiyuan Yang
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(9), 505; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090505 - 8 Sep 2025
Abstract
This study addresses the critical challenge of developing efficient thermal management systems for electric vehicles by proposing and evaluating two novel ejector-expansion heat pump configurations: single-evaporator (SEEHP) and dual-evaporator (DEEHP) systems. Through comprehensive thermodynamic analysis across six representative Chinese cities using four refrigerants
[...] Read more.
This study addresses the critical challenge of developing efficient thermal management systems for electric vehicles by proposing and evaluating two novel ejector-expansion heat pump configurations: single-evaporator (SEEHP) and dual-evaporator (DEEHP) systems. Through comprehensive thermodynamic analysis across six representative Chinese cities using four refrigerants (R134a, R32, R152a, R290), system performance via coefficient of performance (COP) and lifecycle CO2 emissions were assessed. The results demonstrate significant advantages over conventional (CBHP) and vapor injection (VIHP) systems, particularly in extreme cold conditions. The SEEHP configuration achieves 10–30% COP improvements versus CBHP, while DEEHP shows 7–15% enhancement. The corresponding lifecycle emission reductions reach 9–14% for SEEHP and 2–11% for DEEHP relative to conventional systems. Among the refrigerants, R290 systems achieve the lowest equivalent CO2 emissions due to superior COP in Beijing, Shanghai, Chongqing, Kunming and Guangzhou, whereas R32 systems yield minimal emissions owing to its exceptional heating capacity in Harbin. These findings highlight ejector technology’s potential for substantially improving electric vehicle energy efficiency while reducing environmental impact.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Solutions to the Challenge of Implementing Air Conditioning Systems in Electric Vehicles)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Research on Constant-Voltage/Constant-Current Characteristics of Variable-Structure Dual-Frequency Dual-Load Wireless Power Transfer Technology
by
Lu Zhang, Jundan Mao, Yonglin Ke, Yueliang Chen, Yao Dong and Qinzheng Zhang
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(9), 504; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090504 - 8 Sep 2025
Abstract
To address the limitations of conventional magnetically coupled resonant wireless power transfer (MCR-WPT) systems in multi-frequency multi-load applications—specifically inadequate load power independence and high complexity inconstant-voltage/constant-current (CV/CC) control—this paper proposes a variable-structure dual-frequency dual-load wireless power transfer system by first establishing its mathematical
[...] Read more.
To address the limitations of conventional magnetically coupled resonant wireless power transfer (MCR-WPT) systems in multi-frequency multi-load applications—specifically inadequate load power independence and high complexity inconstant-voltage/constant-current (CV/CC) control—this paper proposes a variable-structure dual-frequency dual-load wireless power transfer system by first establishing its mathematical model and implementing hybrid-frequency modulation for multi-frequency output, then developing an improved T/LCC hybrid resonant topology by deriving parameter design conditions for compensation network reconfiguration under CV/CC requirements, subsequently employing an orthogonal planar solenoid coupling mechanism and frequency-division demodulation to achieve load-independent power regulation across wide load ranges for enhanced stability, and finally constructing a 120 W dual-frequency dual-load prototype to validate the system’s CV/CC characteristics, where simulations and experimental results demonstrate stronger consistency with theoretical predictions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Power Electronics for Electric Vehicles)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Flexible Assembly and Gripping Process of Hairpin Baskets
by
Felix Fraider, Peter Dreher, Josette Lindner, Dominik Reichl, Florian Kößler and Jürgen Fleischer
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(9), 503; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090503 - 7 Sep 2025
Abstract
Established hairpin stators for electric traction motors are made up of a large number of so-called hairpins. To produce these stators, the individual hairpins must first be pre-assembled into an auxiliary device in order to achieve the desired winding scheme. The resulting hairpin
[...] Read more.
Established hairpin stators for electric traction motors are made up of a large number of so-called hairpins. To produce these stators, the individual hairpins must first be pre-assembled into an auxiliary device in order to achieve the desired winding scheme. The resulting hairpin basket must then be picked up and transported to the lamination stack. Automated solutions for both processes are characterized by a high degree of complexity and low flexibility. Manual assembly, however, is prone to errors. The new approach presented in this paper is therefore based on the collaborative assembly of the hairpins and a flexible hairpin basket gripper. A cobot hands the hairpins in the correct sequence to the operator. The correct positioning of the hairpins in the auxiliary device is ensured by the use of a monitor located under it. The creation of the correct assembly sequence is partly automated by a collision detection program. In addition, a new and flexible hairpin basket gripping concept is presented. Tests show that the cycle times of both new processes are slow due to hardware limitations. This restricts their use to specific applications, such as complex winding patterns or very small quantities.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue EVS37—International Electric Vehicle Symposium and Exhibition (Seoul, Republic of Korea))
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Prediction of Electric Vehicle Charging Load Considering User Travel Characteristics and Charging Behavior
by
Haihong Bian, Xin Tang, Kai Ji, Yifan Zhang and Yongqing Xie
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(9), 502; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090502 - 6 Sep 2025
Abstract
Accurate forecasting of the electric vehicle (EV) charging load is a prerequisite for developing coordinated charging and discharging strategies. This study proposes a method for predicting the EV charging load by incorporating user travel characteristics and charging behavior. First, a transportation network–distribution network
[...] Read more.
Accurate forecasting of the electric vehicle (EV) charging load is a prerequisite for developing coordinated charging and discharging strategies. This study proposes a method for predicting the EV charging load by incorporating user travel characteristics and charging behavior. First, a transportation network–distribution network coupling framework is established based on a road network model with multi-source information fusion. Second, considering the multiple-intersection features of urban road networks, a time-flow model is developed. A time-optimal path selection method is designed based on the topological structure of the road network. Then, an EV driving energy consumption model is developed, accounting for both the mileage energy consumption and air conditioning energy consumption. Next, the user travel characteristics are finely modeled under two scenarios: working days and rest days. A user charging decision model is established using a fuzzy logic inference system, taking into account the state of charge (SOC), average electricity price, and parking duration. Finally, the Monte Carlo method is applied to simulate user travel and charging behavior. A simulation of the spatiotemporal distribution of the EV charging load was conducted in a specific area of Jiangning District, Nanjing. The simulation results show that there is a significant difference in the time distribution of EV charging loads between working days and rest days, with peak-to-valley differences of 3100.8 kW and 3233.5 kW, respectively.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable EV Rapid Charging, Challenges, and Development)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluating Key Spatial Indicators for Shared Autonomous Vehicle Integration in Old Town Spaces
by
Sucheng Yao, Kanjanee Budthimedhee, Sakol Teeravarunyou, Xinhao Chen and Ziqiang Zhang
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(9), 501; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090501 - 5 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
As Shared Autonomous Vehicles (SAVs) emerge as a transformative force in urban mobility, integrating them into dense, historic urban environments presents distinct spatial and planning challenges—such as narrow street patterns, irregular road networks, and the need to protect cultural heritage. This study investigates
[...] Read more.
As Shared Autonomous Vehicles (SAVs) emerge as a transformative force in urban mobility, integrating them into dense, historic urban environments presents distinct spatial and planning challenges—such as narrow street patterns, irregular road networks, and the need to protect cultural heritage. This study investigates the spatial adaptability of SAVs in Suzhou old town, a representative example of East Asian heritage cities. To assess spatial readiness, a hybrid weighting approach combining the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) and the Entropy Weight Method (EWM) is used to evaluate 22 spatial indicators across livability, mobility, and spatial quality. These weighted indicators are mapped using a spatial density analysis based on Point of Interest (POI) data, revealing urban service distribution patterns and spatial mismatches. Results show that “Accessibility to Transportation Hubs” receives the highest composite weight, emphasizing the priority of linking SAVs with existing subway and bus networks. Environmental comfort factors—such as air quality, noise reduction, and access to green and recreational spaces—also rank highly, reflecting a growing emphasis on urban livability. Drawing on these findings, this study proposes four strategic directions for SAV integration that focus on network flexibility, public service redistribution, ecological enhancement, and cultural preservation. The proposed framework provides a transferable planning reference for historic urban areas transitioning toward intelligent, human-centered mobility systems.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Simulative Consumption Analysis of an All-Electric Vehicle Fleet in an Urban Environment
by
Paul Heckelmann, Tobias Peichl, Johanna Krettek and Stephan Rinderknecht
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(9), 500; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090500 - 5 Sep 2025
Abstract
The increasing shift towards battery electric vehicles (BEVs) in urban environments raises the question of how real-world traffic conditions affect their energy consumption. While BEVs are expected to reduce local emissions, their total energy demand, particularly in city traffic with with low average
[...] Read more.
The increasing shift towards battery electric vehicles (BEVs) in urban environments raises the question of how real-world traffic conditions affect their energy consumption. While BEVs are expected to reduce local emissions, their total energy demand, particularly in city traffic with with low average speeds, and therefore a higher impact of secondary consumption, remains insufficiently understood. To address this, a simulative framework to analyze the average energy consumption of an all-electric vehicle fleet in a mid-sized city, using Darmstadt, Germany, as a case study, is presented. A validated microscopic traffic simulation is built based on 2024 data and enriched with representative powertrain models for various vehicle classes, including passenger cars, trucks, and buses. The simulation allows the assessment of consumption under different traffic densities and speeds, revealing the substantial influence of secondary consumers and traffic flow on total energy demand. Furthermore, the study compares the
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Electric Vehicle Networking and Traffic Control)
►▼
Show Figures
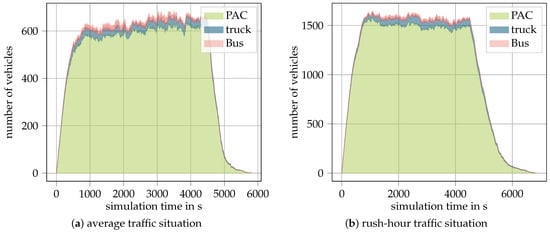
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Systematic Planning of Electric Vehicle Battery Swapping and Charging Station Location and Driver Routing with Bi-Level Optimization
by
Bowen Chen, Jianling Chen and Haixia Feng
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(9), 499; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090499 - 4 Sep 2025
Abstract
The rapid growth of electric vehicles (EVs) has significantly increased the demand for charging infrastructure, posing a challenge in balancing charging demand and infrastructure supply. The development of battery swapping and charging stations (BSCSs) is crucial for addressing these challenges and serves as
[...] Read more.
The rapid growth of electric vehicles (EVs) has significantly increased the demand for charging infrastructure, posing a challenge in balancing charging demand and infrastructure supply. The development of battery swapping and charging stations (BSCSs) is crucial for addressing these challenges and serves as a fundamental pillar for the sustainable advancement of EVs. This study develops a bi-level optimization model for the location and route planning of BSCSs. The upper-level model optimizes station locations to minimize total cost and service delay, while the lower-level model optimizes driver travel routes to minimize total time. An updated Non-Dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm (UNSGA) is applied to enhance solution efficiency. The experimental results show that the bi-level model outperforms the single-level model, reducing total cost by 1.5% and travel time by 6.6%. Compared to other algorithms, the UNSGA achieves 9.43% and 8.23% lower costs than MOPSO and MOSA, respectively. Furthermore, BSCSs, despite 15.42% higher construction costs, reduce driver travel time by 22.43% and waiting time by 71.19%, highlighting their operational advantages. The bi-level optimization method provides more cost-effective decision support for EV infrastructure investors, enabling them to adapt to dynamic drivers’ needs and optimize resource allocation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Electric Vehicle Technology Development, Energy and Environmental Implications, and Decarbonization: 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Research on the Charging Point Business Model of EV Users with Variable Roles
by
Weihua Wu, Jieyun Wei, Yifan Zhang, Eun-Young Nam and Dongphil Chun
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(9), 498; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090498 - 3 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The current global utilization rate of electric vehicle (EV) charging stations ranges from approximately 20% to 40%. Despite numerous studies focusing on enhancing this utilization through single-variable approaches—such as optimizing charging point (CP) locations, analyzing charging behaviors, and adjusting pricing—low utilization rates persist.
[...] Read more.
The current global utilization rate of electric vehicle (EV) charging stations ranges from approximately 20% to 40%. Despite numerous studies focusing on enhancing this utilization through single-variable approaches—such as optimizing charging point (CP) locations, analyzing charging behaviors, and adjusting pricing—low utilization rates persist. This paper examines the business model for EVs and charging stations integrated into the 5G Real-Time System for EVs and Transportation (5gRTS-ET) platform, which was operational in China in 2021. It establishes three distinct business models for EV users: the Government Subsidy Model, the Self-Operating Model without Government Subsidies, and the 5gRTS-ET Operating Model. Utilizing an integrated service modeling approach, the study constructs a dynamic business model for charging stations. Findings indicate that incorporating variables related to EV user roles significantly enhances the utilization rates of charging stations. Furthermore, onboarding EV CPs onto the 5gRTS-ET platform emerges as an effective strategy for ensuring their sustainable operation. This research offers a sustainable business model for EV charging stations in light of the evolving roles of EV users and serves as a reference for applying integrated business modeling methods in practical operational platforms.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of Waveform Distortion in BESS-Integrated Fast-Charging Station
by
Manav Giri and Sarah Rönnberg
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(9), 497; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090497 - 2 Sep 2025
Abstract
This paper presents a detailed, measurement-based assessment of interharmonic, harmonic, and supraharmonic emissions from a Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) supporting electric vehicle (EV) fast charging. In contrast to prior literature, which is largely simulation-based and often neglects interharmonic and even harmonic components,
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a detailed, measurement-based assessment of interharmonic, harmonic, and supraharmonic emissions from a Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) supporting electric vehicle (EV) fast charging. In contrast to prior literature, which is largely simulation-based and often neglects interharmonic and even harmonic components, this study provides real-world data under dynamic operating conditions. Emission limits are established in accordance with relevant international standards, with the observed deviations from standard practices highlighted in existing studies. The operation of the BESS-assisted fast-charging system is classified into five distinct operating stages, and the variations in spectral emissions across these stages are analyzed. A comparative evaluation with a grid-fed fast charger reveals the influence of BESS integration on power quality. Notably, the analysis shows a significant increase in even harmonics during EV charging events. This component is identified as the limiting factor in the network’s harmonic hosting capacity, underscoring the need to account for even harmonics in future grid compatibility assessments. These findings provide valuable insights for grid operators, EV infrastructure planners, and standardization bodies aiming to ensure compliance with power quality standards in evolving charging scenarios.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Fast-Charging Station for Electric Vehicles: Challenges and Issues)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Design of Coordinated EV Traffic Control Strategies for Expressway System with Wireless Charging Lanes
by
Yingying Zhang, Yifeng Hong and Zhen Tan
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(9), 496; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090496 - 1 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
With the development of dynamic wireless power transfer (DWPT) technology, the introduction of wireless charging lanes (WCLs) in traffic systems is seen as a promising trend for electrified transportation. Though there has been extensive discussion about the planning and allocation of WCLs in
[...] Read more.
With the development of dynamic wireless power transfer (DWPT) technology, the introduction of wireless charging lanes (WCLs) in traffic systems is seen as a promising trend for electrified transportation. Though there has been extensive discussion about the planning and allocation of WCLs in different situations, studies on traffic control models for WCLs are relatively lacking. Thus, this paper aims to design a coordinated optimization strategy for managing electric vehicle (EV) traffic on an expressway network, which integrates a corridor traffic flow model with a wireless power transmission model. Two components are considered in the control objective: the total energy increased for the EVs and the total number of EVs served by the expressway, over the problem horizon. By setting the trade-off coefficients for these two objectives, our model can be used to achieve mixed optimization of WCL traffic management. The decisions include metering of different on-ramps as well as routing plans for different groups of EVs defined by origin/destination pairs and initial SOC levels. The control problem is formulated as a novel linear programming model, rendering an efficient solution. Numerical examples are used to verify the effectiveness of the proposed traffic control model. The results show that with the properly designed traffic management strategy, a notable increase in charging performance can be achieved by compromising slightly the traffic performance while maintaining overall smooth operation throughout the expressway system.
Full article
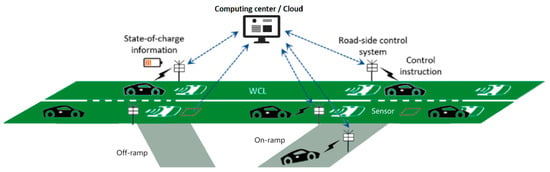
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- WEVJ Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
9 September 2025
World Electric Vehicle Journal | Notable Papers in the Field of Thermal Management in Electric Vehicle
World Electric Vehicle Journal | Notable Papers in the Field of Thermal Management in Electric Vehicle

3 September 2025
Join Us at the MDPI at the University of Toronto Career Fair, 23 September 2025, Toronto, ON, Canada
Join Us at the MDPI at the University of Toronto Career Fair, 23 September 2025, Toronto, ON, Canada

Topics

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
WEVJ
Design, Analysis and Optimization of Electrical Machines and Drives for Electric Vehicles, 2nd Edition
Guest Editors: Syed Sabir Hussain Bukhari, Jorge Rodas, Jesús Doval-GandoyDeadline: 30 September 2025
Special Issue in
WEVJ
Permanent Magnet Motors and Driving Control for Electric Vehicles
Guest Editor: Ming YaoDeadline: 30 September 2025
Special Issue in
WEVJ
Autonomous Electric Vehicles Combined with Non-connected Vehicles in Smart Cities
Guest Editors: Manuela Montangero, Gianluca De MarcoDeadline: 30 September 2025
Special Issue in
WEVJ
Internet of Vehicles for Intelligent Transportation System: Current Trends and Future Perspectives
Guest Editors: Dapeng Wu, Boran YangDeadline: 30 September 2025






