Updating Nutritional Data and Evaluation of Technological Parameters of Italian Milk
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Samples
- 18 samples of whole milk: 3 pasteurized (PW), 3 microfiltered (MW) and 12 UHT (UHTW) milks;
- 20 samples of semi-skimmed milk: 2 pasteurized (PS), 4 microfiltered (MS) and 14 UHT (UHTS) milks.
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Equipments
2.4. Minerals Determination
2.5. Lactose and Lactulose
2.6. Choline
2.7. Unsaponifiable Components and Tracing Parameters
2.8. Color Measurements
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mineral Content
| Milk | Calcium | Phosphorus | Sodium | Ca/P | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whole—18 samples | ||||||||||||
| Mean ± SD | 112.7 ± 5.3 | 94.2 a ± 3.2 | 43.8 ± 3.6 | 0.9 | ||||||||
| Min–Max | 101.5–121.7 | 86.6–98.1 | 36.4–51.9 | 0.9–1.0 | ||||||||
| PW—3 samples | ||||||||||||
| Mean ± SD | 111.1 ± 1.8 | 93.3 ± 0.6 | 41.5 ± 5.0 | 0.9 | ||||||||
| Min–Max | 109.0–112.2 | 92.9–94.0 | 36.3–46.3 | 0.9–0.9 | ||||||||
| MW—3 samples | ||||||||||||
| Mean ± SD | 110.9 ± 5.1 | 92.0 ± 4.6 | 44.5 ± 7.1 | 0.9 | ||||||||
| Min–Max | 105.1–114.2 | 86.6–95.1 | 37.8–51.9 | 0.9–0.9 | ||||||||
| UHTW—12 samples | ||||||||||||
| Mean ± SD | 113.5 ± 6.0 | 95.1 ± 3.1 | 44.1 ± 2.2 | 0.9 | ||||||||
| Min–Max | 101.5–121.7 | 88.1–98.1 | 40.5–47.8 | 0.9–1.0 | ||||||||
| Semi-Skimmed—20 samples | ||||||||||||
| Mean ± SD | 115.5 ± 4.9 | 96.5 b ± 3.4 | 43.3 ± 3.3 | 0.9 | ||||||||
| Min–Max | 105.1–123.3 | 88.8–102.6 | 38.7–52.0 | 0.9–1.0 | ||||||||
| PS—2 samples | ||||||||||||
| Mean ± SD | 114.6 ± 1.1 | 95.4 ± 0.1 | 45.9 ± 2.8 | 0.9 | ||||||||
| Min–Max | 113.8–115.3 | 95.4–95.5 | 43.9–47.8 | 0.9–0.9 | ||||||||
| MS—4 samples | ||||||||||||
| Mean ± SD | 113.7 ± 4.5 | 95.1 ± 4.5 | 44.4 ± 5.4 | 0.9 | ||||||||
| Min–Max | 107.0–116.6 | 88.8–99.1 | 39.0–52.0 | 0.9–0.9 | ||||||||
| UHTS—14 samples | ||||||||||||
| Mean ± SD | 116.2 ± 5.4 | 97.1 ± 3.3 | 42.6 ± 2.6 | 0.9 | ||||||||
| Min–Max | 105.1–123.4 | 91.3–102.6 | 38.7–47.0 | 0.9–1.0 | ||||||||
3.2. Lactose and Lactulose Content
| Milk | Lactose | Lactulose | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Whole—18 samples | |||
| Mean ± SD | 4.8 ± 0.2 | ||
| Min–Max | 4.3–5.3 | ||
| PW—3 samples | |||
| Mean ± SD | 4.5 a ± 0.2 | n.d. | |
| Min–Max | 4.3–4.6 | ||
| MW—3 samples | |||
| Mean ± SD | 4.7 ± 0.1 | n.d. | |
| Min–Max | 4.6–4.8 | ||
| UHTW—12 samples | |||
| Mean ± SD | 4.9 b ± 0.2 | 43.3 ± 28.8 | |
| Min–Max | 4.6–5.3 | 10.2–90.6 | |
| Semi-skimmed—20 samples | |||
| Mean ± SD | 4.9 ± 0.2 | ||
| Min–Max | 4.3–5.4 | ||
| PS—2 samples | |||
| Mean ± SD | 4.9 ± 0.1 | n.d. | |
| Min–Max | 4.8–4.9 | ||
| MS—4 samples | |||
| Mean ± SD | 4.8 ± 0.1 | n.d. | |
| Min–Max | 4.6–4.9 | ||
| UHTS—14 samples | |||
| Mean ± SD | 4.9 ± 0.3 | 44.2 ± 35.4 | |
| Min–Max | 4.3–5.4 | 8.6–104.0 | |
3.3. Choline Content
| Milk | Choline hydroxide (mg/100 g) | |
|---|---|---|
| Whole—18 samples | ||
| Mean ± SD | 13.0 ± 1.0 | |
| Min–Max | 11.3–14.6 | |
| PW—3 samples | ||
| Mean ± SD | 12.2 a ± 0.3 | |
| Min–Max | 11.8–12.4 | |
| MW—3 samples | ||
| Mean ± SD | 11.8 a ± 0.6 | |
| Min–Max | 11.5–12.5 | |
| UHTW—12 samples | ||
| Mean ± SD | 13.4 b ± 0.8 | |
| Min–Max | 11.3–14.6 | |
| Semi-skimmed milk—20 samples | ||
| Mean ± SD | 13.0 ± 1.1 | |
| Min–Max | 11.1–14.7 | |
| PS—2 samples | ||
| Mean ± SD | 11.8 a ± 0.2 | |
| Min–Max | 11.6–11.9 | |
| MS—4 samples | ||
| Mean ± SD | 12.0 a ± 0.8 | |
| Min–Max | 11.1–13.0 | |
| UHTS—14 samples | ||
| Mean ± SD | 13.5 b ± 0.9 | |
| Min–Max | 11.7–14.7 | |
3.4. Unsaponifiable Compounds and Tracing Parameters
| Milk | Cholesterol | β-Carotene | α-Tocopherol | 13 cis retinol | trans retinol | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whole—18 samples | ||||||
| Mean ± SD | 12.8 a ± 0.4 | 7.9 a ± 3.5 | 87.2 a ± 8.8 | 3.3 a ± 2.2 | 46.2 a ± 9.9 | |
| Min–Max | 12.1–13.5 | 4.2–15.3 | 66.2–105.9 | 0.4–7.3 | 31.2–64.4 | |
| PW—3 samples | ||||||
| Mean ± SD | 13.1 ± 0.1 | 5.2 ± 0.9 | 80.4 ± 3.8 | 0.7 A ± 0.3 | 54.7 A ± 8.6 | |
| Min–Max | 13.0–13.2 | 4.4–6.2 | 76.9–84.4 | 0.4–0.9 | 44.9–61.0 | |
| MW—3 samples | ||||||
| Mean ± SD | 12.7 ± 0.2 | 5.5 ± 1.1 | 83.4 ± 14.9 | 1.2 A ± 0.3 | 60.0 A ± 5.8 | |
| Min–Max | 12.5–12.9 | 4.2–6.3 | 66.2–92.5 | 0.9–1.5 | 53.4–64.4 | |
| UHTW—14 samples | ||||||
| Mean ± SD | 12.8 ± 0.5 | 9.2 ± 3.6 | 89.9 ± 7.2 | 4.4 B ± 1.7 | 40.6 B ± 5.1 | |
| Min–Max | 12.1–13.5 | 5.4–15.3 | 81.7–105.9 | 1.9–7.3 | 31.2–48.0 | |
| Semi-skimmed—20 samples | ||||||
| Mean ± SD | 7.0 b ± 0.2 | 4.0 b ± 1.4 | 40.2 b ± 5.9 | 2.1 b ± 1.4 | 21.0 b ± 5.0 | |
| Min–Max | 6.4–7.4 | 2.2–7.1 | 30.4–53.0 | 0.3–4.3 | 14.7–32.5 | |
| PS—2 samples | ||||||
| Mean ± SD | 7.1 ± 0.2 | 2.4 ± 0.0 | 34.8 ± 3.0 | 0.5 A ± 0.0 | 25.6 A ± 0.0 | |
| Min–Max | 7.0–7.2 | 2.4–2.5 | 32.7–36.9 | 0.4–0.5 | 25.6–25.7 | |
| MS—4 samples | ||||||
| Mean ± SD | 7.2 ± 0.2 | 3.1 ± 0.6 | 44.2 ± 9.7 | 0.5 A ± 0.1 | 28.0 A ± 3.5 | |
| Min–Max | 7.0–7.4 | 2.2–3.6 | 30.5–53.0 | 0.3–0.6 | 24.1–32.5 | |
| UHTS—14 samples | ||||||
| Mean ± SD | 7.0 ± 0.2 | 4.4 ± 1.4 | 39.8 ± 4.3 | 2.8 B ± 1.0 | 18.4 B ± 2.9 | |
| Min–Max | 6.4–7.3 | 3.0–7.2 | 32.6–49.4 | 1.3–4.3 | 14.7–23.8 | |
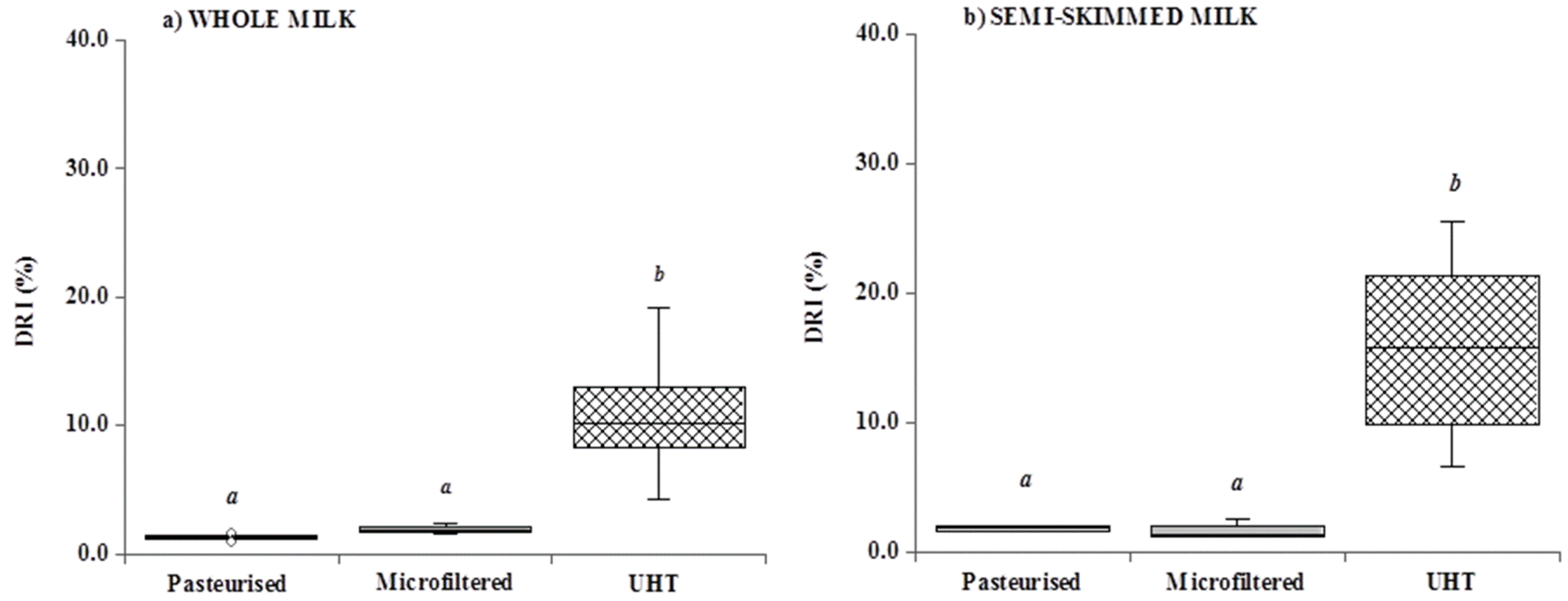
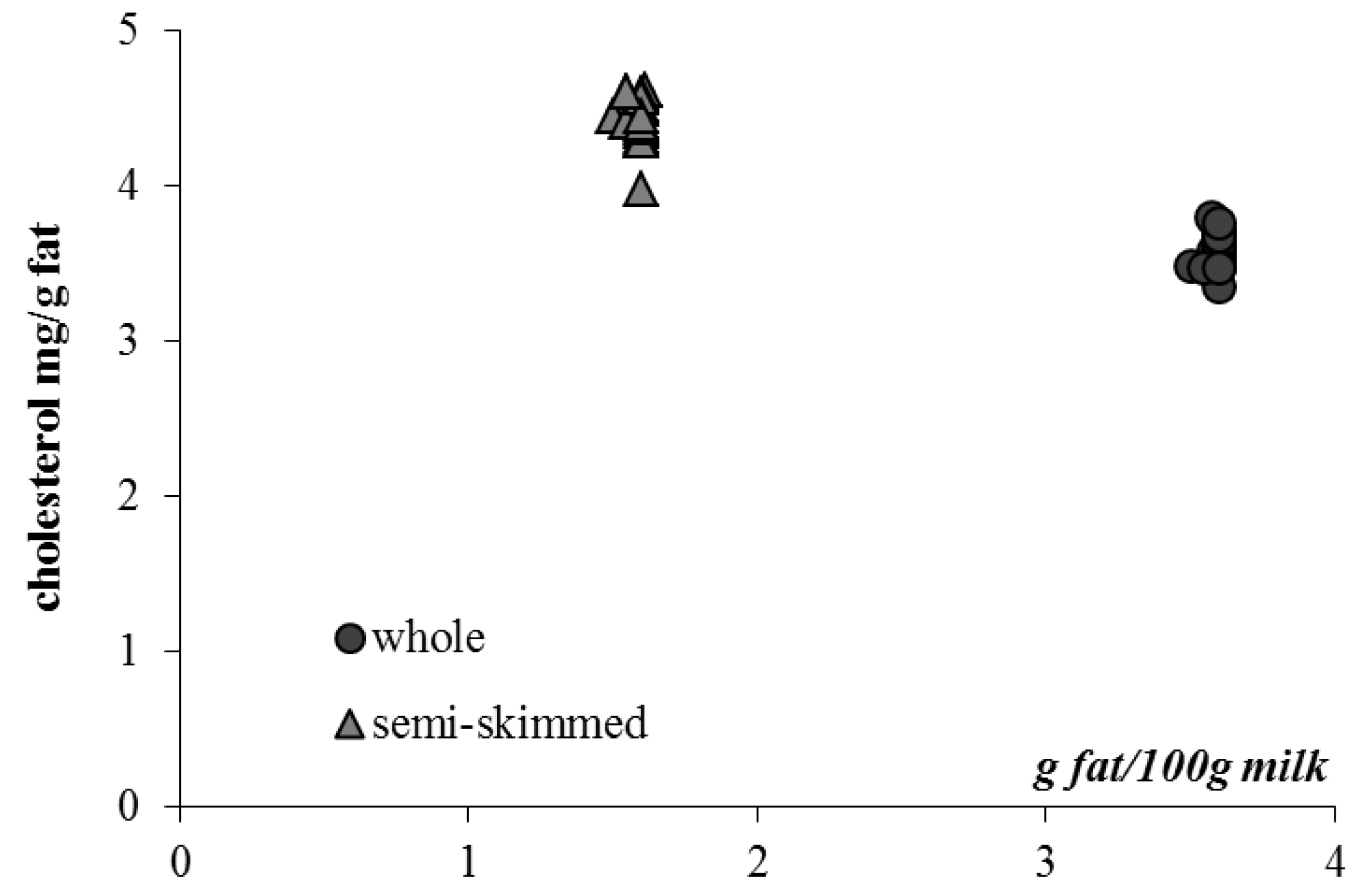
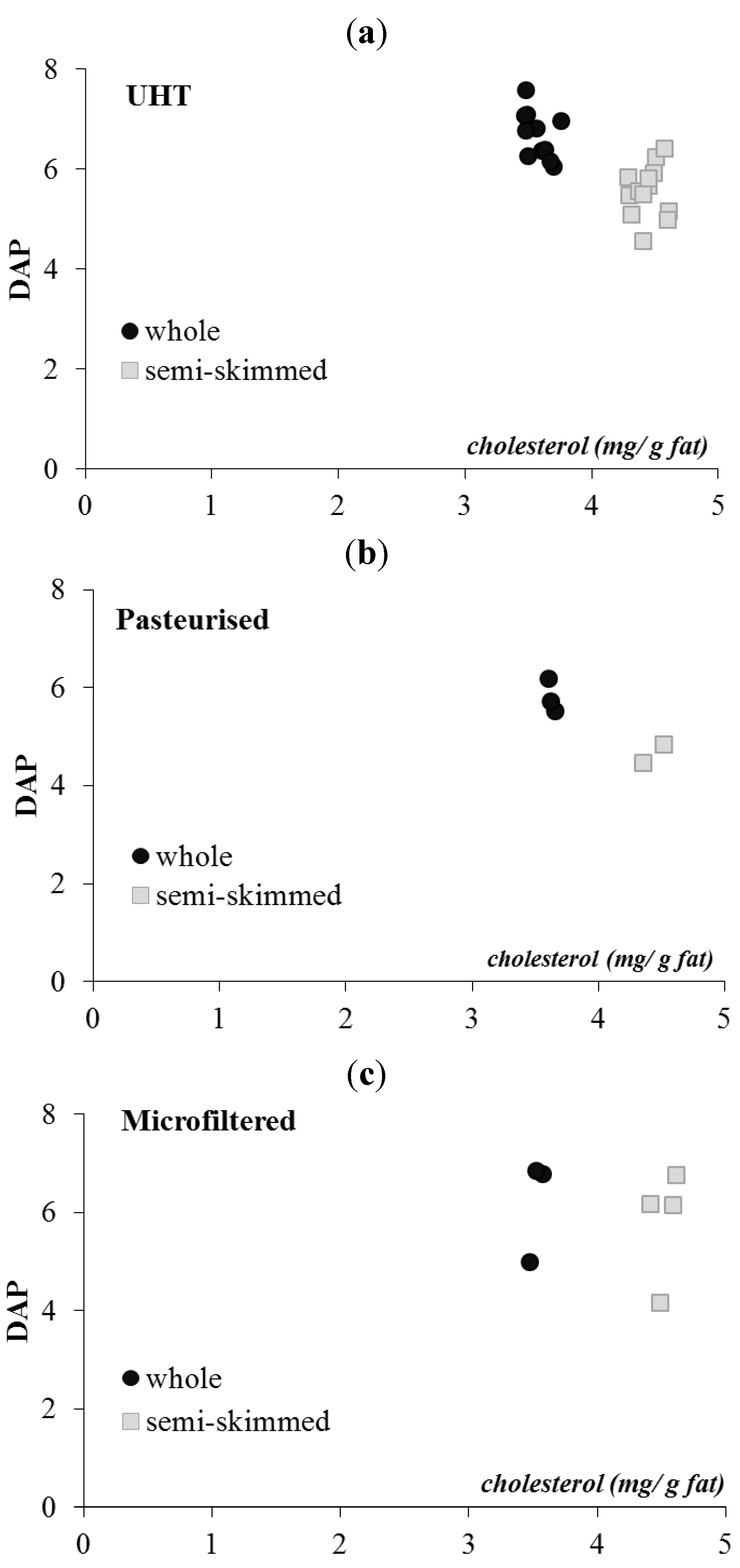
3.5. Color Measurement
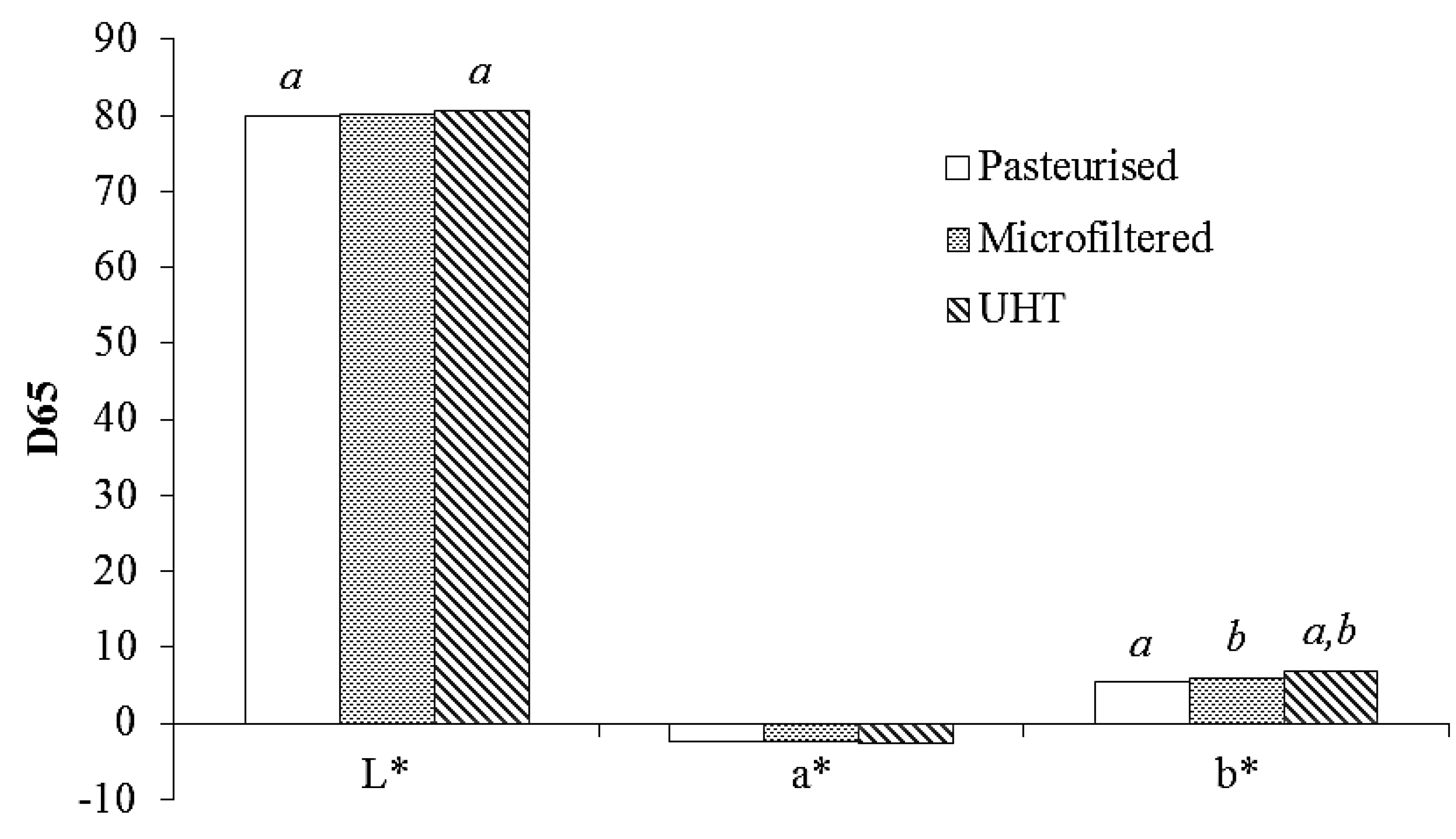
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Dairy Federation, The World Dairy Situation 2010. Bulletin of the International Dairy Federation 446/2010; International Dairy Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2010.
- Gerosa, S.; Skoet, J. Milk Availability: Trends in Production and Demand and Medium-Term Outlook. ESA Working Paper No. 12-01. February 2012. Available online: http://www.fao.org/docrep/015/an450e/an450e00.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2013).
- OECD-FAO. Agricultural Outlook 2012–2021. Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.1787/agr_outlook-2012-en (accessed on 23 April 2013).
- Italian Law. Ministero della Salute, Decreto 12/12/2012. Available online: http://www.trovanorme.salute.gov.it/dettaglioAtto?id=45076&completo=true (accessed on 7 June 2013).
- Konosonoka, I.H.; Jemeljanovs, A.; Osmane, B.; Ikauniece, D.; Gulbe, G. Incidence of Listeria spp. in dairy cows feed and raw milk in Latvia. ISRN Vet. Sci. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, K.; Drummond, N.; Murphy , M.; Butler, F.; Buckley, J.; Jordan, K. A case of bovine raw milk contamination with Listeria monocytogenes. Ir. Vet. J. 2012, 65, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Claeys, W.L.; Cardoen, S.; Daube, G.; de Block, J.; Dewettinck, K.; Dierick, K.; de Zutter, L.; Huyghebaert, A.; Imberechts, H.; Thiange, P.; et al. Raw or heated cow milk consumption: Review of risks and benefits. Food Control 2013, 31, 251–262. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, S.P.; Boor, K.J.; Murphy, S.C.; Murinda, S.E. Food safety hazards associated with consumption of raw milk. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2009, 6, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council Directive 92/46/EEC of 16 June 1992 Laying down the Health Rules for the Production and Placing on the Market of Raw Milk, Heat-Treated Milk and Milk-Based Product. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/food/fs/sfp/mr/mr03_en.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2013).
- Italian Law. Ministero della salute, Decreto 17/6/2002. Available online: http://gazzette.comune.jesi.an.it/2002/178/6.htm (accessed on 7 June 2013).
- Garcia Fernandez, L.; Alvarez Blanco, S.; Riera Rodrıguez, F.A. Microfiltration applied to dairy streams: Removal of bacteria. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboya, L.V.; Maubois, J.L. Current developments of microfiltration technology in the dairy industry. Lait 2000, 80, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwell, M.W.; Barbano, D.M. Use of microfiltration to improve fluid milk quality. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, E10–E30. [Google Scholar]
- Haug, A.; Høstmark, A.T.; Harstad, O.M. Bovine milk in human nutrition—A review. Lipids Health Dis. 2007, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boekel, M.A.J.S. Effect of heating on Maillard reactions in milk. Food Chem. 1998, 62, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, J.E.; Fox, P.F. O’Connell, J.E.; Fox, P.F. Heat Stability of Milk. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences, 1st ed.; Roginski, H., Fuquay, J.W., Fox, P.F., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2002; pp. 1321–1326. [Google Scholar]
- Seiquer, I.; Delgado-Andrade, C.; Haro, A.; Navarro, M.P. Assessing the effects of severe heat treatment of milk on calcium bioavailability: In vitro and in vivo studies. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 5635–5643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Method 991.25. Calcium, Magnesium and Phosphorus in Cheese; Association of Official Method of Analysis: Arlington, VA, USA, 2002.
- Indyk, H.E.; Edwards, M.J.; Woollard, D.C. High performance liquid chromatographic analysis of lactose-hydrolysed milk. Food Chem. 1996, 56, 574–580. [Google Scholar]
- Manzi, P.; Pizzoferrato, L. HPLC determination of lactulose in heat treated milk. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Method 999.14. Choline in Infant Formula and Milk; Association of Official Methods of Analysis: Arlington, VA, USA, 2000.
- Panfili, G.; Manzi, P.; Pizzoferrato, L. High performance liquid chromatographic method for the simultaneous determination of tocopherols, carotenes, and retinol and its geometric isomers in Italian cheeses. Analyst 1994, 119, 1161–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panfili, G.; Manzi, P.; Pizzoferrato, L. Influence of thermal and other manufacturing stresses on retinol isomerization in milk and dairy products. J. Dairy Res. 1998, 65, 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Pizzoferrato, L.; Manzi, P.; Marconi, S.; Fedele, V.; Claps, S.; Rubino, R. Degree of antioxidant protection: A parameter to trace the origin and quality of goat’s milk and cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 4569–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaucheron, F. The minerals of milk. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 2005, 45, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cashman, K.D. Milk minerals including trace elements and bone health. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidiroglou, M.; Proulx, J.G. Factors affecting the calcium, magnesium and phosphorus content of beef cow milk. Can. J. Comp. Med. 1982, 46, 212–214. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, G.D.; di Rienzo, D.D.; Reusser, M.E.; McCarron, D.A. Benefits of dairy product consumption on blood pressure in humans: A summary of the biomedical literature. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2000, 19, 147S–164S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemel, M.B. Role of dietary calcium and dairy products in modulating adiposity. Lipids. 2003, 382, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulgoni, V.L.; Huth, P.J.; di Rienzo, D.B.; Miller, G.D. Determination of the optimal number of dairy servings to ensure a low prevalence of inadequate calcium intake in Americans. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2004, 23, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LARN, Livelli di Assunzione Raccomandati di Energia e Nutrienti per la Popolazione Italiana; EDRA: Milano, Italy, 1996.
- Stephens, A.M.; Haddad, A.C.; Phillips, S.J. Passage of carbohydrates into the colon. Gastroenterology 1983, 85, 589–595. [Google Scholar]
- Adam, A.C.; Rubio-Texeira, M.; Polaina, J. Lactose: The milk sugar from a biotechnological perspective. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2004, 44, 553–557. [Google Scholar]
- Siddique, F.; Anjum, F.M.; Huma, N.; Jamil, A. Effect of different UHT processing temperatures on ash and lactose content of milk during storage at different temperatures. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2010, 12, 439–442. [Google Scholar]
- Berning, L.M.; Shook, G.E. Prediction of mastitis using milk somatic cell count, N-acetyl-beta-d-glucosaminidase and lactose. J. Dairy Sci. 1992, 75, 1840–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, F.J.; Romero, C.; Jimenez-Perez, S. Characterization of industrial processed milk by analysis of heat-induced changes. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 35, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Fandiño, R.; Olano, A. Review: Selected indicators of the quality of thermal processed milk. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 1999, 5, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortier, L.; Braekman, A.; Cartuyvels, D.; van Renterghem, R.; de Block, J. Intrinsic indicators for monitoring heat damage of consumption milk. Biotechnol. Agron. Soc. Environ. 2000, 4, 221–225. [Google Scholar]
- Schuck, P. Spray drying of dairy products, state of the art. Lait 2002, 82, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberfroid, M. Concepts in functional foods: The case of inulin and oligofructose. J. Nutr. 1999, 129, 1398S–1401S. [Google Scholar]
- Milner, J.A. Functional foods and health promotion. J. Nutr. 1999, 129, 1395S–1397S. [Google Scholar]
- Zeisel, S.H.; Blusztajn, J.K. Choline and human nutrition. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1994, 14, 269–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes-McNary, M.Q.; Cheng, W.L.; Mar, M.H.; Fussel, S.; Zeisel, S.H. Choline and choline esters in human and rat milk and infant formulas. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 64, 572–576. [Google Scholar]
- Zeisel, S.H.; Mar, M.H.; Howe, J.C.; Holden, J.M. Concentrations of choline-containing compounds and betaine in common foods. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 1302–1307. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Vance, D.E. Phosphatidylcholine and choline homeostasis. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar]
- Rajaie, S.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Dietary choline and betaine intakes and risk of cardiovascular diseases: Review of epidemiological evidence. ARYA Atheroscler. 2011, 72, 78–86. [Google Scholar]
- Christie, W.W.; Noble, R.C.; Davies, G. Phospholipids in milk and dairy-products. J. Soc. Dairy Technol. 1987, 40, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitman, J.; Wood, D.L. Changes in milk-fat phospholipids during lactation. J. Dairy Sci. 1990, 73, 1208–1216. [Google Scholar]
- Rombaut, R.; Dewettinck, K.; van Camp, J. Phospho- and sphingolipid content of selected dairy products as determined by HPLC coupled to an evaporative light scattering detector (HPLC-ELSD). J. Food Comp. Anal. 2007, 20, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattera, M.; Manzi, P.; Pizzoferrato, L. Colina e Lattulosio nel Latte di Origine Vaccina e Caprina. In Proceedings of VIII Congresso Nazionale di Chimica degli Alimenti—Qualità e Tipicità Degli Alimenti Mediterranei: Alimentazione e Salute, Messina 20–24/9/2010; Società Chimica Italiana: Messina, Italy, 2011; pp. 145–149. [Google Scholar]
- Noziere, P.; Graulet, B.; Lucas, A.; Martin, B.; Grolier, P.; Doreau, M. Carotenoids for ruminants: From forages to dairy products. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2006, 131, 418–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noziere, P.; Grolier, P.; Durand, D.; Ferlay, A.; Pradel, P.; Martin, B. Variations in carotenoids, fat-soluble micronutrients, and colour in cows’ plasma and milk following changes in forage and feeding level. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 2634–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, S.K.; Johannsen, A.K.B.; Hermansen, J.E. Quantitative secretion and maximal secretion capacity of retinol, β-carotene and α-tocopherol into cows’ milk. J. Dairy Res. 1999, 66, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panfili, G.; Fratianni, A.; di Criscio, T.; Gammariello, D.; Sorrentino, E. Influence of microorganisms on retinol isomerization in milk. J. Dairy Res. 2008, 75, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Marconi, E.; Panfili, G. Chemical composition and nutritional properties of commercial products of mare milk powder. J. Food Comp. Anal. 1998, 11, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdman, J.W.; Poor, C.L.; Dietz, J.M. Factors affecting the bioavailability of vitamin A, carotenoids, and vitamin E. Food Technol. 1988, 42, 214–221. [Google Scholar]
- Weiser, H.; Somorjai, G. Bioactivity of cis and dicis isomers of vitamin A esters. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 1992, 62, 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Manzi, P.; Pizzoferrato, L. Cholesterol and antioxidant vitamins in fat fraction of whole and skimmed dairy products. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2010, 3, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerutti, G.; Machado, M.A.; Ribalzi, L. Sulla distribuzione del colesterolo in latte e derivati. Latte 1993, 11, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Esti, M.; Cinquanta, L.; Panfili, G.; Manzi, P.; Marconi, S.; Pizzoferrato, L. Effects of variety and olive ripeness on nutritional quality and oxidative stability of extra virgin olive oils. Food Agric. Environ. 2004, 2, 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Pathare, P.B.; Opara, U.L.; Al-Said, F.A. Colour measurement and analysis in fresh and processed foods: A review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 36–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, D.M.; Beaulieu, J.C.; Shewfelt, R. Colour, flavor, texture, and nutritional quality of fresh-cut fruits and vegetables: Desirable levels, instrumental and sensory measurement, and the effects of processing. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2010, 505, 369–389. [Google Scholar]
- Popov-Raljić, J.V.; Lakić, N.S.; Laličić-Petronijević, J.G.; Barać, M.B.; Sikimić, V.M. Colour changes of UHT milk during storage. Sensors 2008, 8, 5961–5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Manzi, P.; Di Costanzo, M.G.; Mattera, M. Updating Nutritional Data and Evaluation of Technological Parameters of Italian Milk. Foods 2013, 2, 254-273. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods2020254
Manzi P, Di Costanzo MG, Mattera M. Updating Nutritional Data and Evaluation of Technological Parameters of Italian Milk. Foods. 2013; 2(2):254-273. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods2020254
Chicago/Turabian StyleManzi, Pamela, Maria Gabriella Di Costanzo, and Maria Mattera. 2013. "Updating Nutritional Data and Evaluation of Technological Parameters of Italian Milk" Foods 2, no. 2: 254-273. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods2020254




