Inhibitory Effect of PgAFP and Protective Cultures on Aspergillus parasiticus Growth and Aflatoxins Production on Dry-Fermented Sausage and Cheese
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Microbial Strains
2.2. PgAFP Production and Purification
2.3. PgAFP and Microbial Inocula Preparation
2.4. Mold Growth Inhibition and Mycotoxin Extraction in Culture Media
2.5. Mold Growth Inhibition on Dry-Ripened Foods
2.6. Mycotoxin Extraction
2.7. Mycotoxin Quantification
2.8. Gene Expression Studies
2.8.1. RNA Isolation and Complementary DNA Synthesis
2.8.2. Relative Quantification of Gene Expression by Real Time-Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
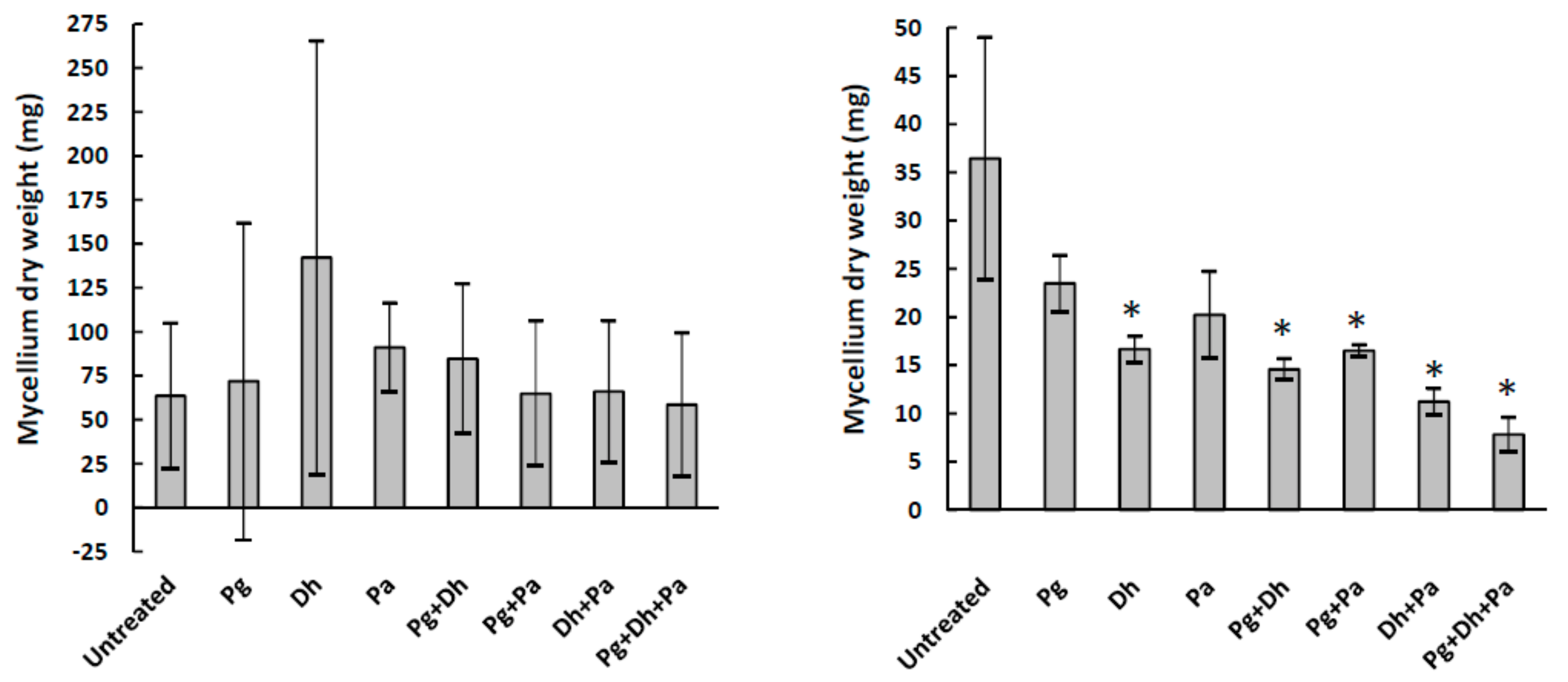
3.1. A. parasiticus Growth Inhibition and Mycotoxin Production in Culture Media
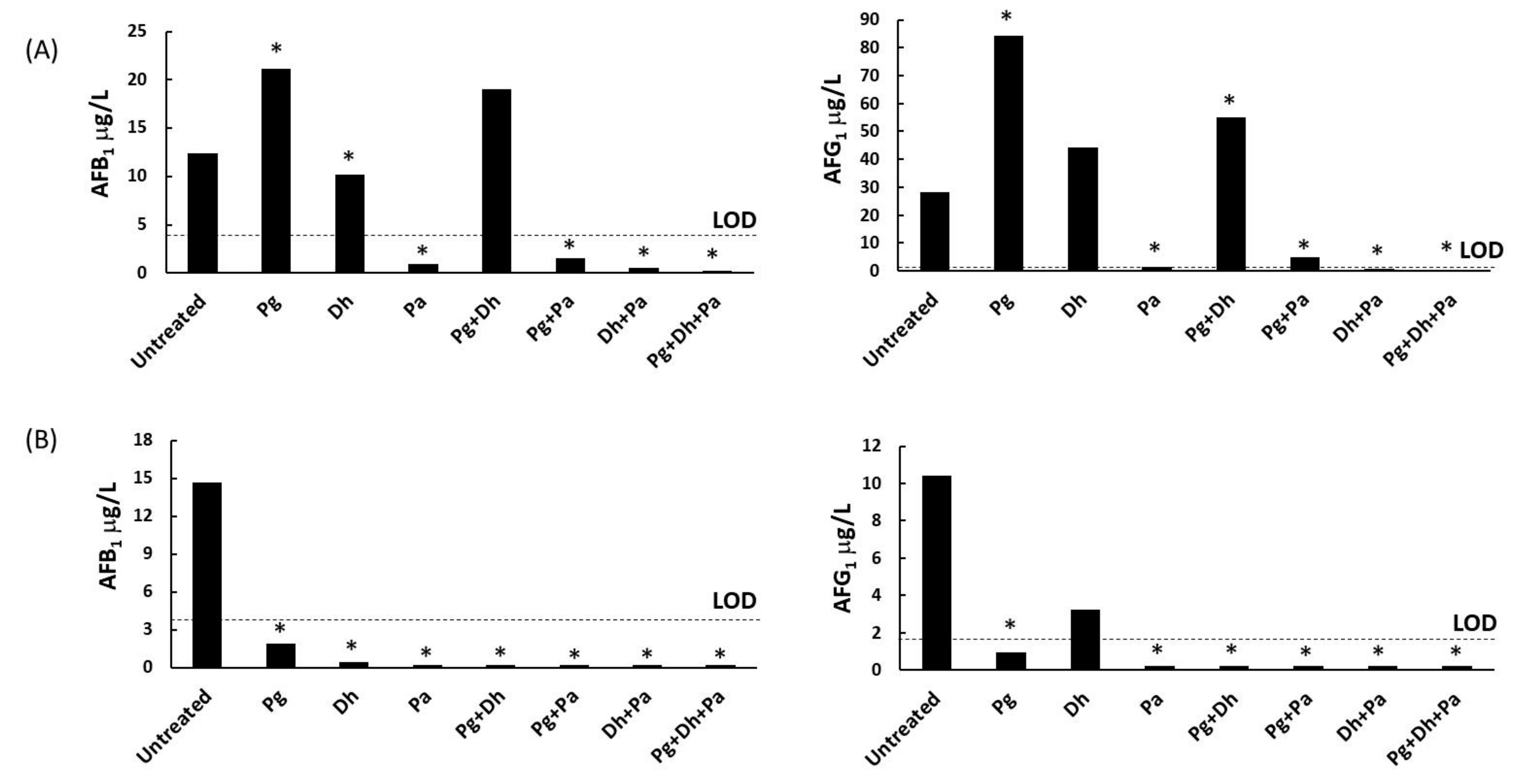
3.2. A parasiticus Growth Inhibition and Mycotoxin Production on Sliced Sausage
3.3. A. parasiticus Growth Inhibition and Mycotoxin Production on Cheese Slices
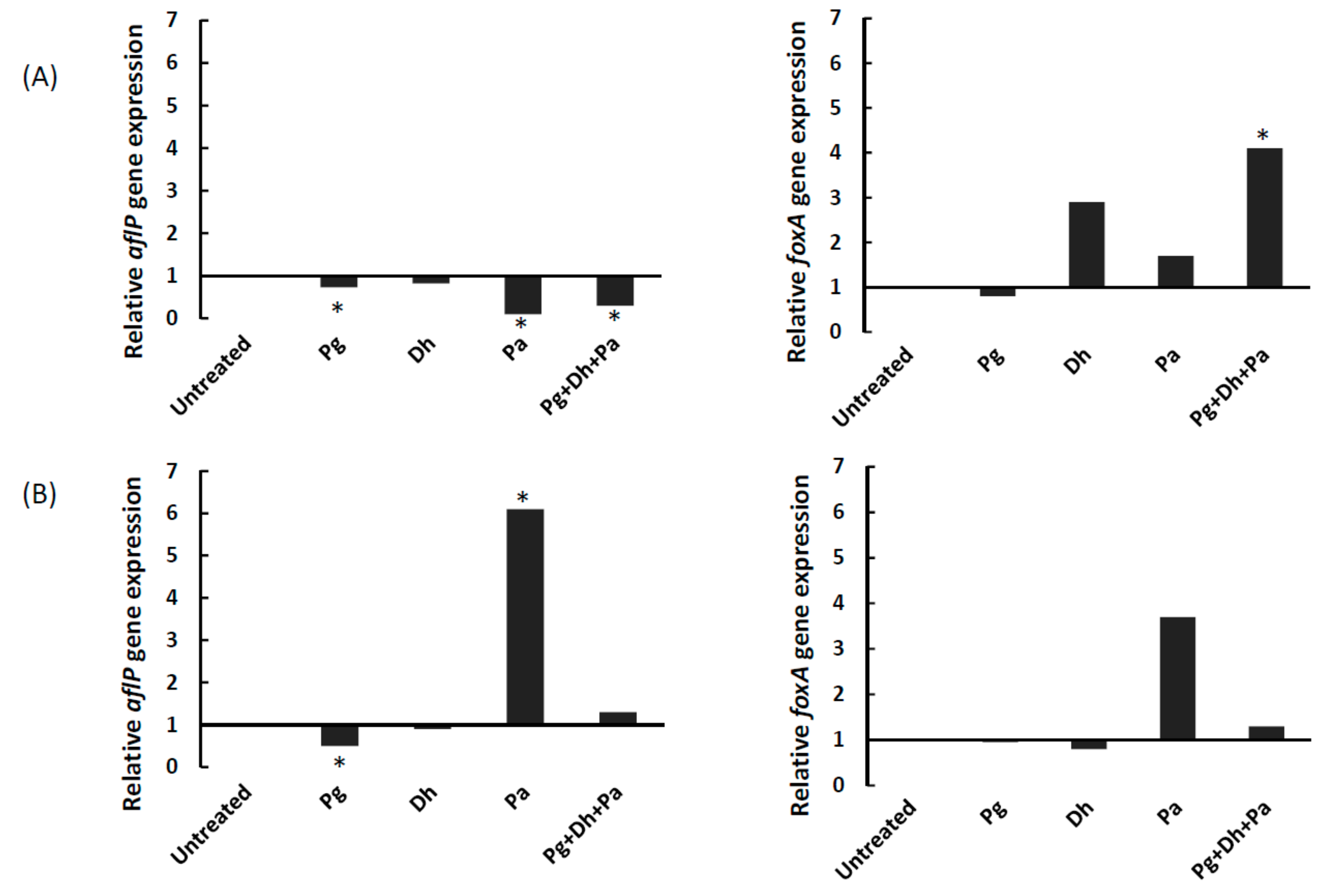
3.4. Gene Expression
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alapont, C.; López-Mendoza, M.C.; Gil, J.V.; Martínez-Culebras, P.V. Mycobiota and toxigenic Penicillium species on two Spanish dry-cured ham manufacturing plants. Food Addit. Contam. A 2014, 31, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, J.L.; Domínguez, L.; Gómez-Lucía, E.; Garayzabal, J.F.F.; Goyache, J.; Suárez, G. Experimental aflatoxin production in Manchego-type cheese. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1988, 64, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hymery, N.; Vasseur, V.; Coton, M.; Mounier, J.; Jany, J.L.; Barbier, G.; Coton, M. Filamentous fungi and mycotoxins in cheese: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. F 2014, 13, 437–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lie, J.L.; Marth, E.H. Formation of aflatoxin in cheddar cheese by Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus. J. Dairy Sci. 1967, 50, 1708–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniwaki, M.H.; Hocking, A.D.; Pitt, J.I.; Fleet, G.H. Growth of fungi and mycotoxin production on cheese under modified atmospheres. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2001, 68, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markov, K.; Pleadin, J.; Bevardi, M.; Vahčić, N.; Sokolić-Mihalak, D.; Frece, J. Natural occurrence of aflatoxin B1, ochratoxin A and citrinin in Croatian fermented meat products. Food Control 2013, 34, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleadin, J.; Malenica, M.; Vah, N.; Milone, S.; Safti, L. Survey of aflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A occurrence in traditional meat products coming from Croatian households and markets. Food Control 2015, 52, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.; Rodríguez, M.; Martín, A.; Delgado, J.; Córdoba, J.J. Presence of ochratoxin A on the surface of dry-cured Iberian ham after initial fungal growth in the drying stage. Meat Sci. 2012, 92, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, A.; Rodríguez, M.; Martín, A.; Núñez, F.; Córdoba, J.J. Evaluation of hazard of aflatoxin B1, ochratoxin A and patulin production in dry-cured ham and early detection of producing moulds by qPCR. Food Control 2012, 27, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, J.; Acosta, R.; Rodríguez-Martín, A.; Bermúdez, E.; Núñez, F.; Asensio, M.A. Growth inhibition and stability of PgAFP from Penicillium chrysogenum against fungi common on dry-ripened meat products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 205, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, F. Small, basic antifungal proteins secreted from filamentous ascomycetes: a comparative study regarding expression, structure, function and potential application. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 65, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tóth, L.; Kele, Z.; Borics, A.; Nagy, L.G.; Váradi, G.; Virágh, M.; Takó, M.; Vágvölgyi, C.; Gallgóczy, L. NFAP2, a novel cysteine-rich anti-yeast protein from Neosartorya fischeri NRRL 181: isolation and characterization. AMB Express 2016, 6, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, A.; Hajdu, D.; Bratschun-Khan, D.; Gáspári, Z.; Varbanov, M.; Philippot, S.; Fizil, A.; Czajlik, A.; Kele, Z.; Sonderegger, C.; et al. New antimicrobial potential and structural properties of PAFB: A cationic, cysteine-rich protein from Penicillium chrysogenum Q176. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tóth, L.; Váradi, G.; Borics, A.; Batta, G.; Kele, Z.; Vendrinszky, A.; Tóth, R.; Ficze, H.; Tóth, G.; Vagvölgy, C.; Marx, F.; Galgóczy, L. Anti-candidal activity and functional mapping of recombinant and synthetic Neosartorya fischeri antifungal protein 2 (NFAP2). Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Martín, A.; Acosta, R.; Liddell, S.; Núñez, F.; Benito, M.J.; Asensio, M.A. Characterization of the novel antifungal protein PgAFP and the encoding gene of Penicillium chrysogenum. Peptides 2010, 31, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, J.; Owens, R.A.; Doyle, S.; Asensio, M.A.; Núñez, F. Impact of the antifungal protein PgAFP from Penicillium chrysogenum on the protein profile in Aspergillus flavus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 8701–8715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Ao, J.; Yang, W.; Jiao, L.; Zheng, T.; Chen, X. Purification and characterization of a novel antifungal protein secreted by Penicillium chrysogenum from an Arctic sediment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 10381–10390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galgóczy, L.; Kovács, L.; Karácsony, Z.; Virágh, M.; Hamari, Z.; Vágvölgyi, C. Investigation of the antimicrobial effect of Neosartorya fischeri antifungal protein (NFAP) after heterologous expression in Aspergillus nidulans. Microbiology 2013, 159, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiserer, L.; Oberparleiter, C.; Weiler-Görz, R.; Burgstaller, W.; Leiter, E.; Marx, F. Characterization of the Penicillium chrysogenum antifungal protein PAF. Arch. Microbiol. 2003, 180, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, J.; Owens, R.A.; Doyle, S.; Núñez, F.; Asensio, M.A. Quantitative proteomics reveals new insights into calcium-mediated resistance mechanisms in Aspergillus flavus against the antifungal protein PgAFP in cheese. Food Microbiol. 2017, 66, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayashree, T.; Subramanyan, C. Oxidative stress as a prerequisite for aflatoxin production by Aspergillus parasiticus. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2000, 29, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverberi, M.; Fabbri, A.A.; Zjalic, S.; Ricelli, A.; Punelli, F.; Fanelli, C. Antioxidant enzymes stimulation in Aspergillus parasiticus by Lentinula edodes inhibits aflatoxin production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 69, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reverberi, M.; Punelli, M.; Smith, C.A.; Zjalic, S.; Scarpari, M.; Scala, V.; Fanelli, C. How peroxisomes affect aflatoxin biosynthesis in Aspergillus flavus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggio-Hall, L.A.; Wilson, R.A.; Keller, N.P. Fundamental contribution of beta-oxidation to polyketide mycotoxin production in planta. Mol. Plant Microbe Int. 2005, 18, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roze, L.V.; Chanda, A.; Laivenieks, M.; Beaudry, R.M.; Artymovich, K.A.; Koptina, A.V.; Linz, J.E. Volatile profiling reveals intracellular metabolic changes in Aspergillus parasiticus: veA regulates branched chain amino acid and ethanol metabolism. BMC Biochem. 2010, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano-Ojalvo, D.; Rodríguez, A.; Bernáldez, V.; Córdoba, J.J.; Rodríguez, M. Influence of temperature and substrate conditions on the omt-1 gene expression of Aspergillus parasiticus in relation to its aflatoxin production. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 166, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Chang, P.; Ehrlich, K.C.; Cary, J.W.; Bhatnagar, D.; Cleveland, T.E.; Payne, G.A.; Linz, J.E.; Woloshuk, C.P.; Bennett, J.W. Clustered pathway genes in aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendonça, R.C.S.; Gouvêa, D.M.; Hungaro, H.M.; Sodré, A. de F.; Querol-Simon, A. Dynamics of the yeast flora in artisanal country style and industrial dry cured sausage (yeast in fermented sausage). Food Control 2013, 29, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, F.; Rodríguez, M.M.; Córdoba, J.J.; Bermúdez, M.E.; Asensio, M.A. Yeast population during ripening of dry-cured Iberian ham. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1996, 29, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, M.J.; Thorsen, L.; Rodríguez, A.; Córdoba, J.J.; Jespersen, L. Inhibition of ochratoxigenic moulds by Debaryomyces hansenii strains for biopreservation of dry-cured meat products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 170, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Núñez, F.; Lara, M.S.; Peromingo, B.; Delgado, J.; Sanchez-Montero, L.; Andrade, M.J. Selection and evaluation of Debaryomyces hansenii isolates as potential bioprotective agents against toxigenic penicillia in dry-fermented sausages. Food Microbiol. 2015, 46, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peromingo, B.; Núñez, F.; Rodríguez, A.; Alía, A.; Andrade, M.J. Potential of yeasts isolated from dry-cured ham to control ochratoxin A production in meat models. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 268, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Lu, J.; Liu, L.; Uluko, H.; Pang, X.; Lv, J. Antifungal activities and effect of Lactobacillus casei AST18 on the mycelia morphology and ultrastructure of Penicillium chrysogenum. Food Control 2014, 43, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effat, B.A.; Ibrahim, G.A.; Tawfik, N.F.; Sharaf, O.M. Comparison of antifungal activity of metabolites from Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Pediococcus acidilactici and Propionibacterium thoenii. Egypt. J. Dairy Sci. 2001, 29, 251–262. [Google Scholar]
- Montiel, R.; Bravo, D.; Medina, M. Commercial biopreservatives combined with salt and sugar to control Listeria monocytogenes during smoked salmon processing. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 1463–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, V.; Sen, S.K.; Mandal, N.C. Production and partial characterisation of an inducer-dependent novel antifungal compound(s) by Pediococcus acidilactici LAB 5. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2013, 93, 2445–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, R.; Rodríguez-Martín, A.; Martín, A.; Núñez, F.; Asensio, M.A. Selection of antifungal protein-producing molds from dry-cured meat products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 135, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Long, G.L.; Winefordner, J.D. Limit of detection, a closer look at the IUPAC definition. Anal. Chem. 1983, 55, 712–724. [Google Scholar]
- Currie, L.A. Nomenclature in evaluation of analytical methods including detection and quantification capabilities. Anal. Chim. Acta 1999, 391, 105–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.; Medina, Á.; Córdoba, J.J.; Magan, N. The influence of salt (NaCl) on ochratoxin A biosynthetic genes, growth and ochratoxin A production by three strains of Penicillium nordicum on a dry-cured ham-based medium. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 178, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, A.; Rodríguez, M.; Luque, M.I.; Martín, A.; Córdoba, J.J. Real-time PCR assays for detection and quantification of aflatoxin-producing molds in foods. Food Microbiol. 2012, 31, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-∆∆CT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Prot. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cizeikiene, D.; Juodeikiene, G.; Paskevicius, A.; Bartkiene, E. Antimicrobial activity of lactic acid bacteria against pathogenic and spoilage microorganism isolated from food and their control in wheat bread. Food Control 2013, 31, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Luo, L.; Long, C. Characterization of competition for nutrients in the biocontrol of Penicillium italicum by Kloeckera apiculata. Biol. Control 2013, 67, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, M.J.; Córdoba, J.J.; Casado, E.M.; Córdoba, M.G.; Rodríguez, M. Effect of selected strains of Debaryomyces hansenii on the volatile compound production of dry fermented sausage “salchichón”. Meat Sci. 2010, 85, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demasi, T.W.; Wardlaw, F.B.; Dick, R.L.; Acton, J.C. Nonprotein nitrogen (NPN) and free amino acid contents of dry, fermented and nonfermented sausages. Meat Sci. 1990, 27, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hierro, E.; de la Hoz, L.; Ordóñez, J.A. Contribution of microbial and meat endogenous enzymes to the lipolysis of dry fermented sausages. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 45, 2989–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalié, D.K.D.; Deschamps, A.M.; Richard-Forget, F. Lactic acid bacteria. Potential for control of mould growth and mycotoxins: A review. Food Control 2010, 21, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Heydt, M.; Stoll, D.; Schütz, P.; Geisen, R. Oxidative stress induces the biosynthesis of citrinin by Penicillium verrucosum at the expense of ochratoxin. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 192, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Yu, J.; Mahoney, N.; Chan, K.L.; Molyneux, R.J.; Varga, J.; Bhatnagar, D.; Thomas, E.; Cleveland, T.E.; Nierman, W.C.; Campbell, B.C. Elucidation of the functional genomics of antioxidant-based inhibition of aflatoxin biosynthesis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 122, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherm, B.; Palomba, M.; Serra, D.; Marcello, A.; Migheli, Q. Detection of transcripts of the aflatoxin genes aflD, aflO, and aflP by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction allows differentiation of aflatoxin-producing and non-producing isolates of Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 98, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roze, L.; Laivenieks, M.; Hong, S.-Y.; Wee, J.; Wong, S.-S.; Vanos, B.; Linz, J. Aflatoxin biosynthesis is a novel source of reactive oxygen species. A potential redox signal to initiate resistance to oxidative stress? Toxins 2015, 7, 1411–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binder, U.; Bencina, M.; Eigentler, A.; Meyer, V.; Marx, F. The Aspergillus giganteus antifungal protein AFPNN5353 activates the cell wall integrity pathway and perturbs calcium homeostasis. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Commission regulation (CE) 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Offic. J. Eur. Union 2006, L364, 5–24. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, J.D. Factors that affect the occurrence of fumonisin. Environ. Health Persp. 2001, 109 (Suppl. 2), 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, G.A.; Hagler, W.M., Jr. Effect of specific amino acids on growth and aflatoxin production by Aspergillus parasiticus and Aspergillus flavus in defined media. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 46, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rüegg, M.; Blanc, B. Influence of water activity on the manufacture and aging of cheese. In Water Activity. Influences on Food Quality; Rockland, L.B., Stewart, G.F., Eds.; Academic Press, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1981; pp. 791–893. [Google Scholar]
- Leistner, L.; Rödel, W.; Krispien, K. Microbiology of meat and meat products in high- and intermediate-moisture ranges. In Water Activity. Influences on Food Quality; Rockland, L.B., Stewart, G.F., Eds.; Academic Press, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1981; pp. 791–893. [Google Scholar]
- Troller, J.A.; Christian, J.H.B. Water Activity and Foods; Academic Press, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Peromingo, B.; Rodríguez, A.; Bernáldez, V.; Delgado, J.; Rodríguez, M. Effect of temperature and water activity on growth and aflatoxin production by Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus on cured meat model systems. Meat Sci. 2016, 122, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedaghat, H.; Eskandari, M.H.; Moosavi-Nasab, M.; Shekarforoush, S.S. Application of non-starter lactic acid bacteria as biopreservative agents to control fungal spoilage of fresh cheese. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 56, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primer Name | Nucleotide Sequences (5′-3′) | Product Size | Position | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-Omt-1 | GGCCGCCGCTTTGATCTAGG | 123 | a 1485 | [42] |
| R-Omt-1 | ACCACGACCGCCGCC | 1593 | ||
| F-foxA | ACCGCAACCCTCTTCACATT | 73 | b 1196 | This study |
| R-foxA | AGACCGTGCAGGATAGGAGT | 1268 | ||
| F-β-tub | TCTTCATGGTTGGCTTCGCT | 98 | c 964s | This study |
| R-β-tub | CTTGGGGTCGAACATCTGCT | 1042 |
| Day 5 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated | Pg + Dh a | Pg + Dh + Pa | |
| Mold counts (log cfu/cm2) | 6.54 ± 0.22 | <3 * | <3 * |
| Yeast counts (log cfu/cm2) | <3.00 | >7.50 * | >7.50 * |
| Lactic acid bacteria (log cfu/cm2) | 4.40 | 3.54 | 7.53 * |
| Aflatoxin B1 (μg/kg) | 86 ± 8 | <LOD b,* | <LOD * |
| Aflatoxin G1 (μg/kg) | 152 ± 9 | <LOD * | <LOD * |
| Day 15 | |||
| Untreated | Pg + Dh | Pg + Dh + Pa | |
| Mold counts (log cfu/cm2) | 7.42 ± 0.09 | 4.26 ± 0.28 * | 4.74 ± 0.38 * |
| Yeast counts (log cfu/cm2) | <3.00 | >7.50 * | 6.05 ± 0.48 * |
| Lactic acid bacteria (log cfu/cm2) | 4.30 | 3.23 | 6.83 * |
| Aflatoxin B1 (μg/kg) | 115 ± 0.43 | <LOD * | <LOD * |
| Aflatoxin G1 (μg/kg) | 170 ± 31 | 8.3 ± 4.5 * | 10 ± 1.3 * |
| Day 5 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated | Pg + Dh a | Pg + Dh + Pa | ||
| Aw | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.89 | |
| Mold count (log cfu/cm2) | 4.12 ± 0.57 | 2.31 ± 0.64 * | 2.39 ± 0.75 * | |
| Yeast count (log cfu/cm2) | <3.00 | >7.50 * | >7.50 * | |
| Lactic acid bacteria (log cfu/cm2) | 2.84 ± 0.35 | 2.49±0.74 | 6.73 ± 0.26 * | |
| Aflatoxin B1 (µg/kg) | <LOD b | <LOD | <LOD | |
| Aflatoxin G1 (µg/kg) | 11 ± 7 | <LOD * | <LOD * | |
| Day 15 | ||||
| Untreated | Pg + Dh | Pg + Dh + Pa | ||
| Aw | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.86 | |
| Mold count (log cfu/cm2) | 4.87 ± 0.21 | <2 * | 2.99 ± 0.67 * | |
| Yeast count (log cfu/cm2) | <3.00 | >7.50 * | >7.50 * | |
| Lactic acid bacteria (log cfu/cm2) | 3.75 | 2.7 | 6.71 * | |
| Aflatoxin B1 (µg/kg) | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
| Aflatoxin G1 (µg/kg) | 29 ± 24 | <LOD | <LOD | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Delgado, J.; Rodríguez, A.; García, A.; Núñez, F.; Asensio, M.A. Inhibitory Effect of PgAFP and Protective Cultures on Aspergillus parasiticus Growth and Aflatoxins Production on Dry-Fermented Sausage and Cheese. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6030069
Delgado J, Rodríguez A, García A, Núñez F, Asensio MA. Inhibitory Effect of PgAFP and Protective Cultures on Aspergillus parasiticus Growth and Aflatoxins Production on Dry-Fermented Sausage and Cheese. Microorganisms. 2018; 6(3):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6030069
Chicago/Turabian StyleDelgado, Josué, Alicia Rodríguez, Alfredo García, Félix Núñez, and Miguel A. Asensio. 2018. "Inhibitory Effect of PgAFP and Protective Cultures on Aspergillus parasiticus Growth and Aflatoxins Production on Dry-Fermented Sausage and Cheese" Microorganisms 6, no. 3: 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6030069
APA StyleDelgado, J., Rodríguez, A., García, A., Núñez, F., & Asensio, M. A. (2018). Inhibitory Effect of PgAFP and Protective Cultures on Aspergillus parasiticus Growth and Aflatoxins Production on Dry-Fermented Sausage and Cheese. Microorganisms, 6(3), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6030069






