Antigenic Determinant of Helicobacter pylori FlaA for Developing Serological Diagnostic Methods in Children
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strain
2.2. Serum Samples of Patients
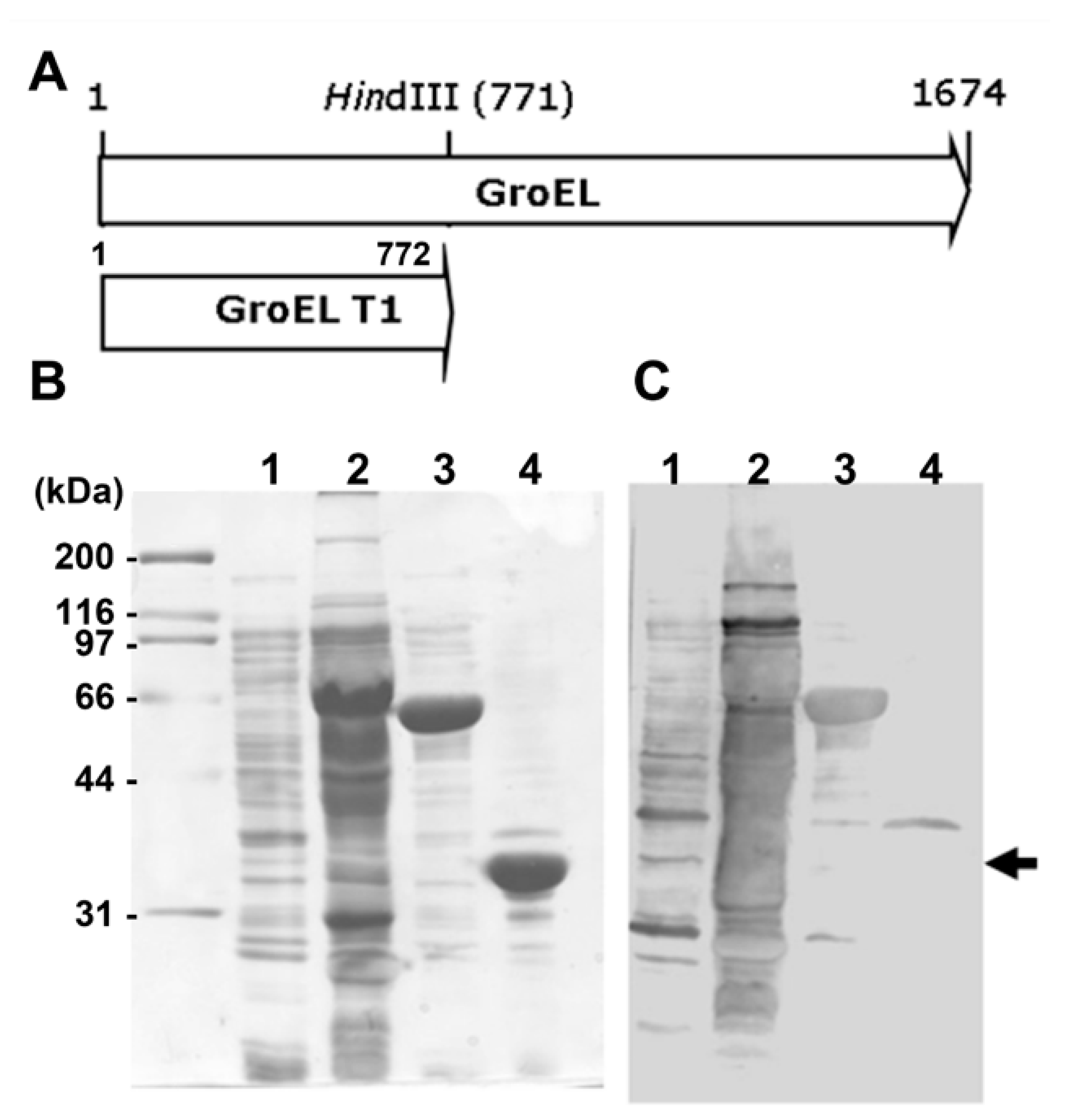
2.3. PCR Amplification of H. pylori FlaA Fragments and Cloning
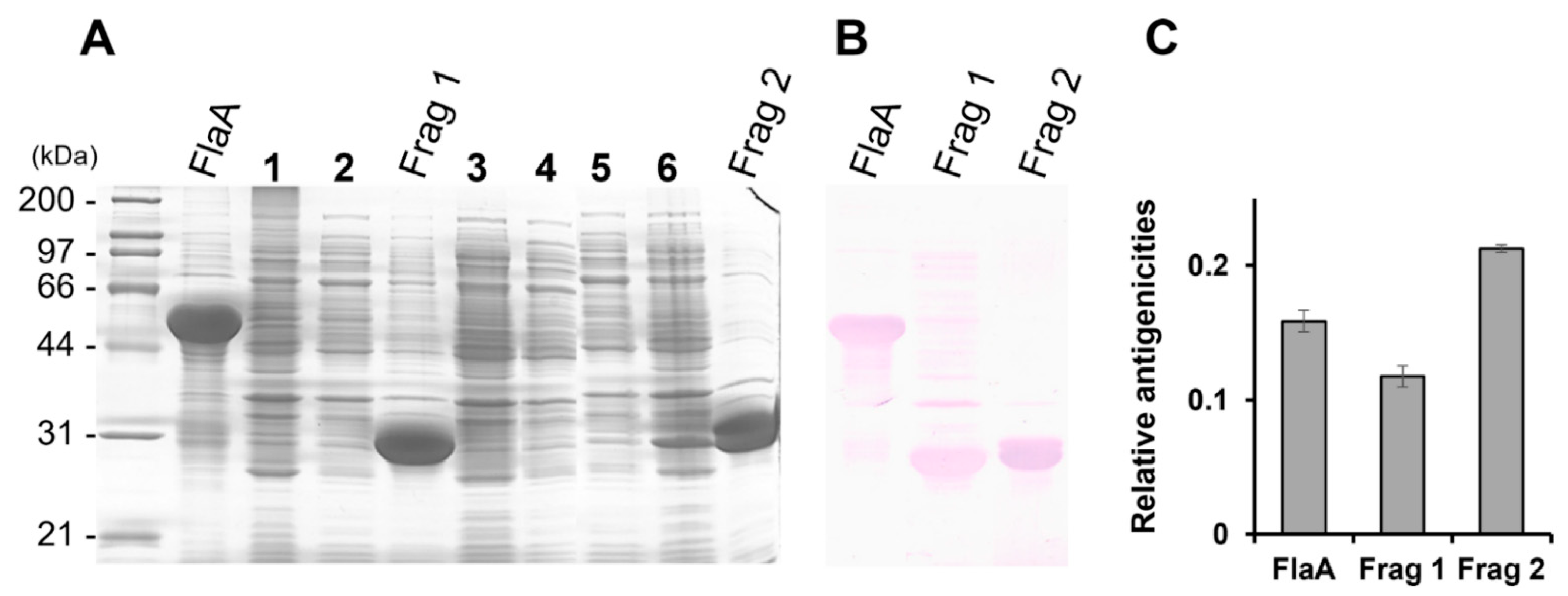
2.4. Expression and Purification of Recombinant Proteins
2.5. Immunoblot Analysis of the Recombinant FlaA Fragments
2.6. Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay Using an Antigenic Determinant of FlaA
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
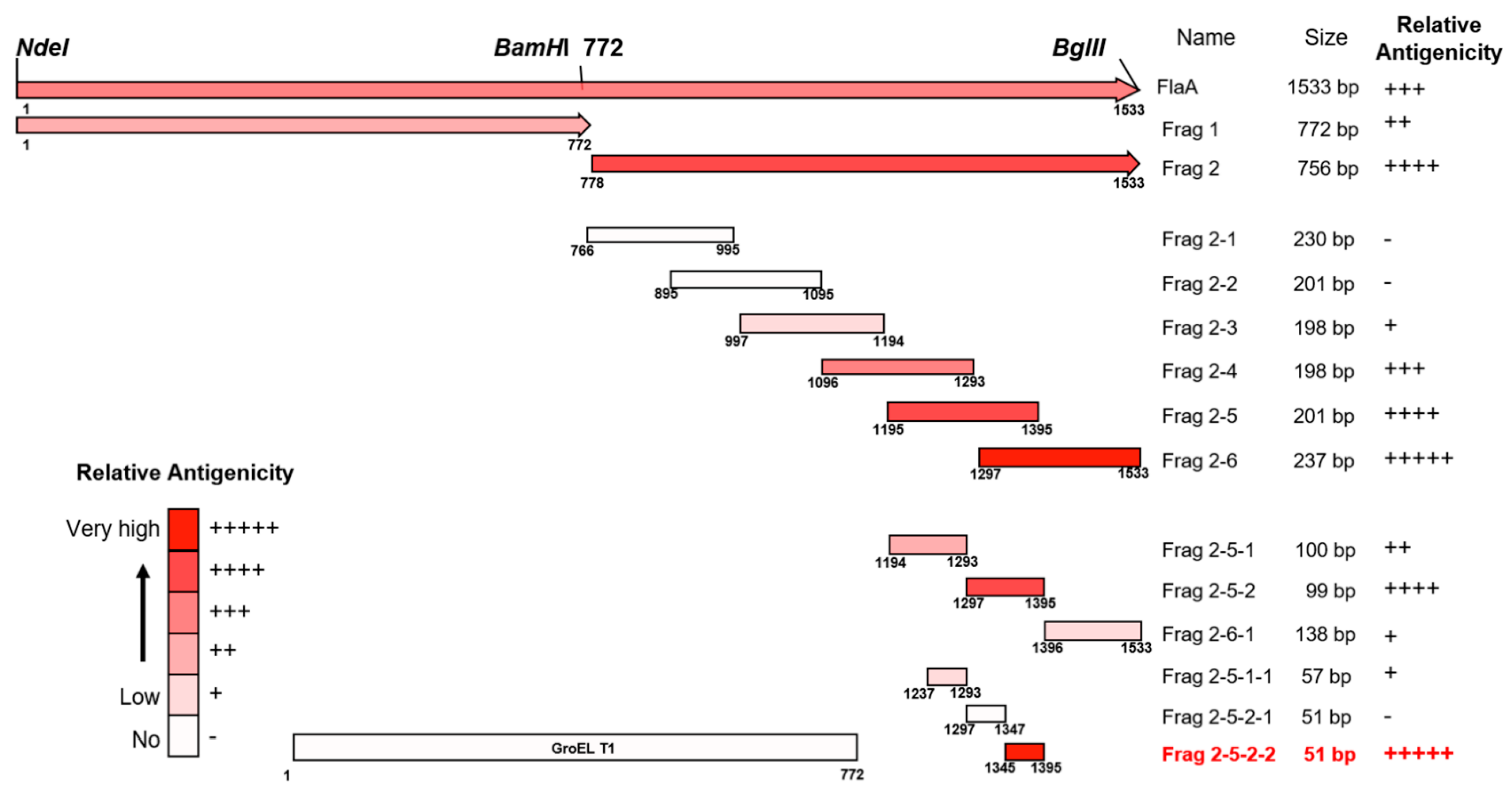
3.1. Antigenic Determination of H. pylori FlaA
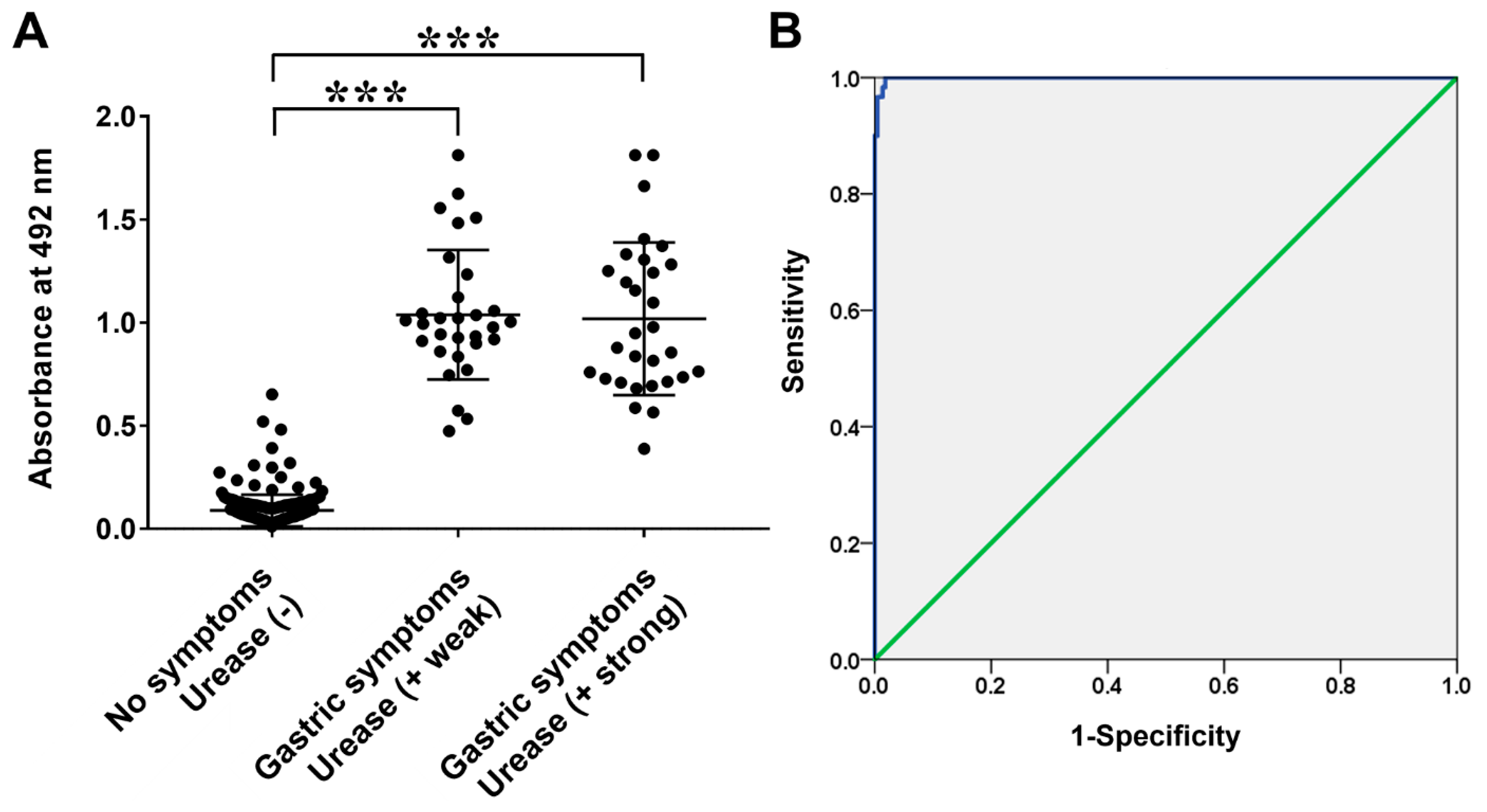
3.2. Analysis of the Reactivity of H. pylori-Infected Pediatric Patients Antibodies to the FlaA Fragment 2–5–2–2
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malaty, H.M. Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2007, 21, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, M.J.; Atherton, J.C. Helicobacter pylori persistence: Biology and disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, Y.; Kido, Y.; Yamaoka, Y. Helicobacter pylori outer membrane protein-related pathogenesis. Toxins 2017, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šterbenc, A.; Jarc, E.; Poljak, M.; Homan, M. Helicobacter pylori virulence genes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 4870–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, Y. Mechanisms of disease: Helicobacter pylori virulence factors. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepat. 2010, 7, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, Y.; Graham, D.Y. Helicobacter pylori virulence and cancer pathogenesis. Future Oncol. 2014, 10, 1487–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axon, A. Helicobacter pylori and public health. Helicobacter 2014, 19, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drumm, B.; Koletzko, S.; Oderda, G. Helicobacter pylori infection in children: A consensus statement. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2000, 30, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, A.; Kim, J.; Park, S. Gastric cancer epidemiology in Korea. J. Gastric Cancer 2011, 11, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, H.S.; Baik, S.C.; Cho, Y.K.; Woo, H.O.; Ahn, Y.O.; Kim, K.; Cho, M.J.; Lee, W.K.; Ko, G.H.; Okada, K. Comparison of Helicobacter pylori infection between Fukuoka, Japan and Chinju, Korea. Helicobacter 1998, 3, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.S.; Kim, K.M.; Oh, Y.L.; Seo, J.K. cagA, vacA, and iceA genotypes of Helicobacter pylori in Korean children. Pediatr. Int. 2008, 50, 628–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homan, M.; Šterbenc, A.; Kocjan, B.J.; Luzar, B.; Zidar, N.; Orel, R.; Poljak, M. Prevalence of the Helicobacter pylori babA2 gene and correlation with the degree of gastritis in infected Slovenian children. Anton. Leeuw. 2014, 106, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalali, B.; Mejías Luque, R.; Javaheri, A.; Gerhard, M. H. pylori virulence factors: Influence on immune system and pathology. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 426309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, B.; Cutler, A.; Israel, N.R.; Perry, M.; Lastovica, A.; Fields, P.I.; Gold, B.D. Use caution with serologic testing for Helicobacter pylori infection in children. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 178, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, N.; Park, R.Y.; Cho, S.I.; Lim, S.H.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, W.; Kang, H.M.; Lee, H.S.; Jung, H.C.; Song, I.S. Helicobacter pylori infection and development of gastric cancer in Korea: Long-term follow-up. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2008, 42, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiota, S.; Suzuki, R.; Yamaoka, Y. The significance of virulence factors in Helicobacter pylori. J. Dig. Dis. 2013, 14, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, C.Y.; Sheu, B.S.; Wu, J.J. Helicobacter pylori infection: An overview of bacterial virulence factors and pathogenesis. Biomed. J. 2016, 39, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alm, R.A.; Trust, T.J. Analysis of the genetic diversity of Helicobacter pylori: The tale of two genomes. J. Mol. Med. 1999, 77, 834–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Ha, J.H.; Shin, J.I.; Kim, K.M.; Choi, J.G.; Park, S.; Park, J.S.; Seo, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Shin, M.K.; et al. Increased Risk of Severe Gastric Symptoms by Virulence Factors vacAs1c, alpA, babA2, and hopZ in Helicobacter pylori Infection. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skene, C.; Young, A.; Every, A.; Sutton, P. Helicobacter pylori flagella: Antigenic profile and protective immunity. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 50, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholi, M.K.; Kalali, B.; Formichella, L.; Göttner, G.; Shamsipour, F.; hassan Zarnani, A.; Hosseini, M.; Busch, D.H.; Shirazi, M.H.; Gerhard, M. Helicobacter pylori FliD protein is a highly sensitive and specific marker for serologic diagnosis of H. pylori infection. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 303, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, S.C.; Youn, H.S.; Chung, M.H.; Lee, W.K.; Cho, M.J.; Ko, G.H.; Park, C.K.; Kasai, H.; Rhee, K.H. Increased oxidative DNA damage in Helicobacter pylori-infected human gastric mucosa. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 1279–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Song, G.Y.; Chang, M.W. Antibiotic susceptibility of Helicobacter pylori and the combination effect of antibiotics on the antibiotic-resistant H. pylori strains. J. Korean Soc. Microbiol. 1999, 34, 543–554. Available online: https://www.koreascience.or.kr/article/JAKO199917153873117.pdf (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Monstein, H.J.; Nikpour Badr, S.; Jonasson, J. Rapid molecular identification and subtyping of Helicobacter pylori by pyrosequencing of the 16S rDNA variable V1 and V3 regions. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 199, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Yeom, J.S.; Lim, J.Y.; Park, C.H.; Woo, H.O.; Baik, S.C.; Lee, W.K.; Cho, M.J.; Rhee, K.H. Correlation between positive rate and number of biopsy samples on urease test in childhood Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2014, 29, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.K.; Jun, J.S.; Kwon, S.W.; Lee, D.H.; Ha, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Kang, H.L.; Baik, S.C.; Park, J.S.; Seo, J.H.; et al. Characterizing antigenic determinants in Helicobacter pylori CagA capable of detecting serum antibodies in children. Pathog. Dis. 2017, 75, ftx103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.K.; Jun, J.S.; Kwon, S.W.; Lee, D.H.; Ha, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Song, D.H.; Jung, M.; Kang, H.L.; Baik, S.C. Characterization of Specific IgA Response to Antigenic Determinants of Helicobacter pylori Urease Encoded by ureA and ureB in Children. J. Bacteriol. Virol. 2018, 48, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Baik, S.C.; Kim, K.M.; Song, S.M.; Kim, D.S.; Jun, J.S.; Lee, S.G.; Song, J.Y.; Park, J.U.; Kang, H.L.; Lee, W.K.; et al. Proteomic analysis of the sarcosine-insoluble outer membrane fraction of Helicobacter pylori strain 26695. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Luo, J.; Li, Y.; Zeng, F.Y.; Li, M. Detection and evaluation of antibodies against neutrophil-activating protein of Helicobacter pylori in patients with gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 2381–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, S.; Kanai, F.; Ogura, K.; Yoshida, H.; Ikenoue, T.; Takahashi, M.; Kawabe, T.; Shiratori, Y.; Omata, M. High seropositivity of anti-CagA antibody in Helicobacter pylori-infected patients irrelevant to peptic ulcers and normal mucosa in Japan. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1997, 42, 1841–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, A.; Kamada, T.; Yokota, K.; Shiotani, A.; Hata, J.; Oguma, K.; Haruma, K. Helicobacter pylori heat shock protein 60 antibodies are associated with gastric cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2009, 205, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Jia, Y.; Yuan, K.; Huang, L.; Nadolny, C.; Dong, X.; Ren, X.; Liu, J. Serum Antibody Against Helicobacter pylori FlaA and Risk of Gastric Cancer. Helicobacter 2014, 19, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fock, K.M.; Ang, T.L. Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric cancer in Asia. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 25, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Woo, C.W.; Lee, Y.M.; Son, B.R.; Kim, J.W.; Chae, H.B.; Youn, S.J.; Park, S.M. Genotyping CagA, VacA subtype, IceA1, and BabA of Helicobacter pylori isolates from Korean patients, and their association with gastroduodenal diseases. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2001, 16, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClain, M.S.; Beckett, A.C.; Cover, T.L. Helicobacter pylori vacuolating toxin and gastric cancer. Toxins 2017, 9, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakoob, J.; Abbas, Z.; Khan, R.; Salim, S.A.; Abrar, A.; Awan, S.; Ahmad, Z. Helicobacter pylori: Correlation of the virulence marker iceA allele with clinical outcome in a high prevalence area. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2015, 72, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, Y.; Kodama, T.; Gutierrez, O.; Kim, J.G.; Kashima, K.; Graham, D.Y. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori iceA, cagA, and vacA status and clinical outcome: Studies in four different countries. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 2274–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Wassenaar, T.M.; Peek, R.M., Jr.; Aras, R.A.; Tschumi, A.I.; van Doorn, L.J.; Kusugami, K.; Blaser, M.J. A Helicobacter pylori restriction endonuclease-replacing gene, hrgA, is associated with gastric cancer in Asian strains. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 2385–2389. [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto, S.; Ojo, O.O.; Arnqvist, A.; Wu, J.Y.; Odenbreit, S.; Haas, R.; Graham, D.Y.; Yamaoka, Y. Helicobacter pylori BabA expression, gastric mucosal injury, and clinical outcome. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 5, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennemann, L.; Brenneke, B.; Andres, S.; Engstrand, L.; Meyer, T.F.; Aebischer, T.; Josenhans, C.; Suerbaum, S. In vivo sequence variation in HopZ, a phase-variable outer membrane protein of Helicobacter pylori. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 4364–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.F.; Maier, R.J. Ammonium metabolism enzymes aid Helicobacter pylori acid resistance. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 196, 3074–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, J.T.; Allen, L.A.H. Role of urease in megasome formation and Helicobacter pylori survival in macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 79, 1214–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akada, J.K.; Shirai, M.; Takeuchi, H.; Tsuda, M.; Nakazawa, T. Identification of the urease operon in Helicobacter pylori and its control by mRNA decay in response to pH. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 36, 1071–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Cruz, M.A.; Ares, M.A.; Von Bargen, K.; Panunzi, L.G.; Martínez-Cruz, J.; Valdez Salazar, H.A.; Jiménez Galicia, C.; Torres, J. Gene expression profiling of transcription factors of Helicobacter pylori under different environmental conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, B.L.; Liu, J. Structural conservation and adaptation of the bacterial flagella motor. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Liang, S.H.; Mao, Y.F.; Li, L.W.; Li, S.P. Construction of expression systems for flaA and flaB genes of Helicobacter pylori and determination of immunoreactivity and antigenicity of recombinant proteins. World J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 9, 2240–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjelm, B. Epitope Mapping of Antibodies towards Human Protein Targets; KTH Royal Institute of Technology: Stockholm, Sweden, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, T.A.; Eweida, A.E.; Sheweita, S.A. B-cell epitope mapping for the design of vaccines and effective diagnostics. Trials Vaccinol. 2016, 5, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allemani, C.; Matsuda, T.; Di Carlo, V.; Harewood, R.; Matz, M.; Nikšić, M.; Bonaventure, A.; Valkov, M.; Johnson, C.J.; Estève, J. Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival 2000–14 (CONCORD-3): Analysis of individual records for 37 513 025 patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based registries in 71 countries. Lancet 2018, 391, 1023–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Miyashiro, I.; Ishikawa, T.; Akazawa, K.; Fukui, K.; Katai, H.; Nunobe, S.; Oda, I.; Isobe, Y.; Tsujitani, S. Determinant factors on differences in survival for gastric cancer between the United States and Japan using nationwide databases. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 31, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Yamaoka, Y. Helicobacter pylori Infection, Its Laboratory Diagnosis, and Antimicrobial Resistance: A Perspective of Clinical Relevance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2022, 35, e00258-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarino, V.; Mela, G.S.; Zentilin, P.; Bisso, G.; Pivari, M.; Mansi, C.; Mele, M.R.; Bilardi, C.; Vigneri, S.; Celle, G. Comparison of isotope ratio mass spectrometry and nondispersive isotope-selective infrared spectroscopy for 13C-urea breath test. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 94, 1203–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Huang, L.L.; Liu, C.; Formichella, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhang, L.; Ma, J.L.; Liu, W.D.; Ulm, K.; et al. Cut-off optimization for 13C-urea breath test in a community-based trial by mathematic, histology and serology approach. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.R.; Seo, J.K. Diagnostic accuracy of the 13C-urea breath test in children: Adjustment of the cut-off value according to age. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 20, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinali, L.d.C.C.; Rocha, G.A.; Rocha, A.M.C.; de Moura, S.B.; de Figueiredo Soares, T.; Esteves, A.M.B.; Nogueira, A.M.M.F.; Cabral, M.M.D.A.; de Carvalho, A.S.T.; Bitencourt, P. Evaluation of [13C] urea breath test and Helicobacter pylori stool antigen test for diagnosis of H. pylori infection in children from a developing country. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 3334–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kato, S.; Ozawa, K.; Okuda, M.; Fujisawa, T.; Kagimoto, S.; Konno, M.; Maisawa, S.; Iinuma, K. Accuracy of the stool antigen test for the diagnosis of childhood Helicobacter pylori infection: A multicenter Japanese study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manes, G.; Balzano, A.; Iaquinto, G.; Ricci, C.; Piccirillo, M.; Giardullo, N.; Todisco, A.; Lioniello, M.; Vaira, D. Accuracy of the stool antigen test in the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection before treatment and in patients on omeprazole therapy. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 15, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oderda, G.; Rapa, A.; Ronchi, B.; Lerro, P.; Pastore, M.; Staiano, A.; De’Angelis, G.; Strisciuglio, P. Detection of Helicobacter pylori in stool specimens by non-invasive antigen enzyme immunoassay in children: Multicentre Italian study. BMJ 2000, 320, 347–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Garza González, E.; Perez Perez, G.I.; Maldonado Garza, H.J.; Bosques Padilla, F.J. A review of Helicobacter pylori diagnosis, treatment, and methods to detect eradication. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisbert, J.; Hermida, C.; Cabrera, M.; Pajares, J. Antibodies against Helicobacter pylori in saliva. Study of their validity versus breath test and its agreement with serology. Aten. Primaria 2000, 25, 390–394. [Google Scholar]
- Herbrink, P.; Van Doorn, L. Serological methods for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection and monitoring of eradication therapy. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2000, 19, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urita, Y.; Hike, K.; Torii, N.; Kikuchi, Y.; Kurakata, H.; Kanda, E.; Sasajima, M.; Miki, K. Comparison of serum IgA and IgG antibodies for detecting Helicobacter pylori infection. Intern. Med. 2004, 43, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Patel, S.K.; Pratap, C.B.; Jain, A.K.; Gulati, A.K.; Nath, G. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori: What should be the gold standard? World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 12847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darma, A.; Nugroho, B.S.T.; Yoanna, V.; Sulistyani, I.; Athiyyah, A.F.; Ranuh, R.G.; Sudarmo, S.M. Comparison of Helicobacter pylori stool antigen, salivary IgG, serum IgG, and serum IgM as diagnostic markers of H. pylori infection in children. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2019, 11, 206. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6711868/ (accessed on 8 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.S.; Jun, J.K.; Park, E.C.; Park, S.; Jung, K.W.; Han, M.A.; Choi, I.J.; Lee, H.Y. Performance of different gastric cancer screening methods in Korea: A population-based study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Primer | Sequences (5′–3′) | Position (bp) | Length (aa) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FlaA (full) | F | gagttacacatATGGCTTTTCGGGTCAAT | 1–1533 | 510 |
| R | cccgggagatCTAAGTTAAAAGCCTTAAGATATTTTGTTG | |||
| Frag 1 | Digestion of pET15b/flaA vector with BamHI and BglII and ligation | 257 | ||
| Frag 2 | F | atgggatccatatgGGTAATATCGCAGATATTAAGAAAAA | 778–1533 | 251 |
| R | cccgggagatCTAAGTTAAAAGCCTTAAGATATTTTGTTG | |||
| Frag 2–1 | F | cccccgaattcGGGATCCATTTGGGTAAT | 766–995 | 76 |
| R | cccccctcgagTTTGTTAAATCCTGACCG | |||
| Frag 2–2 | F | ggcgcggatccTTGCGCAGTATAGATGGT | 895–1095 | 67 |
| R | cccaaactcgagCGCTGTGAAACCTAAATG | |||
| Frag 2–3 | F | cccccgaattcGGCTCTACAAACTACGGA | 997–1194 | 66 |
| R | acagcgctcgaGTTCGCGCCACTGGCTGA | |||
| Frag 2–4 | F | cccccgaattcATTGGTTTTGGGGAATCT | 1096–1293 | 66 |
| R | atccaactcgagCATCGCAGACTCGGCAAT | |||
| Frag 2–5 | F | gtggcgaattcTATAACGCTGTCATCGC | 1195–1395 | 67 |
| R | tttgagctcgAGCCGCTTTAACATTCAC | |||
| Frag 2–6 | F | ctgcggaattcATGTTGGATAAAGTCCGC | 1297–1533 | 78 |
| R | cccccctcgagCTAAGTTAAAAGCCTTAA | |||
| Frag 2–5–1 | F | gtggcgaattCTATAACGCTGTCATCGC | 1194–1293 | 33 |
| R | atccaactcgagCATCGCAGACTCGGCAAT | |||
| Frag 2–5–2 | F | ctgcggaattcATGTTGGATAAAGTCCGC | 1297–1395 | 33 |
| R | tttgagctcgAGCCGCTTTAACATTCAC | |||
| Frag 2–6–1 | F | gggcccgaattcGAATCTCAAATTAGG | 1396–1533 | 45 |
| R | cccccctcgagCTAAGTTAAAAGCCTTAA | |||
| Frag 2–5–1–1 | F | gggcccgaattcGGGGTTACAACCTTA | 1237–1293 | 19 |
| R | atccaactcgagCATCGCAGACTCGGCAAT | |||
| Frag 2–5–2–1 | F | ctgcggaattcATGTTGGATAAAGTCCGC | 1297–1347 | 17 |
| R | gggcccctcgagAATCATTTGATTTTG | |||
| Frag 2–5–2–2 | F | gggcccgaattcATTAGCACCGTGAAT | 1345–1395 | 17 |
| R | tttgagctcgAGCCGCTTTAACATTCAC |
| Frag No. | 2–1 | 2–2 | 2–3 | 2–4 | 2–5 | 2–6 | 2–5-1 | 2–5-2 | 2–6-1 | 2–5-1–1 | 2–5-2–1 | 2–5-2–2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative antigenicity | 0.051 ± 0.04 | 0.001 ± 0.05 | 0.077 ± 0.06 | 0.123 ± 0.08 | 0.210 ± 0.06 | 0.268 ± 0.03 | 0.102 ± 0.05 | 0.210 ± 0.05 | 0.070 ± 0.06 | 0.066 ± 0.06 | 0.017 ± 0.06 | 0.267 ± 0.08 |
| Grade | - | - | + | +++ | ++++ | +++++ | ++ | ++++ | + | + | - | +++++ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, H.-E.; Park, S.; Nizamutdinov, D.; Seo, J.-H.; Park, J.-S.; Jun, J.-S.; Shin, J.-I.; Boonyanugomol, W.; Park, J.-S.; Shin, M.-K.; et al. Antigenic Determinant of Helicobacter pylori FlaA for Developing Serological Diagnostic Methods in Children. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11121544
Park H-E, Park S, Nizamutdinov D, Seo J-H, Park J-S, Jun J-S, Shin J-I, Boonyanugomol W, Park J-S, Shin M-K, et al. Antigenic Determinant of Helicobacter pylori FlaA for Developing Serological Diagnostic Methods in Children. Pathogens. 2022; 11(12):1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11121544
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Hyun-Eui, Seorin Park, Damir Nizamutdinov, Ji-Hyeun Seo, Ji-Shook Park, Jin-Su Jun, Jeong-Ih Shin, Wongwarut Boonyanugomol, Jin-Sik Park, Min-Kyoung Shin, and et al. 2022. "Antigenic Determinant of Helicobacter pylori FlaA for Developing Serological Diagnostic Methods in Children" Pathogens 11, no. 12: 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11121544
APA StylePark, H.-E., Park, S., Nizamutdinov, D., Seo, J.-H., Park, J.-S., Jun, J.-S., Shin, J.-I., Boonyanugomol, W., Park, J.-S., Shin, M.-K., Baik, S.-C., Youn, H.-S., Cho, M.-J., Kang, H.-L., Lee, W.-K., & Jung, M. (2022). Antigenic Determinant of Helicobacter pylori FlaA for Developing Serological Diagnostic Methods in Children. Pathogens, 11(12), 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11121544






