- Article
Energy Savings, Carbon-Equivalent Abatement Cost, and Payback of Residential Window Retrofits: Evidence from a Heating-Dominated Mid-Latitude City—Gyeonggi Province, South Korea
- YeEun Jang,
- Jeongeun Park and
- Yeweon Kim
- + 1 author
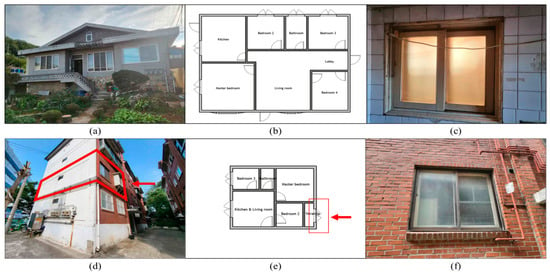
This study presents an integrated ex-post evaluation of a municipal window-retrofit program in Goyang, Republic of Korea (heating-dominated, Dwa). Using field surveys and pre- and post-utility bills for 36 dwellings, mainly pre-2000 low-rise reinforced-concrete buildings, we normalize climate with HDD and CDD and prices with CPI-deflated tariffs to isolate the intrinsic effect of window replacement. Area-normalized indicators (, , DPB, NPV, AC) were computed. Average annual savings were 30.2 kWh per m2 per year ( ≈ 16 percent), consisting of 10.6 kWh per m2 per year of gas and 19.6 kWh per m2 per year of electricity (n = 36). The median discounted payback was 7.0 years. Under a 50 percent subsidy, about 80 percent of projects recovered private investment within 15 years and showed positive NPV with a median of about USD 4944. The electricity-tariff multiplier had the largest influence on cash flows and payback. The median abatement cost was about USD 352 per tCO2-eq. A portfolio view indicates that prioritizing low-cost cases maximizes total abatement, and that higher-cost cases merit design or cost review. Using the first post-retrofit year 2023, portfolio abatement is about 623 tCO2-eq per year. The framework jointly normalizes climate and price effects and yields policy-relevant estimates for heating-dominated contexts.
24 December 2025