A Deeper Statistical Examination of Arrival Dates of Migratory Breeding Birds in Relation to Global Climate Change
Abstract
:1. Introduction
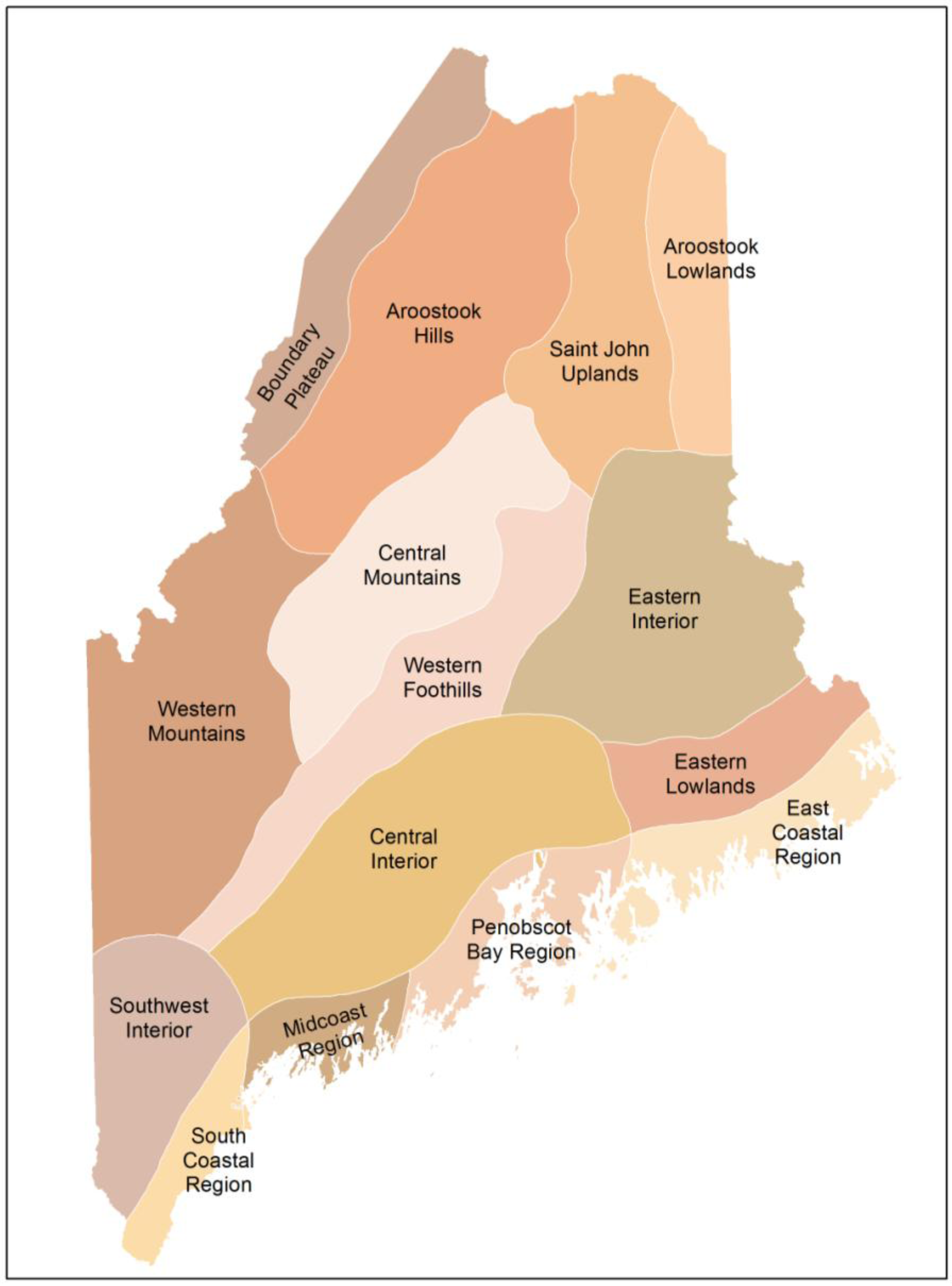
2. Materials and Methods
| Species | Foraging Type | Skewness | Kurtosis | Migration Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ring-necked Duck (Aythya collaris (Donovan)) | Aquatic | 0.240 | 3.354 * | April |
| Great Blue Heron (Ardea herodias (Rackett)) | Aquatic | 0.620 * | 4.667 * | April |
| Turkey Vulture (Cathartes aura (L.)) | Scavenger | 0.509 * | 3.757 * | March/April |
| Osprey (Pandion haliaetus (L.)) | Raptor | 0.699 * | 4.687 * | April |
| Broad-winged Hawk (Buteo platypterus Viellot)) | Raptor | −0.390 | 4.249 * | April |
| American Kestrel (Falco sparverius L.) | Raptor | 0.449 * | 4.001 * | April |
| Killdeer (Charadrius vociferus L.) | Ground predator | 0.873 * | 4.392 * | March/April |
| Spotted Sandpiper (Actitis macularius (L.)) | Ground predator | 0.161 | 2.965 * | May |
| Wilson's Snipe (Gallinago delicata Ord) | Ground predator | 0.476 * | 2.861 * | April |
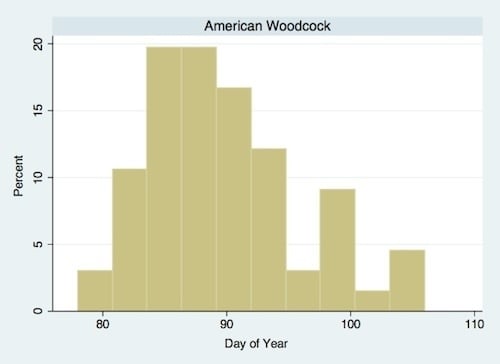
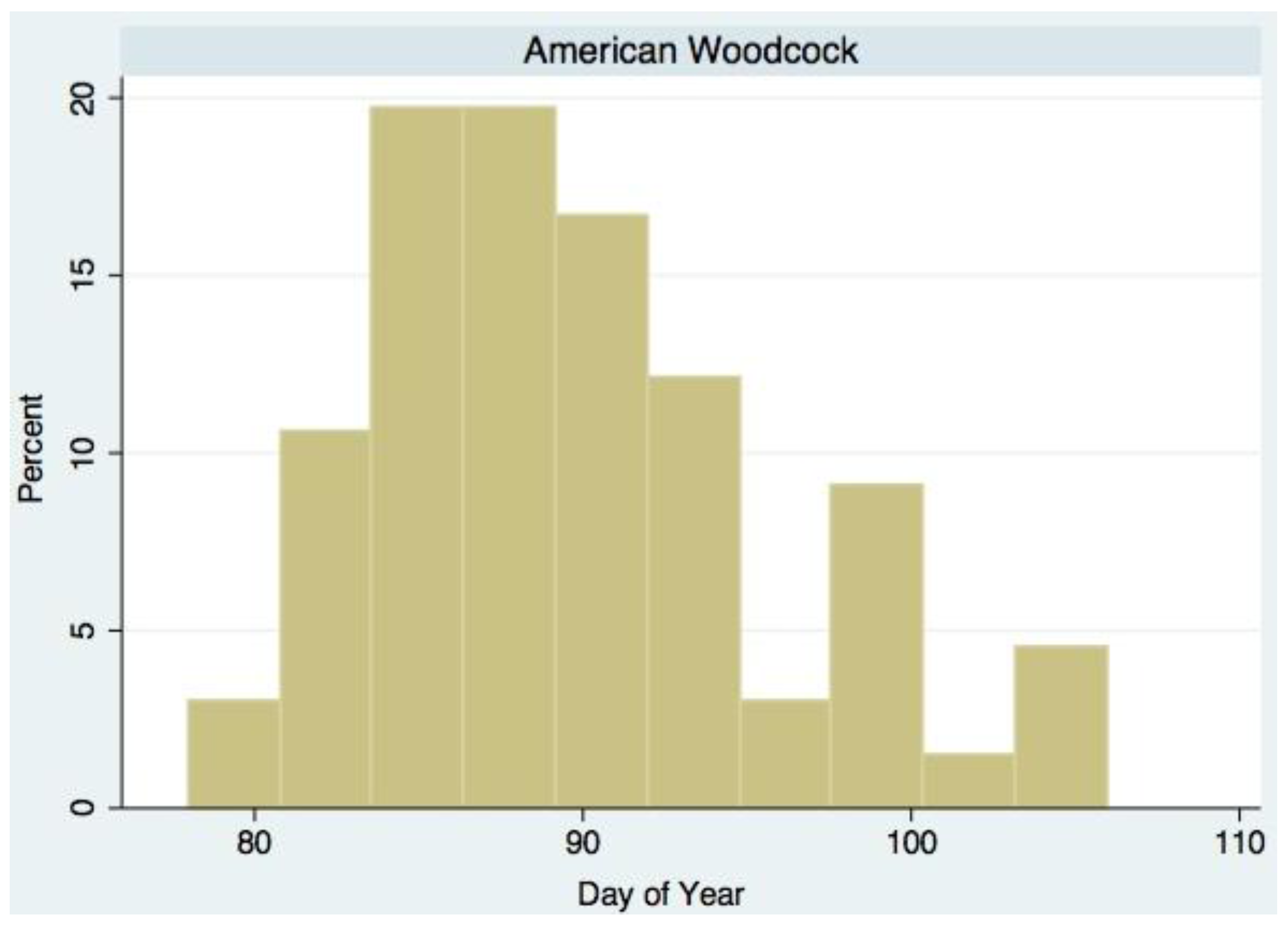
| American Woodcock (Scoloplax minor Gmelin) | Ground predator | 1.231 * | 5.490 * | March/April |
| Chimney Swift (Chaetura pelagica (L.)) | Aerial | 0.523 | 3.863 * | May |
| Ruby-throated Hummingbird (Archilochus colubris (L.)) | Nectarivore | 0.108 | 6.901 * | May |
| Belted Kingfisher (Megaceryle torquata (L.)) | Aquatic | −0.636 | 5.357 * | April |
| Yellow-bellied Sapsucker (Sphyrapicus varius (L.)) | Scansorial | 1.479 * | 3.578 * | April |
| Northern Flicker (Colaptes auratus (L.)) | Scansorial | −0.783 | 7.253 * | April |
| Eastern Wood-Pewee (C. virens (L.)) | Aerial | −0.729 | 6.373 * | May |
| Least Flycatcher (E. minimus (Baird and Baird)) | Aerial | 0.283 | 3.745 * | May |
| Eastern Phoebe (Sayornis phoebe (Latham)) | Aerial | 1.907 * | 5.463 * | March/April |
| Great Crested Flycatcher (Myiarchus crinitus (L.)) | Aerial | 0.582 | 4.525 * | May |
| Eastern Kingbird (Tyrannus tyrannus (L.)) | Aerial | −0.518 | 6.045 * | May |
| Blue-headed Vireo (Vireo solitarius (Wilson)) | Leaf-gleaner | 0.478 | 3.832 * | April/May |
| Warbling Vireo (V. gilvus Viellot) | Leaf-gleaner | 0.533 * | 2.883 * | May |
| Red-eyed Vireo (V. olivaceus (L.)) | Leaf-gleaner | 0.335 | 5.247 * | May |
| Tree Swallow (Tachycineta bicolor (Viellot) | Aerial | 0.945 * | 4.166 * | April |
| Barn Swallow (Hirundo rustica L.) | Aerial | 0.173 | 3.037 * | May |
| House Wren (Troglodytes aedon Viellot) | Ground predator | 0.277 | 3.239 * | May |
| Winter Wren (Troglodytes troglodytes L.) | Ground predator | 0.627* | 2.792* | April |
| Ruby-crowned Kinglet (Regulus calendula (L.)) | Leaf-gleaner | 0.454 | 3.725 * | April/May |
| Eastern Bluebird (Sialia sialis (L.)) | Ground predator | 0.225 | 3.708 * | April |
| Veery (Catharus fuscescens (Stephens)) | Ground predator | −0.181 | 3.808 * | May |
| Hermit Thrush (C. guttatus (Pallas)) | Ground predator | 0.301 | 4.693 * | May |
| Wood Thrush (Hylocichla mustelina (Gmelin)) | Ground predator | 0.175 | 3.891 * | May |
| Gray Catbird (Dumetella carolinensis (L.)) | Ground predator | −0.637 | 8.439 * | May |
| Brown Thrasher (Toxostoma rufum (L.)) | Ground predator | 0.217 | 3.579 * | May |
| Ovenbird (Seiurus aurocapilla (L.)) | Leaf-gleaner | 0.216 | 5.452 * | May |
| Northern Waterthrush (Parkesia novaeboracensis (Gmelin)) | Leaf-gleaner | 0.367 | 3.585 * | May |
| Black-and-white Warbler (Mniotilta varia (L.)) | Leaf-gleaner | 0.653 | 3.838 * | April/May |
| Nashville Warbler (Oreothlypis ruficapilla (Wilson)) | Leaf-gleaner | 0.804 * | 4.546 * | May |
| Common Yellowthroat (G. trichas (L.)) | Leaf-gleaner | 0.928 * | 5.056 * | May |
| American Redstart (Setophaga ruticilla (L.)) | Leaf-gleaner | 0.448 | 5.434 * | May |
| Northern Parula (S. americana (L.)) | Leaf-gleaner | 0.098 | 5.056 * | May |
| Magnolia Warbler (S. magnolia (Wilson)) | Leaf-gleaner | 0.262 | 3.562 * | May |
| Blackburnian Warbler (S. fusca (Forster)) | Leaf-gleaner | 0.628 | 4.514 * | May |
| Yellow Warbler (S. petechia (L.)) | Leaf-gleaner | 0.470 | 4.187 * | May |
| Chestnut-sided Warbler (S. pensylvanica (L.)) | Leaf-gleaner | 0.629 | 4.823 * | May |
| Black-throated Blue Warbler (S. caerulescens (Gmelin)) | Leaf-gleaner | 0.652 * | 3.838 * | May |
| Palm Warbler (S. palmarum (Wilson)) | Leaf-gleaner | 0.579 | 3.824 * | April |
| Pine Warbler(S. pinus (Wilson)) | Leaf-gleaner | 0.651 | 4.208 * | April |
| Yellow-rumped Warbler (S. coronata (L.)) | Leaf-gleaner | −0.835 | 8.506 * | April/May |
| Black-throated Green Warbler (S. virens (Gmelin)) | Leaf-gleaner | 0.667 * | 4.061 * | May |
| Canada Warbler (Cardellina canadensis (L.)) | Leaf-gleaner | 0.320 | 3.429 * | May |
| Chipping Sparrow (Spizella passerina (Bechstein)) | Granivore | −0.254 | 4.446 * | April |
| Savannah Sparrow (Passerculus sandwichensis (Gmelin)) | Granivore | 0.014 | 3.676 * | April |
| Song Sparrow (Melospiza melodia (Wilson)) | Granivore | −0.792 | 8.560 * | Mar/April |
| Swamp Sparrow (M. georgiana (Latham)) | Granivore | 0.094 | 3.426 * | April |
| White-throated Sparrow (Zonotrichia albicollis (Gmelin)) | Granivore | −1.986 * | 7.842 * | April |
| Scarlet Tanager (Piranga olivacea (Gmelin)) | Leaf-gleaner | 0.651 * | 3.746 * | May |
| Rose-breasted Grosbeak (Pheucticus ludovicianus (L.)) | Granivore | 0.764 | 6.092 * | May |
| Indigo Bunting (Passerina cyanea (L.)) | Granivore | 0.157 | 3.026 * | May |
| Bobolink (Dolichonyx oryzivorus (L.)) | Ground predator | 0.605 | 7.210 * | May |
| Red-winged Blackbird (Aegelaius phoeniceus (Müller)) | Ground predator | 1.483 * | 6.222 * | Mar |
| Eastern Meadowlark (Sturnella magna (L.)) | Ground predator | 1.992 | 2.583 * | April |
| Common Grackle (Quisculus quiscala (L.)) | Ground predator | 1.426 * | 7.179 * | Mar |
| Baltimore Oriole (Icterus galbula (L.)) | Leaf-gleaner | 0.010 | 7.857 * | May |
3. Results
| Foraging type | Skewness | Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|
| Aerial insectivore | 0.38 | 4.65 |
| Aquatic feeder | 0.35 | 3.09 |
| Gleaner | 0.45 | 4.59 |
| Granivore | 0.32 | 5.48 |
| Ground predator | 0.31 | 4.41 |
| Nectarivore | 0.06 | 7.38 |
| Piscivore | 0.22 | 4.13 |
| Raptor | 0.03 | 4.90 |
| Scansorial predator | 0.35 | 5.42 |
| Scavenger | 0.51 | 3.76 |
| Migration period | Skewness | Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|
| March | 1.45 | 6.73 |
| March/April | 0.57 | 4.65 |
| April | 0.26 | 4.38 |
| April/May | 0.24 | 4.57 |
| May | −0.29 | 4.83 |
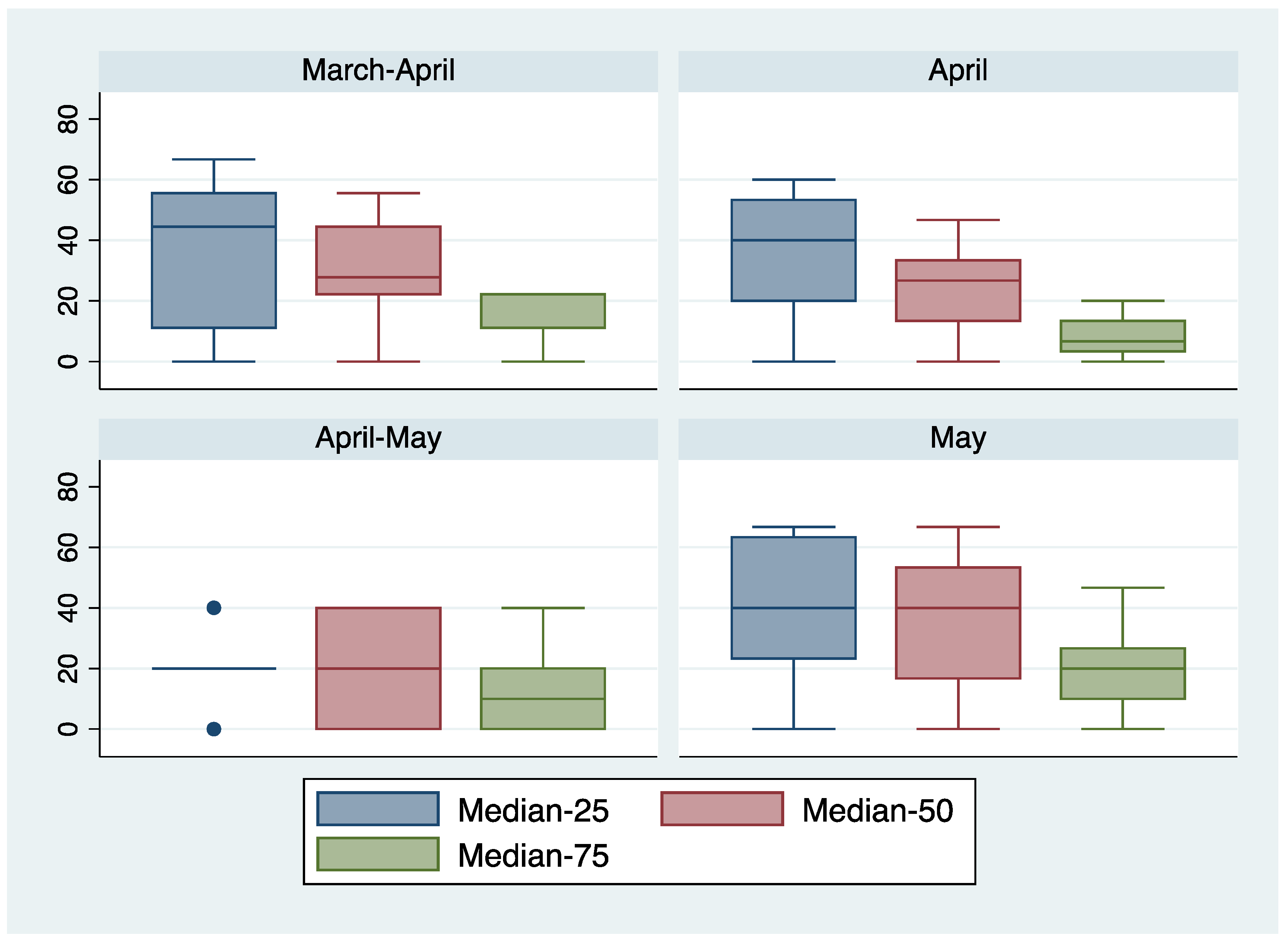
| 5% | 10% | 25% | 50% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10% | 100 | |||
| 25% | 50 | 80 | ||
| 50% | 20 | 50 | 10 | |
| 75% | 20 | 30 | 40 | 100 |
| 5% | 10% | 25% | 50% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10% | 88 | |||
| 25% | 38 | 81 | ||
| 50% | 25% | 43 | 88 | |
| 75% | 25 | 31 | 44 | 69 |
| 5% | 10% | 25% | 50% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10% | 83 | |||
| 25% | 50 | 67 | ||
| 50% | 17 | 17 | 83 | |
| 75% | 0 | 0 | 17 | 67 |
| 5% | 10% | 25% | 50% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10% | 87 | |||
| 25% | 58 | 84 | ||
| 50% | 26 | 55 | 77 | |
| 75% | 6 | 16 | 32 | 94 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Peñuelas, J.; Fillela, I.; Comas, P. Changed plant and animal life cycles from 1952 to 2000 in the Mediterranean region. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2002, 8, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, P.A. Avian migration phenology and global climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 12219–12222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Both, C.; Artemyev, A.V.; Blaauw, B.; Cowie, R.J.; Dekhuijzen, A.J.; Eeva, T.; Enemar, A.; Gustafsson, L.; Ivankina, E.V.; Järviven, A.; et al. Large-scale geographical variation confirms that climate change causes birds to lay earlier. Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. 2004, B 271, 1657–1662. [Google Scholar]
- Crick, H.Q.P. The impact of climate change on birds. Ibis 2004, 146, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, C.F. Long-term trends in the arrival dates of spring migrants. Bird Study 1995, 42, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, T.H.; Carey, P.D. The responses of species to climate over two centuries: An analysis of the Marsham phenological record, 1736–1947. J. Ecol. 1995, 83, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, N.L.; Leopold, A.C.; Ross, J.; Huffaker, W. Phenological changes reflect climate change in Wisconsin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 9701–9704. [Google Scholar]
- Sparks, T.H. Phenology and the changing pattern of bird migration in Britain. Int. J. Biometeorol. 1999, 42, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledneva, A.; Miller-Rushing, A.J.; Primack, R.B.; Imbres, C. Climate change as reflected in a naturalist’s diary, Middleborough, Massachusetts. Wilson Bull. 2004, 116, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, P.M.; Francis, C.M.; Mulvihill, R.M.; Moore, F.R. The influence of climate on the rate and timing of bird migration. Oecologia 2005, 142, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, A.M. Changes in the timing of spring and autumn migration in North American migrant passerines during a period of global warming. Ibis 2005, 147, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tøttrup, A.P.; Rainio, K.; Coppack, T.; Lehikoinen, E.; Rahbek, C.; Thorup, K. Local temperature fine-tunes the timing of spring migration in birds. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2010, 50, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, J.; Schlesinger, W.H. Historical analysis of the spring arrival of migratory birds to Dutchess County, New York: A 123-Year record. Northeast. Nat. 2011, 18, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehikoinen, E.; Sparks, T.H.; Zalakevicius, M. Arrival and departure dates. Adv. Ecol. Res. 2004, 35, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, G.W. Bird Migration and Global Change; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Møller, A.P.; Fiedler, W.; Berthold, P. Effects of Climate Change on Birds; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen, E.; Lindén, A.; Both, C.; Jonzén, N.; Pulido, F.; Saino, N.; Sutherland, W.J.; Bach, L.A.; Coppack, T.; Ergon, T.; et al. Challenging claims in the study of migratory birds and climate change. Biol. Rev. 2011, 86, 928–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, W.H., Jr.; Savage, A.; Zierzow, R.E. Arrival dates of migratory breeding birds in Maine: Results from a volunteer network. Northeast. Nat. 1997, 4, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, W.H., Jr. Spring arrival dates of migratory breeding birds in Maine: Sensitivity to climate change. Wilson J. Ornithol. 2007, 119, 667–679. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, W.H., Jr. Variability of arrival dates of Maine migratory breeding birds: Implications for detecting climate change. Northeast. Nat. 2009, 16, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, W.H., Jr.; Kipervaser, D.; Lilley, S.A. Spring arrival dates of Maine migratory breeding birds: 1994–1997 vs. 1899–1911. Northeast. Nat. 2000, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- McMahon, J.S. The biophysical regions of maine: Patterns in the landscape and vegetation. M.Sc. Thesis, University of Maine, Orono, ME, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrich, P.; Dobkin, D.S.; Wheye, D. The Birder’s Handbook: A Field Guide to the Natural History of North American Birds; Touchstone Press: Beaverton, OR, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Sokal, R.R.; Rohlf, J.R. Biometry; W.H. Freeman Company: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Sparks, T.H.; Barlein, F.; Bojarinov, J.G.; Hüppop, O.; Lehikoinen, E.A.; Rainio, K.; Sokolov, L.V.; Walker, D. Examining the total arrival distribution of migratory birds. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, A.P. Distribution of arrival dates in a migratory bird in relation to environmental conditions, natural selection and sexual selection. Ethol. Ecol. Evol. 2008, 20, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, C.J. The disproportionate effect of global warming on the arrival dates of migratory birds in North America. Ibis 2003, 145, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüppop, O.; Hüppop, K. North Atlantic Oscillation and timing of spring migration in birds. Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. 2003, B270, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vähätalo, A.V.; Rainio, K.; Lehikoinen, A.; Lehikoinen, E. Spring arrival of birds depends on the North Atlantic Oscillation. J. Avian Biol. 2004, 35, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saino, N.; Szép, T.; Romano, M.; Rubolini, D.; Spina, F.; Møller, A.P. Ecological conditions during winter predict arrival date at the breeding quarters in a trans-Saharan migratory bird. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordo, O.; Brotons, L.; Ferrer, X.; Comas, P. Do changes in climate patterns in wintering areas affect the timing of the spring arrival of trans-Saharan migrant birds? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Töttrup, A.; Thorup, K.; Rahbek, C. Patterns of change in timing of spring migration in North European songbird populations. J. Avian Biol. 2006, 37, 84–92. [Google Scholar]
- Both, C. Comment on “Rapid advance of spring arrival dates in long-distance migratory bird”. Science 2007, 315, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Wilson, W.H., Jr. A Deeper Statistical Examination of Arrival Dates of Migratory Breeding Birds in Relation to Global Climate Change. Biology 2013, 2, 742-754. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology2020742
Wilson WH Jr. A Deeper Statistical Examination of Arrival Dates of Migratory Breeding Birds in Relation to Global Climate Change. Biology. 2013; 2(2):742-754. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology2020742
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilson, W. Herbert, Jr. 2013. "A Deeper Statistical Examination of Arrival Dates of Migratory Breeding Birds in Relation to Global Climate Change" Biology 2, no. 2: 742-754. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology2020742
APA StyleWilson, W. H., Jr. (2013). A Deeper Statistical Examination of Arrival Dates of Migratory Breeding Birds in Relation to Global Climate Change. Biology, 2(2), 742-754. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology2020742