Using SPOT-7 for Nitrogen Fertilizer Management in Oil Palm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Pre-Processing
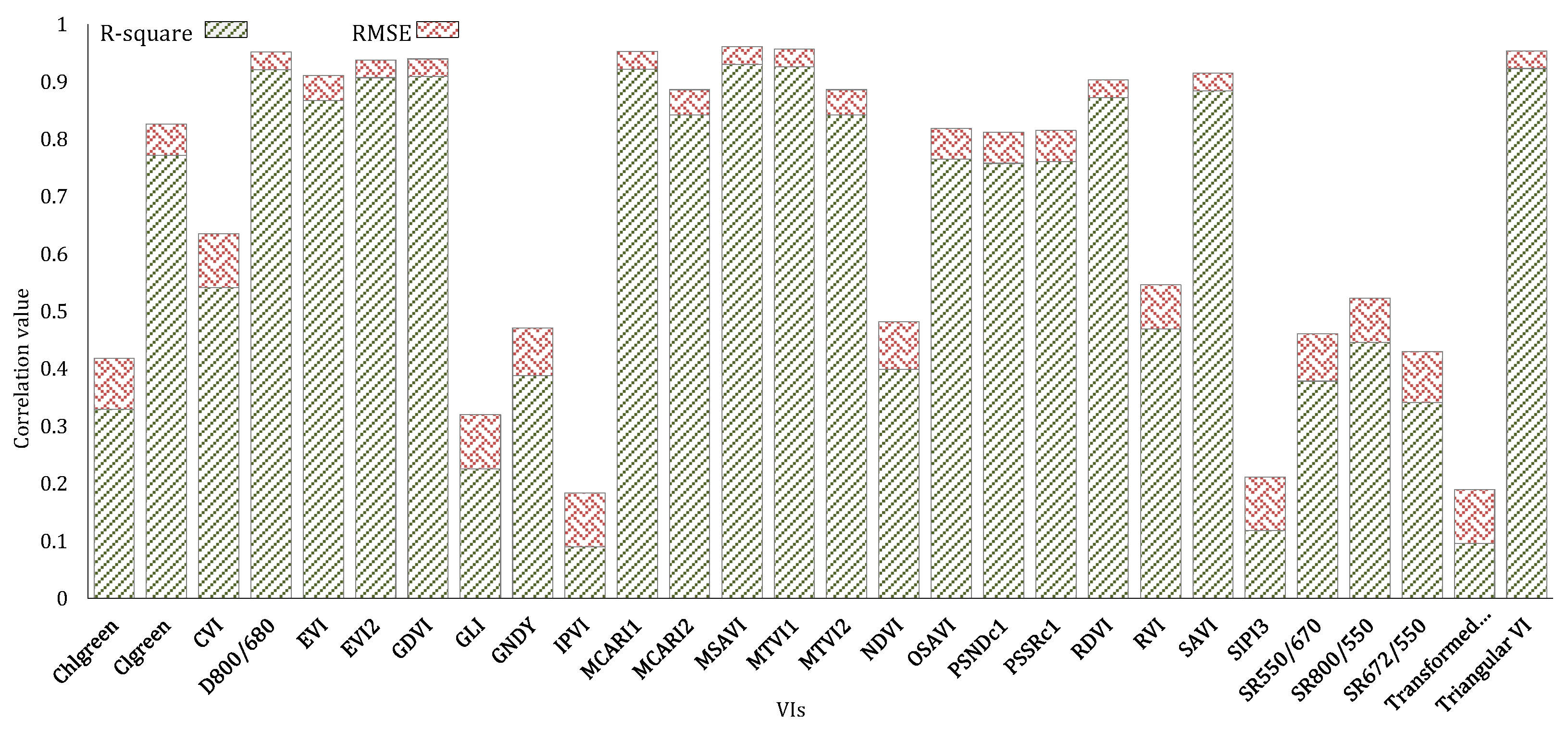
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Bank. The World Bank Group Framework and IFC Strategy for Engagement in the Palm Oil Sector; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sheil, D.; Casson, A.; Meijaard, E.; Van Noordwijk, M.; Gaskell, J.; Sunderland-Groves, J.; Wertz, K.; Kanninen, M. The Impacts and Opportunities of Oil Palm in Southeast Asia: What Do We Know and What Do We Need to Know? Center for International Forestry Research: Bogor, Indonesia, 2009; Volume 51. [Google Scholar]
- Malaysian Palm Oil Board, M. Malaysian Oil Palm Statistics 2015; Malaysian Palm Oil Board: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2012.
- Shamshiri, R.R.; Hameed, I.A.; Balasundram, S.K.; Ahmad, D.; Weltzien, C.; Yamin, M. Fundamental research on unmanned aerial vehicles to support precision agriculture in oil palm plantations. In Agricultural Robots-Fundamentals Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Almodares, A.; Taheri, R.; Chung, M.; Fathi, M. The effect of nitrogen and potassium fertilizers on growth parameters and carbohydrate contents of sweet sorghum cultivars. J. Environ. Biol 2008, 29, 849–852. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohidin, H.; Hanafi, M.M.; Rafii, Y.M.; Abdullah, S.N.A.; Idris, A.S.; Man, S.; Idris, J.; Sahebi, M. Determination of optimum levels of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium of oil palm seedlings in solution culture. Bragantia 2015, 74, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goh, K.; Po, S.B. Fertilizer recommendation systems for oil palm: Estimating the fertilizer rates. In Proceedings of MOSTA Best Practices Workshops-Agronomy and Crop Management; Malaysian Oil Scientists’ and Technologists’ Association: Petaling Jaya, Malaysia, 2005; pp. 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Pardon, L.; Bessou, C.; Nelson, P.N.; Dubos, B.; Ollivier, J.; Marichal, R.; Caliman, J.-P.; Gabrielle, B. Key unknowns in nitrogen budget for oil palm plantations. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silalertruksa, T.; Bonnet, S.; Gheewala, S.H. Life cycle costing and externalities of palm oil biodiesel in Thailand. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 28, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennari, P.; Heyman, A.; Kainu, M. FAO Statistical Pocketbook. World Food and Agriculture; Food and Agriculture Organisation: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Amenumey, S.E.; Capel, P.D. Fertilizer consumption and energy input for 16 crops in the United States. Nat. Resour. Res. 2014, 23, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savci, S. An agricultural pollutant: Chemical fertilizer. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2012, 3, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tilman, D.; Cassman, K.G.; Matson, P.A.; Naylor, R.; Polasky, S. Agricultural sustainability and intensive production practices. Nature 2002, 418, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, G.; Gray, H. Leaf analysis and the nutrition of the oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.). Ann. Bot. 1949, 13, 415–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairhurst, T.; Härdter, R. Oil Palm: Management for Large and Sustainable Yields; Potash & Phosphate Institute: Penang, Malaysia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Khorramnia, K.; Khot, L.R.; Shariff, A.R.B.M.; Ehsani, R.; Mansor, S.B.; Rahim, A.B.A. Oil palm leaf nutrient estimation by optical sensing techniques. Trans. ASABE 2014, 57, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar]
- Balasundram, S.K.; Golhani, K.; Shamshiri, R.R.; Vadamalai, G. Precision Agriculture Technologies for Management of Plant Diseases. In Plant Disease Management Strategies for Sustainable Agriculture through Traditional and Modern Approaches; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 259–278. [Google Scholar]
- Seelan, S.K.; Laguette, S.; Casady, G.M.; Seielstad, G.A. Remote sensing applications for precision agriculture: A learning community approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 88, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendana, M.; Rahim, S.A.; Lihan, T.; Idris, W.M.R.; Rahman, Z.A. A Review of Methods for Detecting Nutrient Stress of Oil Palm in Malaysia. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. Sci 2015, 5, 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Yao, X.; Yang, J.; Cao, W.; Hannaway, D.; Zhu, Y. Assessing newly developed and published vegetation indices for estimating rice leaf nitrogen concentration with ground-and space-based hyperspectral reflectance. Field Crops Res. 2011, 120, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, E.M.; Ahmed, F.B.; Van den Berg, M. Estimation of sugarcane leaf nitrogen concentration using in situ spectroscopy. Int. J. Appli. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2010, 12, S52–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridgen, J.L.; Varco, J.J. Dependency of cotton leaf nitrogen, chlorophyll, and reflectance on nitrogen and potassium availability. Agron. J. 2004, 96, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Reddy, K.R.; Kakani, V.G.; Reddy, V. Nitrogen deficiency effects on plant growth, leaf photosynthesis, and hyperspectral reflectance properties of sorghum. Eur. J. Agron. 2005, 22, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-H.; Ke, W.; Bailey, J.; Ren-Chao, W. Predicting nitrogen status of rice using multispectral data at canopy scale. Pedosphere 2006, 16, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Validation and Application of High Resolution Remote Sensing in Agricultural Fields; University of Minnesota: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Shou, L.; Jia, L.; Cui, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F. Using high-resolution satellite imaging to evaluate nitrogen status of winter wheat. J. Plant Nutr. 2007, 30, 1669–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eitel, J.; Long, D.; Gessler, P.; Smith, A. Using in-situ measurements to evaluate the new RapidEye™ satellite series for prediction of wheat nitrogen status. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 4183–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelling, K. Approaches to Characterize Chlorophyll/Nitrogen Status of Crop Canopies. In Proceedings of the DPGF Workshop Analysis of Remote Sensing Data, Hannover, Germany, 18 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bagheri, N.; Ahmadi, H.; Alavipanah, S.K.; Omid, M. Multispectral remote sensing for site-specific nitrogen fertilizer management. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2013, 48, 1394–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Connell, M.; Whitfield, D.; Abuzar, M. Satellite remote sensing of vegetation cover and nitrogen status in almond. In Proceedings of the XXIX International Horticultural Congress on Horticulture: Sustaining Lives, Livelihoods and Landscapes (IHC2014), Beijing, China, December 2016; pp. 559–566. [Google Scholar]
- Omer, G.; Mutanga, O.; Abdel-Rahman, E.M.; Peerbhay, K.; Adam, E. Mapping leaf nitrogen and carbon concentrations of intact and fragmented indigenous forest ecosystems using empirical modeling techniques and WorldView-2 data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 131, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, M.; Ibrahim, A.; Rasib, A.; Shah, R.; Nordin, L.; Haron, K. Detecting oil palm tree growth variability using a field spectroradiometer. ASIAN-PACIFIC Remote Sens. GIS J. 2001, 14, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Gevaert, C.M.; García-Haro, F.J. A comparison of STARFM and an unmixing-based algorithm for Landsat and MODIS data fusion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houborg, R.; McCabe, M.; Cescatti, A.; Gao, F.; Schull, M.; Gitelson, A. Joint leaf chlorophyll content and leaf area index retrieval from Landsat data using a regularized model inversion system (REGFLEC). Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacquemoud, S.; Verhoef, W.; Baret, F.; Bacour, C.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Asner, G.P.; François, C.; Ustin, S.L. PROSPECT+ SAIL models: A review of use for vegetation characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, S56–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magney, T.S.; Eitel, J.U.; Vierling, L.A. Mapping wheat nitrogen uptake from RapidEye vegetation indices. Precis. Agric. 2017, 18, 429–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousivand, A.; Verhoef, W.; Menenti, M.; Gorte, B. Modeling top of atmosphere radiance over heterogeneous non-Lambertian rugged terrain. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8019–8044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soudani, K.; François, C.; Le Maire, G.; Le Dantec, V.; Dufrêne, E. Comparative analysis of IKONOS, SPOT, and ETM+ data for leaf area index estimation in temperate coniferous and deciduous forest stands. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miky, Y.H.; El Shouny, A.F. Using Space-borne Hyperspectral Imagery on Mapping Nitrogen Fertilizer Excess to the Environment. Int. J. Sci. Res. (IJSR) ISSN (Online Index Copernicus Value Impact Factor) 2013, 14611, 2319–7064. [Google Scholar]
- Naito, H.; Rahimzadeh-Bajgiran, P.; Shimizu, Y.; Hosoi, F.; Omasa, K. Summer-season differences in NDVI and iTVDI among vegetation cover types in lake Mashu, Hokkaido, Japan using landsat TM data. Environ. Control Biol. 2012, 50, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datt, B. Visible/near infrared reflectance and chlorophyll content in Eucalyptus leaves. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 2741–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Gritz, Y.; Merzlyak, M.N. Relationships between leaf chlorophyll content and spectral reflectance and algorithms for non-destructive chlorophyll assessment in higher plant leaves. J. Plant Physiol. 2003, 160, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datt, B.; McVicar, T.R.; Van Niel, T.G.; Jupp, D.L.; Pearlman, J.S. Preprocessing EO-1 Hyperion hyperspectral data to support the application of agricultural indexes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1246–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sims, D.A.; Gamon, J.A. Relationships between leaf pigment content and spectral reflectance across a wide range of species, leaf structures and developmental stages. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Justice, C.; Liu, H. Development of vegetation and soil indices for MODIS-EOS. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 49, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Huete, A.R.; Didan, K.; Miura, T. Development of a two-band enhanced vegetation index without a blue band. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3833–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C. Monitoring the grasslands of the sahel 1984–1985. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gobron, N.; Pinty, B.; Verstraete, M.M.; Widlowski, J.-L. Advanced vegetation indices optimized for up-coming sensors: Design, performance, and applications. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2489–2505. [Google Scholar]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Kaufman, Y.; Merzlyak, M.N. Use of a green channel in remote sensing of global vegetation from EOS-MOD1S. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.M. Evaluation of vegetation indices and a modified simple ratio for boreal applications. Can. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 22, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Miao, Y.; Wang, H.; Huang, S.; Cheng, S.; Khosla, R.; Jiang, R. Non-destructive estimation of rice plant nitrogen status with Crop Circle multispectral active canopy sensor. Field Crops Res. 2013, 154, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.-K.; Diem, M.D.; Dreyfuss, G.; Van Duyne, G.D. Structure of the Y14-Magoh core of the exon junction complex. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haboudane, D.; Miller, J.R.; Pattey, E.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Strachan, I.B. Hyperspectral vegetation indices and novel algorithms for predicting green LAI of crop canopies: Modeling and validation in the context of precision agriculture. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Chehbouni, A.; Huete, A.R.; Kerr, Y.H.; Sorooshian, S. A modified soil adjusted vegetation index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 48, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, J.W., Jr.; Haas, R.H.; Schell, J.; Deering, D. Monitoring the vernal advancement and retrogradation (green wave effect) of natural vegetation. Remote Sensing Center 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Geneviève, R.; Michael, S.; Frédéric, B. Optimization of soil-adjusted vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 55, 95–107. [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn, G.A. Spectral indices for estimating photosynthetic pigment concentrations: A test using senescent tree leaves. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 657–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roujean, J.-L.; Breon, F.-M. Estimating PAR absorbed by vegetation from bidirectional reflectance measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 51, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlerf, M.; Atzberger, C.; Hill, J. Remote sensing of forest biophysical variables using HyMap imaging spectrometer data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Penuelas, J.; Baret, F.; Filella, I. Semi-empirical indices to assess carotenoids/chlorophyll a ratio from leaf spectral reflectance. Photosynthetica 1995, 31, 221–230. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, G.A. Ratios of leaf reflectances in narrow wavebands as indicators of plant stress. Remote Sens. 1994, 15, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschmann, C.; Nagel, E. In vivo spectroscopy and internal optics of leaves as basis for remote sensing of vegetation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 14, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datt, B. Remote sensing of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, chlorophyll a+ b, and total carotenoid content in eucalyptus leaves. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannari, A.; Morin, D.; Bonn, F.; Huete, A. A review of vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Rev. 1995, 13, 95–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartanto, I.M.; Van Der Kwast, J.; Alexandridis, T.K.; Almeida, W.; Song, Y.; van Andel, S.; Solomatine, D. Data assimilation of satellite-based actual evapotranspiration in a distributed hydrological model of a controlled water system. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 57, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, F.S.Y.; Alcântara, E.; Rodrigues, T.W.P.; Imai, N.N.; Barbosa, C.C.F.; Rotta, L.H.D.S. Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration and the trophic state of the Barra Bonita hydroelectric reservoir using OLI/Landsat-8 images. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 10391–10417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Casero, M.T.; López-Granados, F.; Peña-Barragán, J.M.; Jurado-Expósito, M.; García-Torres, L.; Fernández-Escobar, R. Assessing nitrogen and potassium deficiencies in olive orchards through discriminant analysis of hyperspectral data. J. Am. Soc. Horticult. Sci. 2007, 132, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, P.; Singh, R.K.; Song, Q.-Q.; Li, H.-B.; Yang, L.-T.; Li, Y.-R. Methods for Estimation of Nitrogen Components in Plants and Microorganisms. In Nitrogen Metabolism in Plants; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 103–112. [Google Scholar]





| Satellite Sensor | Application | Indices | Correlation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IKONOS | Nitrogen detection in rice | > 0.9 | [24] | |
| QuickBird | Detect the biophysical and biochemical characteristics of potato (predicting the amount of nitrogen) | MSAVI | > 0.9 | [25] |
| QuichBird | Evaluate the status of N in winter wheat (Correlation between satellite images and the amount of N concentration) | all broadband indices | > 0.9 | [26] |
| RapidEye | to predict N status of spring wheat | MCARI/MTVI2 | [27] | |
| RapidEye | measure the amount of N in the wheat leaf (Finding a relationship between RapidEye satellite imagery and SPAD | NDRE/NDVI | 0.77 | [28] |
| Aster | predicted corn canopy N content by generating N fertilization map using SAM | MTVI2 | 0.87 | [29] |
| RapidEye | estimated the status of N in almond | NDVI and CCCI | > 0.9 | [30] |
| WorldView-2 | Monitored the N concentration and the amount of C in forest trees | SVM and ANN | > 0.9 | [31] |
| Trial Site Code | FASSB PPPTR | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Plot Size | 6 × 8 Palms (4 × 6 recorded) | ||
| No. of Plot | 18 Plots (3 treatments × 6 replication) | ||
| Trial Design | RCBD | ||
| Land Area | 6.35 ha | ||
| Planting Material | D × P Yangambi (ML 161) | ||
| Soil Series | Katong | ||
| Terrain | Moderately Undulating | ||
| Coordinate points | Top Left: Lat: 3°54′41.84″ N Lon: 102°31′46.38″ E | Top Right: Lat: 3°54′41.80″ N Lon: 102°32′8.02″ E | |
| Down Left: Lat: 3°54′35.59″ N Lon: 102°31′46.71″ E | Down Right: Lat: 3°54′35.68″ N Lon: 102°32′7.99″ E | ||
| Treatment | A Good Agronomic Practice | B Standard Practice | C Sub-Standard |
| Plowing | ✓ Planting row | X | X |
| Liming | ✓ 2 t/ha | X | X |
| Legume | ✓ Mb: CM: Pj | ✓ Mb | X |
| Mulching | ✓ FM + compost | ✓ Chipping | X |
| Ablation | ✓ 4 times | ✓ 2 times | X |
| 2015 | |||
| Round | Fert. Type | Rate kg per Tree | Date Applied |
| 1 | CPD | 3.00 | 17 April |
| 2 | NK Mix | 1.50 | 7 Jun |
| 3 | CPD | 2.75 | 29 August |
| 4 | NK Mix | 1.50 | 15 November |
| Sum = 8.75 | |||
| 2016 | |||
| 1 | NK Mix | 2.25 | 25 April |
| 2 | CPD | 1.00 | 20 May |
| 3 | NK Mix | 2.00 | 15 August |
| 4 | GML * | 2.50 | 9 October |
| 5 | NK Mix | 2.00 | 22 November |
| Sum = 9.75 | |||
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Launch Date | 30 June 2014 |
| Spectral Bands | Panchromatic: 0.450–0.745 mm Blue (0.455–0.525 µm) Green (0.530–0.590 µm) Red (0.625–0.695 µm) Near-Infrared (0.760–0.890 µm) |
| Resolution (GSD) | Panchromatic-1.5m Multispectral 6.0 m (B,G,R,NIR) |
| Imaging Swath | 60 km at Nadir |
| Altitude | 694 km |
| Bit Depth | 12 bits per pixel (4096 values) |
| Detectors | PAN array assembly: 28,000 pixels MS array assembly: 4 × 7000 pixels |
| Revisit | 1 day with SPOT-6 and SPOT-7 operating simultaneously between 1 and 3 days with only one satellite in operation |
| No. | Vegetation Indices | Common Name | Equation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chlorophyll Green | Chlgreen | [41] | |
| 2 | Chlorophyll Index Green | CIgreen | [42] | |
| 3 | Chlorophyll Vegetation Index | CVI | [43] | |
| 4 | Difference 800/680 | D800/680 | [44] | |
| 5 | Enhanced Vegetation Index | EVI | [45] | |
| 6 | Enhanced Vegetation Index 2 | EVI2 | [46] | |
| 7 | Difference NIR/Green Green Difference Vegetation Index | GDVI | [47] | |
| 8 | Green Leaf Index | GLI | [48] | |
| 9 | Normalized Difference NIR/Green Green NDVI | GNDVI | [49] | |
| 10 | Infrared Percentage Vegetation index | IPVI | [50] | |
| 11 | Modified Chlorophyll Absorption in Reflectance Index 1 | MCARI1 | [51,52] | |
| 12 | Modified Chlorophyll Absorption in Reflectance Index 2 | MCARI2 | [51,53] | |
| 13 | Modified Soil Adjusted Vegetation Index | MSAVI | [54] | |
| 14 | Modified Triangular Vegetation Index 1 | MTVI1 | [53] | |
| 15 | Modified Triangular Vegetation Index 2 | MTVI2 | [53] | |
| 16 | Normalized Difference Vegetation Index | NDVI | [55] | |
| 17 | Optimized Soil Adjusted Vegetation Index | OSAVI | [56] | |
| 18 | Normalized Difference 800/500 Pigment Specific Normalized Difference C1 | PSNDc1 | [57] | |
| 19 | Simple Ratio 800/500 Pigment Specific Simple Ratio C1 | PSSRc1 | [57] | |
| 20 | Renormalized Difference Vegetation Index | RDVI | [58] | |
| 21 | Simple Ratio 800/670 Ratio Vegetation Index | RVI | [59] | |
| 22 | Soil Adjusted Vegetation Index | SAVI | [55] | |
| 23 | Structure Intensive Pigment Index 3 | SIPI3 | [60] | |
| 24 | Simple Ratio 550/670 | SR550/670 | [61] | |
| 25 | Simple Ratio 800/550 | SR800/550 | [62] | |
| 26 | Simple Ratio 672/550 Datt5 | SR672/550 | [63] | |
| 27 | Transformed Vegetation Index | TVI | [64] | |
| 28 | Triangular Vegetation Index | TVI | [55] |
| Sample Description | Parameters | Covariance | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total-N | P | K | Mg | |||||||
| (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | |||||||
| R1/A | 2.96 | 0.167 | 1.171 | 0.290 | 63.67 | |||||
| R2/A | 3.18 | 0.172 | 1.170 | 0.344 | 66.88 | 70.25 | ||||
| R3/A | 2.99 | 0.166 | 1.004 | 0.302 | 51.30 | 53.89 | 41.38 | |||
| R4/A | 3.09 | 0.167 | 1.131 | 0.290 | 54.34 | 57.08 | 43.82 | 46.41 | ||
| R5/A | 2.94 | 0.165 | 0.978 | 0.286 | 54.53 | 57.28 | 43.97 | 46.51 | 46.72 | |
| R6/A | 3.03 | 0.167 | 0.840 | 0.263 | 54.62 | 57.38 | 44.05 | 46.65 | 46.81 | 46.9 |
| mean | 3.03 | 0.167 | 1.049 | 0.296 | ||||||
| Standard Dev | 0.0902 | 0.0024 | 0.1319 | 0.0268 | ||||||
| %CV | 2.97 | 1.43 | 12.57 | 9.05 | ||||||
| R1/B | 3.03 | 0.168 | 1.068 | 0.330 | 64.08 | |||||
| R2/B | 3.07 | 0.167 | 1.077 | 0.377 | 70.36 | 77.27 | ||||
| R3/B | 3.22 | 0.174 | 1.007 | 0.339 | 64.02 | 70.29 | 63.96 | |||
| R4/B | 3.12 | 0.167 | 1.105 | 0.306 | 54.51 | 59.84 | 54.47 | 46.40 | ||
| R5/B | 3.07 | 0.167 | 0.936 | 0.279 | 54.69 | 60.04 | 54.65 | 46.56 | 46.71 | |
| R6/B | 3.10 | 0.167 | 1.181 | 0.333 | 63.96 | 70.23 | 63.89 | 54.41 | 54.59 | 63.84 |
| mean | 3.10 | 0.168 | 1.062 | 0.327 | ||||||
| Standard Dev | 0.0841 | 0.0028 | 0.0838 | 0.0329 | ||||||
| %CV | 2.71 | 1.66 | 7.89 | 10.06 | ||||||
| R1/C | 2.99 | 0.165 | 1.193 | 0.343 | 57.71 | |||||
| R2/C | 3.12 | 0.170 | 1.190 | 0.325 | 63.70 | 70.31 | ||||
| R3/C | 2.99 | 0.165 | 0.993 | 0.355 | 51.88 | 57.26 | 46.64 | |||
| R4/C | 3.04 | 0.168 | 1.061 | 0.307 | 57.82 | 63.82 | 51.98 | 57.93 | ||
| R5/C | 2.97 | 0.163 | 0.912 | 0.280 | 52.01 | 57.41 | 46.76 | 52.12 | 46.89 | |
| R6/C | 2.99 | 0.167 | 1.067 | 0.282 | 48.82 | 53.88 | 43.90 | 48.92 | 44.02 | 41.33 |
| mean | 3.01 | 0.166 | 1.069 | 0.315 | ||||||
| Standard Dev | 0.1068 | 0.0025 | 0.11 | 0.0311 | ||||||
| %CV | 3.54 | 1.5 | 10.28 | 9.87 | ||||||
| Nutrient | Deficiency | Marginal | Optimum | Marginal | Excess |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | < 2.3 | 2.3 to 2.4 | 2.4 to 2.80 | 2.8 to 3 | > 3 |
| P | < 0.14 | 0.14 to 0.15 | 0.15 to 0.18 | 0.18 to 0.25 | > 0.25 |
| K | < 0.75 | 0.75 to 0.9 | 0.9 to 1.2 | 0.9 to 1.6 | > 1.6 |
| Mg | < 0.2 | 0.2 to 0.25 | 0.25 to 0.4 | 0.4 to 0.7 | > 0.7 |
| Model Name | Model Summary | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | R-Square | Adjusted R-Square | Std. Error of the Estimate | |
| Linear | 0.070 | 0.005 | −0.137 | 0.099 |
| Logarithmic | 0.022 | 0.000 | −0.142 | 0.099 |
| Quadratic | 0.964 | 0.930 | 0.906 | 0.028 |
| Compound a | 0.063 | 0.004 | −0.138 | 0.032 |
| Power a | 0.015 | 0.000 | −0.143 | 0.032 |
| S a | 0.032 | 0.001 | −0.142 | 0.032 |
| Growth a | 0.063 | 0.004 | −0.138 | 0.032 |
| Exponential a | 0.063 | 0.004 | −0.138 | 0.032 |
| Independent Variable | MSAVI | |||
| Constant | Included | |||
| Variable Whose Values Label Observations in Plots | Unspecified | |||
| Tolerance for Entering Terms in Equations | 0.0001 | |||
| Sum of Squares | Degrees of Freedom (DF) | Mean Square | F ratio | p-value. | |
| Regression | 0.064 | 2 | 0.032 | 39.657 | 0.000 |
| Residual | 0.005 | 6 | 0.001 | ||
| Total | 0.069 | 8 | |||
| Coefficients of MSAVI | |||||
| Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients Beta | t | p-value. | ||
| B | Std. Error | ||||
| MSAVI_9S | −12.921 | 1.462 | −19.228 | −8.839 | 0.000 |
| MSAVI_9S ** 2 | 4.145 | 0.467 | 19.322 | 8.882 | 0.000 |
| (Constant) | 13.052 | 1.138 | 11.467 | 0.000 | |
| Plot | MSAVI | Actual N (%) | Plot | MSAVI | Actual N (%) | Predicted N (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1B | 1.556866655748 | 3.03 | 6B | 1.755091701945 | 3.10 | 3.14 |
| 1C | 1.497733329733 | 2.99 | 6C | 1.673120826483 | 2.99 | 3.04 |
| 1A | 1.572449992101 | 2.96 | 6A | 1.671252056957 | 3.03 | 3.04 |
| 2C | 1.364485422771 | 3.12 | 5C | 1.559139554700 | 2.97 | 2.98 |
| 2A | 1.360270857811 | 3.18 | 5A | 1.502304171522 | 2.94 | 3.00 |
| 2B | 1.400625000397 | 3.07 | 5B | 1.500858326754 | 3.07 | 3.00 |
| 3A | 1.485445639362 | 2.99 | 4A | 1.435083339612 | 3.09 | 3.05 |
| 3B | 1.799166644614 | 3.22 | 4B | 1.754893735051 | 3.12 | 3.14 |
| 3C | 1.597421970367 | 2.99 | 4C | 1.489568730196 | 3.04 | 3.00 |
| Group Independen t-test | N | Mean | Std. Deviation | Std. Error Mean | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Independent t-test | 1 | 9 | 3.0389 | 0.06214 | 0.02071 |
| 2 | 9 | 3.0433 | 0.05958 | 0.01986 | |
| Levene’s Test for Equality of Variances | t-test for Equality of Means | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | Sig. | t | df | Sig. (2-tailed) | Mean Difference | Std. Error Difference | 95% Confidence Interval of the Difference | |||
| Lower | Upper | |||||||||
| Independent t-test | Equal variances assumed | 0.123 | 0.731 | −0.155 | 16 | 0.879 | −0.00444 | 0.02870 | −0.06528 | 0.05639 |
| Equal variances not assumed | −0.155 | 15.97 | 0.879 | −0.00444 | 0.02870 | −0.06529 | 0.05640 | |||
| MSAVI | Actual N% | Predicted | Three-level N Content | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual | Predicted | True/false | |||
| 1.755091701945 | 3.10 | 3.14 | Excess | Excess | 1 |
| 1.673120826483 | 2.99 | 3.04 | Marginal | Excess | 0 |
| 1.671252056957 | 3.03 | 3.04 | Excess | Excess | 1 |
| 1.559139554700 | 2.97 | 2.98 | Marginal | Marginal | 1 |
| 1.502304171522 | 2.94 | 3.00 | Marginal | Excess | 0 |
| 1.500858326754 | 3.07 | 3.00 | Excess | Excess | 1 |
| 1.435083339612 | 3.09 | 3.05 | Excess | Excess | 1 |
| 1.754893735051 | 3.12 | 3.14 | Excess | Excess | 1 |
| 1.489568730196 | 3.04 | 3.00 | Excess | Excess | 1 |
| Total Sample | 9 | ||||
| Percent of true (Accuracy) | 77.7% | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yadegari, M.; Shamshiri, R.R.; Mohamed Shariff, A.R.; Balasundram, S.K.; Mahns, B. Using SPOT-7 for Nitrogen Fertilizer Management in Oil Palm. Agriculture 2020, 10, 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10040133
Yadegari M, Shamshiri RR, Mohamed Shariff AR, Balasundram SK, Mahns B. Using SPOT-7 for Nitrogen Fertilizer Management in Oil Palm. Agriculture. 2020; 10(4):133. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10040133
Chicago/Turabian StyleYadegari, Mohammad, Redmond R. Shamshiri, Abdul Rashid Mohamed Shariff, Siva K. Balasundram, and Benjamin Mahns. 2020. "Using SPOT-7 for Nitrogen Fertilizer Management in Oil Palm" Agriculture 10, no. 4: 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10040133






