Surface Plasmon Resonance Immunosensor for the Detection of Campylobacter jejuni
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Instrumentation
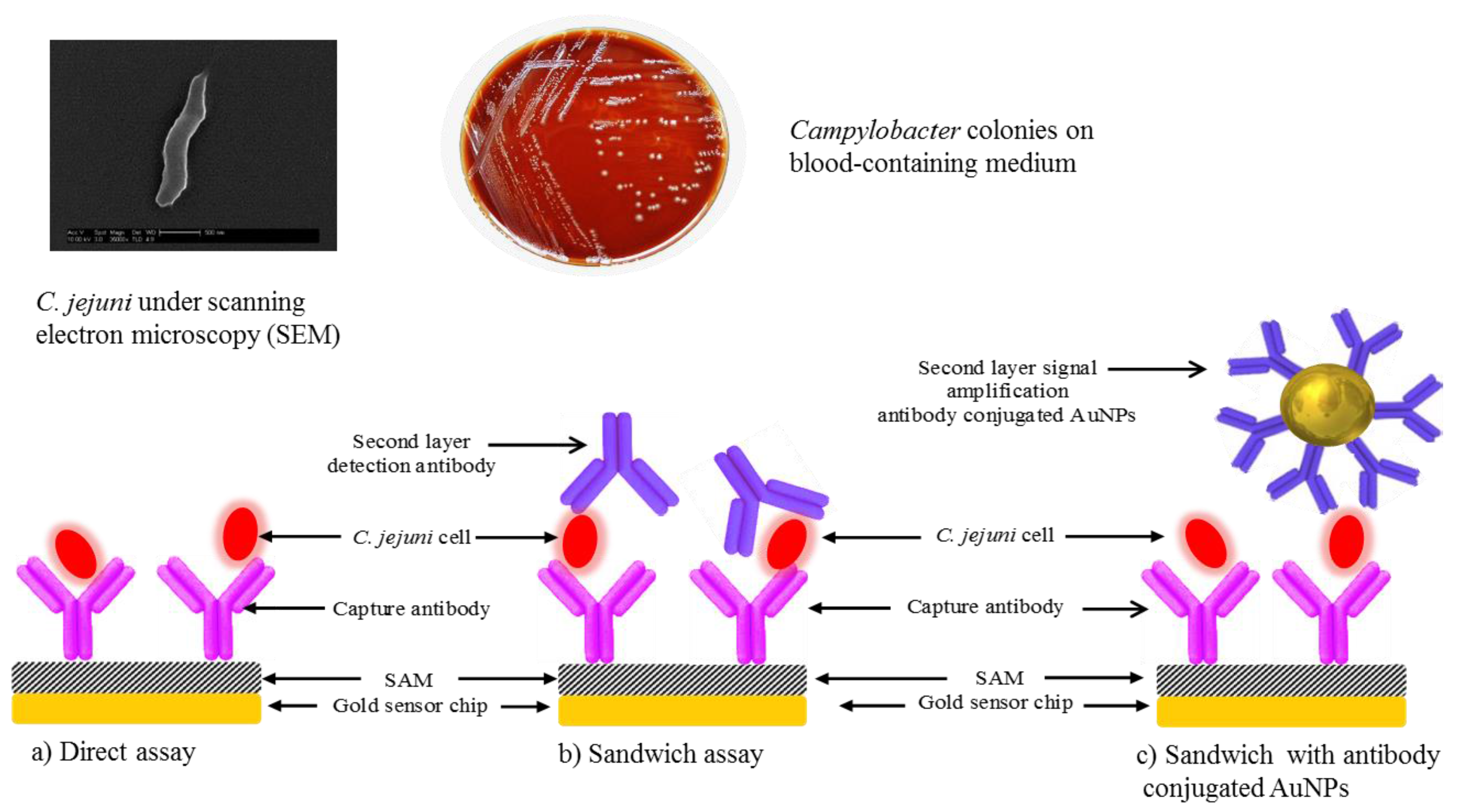
2.3. Bacterial Strains and Preparation of C. jejuni Cells
2.4. Sensor Chip Preparation and SAM Formation
2.5. Surface Activation and Antibody Immobilization
2.6. Optimization of C. jejuni Detection
2.7. Modification of AuNPs with Anti-C. jejuni Detection Antibody
2.8. Antibody-Modified AuNPs Sandwich Detection Assay for C. jejuni
2.9. Specificity Studies
2.10. Limit of Detection and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
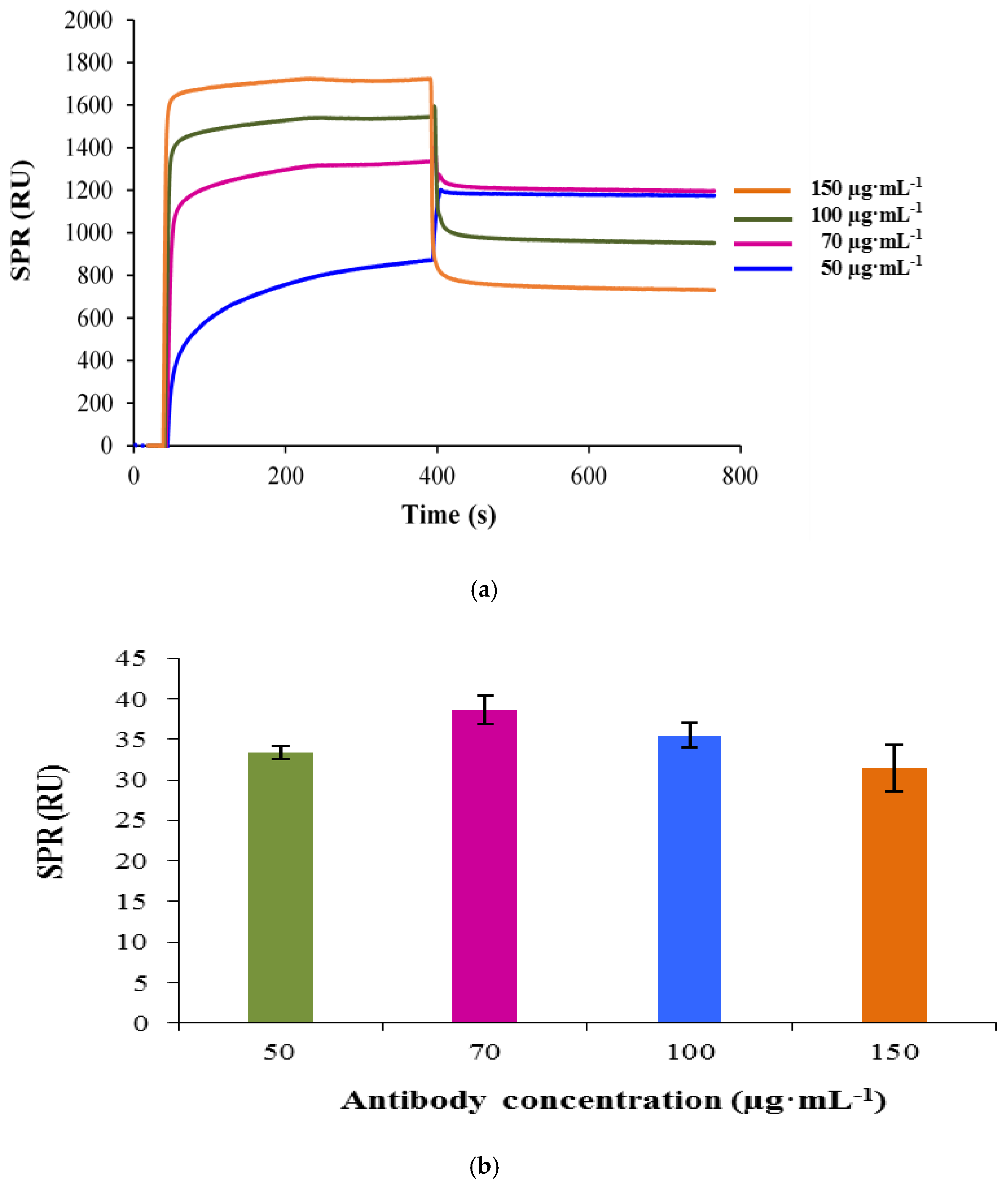
3.1. Immobilization of the Antibody on SAM
3.2. Optimization of C. jejuni Binding Assay
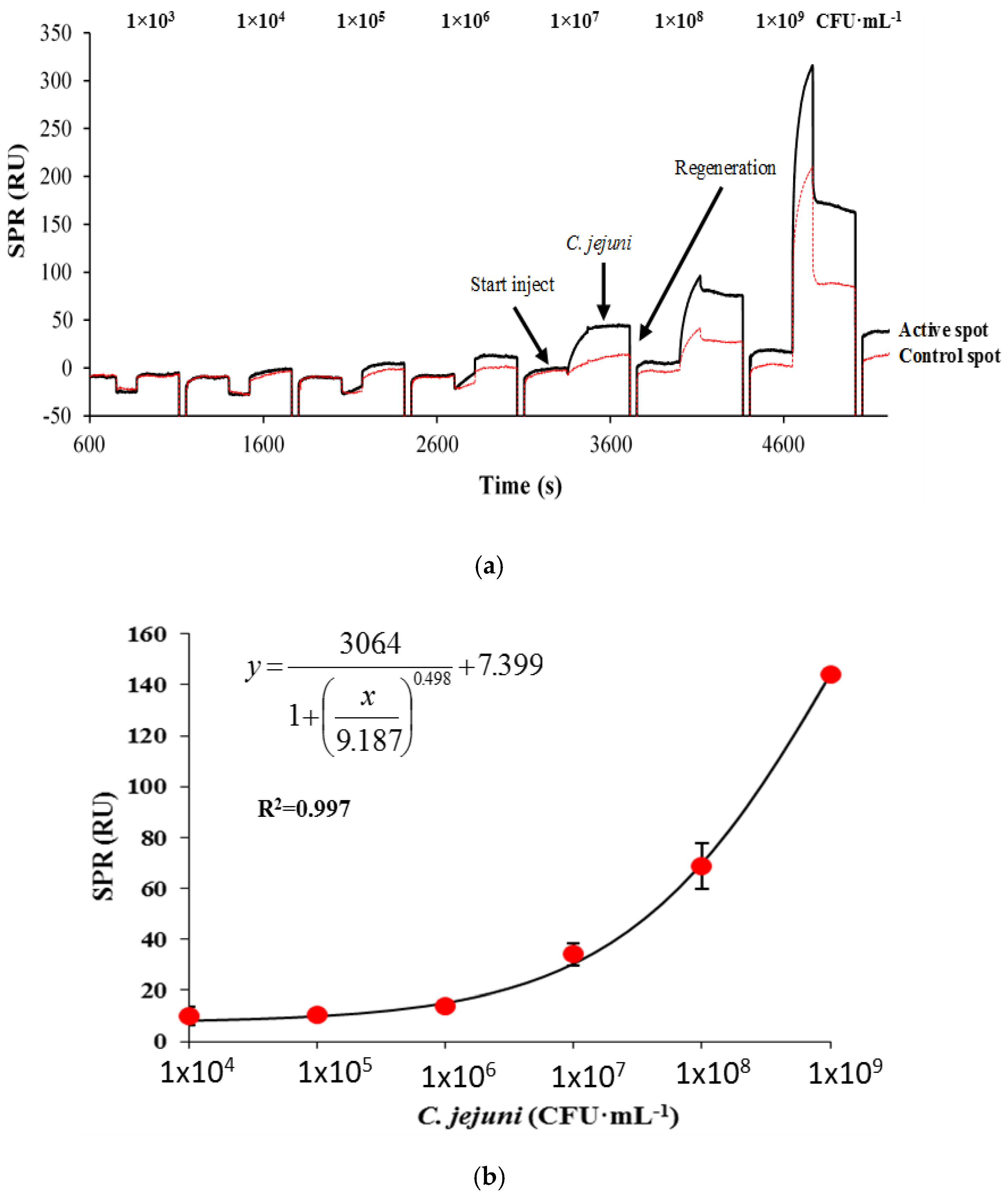
3.2.1. Direct Assay
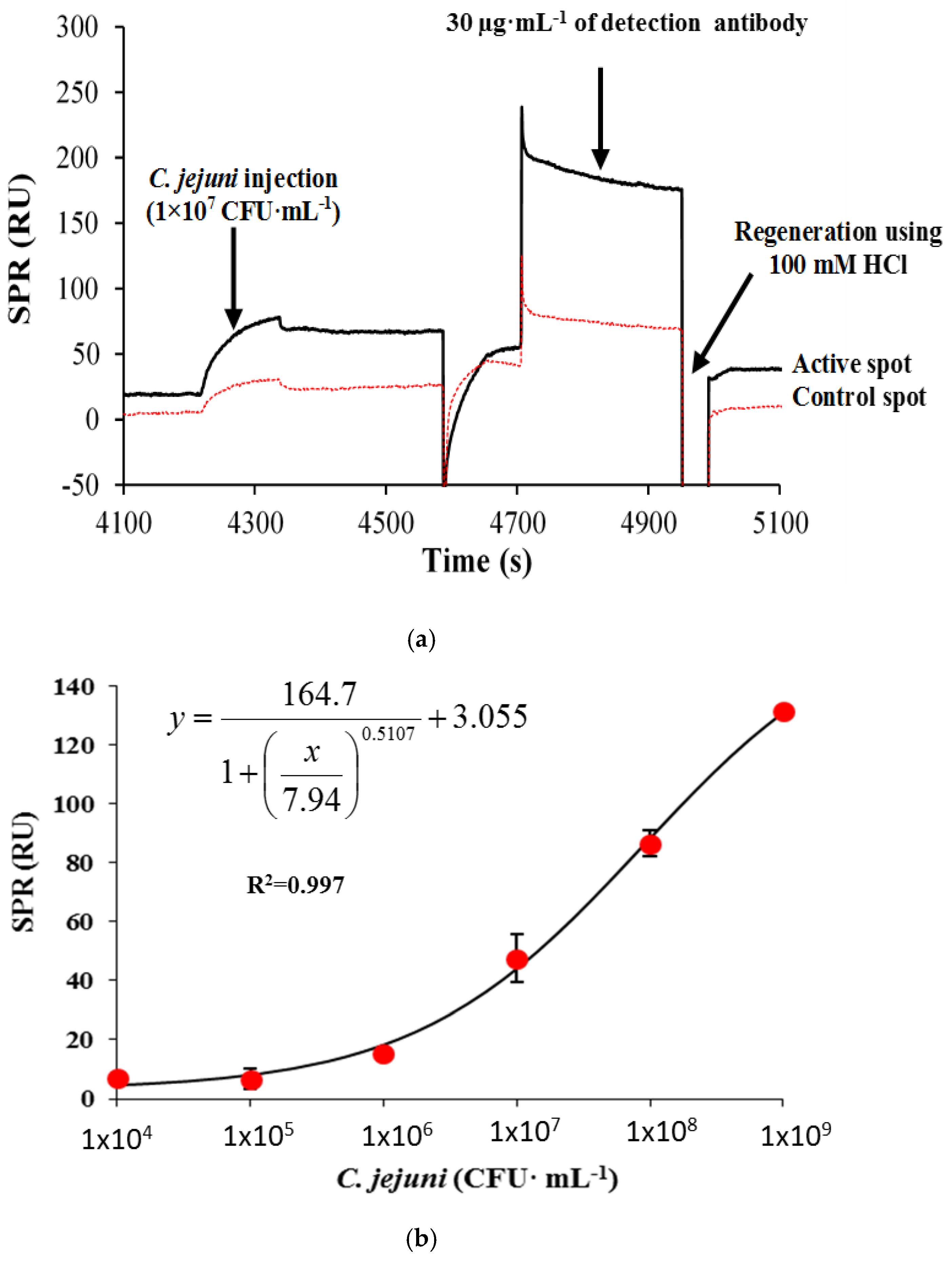
3.2.2. Sandwich Assay
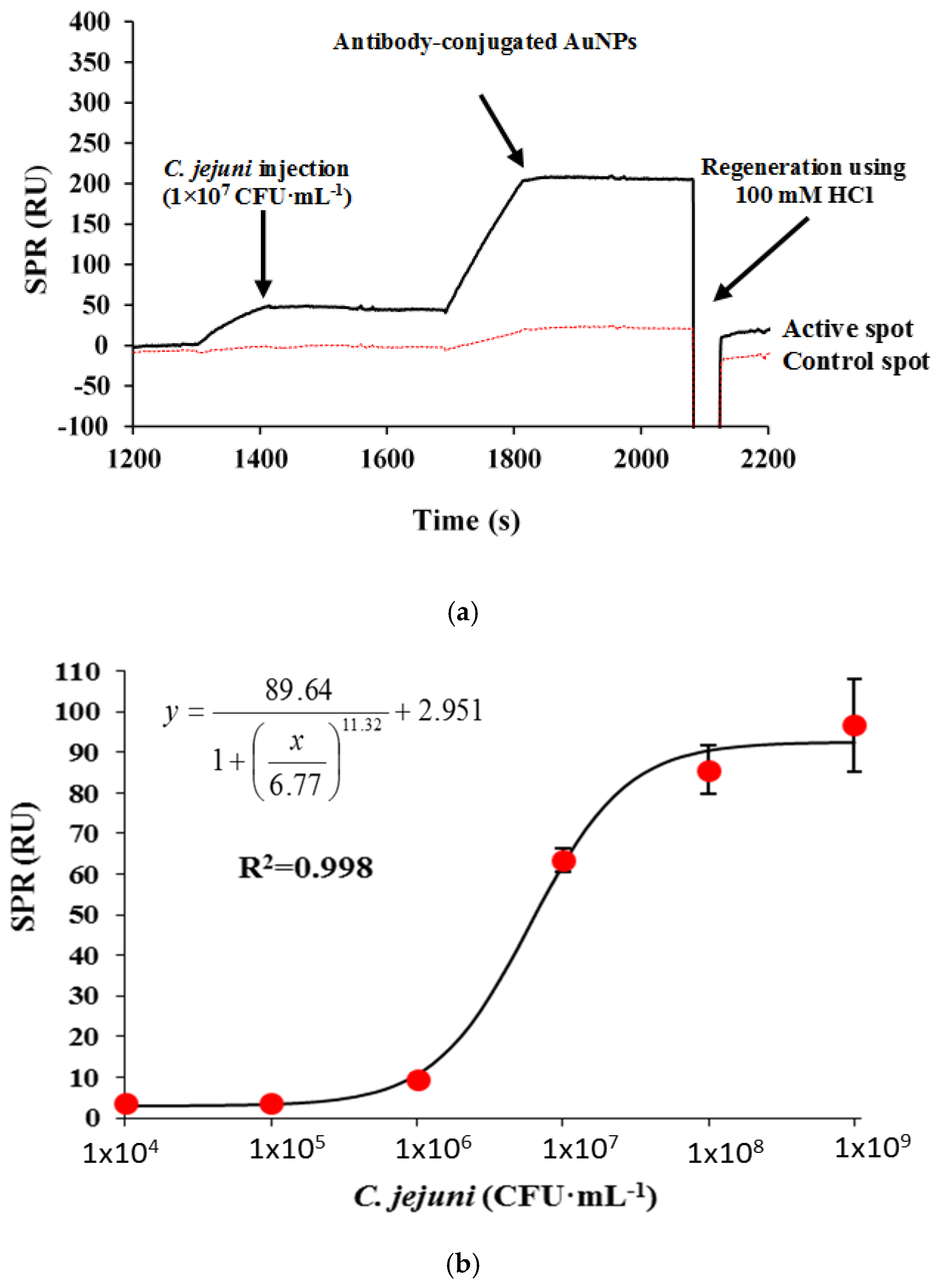
3.2.3. Sandwich Assay with Signal Amplification Using AuNPs
3.3. Cross-Reactivity Studies Against Other Bacteria
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 11-MUDA | 11-mercaptoundecanoic acid |
| CFU | Colony forming unit |
| EDC | 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| AuNPs | Gold colloidal |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| NHS | N-hydroxysuccinimide |
| PBS | Phosphate buffered saline |
| QCM | Quartz crystal microbalance |
| RU | Response unit |
| SAM | Self-assembled monolayer |
| SD | Standard deviations |
| SPR | Surface plasmon resonance |
References
- Walker, R.I.; Caldwell, M.B.; Lee, E.C. Pathophysiology of Campylobacter enteritis. Microbiol. Rev. 1986, 50, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Friedman, C.; Neimann, J.; Wegener, H.; Tauxe, R.V. Epidemiology of Campylobacter jejuni infections in the United States and other industrialized nations. In Campylobacter; Nachamkin, I., Blaser, M.J., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; pp. 121–138. [Google Scholar]
- Vandeplas, S.; Dubois Dauphin, R.; Beckers, Y.; Thonart, P.; Théwis, A. Salmonella in chicken: Current and developing strategies to reduce contamination at farm level. J. Food Prot. 2010, 73, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, T.; O’Brien, S.; Madsen, M. Campylobacters as zoonotic pathogens: A food production perspective. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 117, 237–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hänninen, M.-L.; Haajanen, H.; Pummi, T.; Wermundsen, K.; Katila, M.-L.; Sarkkinen, H.; Miettinen, I.; Rautelin, H. Detection and typing of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli and analysis of indicator organisms in three waterborne outbreaks in Finland. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 1391–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenraad, P.M.F.J.; Rombouts, F.M.; Notermans, S.H.W. Epidemiological aspects of thermophilic Campylobacter in water-related environments: A review. Water Environ. Res. 1997, 69, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA—European Food Safety Authority. Scientific opinion on quantification of the risk posed by broiler meat to human Campylobacteriosis in the EU. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1437–1526. [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan, H.; Murphy, G.A.; Kempf, I. Campylobacter jejuni: Public health hazards and potential control methods in poultry: A review. Vet. Med. (Praha) 2004, 49, 441–446. [Google Scholar]
- Oyarzabal, O.A.; Battie, C. Immunological methods for the detection of Campylobacter spp.—Current applications and potential use in biosensors. In Trends in Immunolabelled and Related Techniques; Abuelzein, E., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Masdor, N.A.; Altintas, Z.; Tothill, I.E. Sensitive detection of Campylobacter jejuni using nanoparticles enhanced QCM sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 78, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonjoch, X.; Calvó, L.; Soler, M.; Ruiz-Rueda, O.; Garcia-Gil, L.J. A new multiplexed real-time PCR assay to detect Campylobacter jejuni, C. coli, C. lari, and C. upsaliensis. Food Anal. Methods 2010, 3, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Oyarzabal, O.A.; Huang, T.-S.; Balasubramanian, S.; Sista, S.; Simonian, A.L. Development of a surface plasmon resonance biosensor for the identification of Campylobacter jejuni. J. Microbiol. Methods 2007, 69, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schasfoort, R.B.M.; Tudos, A.J. Handbook of Surface Plasmon Resonance; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Yang, G.; Meng, W.; Wu, L.; Zhu, A.; Jiao, X. An electrochemical impedimetric immunosensor for label-free detection of Campylobacter jejuni in diarrhea patients’ stool based on O-carboxymethylchitosan surface modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 1204–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawula, M.; Altintas, Z.; Tothill, I.E. SPR detection of cardiac troponin T for acute myocardial infarction. Talanta 2016, 146, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altintas, Z.; Uludag, Y.; Gurbuz, Y.; Tothill, I. Development of surface chemistry for surface plasmon resonance based sensors for the detection of proteins and DNA molecules. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 712, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altintas, Z.; Uludag, Y.; Gurbuz, Y.; Tothill, I.E. Surface plasmon resonance based immunosensor for the detection of the cancer biomarker carcinoembryonic antigen. Talanta 2011, 86, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpinski, K.F. Optimality assessment in the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Biometrics 1990, 46, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchatip, S.; Ananthanawat, C.; Sithigorngul, P.; Sangvanich, P.; Rengpipat, S.; Hoven, V.P. Detection of the shrimp pathogenic bacteria, Vibrio harveyi, by a quartz crystal microbalance-specific antibody based sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 145, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.R.; Kim, G.; Kothapalli, A.; Morgan, M.T.; Ess, D. Detection of Salmonella enteritidis using a miniature optical surface plasmon resonance biosensor. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2007, 61, 1086–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeusen, C.A.; Alocilja, E.C.; Osburn, W.N. Detection of E. coli O157:H7 using a miniaturized surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2005, 48, 2409–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraldo, D.; Mutharasan, R. Detection and confirmation of Staphylococcal enterotoxin B in apple juice and milk using piezoelectric-excited millimeter-sized cantilever sensors at 2.5 fg/mL. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 7636–7643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salam, F.; Uludag, Y.; Tothill, I.E. Real-time and sensitive detection of Salmonella Typhimurium using an automated quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) instrument with nanoparticles amplification. Talanta 2013, 115, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.L.; Li, Y. A QCM immunosensor for Salmonella detection with simultaneous measurements of resonant frequency and motional resistance. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 21, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puttharugsa, C.; Wangkam, T.; Huangkamhang, N.; Gajanandana, O.; Himananto, O.; Sutapun, B.; Amarit, R.; Somboonkaew, A.; Srikhirin, T. Development of surface plasmon resonance imaging for detection of Acidovorax avenae subsp. citrulli (Aac) using specific monoclonal antibody. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2341–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlermroj, R.; Oplatowska, M.; Gajanandana, O.; Himananto, O.; Grant, I.R.; Karoonuthaisiri, N.; Elliott, C.T. Strategies to improve the surface plasmon resonance-based immmunodetection of bacterial cells. Microchim. Acta 2013, 180, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, N.B.; Salgado, A.M.; Valdman, B. The evolution and developments of immunosensors for health and environmental monitoring: Problems and perspectives. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2009, 26, 227–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waswa, J.W.; Debroy, C.; Irudayaraj, J. Rapid detection of Salmonella enteritidis and Escherichia coli using surface plasmon resonance biosensor. J. Food Process Eng. 2006, 29, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Mutharasan, R. Rapid and sensitive immunodetection of Listeria monocytogenes in milk using a novel piezoelectric cantilever sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 45, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Arutyunov, D.; McDermott, M.T.; Szymanski, C.M.; Evoy, S. Specific detection of Campylobacter jejuni using the bacteriophage NCTC 12673 receptor binding protein as a probe. Analyst 2011, 136, 4780–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, M.; Sim, J.; Kang, T.; Nguyen, H.H.; Park, H.K.; Chung, B.H.; Ryu, S. A novel and highly specific phage endolysin cell wall binding domain for detection of Bacillus cereus. Eur. Biophys. J. 2015, 44, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karoonuthaisiri, N.; Charlermroj, R.; Morton, M.J.; Oplatowska-Stachowiak, M.; Grant, I.R.; Elliott, C.T. Development of a M13 bacteriophage-based SPR detection using Salmonella as a case study. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 190, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farka, Z.; Kovár, D.; Pribyl, J.; Skládal, P. Piezoelectric and surface plasmon resonance biosensors for Bacillus atrophaeus spores. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 100–112. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Si, C.; Ying, Y. Subtractive inhibition assay for the detection of E. coli O157:H7 using surface plasmon resonance. Sensors 2011, 11, 2728–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skottrup, P.D.; Leonard, P.; Kaczmarek, J.Z.; Veillard, F.; Enghild, J.J.; O’Kennedy, R.; Sroka, A.; Clausen, R.P.; Potempa, J.; Riise, E. Diagnostic evaluation of a nanobody with picomolar affinity toward the protease RgpB from Porphyromonas gingivalis. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 415, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.-B.; Bi, L.-J.; Zhang, Z.-P.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Yang, R.-F.; Wei, H.-P.; Zhou, Y.-F.; Zhang, X.-E. Label-free detection of B. anthracis spores using a surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Analyst 2009, 134, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, A.; Irudayaraj, J.; Ryan, T. Mono and dithiol surfaces on surface plasmon resonance biosensors for detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 114, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Vinuesa, J.L.; Hidalgo-Álvarez, R.; De, L.N.F.J.; Davey, C.L.; Newman, D.J.; Price, C.P. Characterization of immunoglobulin G bound to latex particles using surface plasmon resonance and electrophoretic mobility. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 204, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnedenko, O.V.; Mezentsev, Y.V.; Molnar, A.A.; Lisitsa, A.V.; Ivanov, A.S.; Archakov, A.I. Highly sensitive detection of human cardiac myoglobin using a reverse sandwich immunoassay with a gold nanoparticle-enhanced surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 759, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Phipps-Todd, B. Improvement of capture efficacy of immunomagnetic beads for Campylobacter jejuni using reagents that alter its motility. Can. J. Microbiol. 2013, 59, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, R.-P.; Yao, G.-H.; Fan, L.-X.; Qiu, J.-D. Magnetic Fe3O4@Au composite-enhanced surface plasmon resonance for ultrasensitive detection of magnetic nanoparticle-enriched α-fetoprotein. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 737, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, M.Z.; Chen, H.-Y.; Wu, S.-H.; Peng, S.-W.; Lee, K.-L.; Wei, P.-K.; Cheng, J.-Y. Magnetic nanoparticle-enhanced SPR on gold nanoslits for ultra-sensitive, label-free detection of nucleic acid biomarkers. Analyst 2013, 138, 2740–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Song, D. A novel surface plasmon resonance biosensor based on graphene oxide decorated with gold nanorod-antibody conjugates for determination of transferrin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 45, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenzl, C.; Hirsch, T.; Baeumner, A.J. Liposomes with high refractive index encapsulants as tunable signal amplification tools in surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 11157–11163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makszin, L.; Péterfi, Z.; Blaskó, A.; Sándor, V.; Kilár, A.; Dörnyei, A.; Osz, E.; Kilár, F.; Kocsis, B. Structural background for serological cross-reactivity between bacteria of different enterobacterial serotypes. Electrophoresis 2015, 36, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochel, I.; Slavíčková, D.; Viochna, D.; Škvor, J.; Steinhauserová, I. Detection of Campylobacter species in foods by indirect competitive ELISA using hen and rabbit antibodies. Food Agric. Immunol. 2007, 18, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Bacteria Tested (1 × 109 CFU·mL−1) | SPR (RU) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| (a) Campylobacter jejuni | 138.8 ± 0.14 | 100 |
| (b) Salmonella Typhimurium | 14.4 ± 1.42 | 10.4 |
| (c) Listeria monocytogenes | 9.1 ± 1.30 | 6.6 |
| (d) Escherichia coli | 7.4 ± 0.20 | 5.3 |
| (e) Control | 0.8 ± 1.60 | 0.5 |
| Assay | LOD (CFU·mL−1) |
|---|---|
| Direct | 8 × 106 |
| Sandwich assay | 4 × 104 |
| Sandwich assay AuNPs signal amplification | 8 × 105 |
| Instrument | Pathogen | Limits of Detection (CFU·mL−1) | Format of Detection Assay | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIAcore (USA) | B. cereus | 105–108 | Direct | [31] |
| BIAcore (USA) | B. cereus | 102 | Subtractive | [31] |
| BIAcore (USA) | Salmonella | 8 × 107 | Direct | [32] |
| BIAcore (USA) | B. atrophaeus | 1 × 105 | Sandwich | [33] |
| GWC technologies (USA) | C. jejuni | 1 × 102 | Direct | [30] |
| BIAcore (USA) | E. coli O157:H7 | 3 × 104 | Subtractive | [34] |
| BIAcore (USA) | E. coli O157:H7 | 3 × 105 | Direct | [34] |
| BIAcore (USA) | Porphyromonas gingivalis | 7.8 × 106 | Subtractive | [35] |
| BIAcore (USA) | B. anthracis | 1 × 104 | Subtractive | [36] |
| Spreeta (USA) | C. jejuni | 1 × 103 | Direct | [12] |
| Reichert SR7000(USA) | E. coli O157:H7 | 1 × 103 | Sandwich | [37] |
| Spreeta (USA) | E. coli O157:H7 | 8.7 × 106 | Direct | [21] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Masdor, N.A.; Altintas, Z.; Tothill, I.E. Surface Plasmon Resonance Immunosensor for the Detection of Campylobacter jejuni. Chemosensors 2017, 5, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors5020016
Masdor NA, Altintas Z, Tothill IE. Surface Plasmon Resonance Immunosensor for the Detection of Campylobacter jejuni. Chemosensors. 2017; 5(2):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors5020016
Chicago/Turabian StyleMasdor, Noor Azlina, Zeynep Altintas, and Ibtisam E. Tothill. 2017. "Surface Plasmon Resonance Immunosensor for the Detection of Campylobacter jejuni" Chemosensors 5, no. 2: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors5020016







