Pneumatic Compression Combined with Standard Treatment after Total Hip Arthroplasty and Its Effects on Edema of the Operated Limb and on Physical Outcomes: A Pilot Clinical Randomized Controlled Study
Abstract
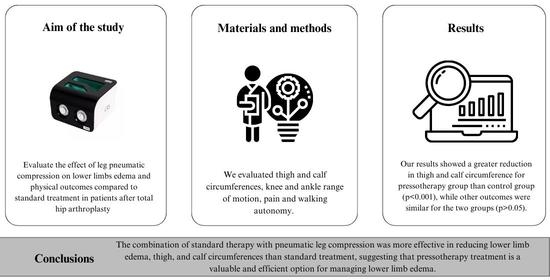
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Anthropometric Characteristics
2.3. Study Protocol and Evaluation
- The circumference of the distal third of the thigh (15 cm above the upper border of the patella);
- The circumference of the proximal third of the leg (20 cm above the lateral malleolus);
- The knee flexion range of motion (ROM);
- The ankle dorsiflexion ROM.
2.4. The Pneumatic Compression Therapy
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, R.W.; Pellisier, J.M.; Hazen, G.B. A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Total Hip Arthroplasty for Osteoarthritis of the Hip. JAMA 1996, 275, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozic, K.J.; Kurtz, S.M.; Lau, E.; Ong, K.; Vail, T.P.; Berry, D.J. The Epidemiology of Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty in the United States. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2009, 91, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetta Report Annuale Riap 2019 e Compendio. Available online: https://riap.iss.it/riap/it/attivita/report/2020/10/19/report-riap-2019/ (accessed on 2 May 2023).
- Santana, D.C.; Emara, A.K.; Orr, M.N.; Klika, A.K.; Higuera, C.A.; Krebs, V.E.; Molloy, R.M.; Piuzzi, N.S. An Update on Venous Thromboembolism Rates and Prophylaxis in Hip and Knee Arthroplasty in 2020. Medicina 2020, 56, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, R.F.; Burgess, I.A.; Zicat, B. The Prevalence of Venous Thromboembolism after Hip and Knee Replacement Surgery. Med. J. Aust. 2005, 182, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righini, M.; Le Gal, G.; De Lucia, S.; Roy, P.-M.; Meyer, G.; Aujesky, D.; Bounameaux, H.; Perrier, A. Clinical Usefulness of D-Dimer Testing in Cancer Patients with Suspected Pulmonary Embolism. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 95, 715–719. [Google Scholar]
- Dahl, O.E.; Harenberg, J.; Wexels, F.; Preissner, K.T. Arterial and Venous Thrombosis Following Trauma and Major Orthopedic Surgery: Molecular Mechanisms and Strategies for Intervention. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2015, 41, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albayati, M.A.; Grover, S.P.; Saha, P.; Lwaleed, B.A.; Modarai, B.; Smith, A. Postsurgical Inflammation as a Causative Mechanism of Venous Thromboembolism. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2015, 41, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanderling, C.; Liles, J.; Finkler, E.; Carlsgaard, P.; Hopkinson, W.; Guler, N.; Hoppensteadt, D.; Fareed, J. Dysregulation of Tissue Factor, Thrombin-Activatable Fibrinolysis Inhibitor, and Fibrinogen in Patients Undergoing Total Joint Arthroplasty. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2017, 23, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thromboembolic Risk Factors (THRIFT) Consensus Group. Risk of and Prophylaxis for Venous Thromboembolism in Hospital Patients. BMJ 1992, 305, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foldi, E.; Foldi, M.; Rockson, S. Complete decongestive physiotherapy. In Lymphedema: A Concise Compendium of Therapy and Practice; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 403–411. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, G.K.; Henry, A.P.; Preston, B.J. Prevention of Deep-Vein Thrombosis by Low-Dose Heparin in Patients Undergoing Total Hip Replacement. Lancet 1974, 2, 797–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agu, O.; Hamilton, G.; Baker, D. Graduated Compression Stockings in the Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism. Br. J. Surg. 1999, 86, 992–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snyder, M.A.; Sympson, A.N.; Scheuerman, C.M.; Gregg, J.L.; Hussain, L.R. Efficacy in Deep Vein Thrombosis Prevention with Extended Mechanical Compression Device Therapy and Prophylactic Aspirin Following Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Randomized Control Trial. J. Arthroplast. 2017, 32, 1478–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakkos, S.K.; Caprini, J.A.; Geroulakos, G.; Nicolaides, A.N.; Stansby, G.; Reddy, D.J.; Ntouvas, I. Combined Intermittent Pneumatic Leg Compression and Pharmacological Prophylaxis for Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 9, CD005258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.M.; He, M.L.; Xiao, Z.M.; Li, T.S.; Wu, H.; Jiang, H. Different Types of Intermittent Pneumatic Compression Devices for Preventing Venous Thromboembolism in Patients after Total Hip Replacement. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 11, CD009543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Thaher, Y.; Alfuqaha, O.A.; Dweidari, A. Health-Related Quality of Life and Outcome after Total Knee Replacement: Results from a Cross-Sectional Survey in Jordan. Adv. Orthop. 2021, 2021, 5506809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canovas, F.; Dagneaux, L. Quality of Life after Total Knee Arthroplasty. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2018, 104, S41–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.K.; Jerosch-Herold, C.; Shepstone, L. Effectiveness of Edema Management Techniques for Subacute Hand Edema: A Systematic Review. J. Hand Ther. 2017, 30, 432–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Medical Association World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farrar, J.T.; Young, J.P.; LaMoreaux, L.; Werth, J.L.; Poole, M.R. Clinical Importance of Changes in Chronic Pain Intensity Measured on an 11-Point Numerical Pain Rating Scale. Pain 2001, 94, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.P.; Karoly, P.; Braver, S. The Measurement of Clinical Pain Intensity: A Comparison of Six Methods. Pain 1986, 27, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, E.; Atkinson, H.J.; Ignelzi, R.J. Measurement of Pain: Patient Preference Does Not Confound Pain Measurement. Pain 1981, 10, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motyl, J.M.; Driban, J.B.; McAdams, E.; Price, L.L.; McAlindon, T.E. Test-Retest Reliability and Sensitivity of the 20-Meter Walk Test among Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2013, 14, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fujisawa, M.; Naito, M.; Asayama, I.; Kambe, T.; Koga, K. Effect of Calf-Thigh Intermittent Pneumatic Compression Device after Total Hip Arthroplasty: Comparative Analysis with Plantar Compression on the Effectiveness of Reducing Thrombogenesis and Leg Swelling. J. Orthop. Sci. 2003, 8, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westrich, G.H.; Sculco, T.P. Prophylaxis against Deep Venous Thrombosis after Total Knee Arthroplasty. Pneumatic Plantar Compression and Aspirin Compared with Aspirin Alone. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1996, 78, 826–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, H.S.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, J.T.; Yoo, J.J.; Kim, H.J. Intermittent Pneumatic Compression for the Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism after Total Hip Arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2017, 9, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michinaga, S.; Koyama, Y. Pathogenesis of Brain Edema and Investigation into Anti-Edema Drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 9949–9975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aldrich, M.B.; Gross, D.; Morrow, J.R.; Fife, C.E.; Rasmussen, J.C. Effect of Pneumatic Compression Therapy on Lymph Movement in Lymphedema-Affected Extremities, as Assessed by near-Infrared Fluorescence Lymphatic Imaging. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2017, 10, 1650049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nose, Y.; Murata, K.; Wada, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Fukagawa, Y.; Yoshino, H.; Susa, T.; Kihara, C.; Matsuzaki, M. The Impact of Intermittent Pneumatic Compression Devices on Deep Venous Flow Velocity in Patients with Congestive Heart Failure. J. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuj, K.A.; Prince, C.N.; Hughson, R.L.; Peterson, S.D. Superficial Femoral Artery Blood Flow with Intermittent Pneumatic Compression of the Lower Leg Applied during Walking Exercise and Recovery. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 2019, 127, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeroushalmi, D.; Padilla, J.A.; Slover, J.; Schwarzkopf, R.; Macaulay, W. Patient Satisfaction and Risk of Falls with the Use of Intermittent Pneumatic Compression Devices Following Total Joint Arthroplasty. Bull. Hosp. Jt. Dis. (2013) 2022, 80, 246–252. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelhalim, N.M.; Samhan, A.F. Influences of Intermittent Pneumatic Compression Therapy on Edema and Postoperative Patient’s Satisfaction after Lipoabdominoplasty. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2021, 45, 1667–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| PG (n = 24) | CG (n = 23) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male:Female | 9:15 | 8:15 | // |
| Age (years) | 68.38 ± 9.35 | 68.09 ± 9.11 | >0.05 |
| Weight (kg) | 71.71 ± 12.77 | 73.57 ± 12.28 | >0.05 |
| Height (m) | 1.65 ± 0.09 | 1.68 ± 0.10 | >0.05 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.96 ± 3.14 | 25.72 ± 2.59 | >0.05 |
| T0 | T1 | Delta (Post-Pre) | p-Value | Effect Size | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thigh circumference (cm) | PG (n = 24) | 51.6 ± 4.1 | 49.1 ± 4.5 | −2.0 (2.0) | <0.001 *** | 0.850 |
| CG (n = 23) | 50.9 ± 6.3 | 50.9 ± 4.7 | 0.2 (1.4) | |||
| Calf circumference (cm) | PG (n = 24) | 33.4 ± 2.9 | 31.8 ± 2.9 | −1.9 (1.6) | <0.001 *** | 0.690 |
| CG (n = 23) | 34.5 ± 4.5 | 35.7 ± 4.5 | 0.0 (0.7) | |||
| Knee ROM (°) | PG (n = 24) | 99.38 ± 23.95 | 117.20 ± 9.97 | 12.5 (14.0) | 0.528 | // |
| CG (n = 23) | 93.91 ± 23.95 | 110.57 ± 12.09 | 15 (11.00) | |||
| Ankle ROM (°) | PG (n = 24) | 91.79 ± 4.37 | 95.58 ± 6.07 | 4.00 (6.00) | 0.966 | // |
| CG (n = 23) | 87.96 ± 6.26 | 92.09 ± 3.90 | 3.00 (7.00) | |||
| NRS | PG (n = 24) | 4.92 ± 2.00 | 2.46 ± 1.61 | −2.50 (1.00) | 0.697 | // |
| CG (n = 23) | 6.13 ± 2.24 | 4.00 ± 1.73 | −2.00 (1.00) | |||
| 20 mwt (s) | PG (n = 24) | 52.44 ± 22.79 | 25.27 ± 4.83 | −15.50 (23.75) | 0.983 | // |
| CG (n = 23) | 58.39 ± 20.62 | 34.52 ± 10.24 | −23.00 (21.00) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carnevale Pellino, V.; Gatti, A.; Vandoni, M.; Patanè, P.; Febbi, M.; Ballarin, S.; Cavallo, C.; Marin, L. Pneumatic Compression Combined with Standard Treatment after Total Hip Arthroplasty and Its Effects on Edema of the Operated Limb and on Physical Outcomes: A Pilot Clinical Randomized Controlled Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4164. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124164
Carnevale Pellino V, Gatti A, Vandoni M, Patanè P, Febbi M, Ballarin S, Cavallo C, Marin L. Pneumatic Compression Combined with Standard Treatment after Total Hip Arthroplasty and Its Effects on Edema of the Operated Limb and on Physical Outcomes: A Pilot Clinical Randomized Controlled Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(12):4164. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124164
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarnevale Pellino, Vittoria, Alessandro Gatti, Matteo Vandoni, Pamela Patanè, Massimiliano Febbi, Stefania Ballarin, Caterina Cavallo, and Luca Marin. 2023. "Pneumatic Compression Combined with Standard Treatment after Total Hip Arthroplasty and Its Effects on Edema of the Operated Limb and on Physical Outcomes: A Pilot Clinical Randomized Controlled Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 12: 4164. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124164
APA StyleCarnevale Pellino, V., Gatti, A., Vandoni, M., Patanè, P., Febbi, M., Ballarin, S., Cavallo, C., & Marin, L. (2023). Pneumatic Compression Combined with Standard Treatment after Total Hip Arthroplasty and Its Effects on Edema of the Operated Limb and on Physical Outcomes: A Pilot Clinical Randomized Controlled Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(12), 4164. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124164