- Communication
Prevalence of Lungworm Infections in Hedgehogs (Erinaceus roumanicus) in Greece and a Novel Therapeutic Approach for Treatment
- Grigorios Markakis,
- Isaia Symeonidou and
- Anastasia Komnenou
- + 3 authors
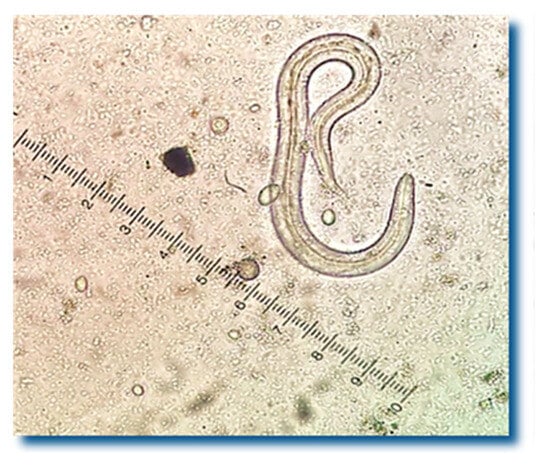
The most common causes of respiratory diseases in wild hedgehogs are the lungworms Crenosoma striatum and Capillaria aerophila, which can lead to life-threatening pneumonia. The aim of the current study was (A) to assess the prevalence of common lungworm infections in northern white-breasted hedgehogs (Erinaceus roumanicus) in Greece and (B) to identify an efficient and easy to administer treatment option. (A) Fifty-six hedgehogs were admitted to a Greek wildlife rehabilitation center and included in the present study. Fecal tests were performed using the flotation method (ZnSO4 33.2%) combined with the Baermann technique. In total, 49 hedgehogs excreted Crenosoma spp. larvae (87.5%), and 27 of them were also infected with Capillaria spp. (48.2%). One of them died, and the necropsy and lung histopathology confirmed the diagnosis of crenosomosis. (B) Fourteen animals with mixed infections were treated using NexGard® Combo (esafoxolaner, eprinomectin, praziquantel) administered orally at a dose rate of 0.2 mL/kg body weight, once. On days 10 and 14 post-treatment, no parasitic elements were detected in the feces of the infected animals. All the animals had gained weight by day 14, and their biochemical parameters were normal. It was concluded that this combination given orally was safe and successful against hedgehog respiratory nematodes.
21 December 2025