- Article
Heritage Conservation and Sustainable Tourism Through Community Participation: Insights from Mt. Rtanj, Serbia
- Sanja Obradović Strålman and
- Nikola Milentijević
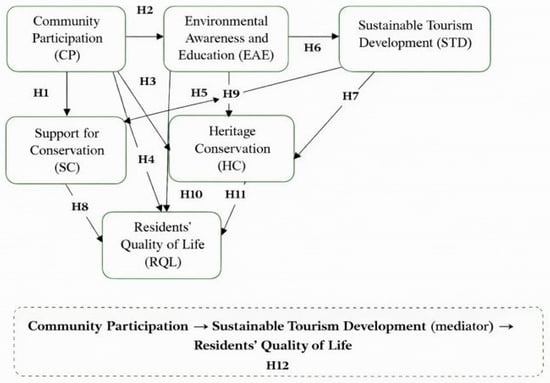
This study explores the interrelationships between community participation, environmental awareness and education, heritage conservation, and sustainable tourism development in shaping quality of life and conservation support in the Mt. Rtanj protected area, Serbia. Using a quantitative approach, data were collected from local residents of Boljevac and Sokobanja municipalities and analyzed through structural equation modeling (SEM). The results confirmed all hypothesized relationships, indicating that active participation and environmental education significantly enhance sustainable tourism development, conservation support, and quality of life. The findings highlight the need for inclusive governance, environmental education programs, and equitable benefit-sharing mechanisms to strengthen local engagement in sustainable tourism. This study contributes to the limited body of literature on sustainable tourism in Southeast European Mountain regions and offers a replicable framework for community-based conservation and development, aligned with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs 8, 12, and 15).
19 December 2025