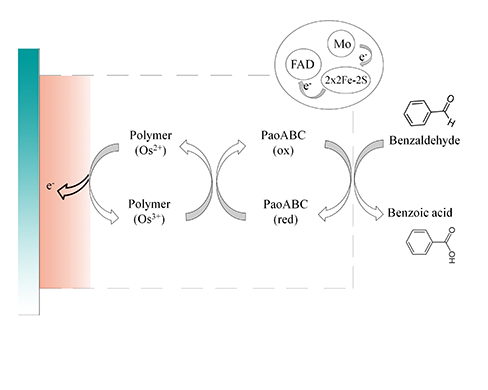
Electrical Wiring of the Aldehyde Oxidoreductase PaoABC with a Polymer Containing Osmium Redox Centers: Biosensors for Benzaldehyde and GABA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Apparatus and Procedure
2.3. Electrode Modification
2.3.1. Benzaldehyde Biosensor
2.3.2. GABA-Biosensor
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. PaoABC in Osmium Containing Polymer
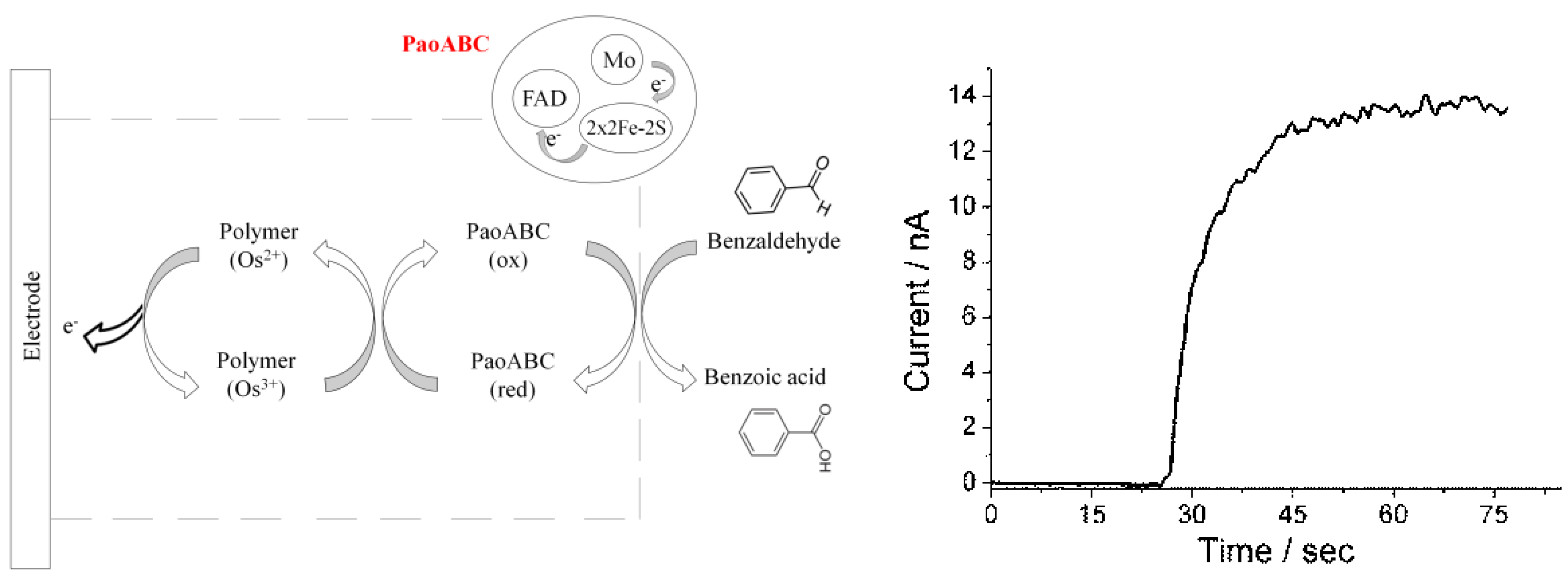
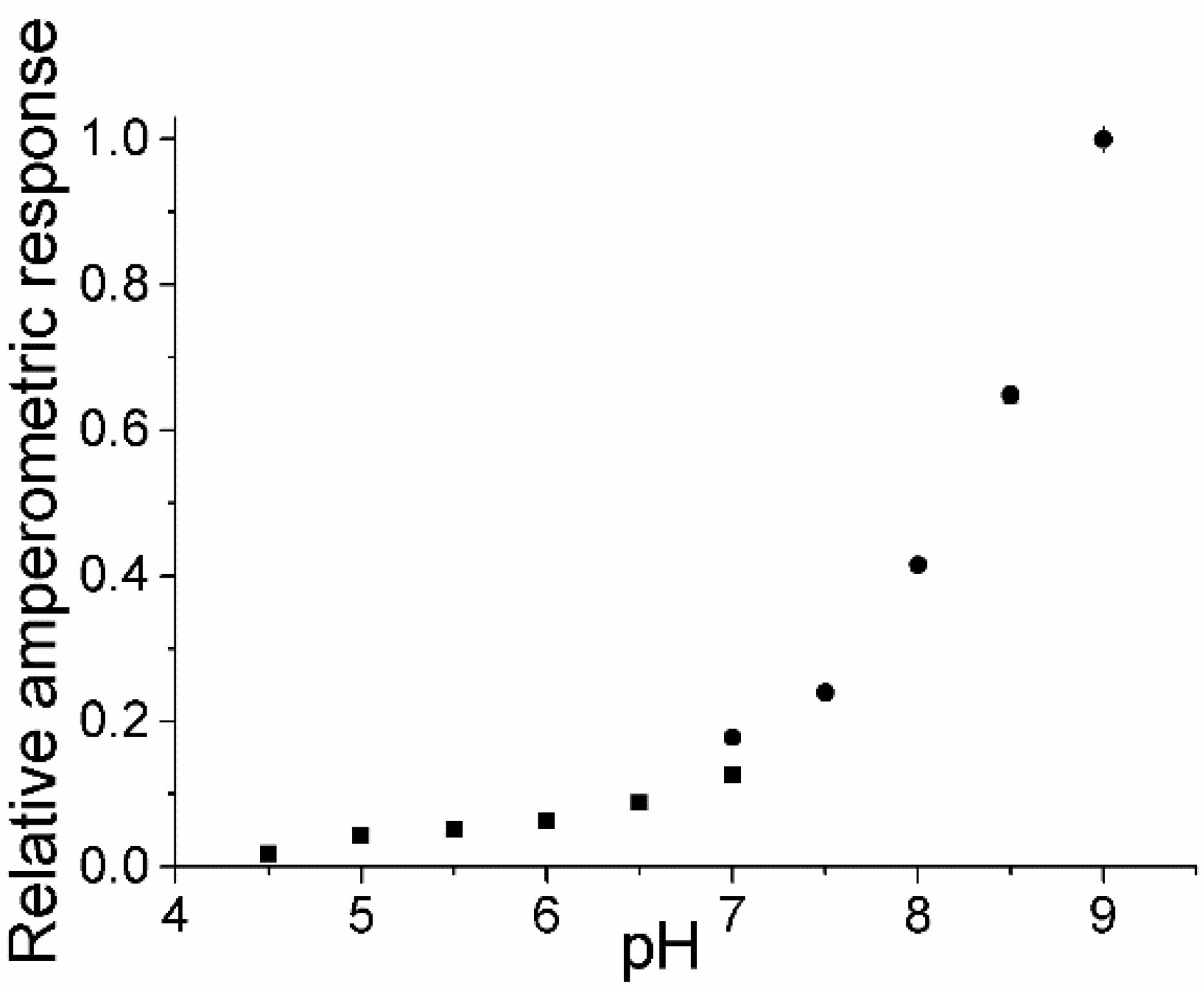
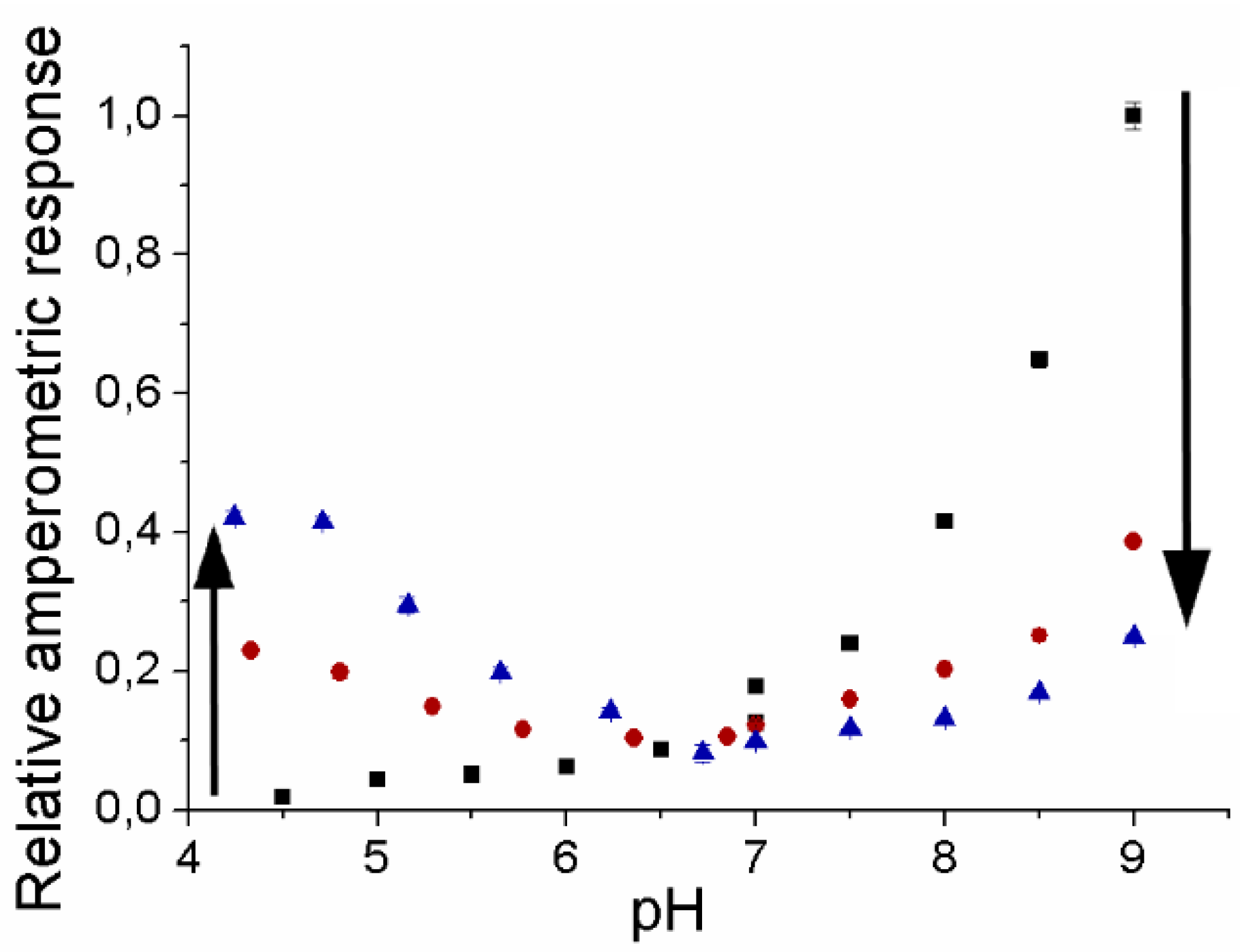
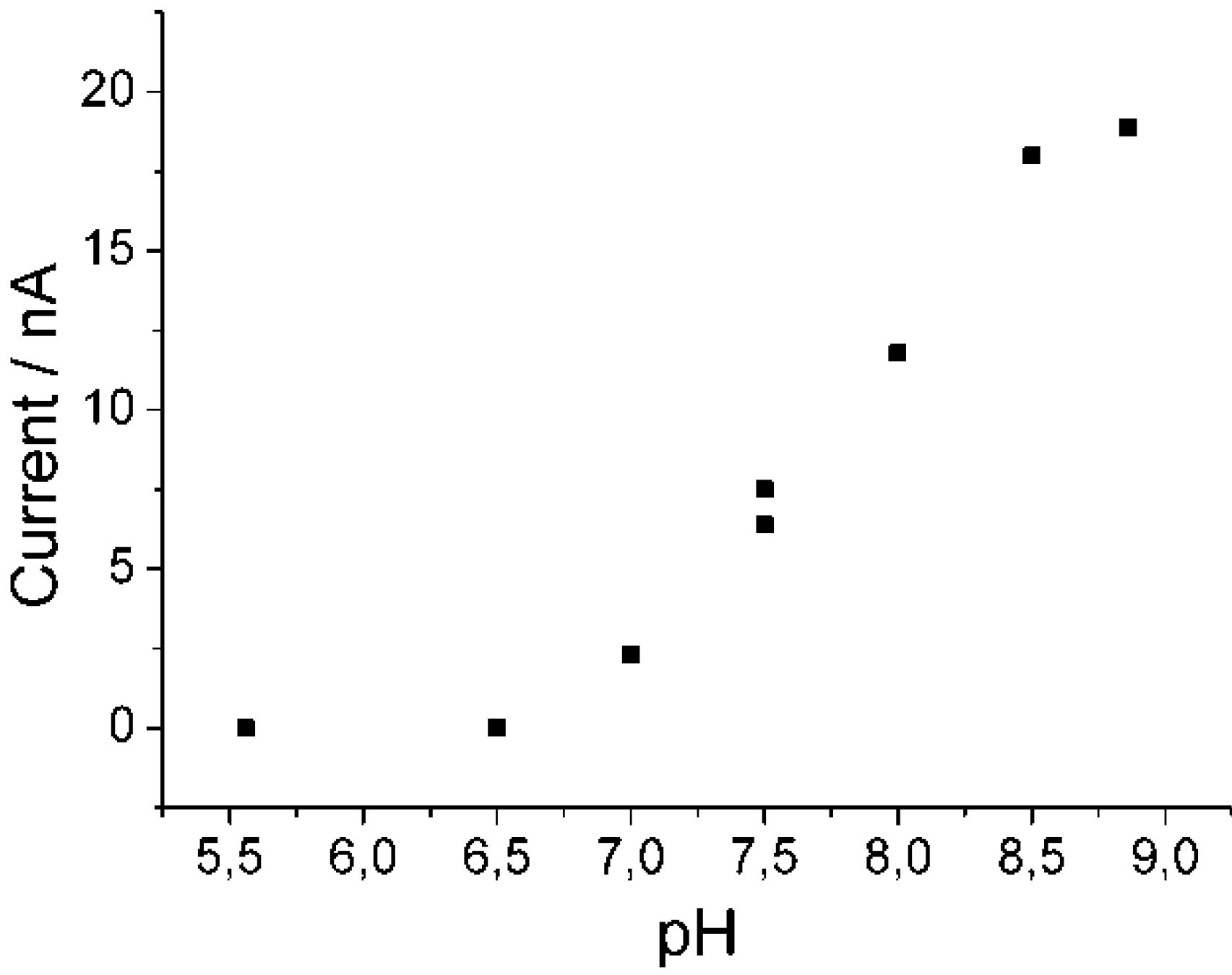
3.2. pH-Dependence at Different Ionic Strengths for PaoABC Immobilized in Osmium Complex Containing Redox Polymer
3.3. Biosensor for Benzaldehyde


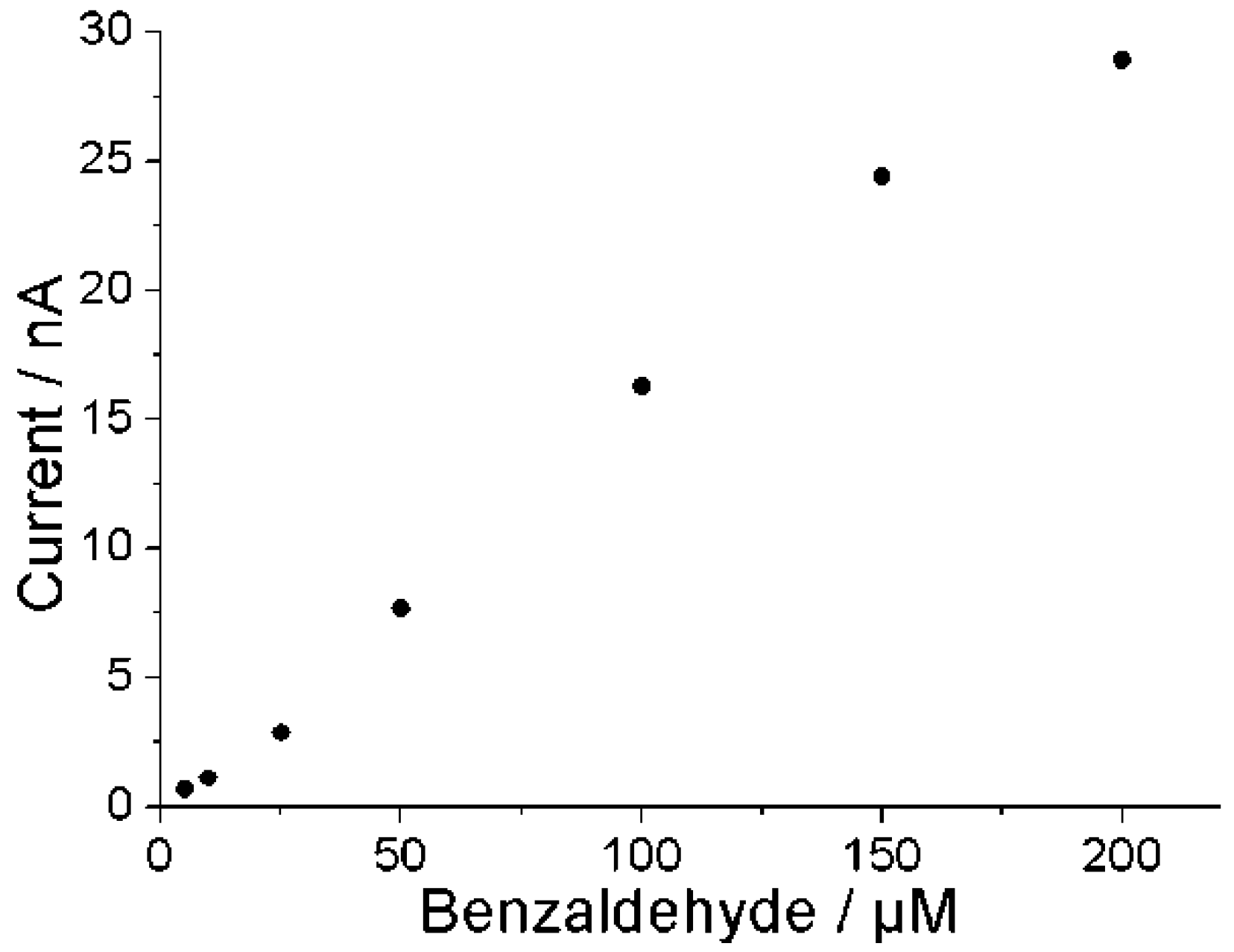
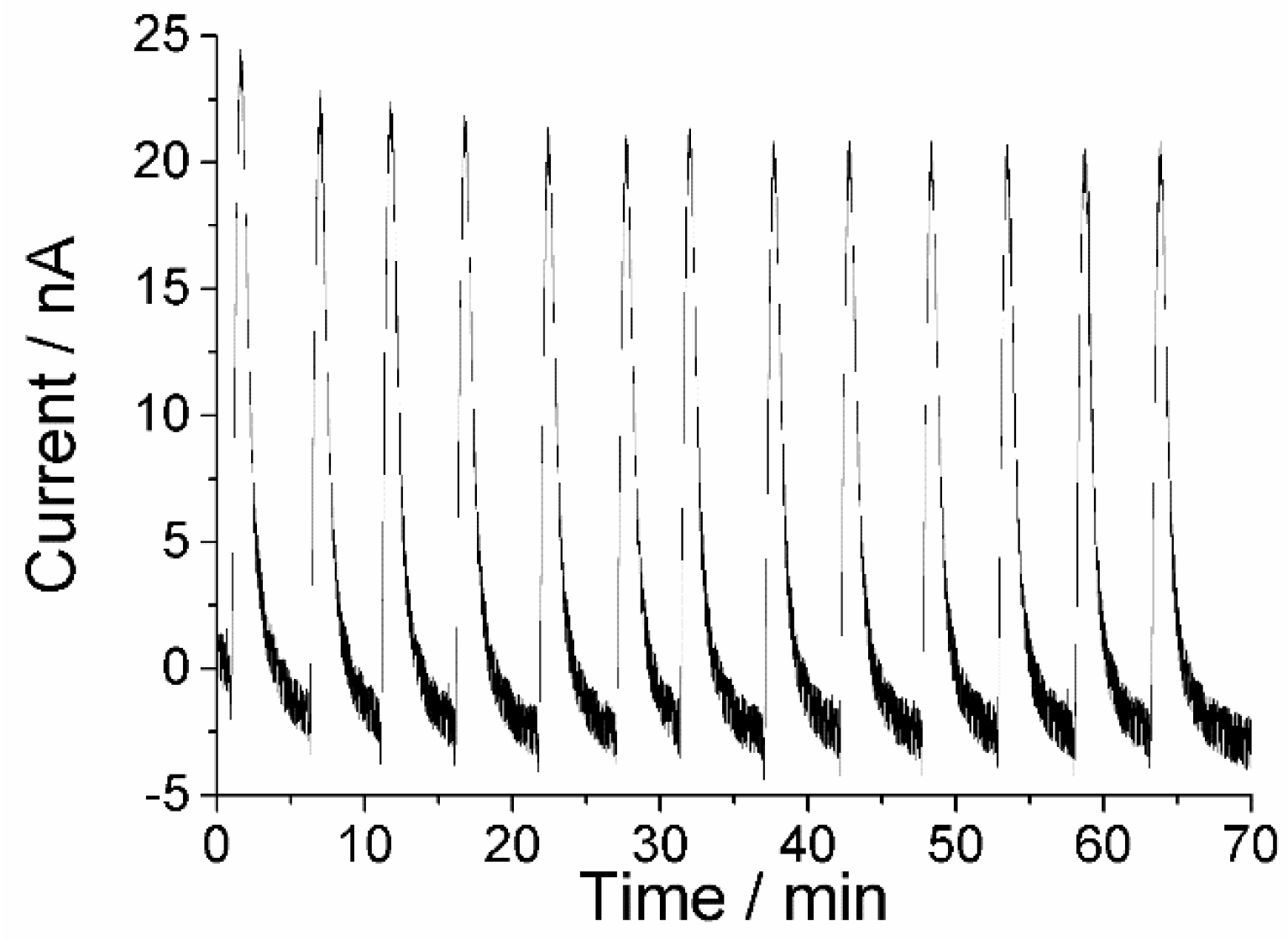
3.4. Biosensor for GABA

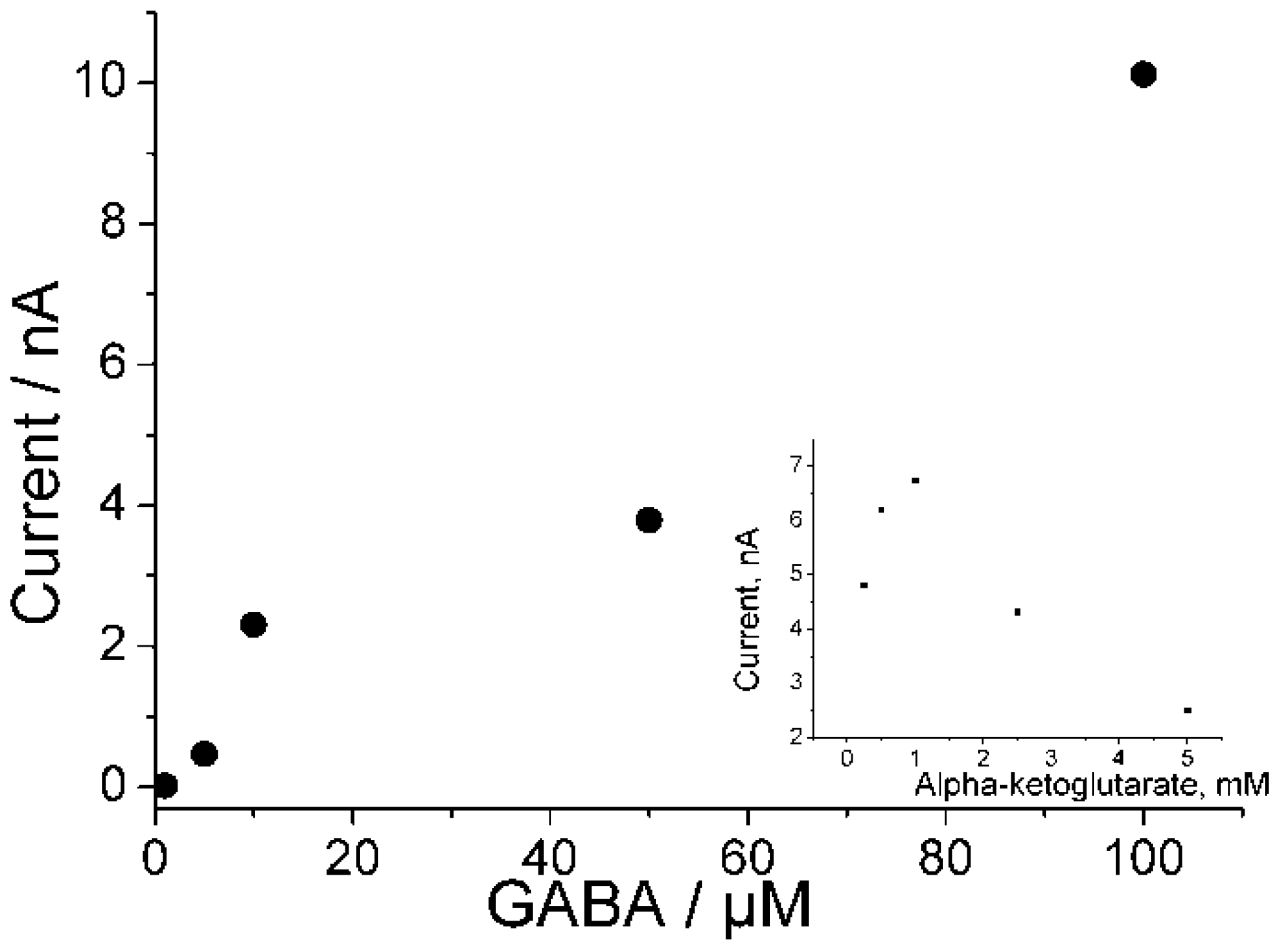
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contribution
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neumann, M.; Mittelstädt, G.; Iobbi-Nivol, C.; Saggu, M.; Lendzian, F.; Hildebrandt, P.; Leimkühler, S. A periplasmic aldehyde oxidoreductase represents the first molybdopterin cytosine dinucleotide cofactor containing molybdo-flavoenzyme from Escherichia coli. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 2762–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badalyan, A.; Neumann-Schaal, M.; Leimkühler, S.; Wollenberger, U. A biosensor for aromatic aldehydes comprising the mediator dependent PaoABC-aldehyde oxidoreductase. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badalyan, A.; Yoga, E.G.; Schwuchow, V.; Pöller, S.; Schuhmann, W.; Leimkühler, S.; Wollenberger, U. Analysis of the interaction of the molybdenum hydroxylase PaoABC from Escherichia coli with positively and negatively charged metal complexes. Electrochem. Commun. 2013, 37, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pietra, A.M.; Cavrini, V.; Raggi, M.A. Determination of benzaldehyde traces in benzyl alcohol by liquid chromatography (HPLC) and derivative UV spectrophotometry. Int. J. Pharm. 1987, 35, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemifard, A.G.; Moore, D.E.; Mohammadi, A. Polarographic determination of benzaldehyde in benzyl alcohol and sodium diclofenac injection formulations. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2002, 30, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshy, V.J.; Prasad, J.V.; Kalpana, G.; Satish, S. Investigations on intermediate acetal formation during polarographic estimation of certain benzaldehyde derivatives. Anal. Chim. Acta 1995, 307, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaCourse, W.R.; Krull, I.S. Photoelectrochemical detection of benzaldehyde in foodstuffs. Anal. Chem. 1987, 59, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Pharmacopoeia, 5th ed.; Council of Europe (COE)—European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines (EDQM): Strasbourg, France, 2005.
- The International Pharmacopoeia (Electronic Resource); World Health Organization,Department of Essential Medicines and Pharmaceutical Policies: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- Ismail, I.H. Difference spectrophotometric assay of benzaldehyde in benzyl alcohol. Talanta 1993, 40, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobi, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Toko, K.; Ikezaki, H.; Miura, N. Enhanced sensitivity of self-assembled-monolayer-based SPR immunosensor for detection of benzaldehyde using a single-step multi-sandwich immunoassay. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 2727–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Na, N.; Zhang, Z. Development of a benzaldehyde sensor utilizing chemiluminescence on nanosized Y2O3. Luminescence 2008, 23, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregg, B.A.; Heller, A. Redox polymer films containing enzymes. 2. Glucose oxidase containing enzyme electrodes. J. Phys. Chem. 1991, 95, 5976–5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spricigo, R.; Richter, C.; Leimkühler, S.; Gorton, L.; Scheller, F.W.; Wollenberger, U. Sulfite biosensor based on osmium redox polymer wired sulfite oxidase. Colloid Surface A Physicochem. Eng. Aspect 2010, 354, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, T.K.; Ornatska, M.; Pita, M.; Minko, S.; Katz, E. Polymer brush-modified electrode with switchable and tunable redox activity for bioelectronic applications. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 8438–8445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, M.N.; Tasca, F.; Boland, S.; Kujawa, M.; Patel, I.; Peterbauer, C.K.; Leech, D.; Gorton, L. Wiring of pyranose dehydrogenase with osmium polymers of different redox potentials. Bioelectrochemistry 2010, 80, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Barton, S.C.; Binyamin, G.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Kim, H.-H.; Heller, A. A miniature biofuel cell. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 8630–8631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, F.; Higson, S.P.J. Biofuel cells—Recent advances and applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1224–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.-H.; Mano, N.; Zhang, Y.; Heller, A. A miniature membrane-less biofuel cell operating under physiological conditions at 0.5 V. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, A209–A213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mano, N.; Fernandez, J.L.; Kim, Y.; Shin, W.; Bard, A.J.; Heller, A. Oxygen is electroreduced to water on a “wired” enzyme electrode at a lesser overpotential than on platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 15290–15291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mano, N.; Kim, H.-H.; Heller, A. On the relationship between the characteristics of bilirubin oxidases and O2 cathodes based on their “wiring”. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 8842–8848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusling, J.F.; Forster, R.J. Electrochemical catalysis with redox polymer and polyion–protein films. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 262, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, F.; Mano, N.; Heller, A. Long tethers binding redox centers to polymer backbones enhance electron transport in enzyme “wiring” hydrogels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 4951–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, M.N.; Wang, X.; Sygmund, C.; Ludwig, R.; Leech, D.; Gorton, L. Electron-transfer studies with a new flavin adenine dinucleotide dependent glucose dehydrogenase and osmium polymers of different redox potentials. Anal. Chem. 2011, 84, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, M.; Zafar, M.N.; Sygmund, C.; Guschin, D.A.; Ludwig, R.; Peterbauer, C.K.; Schuhmann, W.; Gorton, L. Mutual enhancement of the current density and the coulombic efficiency for a bioanode by entrapping bi-enzymes with Os-complex modified electrodeposition paints. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 40, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasca, F.; Gorton, L.; Kujawa, M.; Patel, I.; Harreither, W.; Peterbauer, C.K.; Ludwig, R.; Nöll, G. Increasing the coulombic efficiency of glucose biofuel cell anodes by combination of redox enzymes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 1710–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Peterson, P.E.; Carter, R.J.; Zhou, X.; Langston, J.A.; Fisher, A.J.; Toney, M.D. Crystal structures of unbound and aminooxyacetate-bound Escherichia coli γ-aminobutyrate aminotransferase. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 10896–10905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Peterson, P.E.; Langston, J.A.; Jin, X.; Zhou, X.; Fisher, A.J.; Toney, M.D. Kinetic and crystallographic analysis of active site mutants of Escherichia coli γ-aminobutyrate aminotransferase. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 2982–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timur, S.; Yigzaw, Y.; Gorton, L. Electrical wiring of pyranose oxidase with osmium redox polymers. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2006, 113, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.L.; Hermans, A.; Seipel, A.T.; Wightman, R.M. Monitoring rapid chemical communication in the brain. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2554–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabauskas, G. Time course of GABA in the synaptic clefts of inhibitory synapses in the rostral nucleus of the solitary tract. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 373, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horie, H.; Rechnitz, G.A. Enzymatic flow injection determination of gamma-aminobutyric acid. Anal. Lett. 1995, 28, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, O.; Kurita, R.; Horiuchi, T.; Torimitsu, K. Small-volume on-line sensor for continuous measurement of γ-aminobutyric acid. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzei, F.; Botrè, F.; Lorenti, G.; Porcelli, F. Peroxidase based amperometric biosensors for the determination of γ-aminobutyric acid. Anal. Chim. Acta 1996, 328, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, J.E. Oxidation-reduction potential of the ferro-ferricyanide system in buffer solutions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 1973, 292, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Appendix
Effect of Working Potential
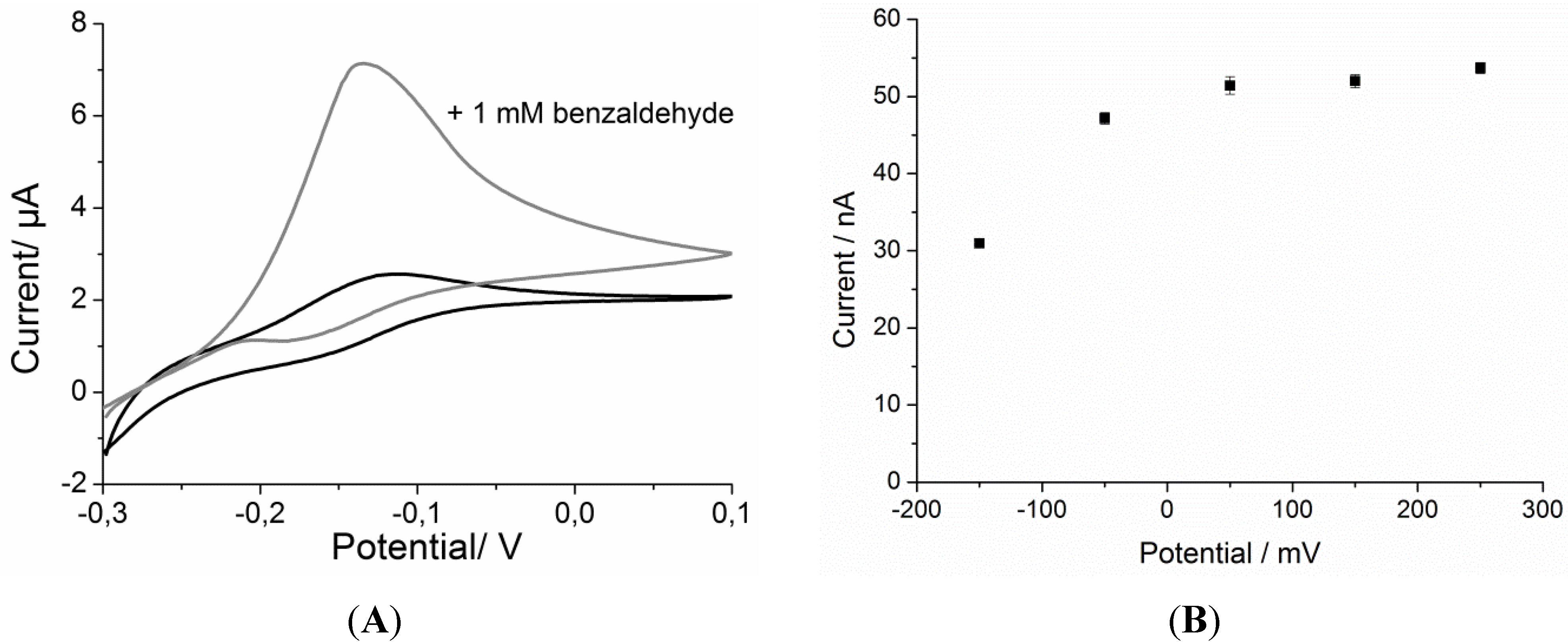
Electrochemical Behavior of Redox Polymer with Bound Osmium Complexes
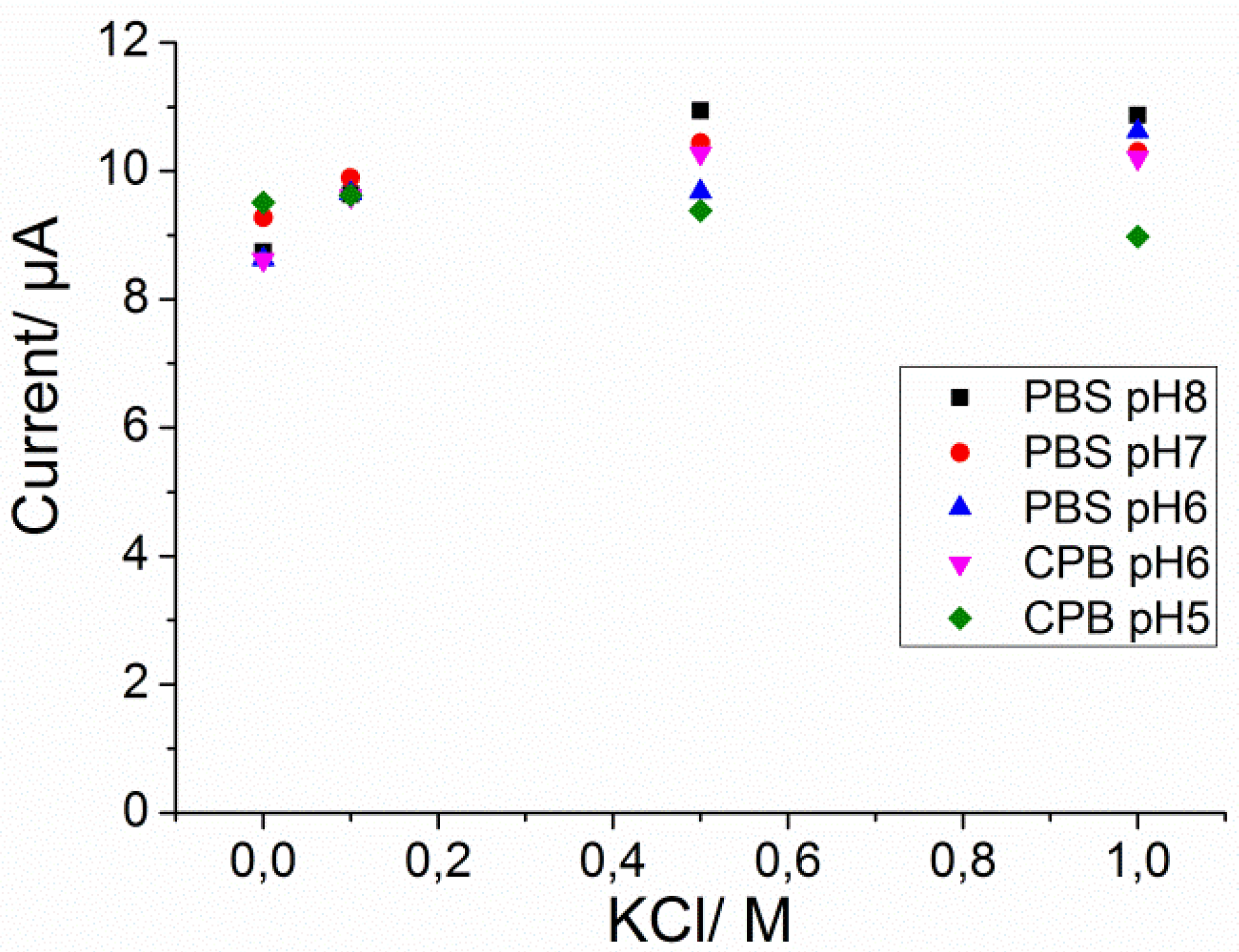
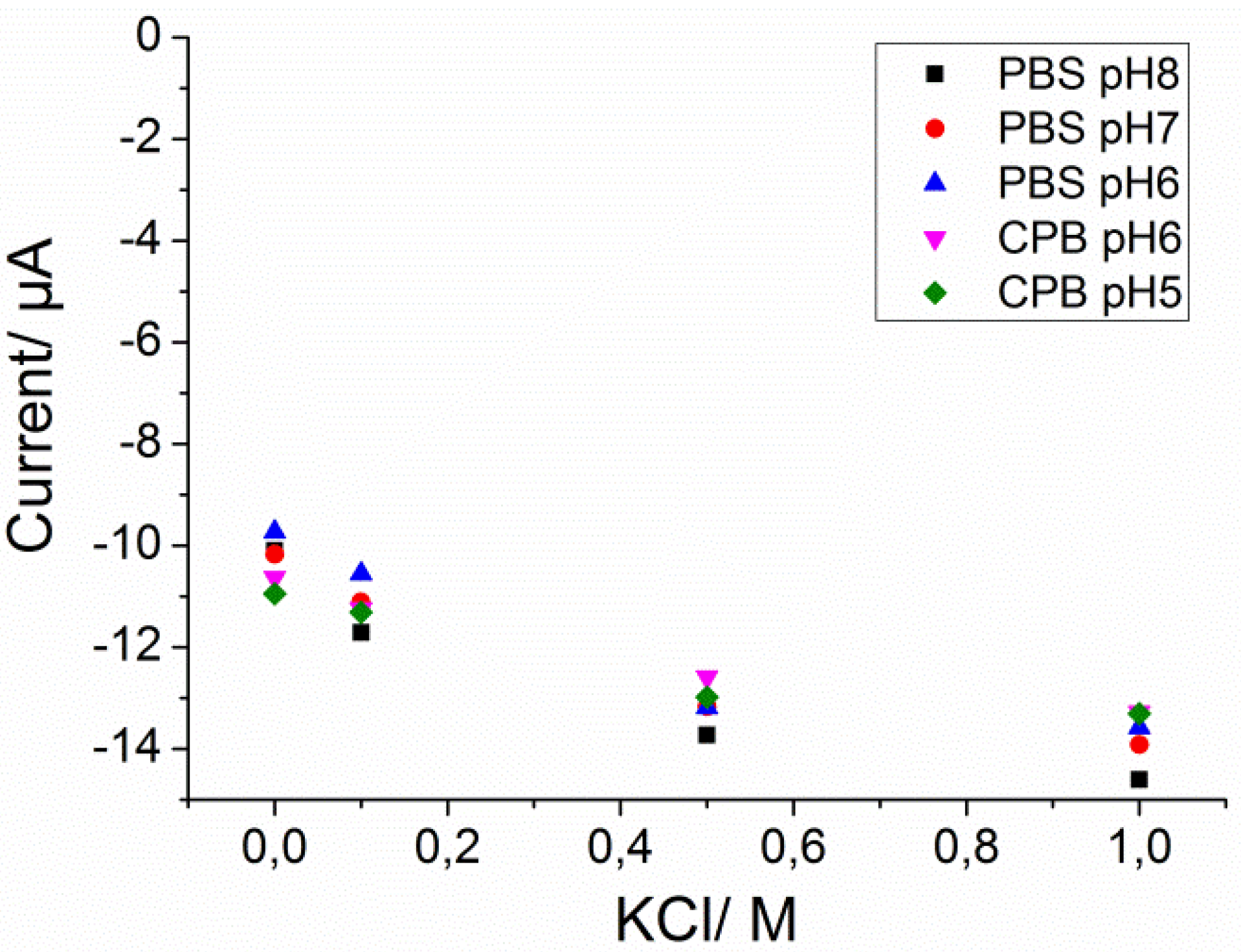
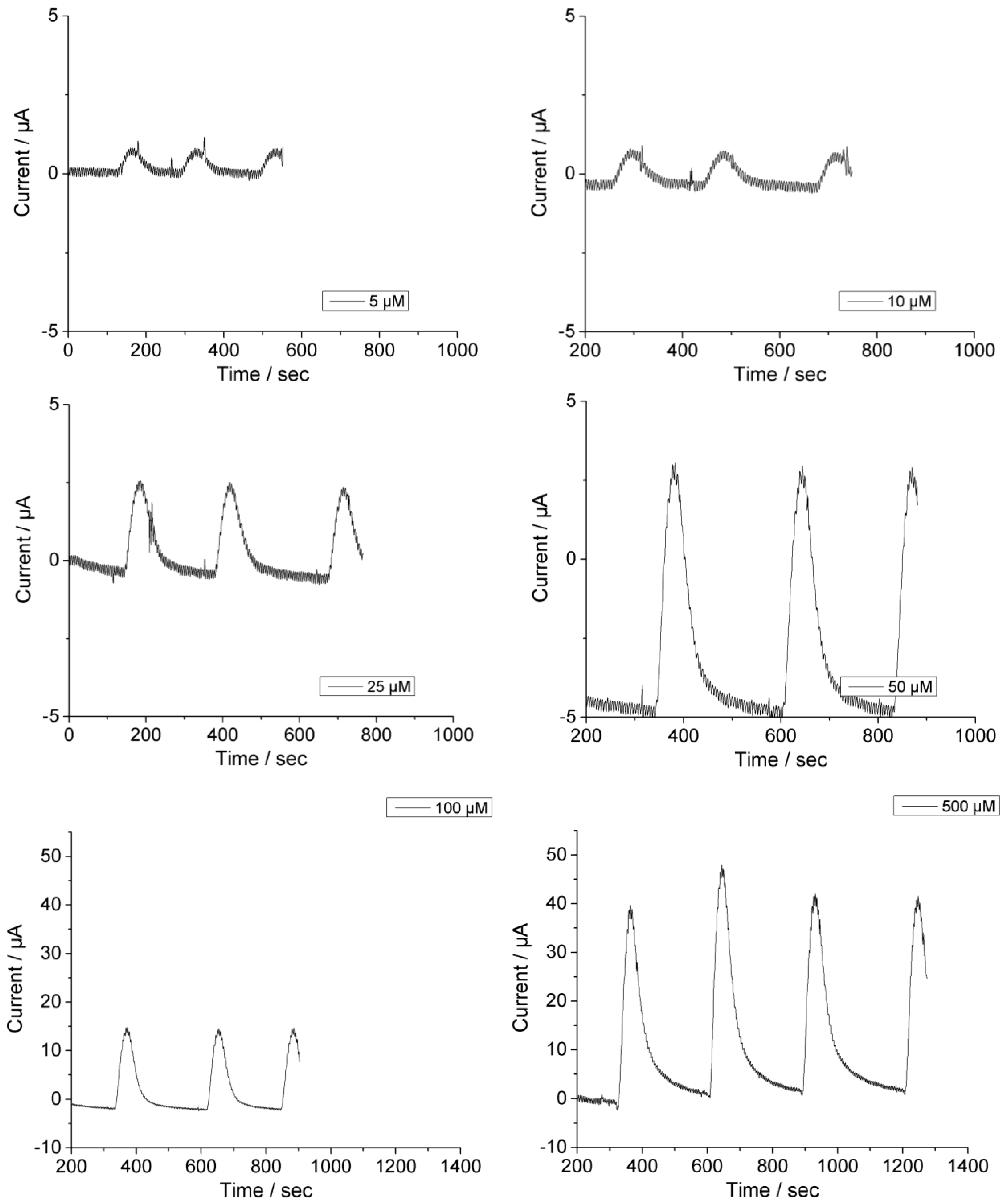
Current Traces for Calibration Graph
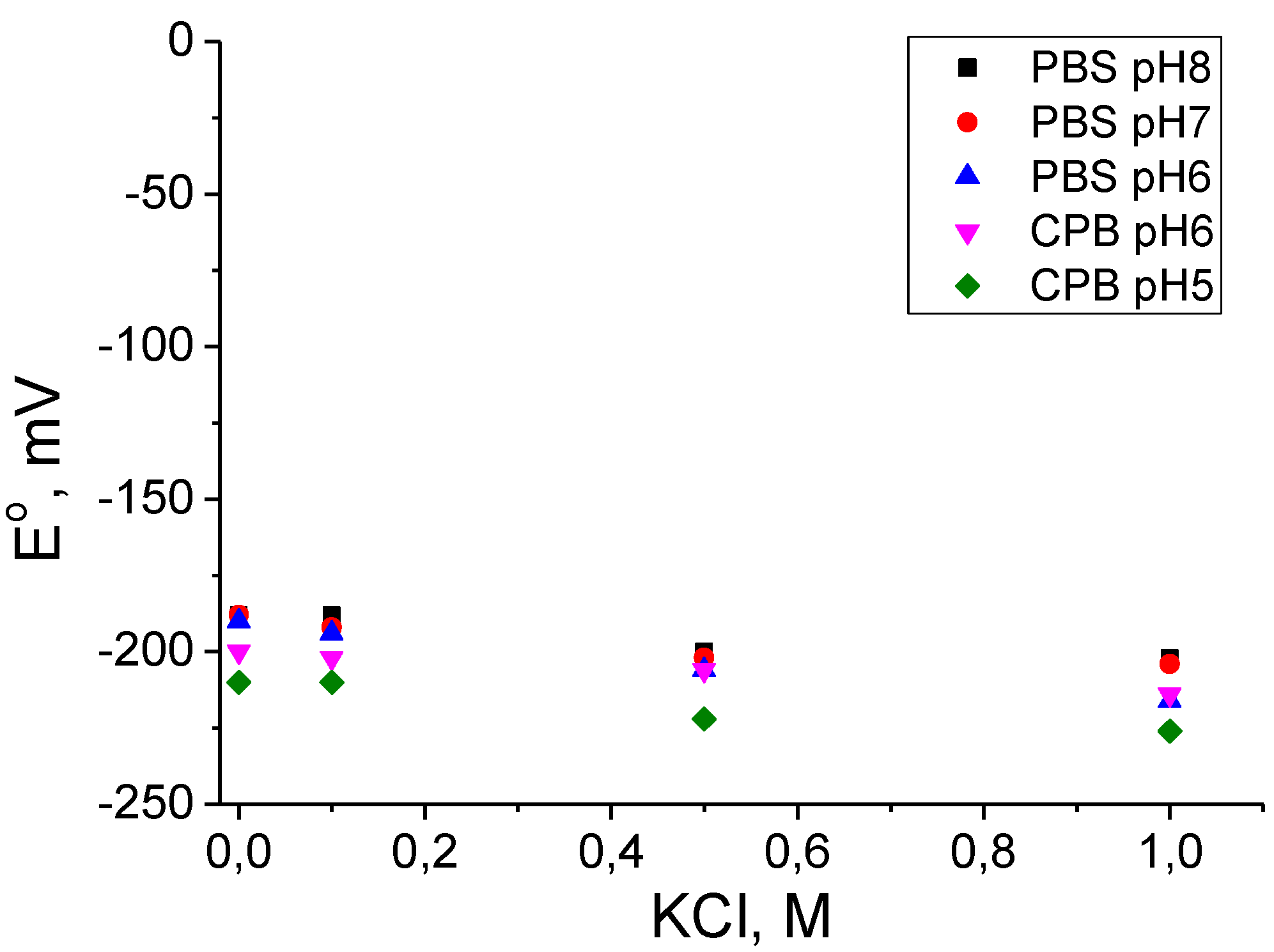
The Driving Force Estimation
 ) or ferricyanide (■).
) or ferricyanide (■).
 ) or ferricyanide (■).
) or ferricyanide (■).
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Badalyan, A.; Dierich, M.; Stiba, K.; Schwuchow, V.; Leimkühler, S.; Wollenberger, U. Electrical Wiring of the Aldehyde Oxidoreductase PaoABC with a Polymer Containing Osmium Redox Centers: Biosensors for Benzaldehyde and GABA. Biosensors 2014, 4, 403-421. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios4040403
Badalyan A, Dierich M, Stiba K, Schwuchow V, Leimkühler S, Wollenberger U. Electrical Wiring of the Aldehyde Oxidoreductase PaoABC with a Polymer Containing Osmium Redox Centers: Biosensors for Benzaldehyde and GABA. Biosensors. 2014; 4(4):403-421. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios4040403
Chicago/Turabian StyleBadalyan, Artavazd, Marlen Dierich, Konstanze Stiba, Viola Schwuchow, Silke Leimkühler, and Ulla Wollenberger. 2014. "Electrical Wiring of the Aldehyde Oxidoreductase PaoABC with a Polymer Containing Osmium Redox Centers: Biosensors for Benzaldehyde and GABA" Biosensors 4, no. 4: 403-421. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios4040403
APA StyleBadalyan, A., Dierich, M., Stiba, K., Schwuchow, V., Leimkühler, S., & Wollenberger, U. (2014). Electrical Wiring of the Aldehyde Oxidoreductase PaoABC with a Polymer Containing Osmium Redox Centers: Biosensors for Benzaldehyde and GABA. Biosensors, 4(4), 403-421. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios4040403