Journal Description
Non-Coding RNA
Non-Coding RNA
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on non-coding RNA research dealing with elucidating the structure, function and biology of regulatory non-coding RNAs. Non-Coding RNA is published bimonthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Genetics and Heredity) / CiteScore - Q1 (Genetics)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 23.4 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
3.0 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
4.2 (2024)
Latest Articles
CARINH, an Interferon-Induced LncRNA in Cancer and Inflammation
Non-Coding RNA 2025, 11(6), 79; https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11060079 - 21 Nov 2025
Abstract
►
Show Figures
CARINH is an intriguing long noncoding RNA whose unique regulatory functions intersect the seemingly distinct processes of innate immunity and cancer development. Notably, CARINH is conserved across species, offering powerful experimental models for uncovering its mechanistic roles and physiological functions across diverse biological
[...] Read more.
CARINH is an intriguing long noncoding RNA whose unique regulatory functions intersect the seemingly distinct processes of innate immunity and cancer development. Notably, CARINH is conserved across species, offering powerful experimental models for uncovering its mechanistic roles and physiological functions across diverse biological contexts. Stimulated by interferons and viral infections, CARINH stands out as a key player in the body’s antiviral defense mechanisms. Additionally, its dysregulation has been implicated in autoimmune disorders such as psoriasis, asthma, and inflammatory bowel disease, underscoring its broader role in maintaining immune homeostasis. Furthermore, alterations in CARINH expression have been connected to cancer progression, highlighting its dual role in immune response and tumor suppression. In this review, we delve into CARINH’s pivotal function in modulating interferon responses and influencing cancer development, with a focus on the molecular pathways that regulate its expression and contribute to its diverse roles. Understanding these pathways is crucial for evaluating CARINH’s significance as a biomarker and therapeutic target, potentially leading to groundbreaking advancements in medical research and treatment strategies.
Full article
Open AccessReview
miRNA and Its Implications in the Treatment Resistance in Breast Cancer—Narrative Review of What Do We Know So Far
by
Isabela Anda Komporaly, Adelina Silvana Gheorghe, Lidia Anca Kajanto, Elena Adriana Iovănescu, Bogdan Georgescu, Raluca Ioana Mihăilă, Andreea Mihaela Radu, Daniela Luminița Zob, Mara Mădălina Mihai, Mihai Teodor Georgescu and Dana Lucia Stănculeanu
Non-Coding RNA 2025, 11(6), 78; https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11060078 - 18 Nov 2025
Abstract
Breast cancer remains a leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, with treatment resistance and tumor heterogeneity posing major clinical challenges. MicroRNAs (miRNAs), small non-coding RNAs regulating gene expression, have emerged as key players in breast cancer biology, influencing tumor initiation, progression, and therapy
[...] Read more.
Breast cancer remains a leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, with treatment resistance and tumor heterogeneity posing major clinical challenges. MicroRNAs (miRNAs), small non-coding RNAs regulating gene expression, have emerged as key players in breast cancer biology, influencing tumor initiation, progression, and therapy resistance. This narrative review synthesizes recent evidence on the involvement of miRNAs in breast cancer subtypes and their impact on treatment response. Notably, miR-155, miR-503, and miR-21 have shown potential as non-invasive biomarkers and modulators of pathways such as PI3K-Akt, MAPK, and TNF signaling. Additionally, exosomal miRNAs may reflect chemoresistance profiles and predict pathological response to neoadjuvant therapy. Emerging data also support the use of specific miRNAs to sensitize tumors to radiotherapy or modulate immune checkpoints like PD-L1 in triple-negative breast cancer. However, challenges persist regarding standardization, sample types, and study heterogeneity. Further translational research is needed to validate miRNA signatures and their utility in guiding personalized treatment. By highlighting mechanistic insights and potential clinical applications, this review aims to contribute to the ongoing efforts of integrating miRNAs into precision oncology for breast cancer.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Non-coding RNA as Biomarker in Cancer)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Prolonged Survival with Dieting for Improved Autophagy
by
Akari Fukumoto, Moeka Nakashima and Satoru Matsuda
Non-Coding RNA 2025, 11(6), 77; https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11060077 - 4 Nov 2025
Abstract
Food is a crucial component affecting the health of individuals, which may have the potential to expand lifespan. It has been shown that a long lifespan may be related to fine-tuned autophagy. In general, suitable autophagy could play a significant role in the
[...] Read more.
Food is a crucial component affecting the health of individuals, which may have the potential to expand lifespan. It has been shown that a long lifespan may be related to fine-tuned autophagy. In general, suitable autophagy could play a significant role in the anti-aging biological exertion of the host. AMPK, a member of serine and threonine kinases, could play vital roles within the autophagy signaling pathway in various cells. In addition, alterations in the kinase activity of AMPK have been shown to be connected to several pathologies of aging-related diseases. Therefore, autophagy could control the lifespan-related homeostasis within the host from cells to a body via the modification of AMPK. The design of the diet and/or nutrition targeting the AMPK would be a possibility to expand the lifespan. Some analyses of the molecular biology underlying the autophagy suggest that supplementation of accurate nutraceuticals, as well as dietary restriction, mild fasting, and/or appropriate physical exercise, could modulate AMPK signaling, which may be advantageous for life extension with the alteration of autophagy. Remarkably, it has been revealed that several non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) might also play significant roles in the regulation of autophagy. In addition, the production of some ncRNAs may be associated with the alteration of gut microbiota with certain diets. Therefore, the modulation of AMPK action with ncRNAs through choosing the relevant diet could be a therapeutic tactic for promoting longevity, which is also accompanied by a reduced risk for several aging-related diseases.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Non-coding RNAs in Stem Cell Differentiation and Disease)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of Expression and Clinicopathological Relevance of Small Nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) in Invasive Breast Cancer
by
Luděk Záveský, Eva Jandáková, Vít Weinberger, Luboš Minář, Radovan Turyna, Adéla Tefr Faridová, Veronika Hanzíková and Ondřej Slanař
Non-Coding RNA 2025, 11(6), 76; https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11060076 - 31 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Breast cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related mortality among women worldwide. Small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) represent a class of non-coding RNAs with potential as novel biomarkers applicable to improve diagnostic and prognostic applications. Methods: We performed a comprehensive evaluation of the
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Breast cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related mortality among women worldwide. Small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) represent a class of non-coding RNAs with potential as novel biomarkers applicable to improve diagnostic and prognostic applications. Methods: We performed a comprehensive evaluation of the snoRNA-related gene expression by qPCR using benign and tumor tissue samples associated with invasive breast carcinomas of no special type (NST). Selected candidate snoRNAs, i.e., SCARNA2, SCARNA3, SNORD15B, SNORD94, SNORA68, and SNHG1, along with RNU2-1 snRNA, were further validated and their associations with clinicopathological parameters were examined. External datasets and plasma samples were used for additional validation. Results: SCARNA2 was identified as the most promising snoRNA biomarker candidate, showing a positive association with better progression-free survival (PFS) in our data (13.3-month survival difference between low- and high-expression groups) and with both PFS and overall survival in external RNA-seq datasets. SNORD94, SNORD15B, SCARNA3, and RNU2-1 snRNA were also indicated as putative tumor suppressors. SNORD94 was associated with better progression-free survival (PFS) in our data as well (12.4-month survival difference between low- and high expression groups). Greater downregulation in the low-expression tumor subgroup compared to benign samples further supports the prognostic potential of SCARNA2 and SNORD94. Evidence for SNHG1 and SNORA68 as putative oncogenes was less conclusive. Conclusions: Several small nucleolar RNAs were found to be dysregulated in breast cancer specimens, supporting their further evaluation as potential biomarkers. In particular, SCARNA2, SNORD94, SNORD15B, SCARNA3, and RNU2-1 snRNA merit further investigation to determine their clinical relevance and biological roles in breast cancer.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Non-coding RNA as Biomarker in Cancer)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
The Non-Coding RNA Journal Club: Highlights on Recent Papers—14
by
El Cheima Mhamedi, Florent Hubé, Suresh K. Alahari, Francisco J. Enguita, Barbara Pardini, Mark W. Feinberg, Laura Poliseno, Beshoy Armanios, Jing Jin, Xiao-Bo Zhong, Nikolaos Sideris, Salih Bayraktar, Leandro Castellano, Gaetano Santulli, Stanislovas S. Jankauskas, Will S. Plewa, Simon J. Conn, Ling Yang, Patrick K. T. Shiu, Abhishek Kaushik, Alexander Serganov, Massimo Gentile, Giuseppe Viglietto, Nicola Amodio, Tijana Mitić and Andrea Caporaliadd
Show full author list
remove
Hide full author list
Non-Coding RNA 2025, 11(6), 75; https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11060075 - 31 Oct 2025
Abstract
The field of non-coding RNA research is advancing at a breathtaking pace, continually uncovering new layers of regulatory complexity and functional diversity [...]
Full article
Open AccessArticle
The Chromosome 19 microRNA Cluster Facilitates Cancer Stemness in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
by
Marian T. Underwood, Varsha Devarapalli, Goodwin G. Jinesh, John H. Lockhart, Marco Napoli, Nino Mtchedlidze, Elsa R. Flores and Andrew S. Brohl
Non-Coding RNA 2025, 11(6), 74; https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11060074 - 29 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the world’s deadliest cancers; however, the mechanisms that contribute to its aggressiveness are poorly understood. In the recent literature, overexpression of the Chromosome 19 MicroRNA Cluster (C19MC) has been associated with an aggressive phenotype and unfavorable
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the world’s deadliest cancers; however, the mechanisms that contribute to its aggressiveness are poorly understood. In the recent literature, overexpression of the Chromosome 19 MicroRNA Cluster (C19MC) has been associated with an aggressive phenotype and unfavorable prognosis in HCC. However, the molecular consequences of C19MC overexpression in HCC remain poorly understood. Methods: Here, we created a constitutive C19MC-overexpressing HCC model and used two different CRISPR-engineered C19MC-overexpressing HCC models to analyze phenotype and transcriptomic changes. Results: We observed that C19MC overexpression induces cancer stem cell (CSC) phenotypic features in vitro and analyzed transcriptomic changes in genes correlating with stemness, such as NFκB and EMT. Conclusions: C19MC induces changes in HCC that are consistent with stemness and aggression, which provides a better understanding of why C19MC could be a biomarker of poor prognosis.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessPerspective
Exploring microRNAs, One Cell at a Time
by
Jessica Kreutz, Tijana Mitić and Andrea Caporali
Non-Coding RNA 2025, 11(6), 73; https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11060073 - 22 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The emergence of single-cell sequencing and computational analysis has dramatically improved our understanding of cellular diversity and gene expression dynamics. The rapid advancement of high-throughput omics technologies has led to an exponential growth in biological data. However, many gene regulatory processes at the
[...] Read more.
The emergence of single-cell sequencing and computational analysis has dramatically improved our understanding of cellular diversity and gene expression dynamics. The rapid advancement of high-throughput omics technologies has led to an exponential growth in biological data. However, many gene regulatory processes at the single-cell level remain underexplored, especially those regulated by post-transcriptional mechanisms involving microRNAs (miRNAs). miRNAs are essential regulators of gene expression, affecting cellular functions in both normal and disease states. Recent innovations, such as single-cell gene expression profiling and bioinformatic analysis, have enabled comprehensive studies that uncover previously hidden miRNA profiles. In this context, we present experimental tools and computational methods for analysing cell-specific miRNA abundance and investigating their mechanisms. These approaches are expected to reveal the complex nature of miRNA biology and, more broadly, enhance our understanding of life sciences and diseases.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Identification and Functions of lncRNAs in Fungi
by
Javier Avalos, Adrián Perera-Bonaño and M. Carmen Limón
Non-Coding RNA 2025, 11(5), 72; https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11050072 - 7 Oct 2025
Abstract
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are transcripts generated by polymerase II, therefore subject to 5′ capping and 3′ polyadenylation, categorized as such when they are at least 200 nt in size and lack coding function. The lncRNAs were initially interpreted as spurious transcription products,
[...] Read more.
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are transcripts generated by polymerase II, therefore subject to 5′ capping and 3′ polyadenylation, categorized as such when they are at least 200 nt in size and lack coding function. The lncRNAs were initially interpreted as spurious transcription products, but over the last two decades an increasing amount of evidence has accumulated for regulatory functions. They are found in all taxonomic groups, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, animals and plants. In fungi, global analyses anticipate their presence in higher numbers than initially expected considering the simplicity of these organisms. Except for the numerous studies performed in budding and fission yeast, relatively few lncRNAs have been investigated in sufficient detail in the rest of the fungi, but their number has increased steadily in recent years. The lncRNAs can be transcribed from intergenic regions or coincide totally or partially with protein-coding genes, in which case they are most frequently antisense transcripts. Their regulatory functions can be performed by a wide variety of mechanisms, both in cis on neighboring genes and in trans on distant genes or on proteins. Among the most frequent mechanisms are interference on the transcription of neighboring genes and generation of epigenetic modifications in the environment of target genes. Here, we review the most representative cases of global analyses of the presence of lncRNAs in fungal transcriptomes and describe the lncRNAs that have received more detailed attention.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Long Non-Coding RNA)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
microRNA Biomarkers in Paediatric Infection Diagnostics—Bridging the Gap Between Evidence and Clinical Application: A Scoping Review
by
Oenone Rodgers, Anna De Beer and Thomas Waterfield
Non-Coding RNA 2025, 11(5), 71; https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11050071 - 24 Sep 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
Background: Distinguishing between bacterial and viral infections in children remains a significant challenge for clinicians. Traditional biomarkers have limited utility, often leading to antibiotic overprescription due to clinician uncertainty. With rising antimicrobial resistance, novel biomarkers are needed to improve diagnosis. This scoping review
[...] Read more.
Background: Distinguishing between bacterial and viral infections in children remains a significant challenge for clinicians. Traditional biomarkers have limited utility, often leading to antibiotic overprescription due to clinician uncertainty. With rising antimicrobial resistance, novel biomarkers are needed to improve diagnosis. This scoping review examines current host miRNA biomarkers for acute bacterial and viral infections in children (0–18), focusing on study methods, diagnostic metrics, and research gaps to support clinical translation. Results: Of the 1147 articles identified, 36 studies were included. Notably, 72.2% of the studies originated from Asia, and the distribution across the paediatric age groups was relatively even. A total of 17 miRNAs were validated in at least two independent studies. Three miRNAs, hsa-miR-182-5p, hsa-miR-363-3p, and hsa-miR-206, were consistently associated with bacterial infection in children. Meanwhile, nine miRNAs were associated with viral infections: hsa-miR-155, hsa-miR-29a-3p, hsa-miR-155-5p, hsa-miR-150-5p, hsa-miR-140-3p, hsa-miR-142-3p, hsa-miR-149-3p, hsa-miR-210-3p, and hsa-miR-34a-5p. Across the 12 studies reporting diagnostic accuracy metrics, miRNA biomarkers exhibited a sensitivity ranging from 70% to 100%, and a specificity ranging from 72% to 100%. The area under the curve across the studies demonstrated a range from 0.62 to 0.99. Conclusions: This scoping review highlights the potential of miRNA targets for diagnosing paediatric infections when studied rigorously. However, clinical translation is limited by poor adherence to STARD guidelines, lack of robust diagnostic metrics, and study heterogeneity. Many studies were set up with a case–control design, a design that, while highlighting differences, is more likely to identify non-specific biomarkers rather than those that are useful for novel clinical diagnostics.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Detection and Biomarkers of Non-Coding RNA)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
by
Shailendra S. Maurya, Sarita Maurya and Sumit K. Chaturvedi
Non-Coding RNA 2025, 11(5), 70; https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11050070 - 19 Sep 2025
Abstract
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a highly heterogeneous disease, with significantly higher incidence and fatality rates in the elderly. Even with recent decades of research progress in AML, the exact etiology of this deadly disease is still not fully understood, with recent advancements
[...] Read more.
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a highly heterogeneous disease, with significantly higher incidence and fatality rates in the elderly. Even with recent decades of research progress in AML, the exact etiology of this deadly disease is still not fully understood, with recent advancements in sequencing technologies highlighting the role of a growing number of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) that are intimately associated with AML leukemogenesis. These ncRNAs have been found to have a significant role in leukemia-related cellular processes such as cell division, proliferation, and death. A few of these non-coding RNAs exhibit potential as prognostic biomarkers. The three main groups of ncRNAs that contribute unique activities, especially in cancer, are microRNAs (miRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs). Their existence or altered expression levels frequently offer vital information on the diagnosis, course of treatment, and follow-up of cancer patients. The identification of ncRNAs has opened up new avenues for the diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy of acute myeloid leukemia. In order to provide a clear understanding of the significant influence that lncRNAs have on prognostic predictions and diagnostic accuracy in AML, this review aims to provide a comprehensive and insightful understanding of how these molecules actively participate in the complex landscape of the disease.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Long Non-Coding RNA)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Long Non-Coding RNAs in Psoriasis: A Comprehensive Review of Expression Profiles, Mechanistic Insights, Genetic Associations, and Their Clinical Implications
by
Judit Danis and Márta Széll
Non-Coding RNA 2025, 11(5), 69; https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11050069 - 19 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder affecting approximately 2% of the global population, characterized by abnormal keratinocyte proliferation and dysregulated immune responses. This review examines the emerging role of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in psoriasis pathogenesis, highlighting their significance as regulatory molecules
[...] Read more.
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder affecting approximately 2% of the global population, characterized by abnormal keratinocyte proliferation and dysregulated immune responses. This review examines the emerging role of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in psoriasis pathogenesis, highlighting their significance as regulatory molecules in disease initiation, progression, and chronicity. LncRNAs demonstrate distinct expression patterns in psoriatic lesions, with upregulated transcripts such as MALAT1, XIST, MIR31HG, and HOTAIR promoting keratinocyte hyperproliferation, inhibiting apoptosis, and amplifying inflammatory cascades through mechanisms including microRNA sponging and transcription factor modulation. These molecules primarily target key signaling pathways including NF-κB, STAT3, and PI3K/AKT. Conversely, downregulated lncRNAs like NEAT1, MEG3, and PRINS normally function as tumor suppressor molecules that maintain epidermal homeostasis through pro-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Their reduced expression contributes to the pathological hyperproliferative phenotype characteristic of psoriatic skin. Importantly, genetic variants within lncRNA loci have been identified as significant contributors to psoriasis susceptibility and treatment responses across different populations. Single- nucleotide polymorphisms in genes such as TRAF3IP2-AS1, HOTAIR, and CDKN2B-AS1 demonstrate population-specific associations with disease risk and therapeutic outcomes, suggesting their potential utility as pharmacogenomic markers. The complex regulatory networks involving lncRNAs provide new insights into psoriasis pathogenesis and offer promising avenues for personalized treatment strategies. Integration of lncRNA profiling into clinical practice may enhance our understanding of disease heterogeneity and improve therapeutic outcomes for psoriatic patients.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Chromatin-Associated RNAs Regulate Gene Expression and Chromatin Structure
by
Bingning Xie and Ann Dean
Non-Coding RNA 2025, 11(5), 68; https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11050068 - 12 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Inside the eukaryotic nucleus, various RNAs are associated with chromatin. These include protein-coding pre-mRNA and different types of non-coding RNAs that are referred to as chromatin-associated RNAs (caRNAs). Recent studies have revealed the important roles of these caRNAs in regulating gene expression and
[...] Read more.
Inside the eukaryotic nucleus, various RNAs are associated with chromatin. These include protein-coding pre-mRNA and different types of non-coding RNAs that are referred to as chromatin-associated RNAs (caRNAs). Recent studies have revealed the important roles of these caRNAs in regulating gene expression and chromatin interactions. In this review, we discuss the recent advances in understanding caRNAs. We first focus on their mode of action, then we summarize the methods used to detect caRNAs and categorize them into three classes: RNA-centric, DNA-centric and protein-centric. Finally, we turn to the proteins that mediate their functions.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
XIST Loss Induces Variable Transcriptional Responses Dependent on Cell States
by
Dongning Chen, Ikrame Naciri, Jie Wu and Sha Sun
Non-Coding RNA 2025, 11(5), 67; https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11050067 - 12 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: The X-inactivation specific transcript (XIST) is a long noncoding RNA playing a crucial regulatory role in X chromosome inactivation (XCI)—a transcriptional regulatory process that silences one of the two X chromosomes in females to ensure proper dosage compensation between male and
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The X-inactivation specific transcript (XIST) is a long noncoding RNA playing a crucial regulatory role in X chromosome inactivation (XCI)—a transcriptional regulatory process that silences one of the two X chromosomes in females to ensure proper dosage compensation between male and female mammals. The transcription of XIST is maintained throughout a female’s lifespan in all somatic cells, where XIST RNA binds to the X chromosome in cis and ensures chromosome-wide gene silencing. Disrupting XIST expression can lead to transcriptional reactivation of X-linked genes and epigenetic changes affecting cell development. The prevalence of XIST regulatory effects on mammalian transcription, however, remains unclarified. Methods: Here we performed a comparative expression analysis using RNA-sequencing datasets from recently published studies and examined the consequences of XIST-deletion on transcription at the whole genome, individual chromosome, and specific gene levels. We investigated the common differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and biological pathways following XIST loss across cell types, together with differential transcriptional analysis comparing the X chromosome and autosomes using cumulative distribution fractions. We analyzed the distribution of DEGs along the X chromosome with scatterplots and correlation analysis incorporating gene density and transposable elements. Results: Our findings indicate that the loss of XIST causes transcriptional changes in the X chromosome and autosomes that differ depending on cell type and state. XIST-deletion results in differential expression of genes subject to XCI-silencing as well as genes escaping XCI. In all the cell types we analyzed, X-linked genes show differential expression across the entire X chromosome in a cluster-like pattern according to gene density and, in certain cell types, correlate strongly with short interspersed nuclear element (SINE) distributions. Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that transcriptional roles of XIST can be highly associated with cell state: stem cells have different transcriptional responses compared to differentiated cells following XIST loss.
Full article
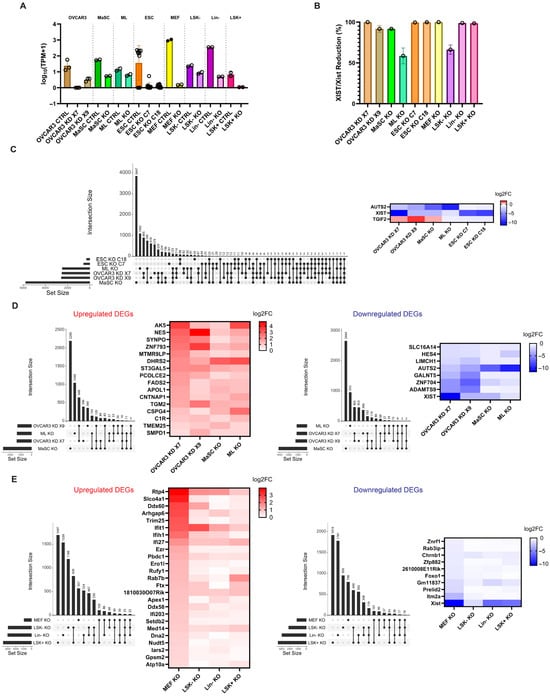
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Cellular Delivery of Functional AntimiR Conjugated to Bio-Produced Gold Nanoparticles
by
Parastoo Pourali and Veronika Benson
Non-Coding RNA 2025, 11(5), 66; https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11050066 - 11 Sep 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Bio-produced gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) are effective carriers of short RNAs into specialized mammalian cells. Their potential application is still limited by scarce knowledge on their uptake and intracellular fate. Gold nanoparticles that are not biologically produced (NB-AuNPs) enter specialized cells primarily
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Bio-produced gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) are effective carriers of short RNAs into specialized mammalian cells. Their potential application is still limited by scarce knowledge on their uptake and intracellular fate. Gold nanoparticles that are not biologically produced (NB-AuNPs) enter specialized cells primarily via clathrin-dependent endocytosis. Unlike the NB-AuNPs, the bio AuNPs possess natural surface coatings that significantly alter the AuNPs properties. Our research aimed to reveal the cellular uptake of the AuNPs with respect to delivering a functional RNA cargo. Methods: The AuNPs were conjugated with short inhibitory RNA specific to miR 135b. Mammary cancer cells 4T1 were pretreated with inhibitors of caveolin- and clathrin-mediated endocytosis and macropinocytosis. AuNPs’ uptake, fate, and miR 135b knock-down were assessed with TEM and qPCR. Results: The AuNPs-antimiR 135b conjugates entered 4T1 cells via all the tested pathways and could be seen inside the cells in early and late endosomes as well as cytoplasm. In contrast to the clathrin-dependent pathway, the caveolae-mediated endocytosis and the macropinocytosis of the AuNPs resulted in the effective targeting and reduction of the miR 135b. Conclusions: The bio-produced AuNPs can effectively enter mammalian cells simultaneously by different endocytic pathways but the delivery of functional cargo is not achieved via the clathrin-dependent endocytosis.
Full article
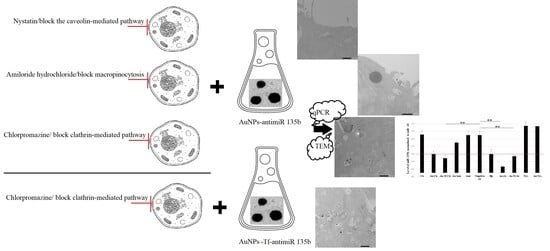
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Human-Specific Suppression of Hepatic Fatty Acid Catabolism by RNA-Binding Protein HuR
by
Shohei Takaoka, Marcos E. Jaso-Vera and Xiangbo Ruan
Non-Coding RNA 2025, 11(5), 65; https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11050065 - 1 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) play essential roles in all major steps of RNA processing. Genetic studies in human and mouse models support that many RBPs are crucial for maintaining homeostasis in key tissues/organs, but to what extent the function of RBPs is conserved between
[...] Read more.
RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) play essential roles in all major steps of RNA processing. Genetic studies in human and mouse models support that many RBPs are crucial for maintaining homeostasis in key tissues/organs, but to what extent the function of RBPs is conserved between humans and mice is not clear. Our recent study using a chimeric humanized liver mouse model found that knocking down human HuR in human hepatocytes resulted in a broad upregulation of human genes involved in fatty acid catabolism. This regulation is human-specific, as the knocking down of mouse HuR in the liver of traditional mouse models did not show these effects. To further study this human-specific role of HuR, we co-overexpressed HuR with PPARα, a master transcription factor that promotes fatty acid catabolism, in cultured cells. We found that HuR suppressed the expression of PPARα-induced fatty acid catabolism genes in human cells but not in mouse cells. We provide evidence supporting that the human-specific suppressive effect of HuR is independent of PPARα expression or location. The regulatory effects of HuR are also independent of its role in regulating mRNA stability. Using the human HMGCS2 gene as an example, we found that the suppressive effect of HuR cannot be explained by decreased promoter activity. We further provide evidence supporting that HuR suppresses the pre-mRNA processing of HMGCS2 gene, leading to accumulated intron/pre-mRNA expression of HMGCS2 gene. Furthermore, overexpression of HuR blocked and knocking down of HuR sensitized PPARα agonist-induced gene expression. By analyzing published RNA-seq data, we found compromised pre-mRNA processing for fatty acid catabolism genes in patients with fatty liver diseases, which was not observed in mouse fatty liver disease models. Our study supports the model that HuR suppresses the expression of fatty acid catabolism genes by blocking their pre-mRNA processing, which may partially explain the mild effects of PPARα agonists in treating fatty liver diseases in humans as compared with studies in mice.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Navigating the Landscape of Exosomal microRNAs: Charting Their Pivotal Role as Biomarkers in Hematological Malignancies
by
Manlio Fazio, Fabio Stagno, Giuseppa Penna, Giuseppe Mirabile and Alessandro Allegra
Non-Coding RNA 2025, 11(5), 64; https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11050064 - 31 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Under physiological and pathological conditions, all cells release extracellular vesicles named exosomes, which act as transporters of lipidic, protein, and genetic material from parent to recipient cells. Neoplastic cells can secrete higher number of exosomes to exert pro-tumoral effects such as microenvironmental changes,
[...] Read more.
Under physiological and pathological conditions, all cells release extracellular vesicles named exosomes, which act as transporters of lipidic, protein, and genetic material from parent to recipient cells. Neoplastic cells can secrete higher number of exosomes to exert pro-tumoral effects such as microenvironmental changes, disease progression, immunosuppression and drug-resistance. This holds true for both organ-specific cancers and hematologic malignancies. One of the most important components of exosomal cargo are microRNAs which can mediate all the abovementioned effects. More specifically, microRNAs are small non-coding RNAs, routinely detected through quantitative real-time PCR, which act as translational suppressors by regulating protein-coding genes. Considering their high stability in all body fluids and viability in circulation, research is currently focusing on this type of RNAs for the so called “liquid biopsy”, a non-invasive tool for disease diagnosis and longitudinal monitoring. However, several issues remain to be solved including the lack of standardized protocols for exosome isolation and miRNA detection. Starting with this premise, our review aims to provide a wide description of the known microRNA panels employed in the prominent hematological malignancies, which will hopefully redefine the approach to these very challenging diseases in the near future.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Same Fragments, Different Diseases: Analysis of Identical tRNA Fragments Across Diseases Utilizing Functional and Abundance-Based Databases
by
Adesupo Adetowubo, Sathyanarayanan Vaidhyanathan and Andrey Grigoriev
Non-Coding RNA 2025, 11(5), 63; https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11050063 - 29 Aug 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Transfer RNA-derived fragments (tRFs) are small non-coding RNAs increasingly implicated in gene regulation and disease, yet their target specificity and disease relevance remain poorly understood. This is an exploratory study that investigates the phenomenon of identical tRF sequences reported in distinct disease
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Transfer RNA-derived fragments (tRFs) are small non-coding RNAs increasingly implicated in gene regulation and disease, yet their target specificity and disease relevance remain poorly understood. This is an exploratory study that investigates the phenomenon of identical tRF sequences reported in distinct disease contexts and evaluates the consistency between experimental findings and predictions from both target-based and abundance-based tRF databases. Methods: Five tRFs with identical sequences across at least two peer-reviewed disease studies were selected from a recent systematic review. Their validated targets and disease associations were extracted from the literature. Motifs and predicted targets were cross-referenced using three target-oriented databases: tatDB, tRFTar, and tsRFun. In parallel, the abundance enrichment of cancer-associated tRFs was assessed in OncotRF and MINTbase using TCGA-based abundance data. Results: Among the five tRFs, only LeuAAG-001-N-3p-68-85 showed complete alignment between experimental data and both tatDB and tRFTar predictions. Most of the other four displayed at least partial overlaps in motif/binding regions with some of validated targets. tRF abundance data from MINTbase and OncotRF showed inconsistent enrichment, with only AlaAGC-002-N-3p-58-75 exhibiting concordance with its experimentally validated cancer type. Most functionally relevant tRFs were not strongly represented in abundance-only databases. Conclusions: Given the limited number of tRFs analyzed, this study serves primarily as a pilot analysis designed to generate hypotheses and guide future in-depth research, rather than offering comprehensive conclusions. We did, however, illustrate how the analysis of tRFs can benefit from utilizing currently available databases. Target-based databases more closely reflected experimental evidence for mechanistic details when a tRF or a motif match is found. Yet all database types are incomplete, including the abundance-focused tools, which often fail to capture disease-specific regulatory roles of tRFs. These findings underscore the importance of using integrated data sources for tRF annotation. As a pilot analysis, the study provides insights into how identical tRF sequences might function differently across disease contexts, highlighting areas for further investigation while pointing out the limitations of relying on expression data alone to infer functional relevance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Small Non-Coding RNA)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Partners in Silencing: Decoding the Mammalian Argonaute Interactome
by
Srinaath Narasimhan and Stefan J. Erkeland
Non-Coding RNA 2025, 11(4), 62; https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11040062 - 19 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are key post-transcriptional regulators controlling gene expression across several cellular processes, including development, proliferation, and apoptosis. Their biogenesis involves a multi-step pathway, including the processing of primary transcripts and the assembly of the RNA-Induced Silencing Complex (RISC) with Argonaute (AGO) proteins
[...] Read more.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are key post-transcriptional regulators controlling gene expression across several cellular processes, including development, proliferation, and apoptosis. Their biogenesis involves a multi-step pathway, including the processing of primary transcripts and the assembly of the RNA-Induced Silencing Complex (RISC) with Argonaute (AGO) proteins at its core. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the molecular dynamics of miRNA-loaded RISC (miRISC), focusing on the post-translational modifications, the interactors of AGOs and the mechanisms that fine-tune and coordinate miRISC activity. The composition of miRISC influences AGO stability, localization, and silencing efficiency, thereby maintaining cellular homeostasis and development and mediating the response to various types of cellular stress. Uncommon regulatory mechanisms, including AGO modifications during, e.g., hypoxia or Type 2 T cell responses and miRISC functionality, with myriad RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), will be discussed. This review aims at highlighting the recent advances in the understanding of the intricate regulation of miRISC-driven gene silencing.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Role of Non-Coding RNAs in the Regulation of Oncogenic Pathways in Breast and Gynaecological Cancers
by
Ammar Ansari, Aleksandra Szczesnowska, Natalia Haddad, Ahmed Elbediwy and Nadine Wehida
Non-Coding RNA 2025, 11(4), 61; https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11040061 - 6 Aug 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Female cancers such as breast and gynaecological cancers contribute to a significant global health burden and are a leading cause of fatality among women. With current treatment options often limited by resistance to cytotoxic drugs, side effects and lack of specificity to the
[...] Read more.
Female cancers such as breast and gynaecological cancers contribute to a significant global health burden and are a leading cause of fatality among women. With current treatment options often limited by resistance to cytotoxic drugs, side effects and lack of specificity to the cancer, there is a pressing need for alternative treatments. Recent research has highlighted the promising role of non-coding RNAs (ncRNA) in regulating these issues and providing more targeted approaches to suppressing key cancer pathways. This review explores the involvement of the various types of non-coding RNAs in regulating key oncogenic pathways, namely, the MAPK, PI3K/Akt/mTOR, Wnt/β-catenin and p53 pathways, in a range of female cancers such as breast, cervical, ovarian and endometrial cancers. Evidence from a multitude of studies suggests that non-coding RNAs function as double-edged swords, serving as both oncogenes and tumour suppressors, depending on their expression and cellular interactions. By mapping and investigating these regulatory interactions, this review demonstrates the complexity and dual functionality of ncRNAs in cancer. Understanding these complex mechanisms is essential for the development of new and effective ncRNA-based diagnostic methods and targeted therapies in female cancer treatment.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
MALAT1 Expression Is Deregulated in miR-34a Knockout Cell Lines
by
Andrea Corsi, Tonia De Simone, Angela Valentino, Elisa Orlandi, Chiara Stefani, Cristina Patuzzo, Stefania Fochi, Maria Giusy Bruno, Elisabetta Trabetti, John Charles Rotondo, Chiara Mazziotta, Maria Teresa Valenti, Alessandra Ruggiero, Donato Zipeto, Cristina Bombieri and Maria Grazia Romanelli
Non-Coding RNA 2025, 11(4), 60; https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11040060 - 5 Aug 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Non-coding microRNA-34a (miR-34a) regulates the expression of key factors involved in several cellular processes, such as differentiation, apoptosis, proliferation, cell cycle, and senescence. Deregulation of the expression of these factors is implicated in the onset and progression of several human diseases, including
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Non-coding microRNA-34a (miR-34a) regulates the expression of key factors involved in several cellular processes, such as differentiation, apoptosis, proliferation, cell cycle, and senescence. Deregulation of the expression of these factors is implicated in the onset and progression of several human diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and pathologies associated with viral infections and inflammation. Despite numerous studies, the molecular mechanisms regulated by miR-34a remain to be fully understood. The present study aimed to generate miR-34a knockout cell lines to identify novel genes potentially regulated by its expression. Methods: We employed the CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing system to knock out the hsa-miR-34a gene in HeLa and 293T cell lines, two widely used models for studying molecular and cellular mechanisms. We compared proliferation rates and gene expression profiles via RNA-seq and qPCR analyses between the wild-type and miR-34a KO cell lines. Results: Knockout of miR-34a resulted in a decreased proliferation rate in both cell lines. Noteworthy, the ablation of miR-34a resulted in increased expression of the long non-coding RNA MALAT1. Additionally, miR-34a-5p silencing in the A375 melanoma cell line led to MALAT1 overexpression. Conclusions: Our findings support the role of the miR-34a/MALAT1 axis in regulating proliferation processes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Long Non-Coding RNA)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- ncRNA Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
- 10th Anniversary
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
ncRNA
Non-Coding RNA: 10th Anniversary
Guest Editor: George A. CalinDeadline: 31 March 2026
Special Issue in
ncRNA
Women’s Special Issue Series: Worldwide Advances in Non-Coding RNA Research
Guest Editors: Ling Yang, Barbara PardiniDeadline: 30 June 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
ncRNA
Regulatory RNAs in Cardiovascular Development and Disease
Collection Editors: Yvan Devaux, Francisco J. Enguita, Andrea Caporali
Topical Collection in
ncRNA
Research on RNA Modification
Collection Editors: Clément Carré, Damien Brégeon
Topical Collection in
ncRNA
Non-Coding RNAs, COVID-19, and Long-COVID
Collection Editors: Gaetano Santulli, Jessica Gambardella











