Dynamics of Bacterioplankton Communities during Wet and Dry Seasons in the Danjiangkou Reservoir in Hubei, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. Physicochemical Parameters
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Illumina NovaSeq Sequencing
2.4. Data Analyses
3. Results
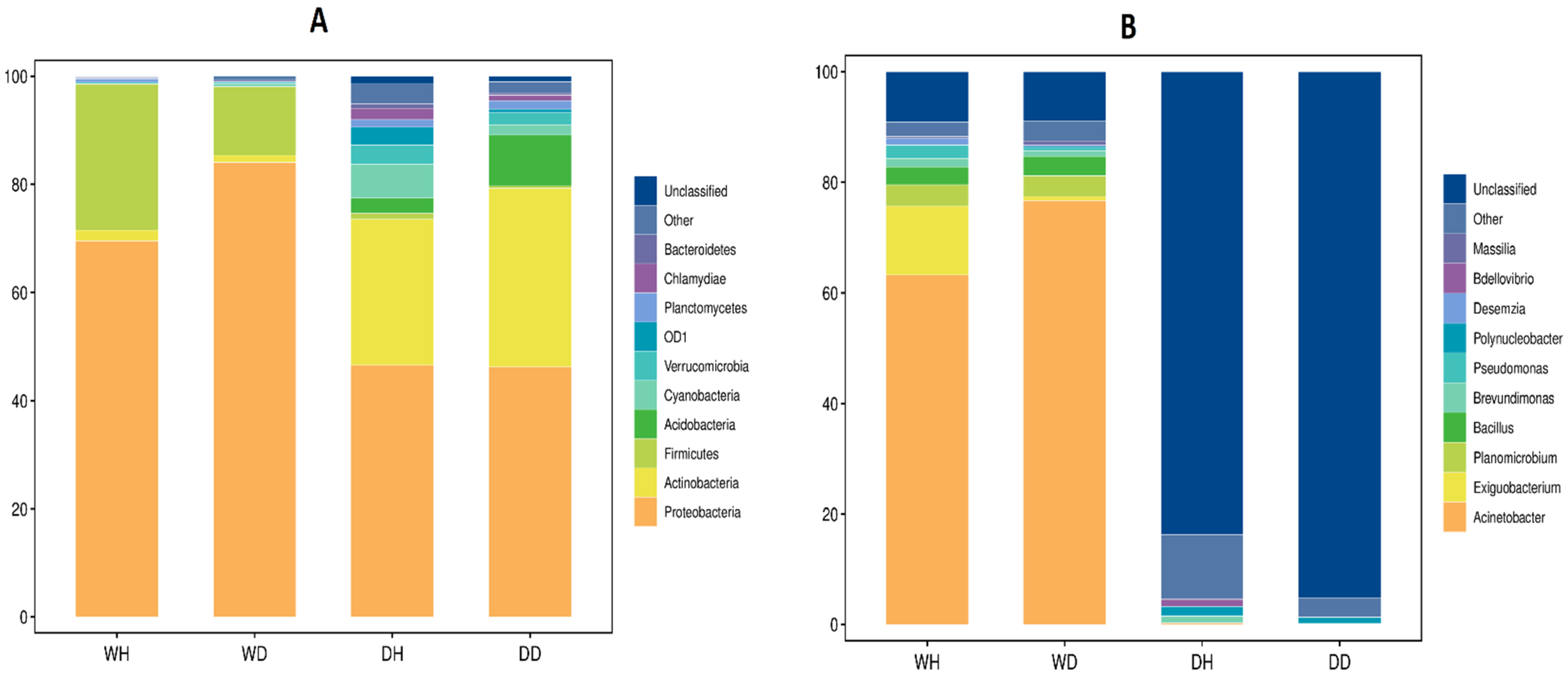
3.1. High-Throughput Sequencing Data Annotation Results
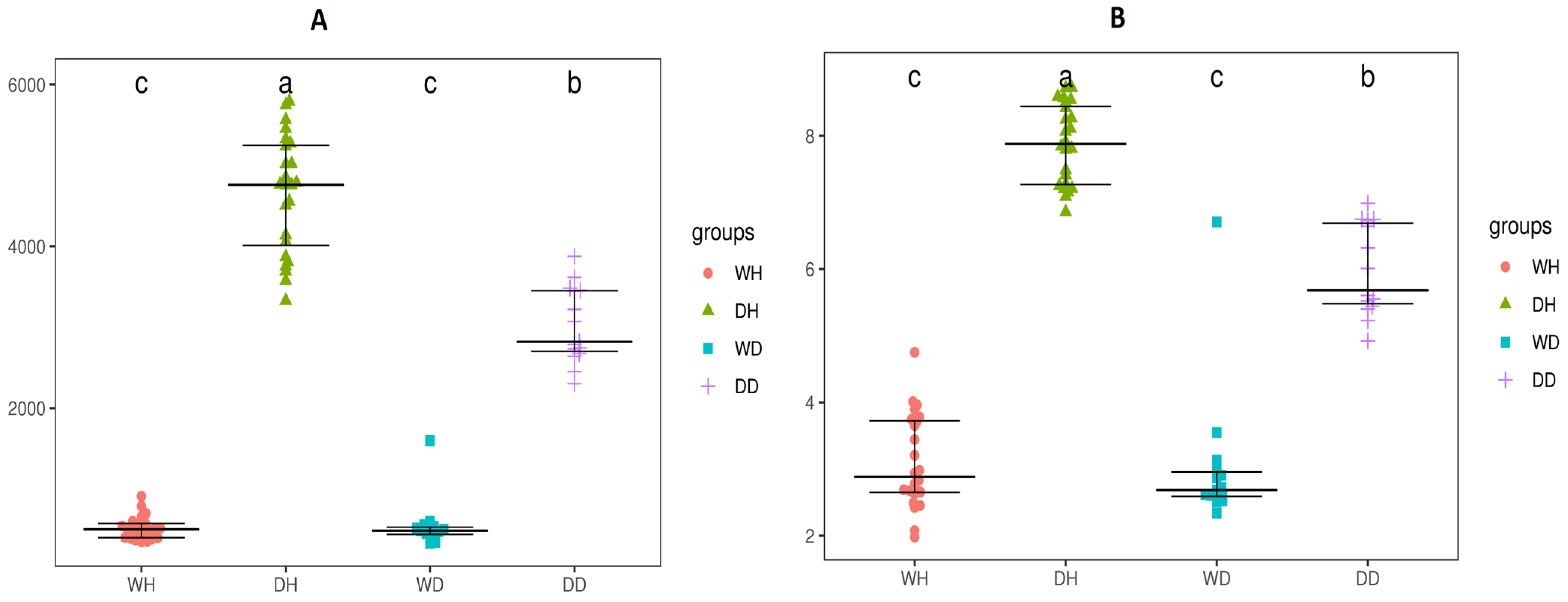
3.2. Alpha Diversity
3.3. Differential Bacterial Communities
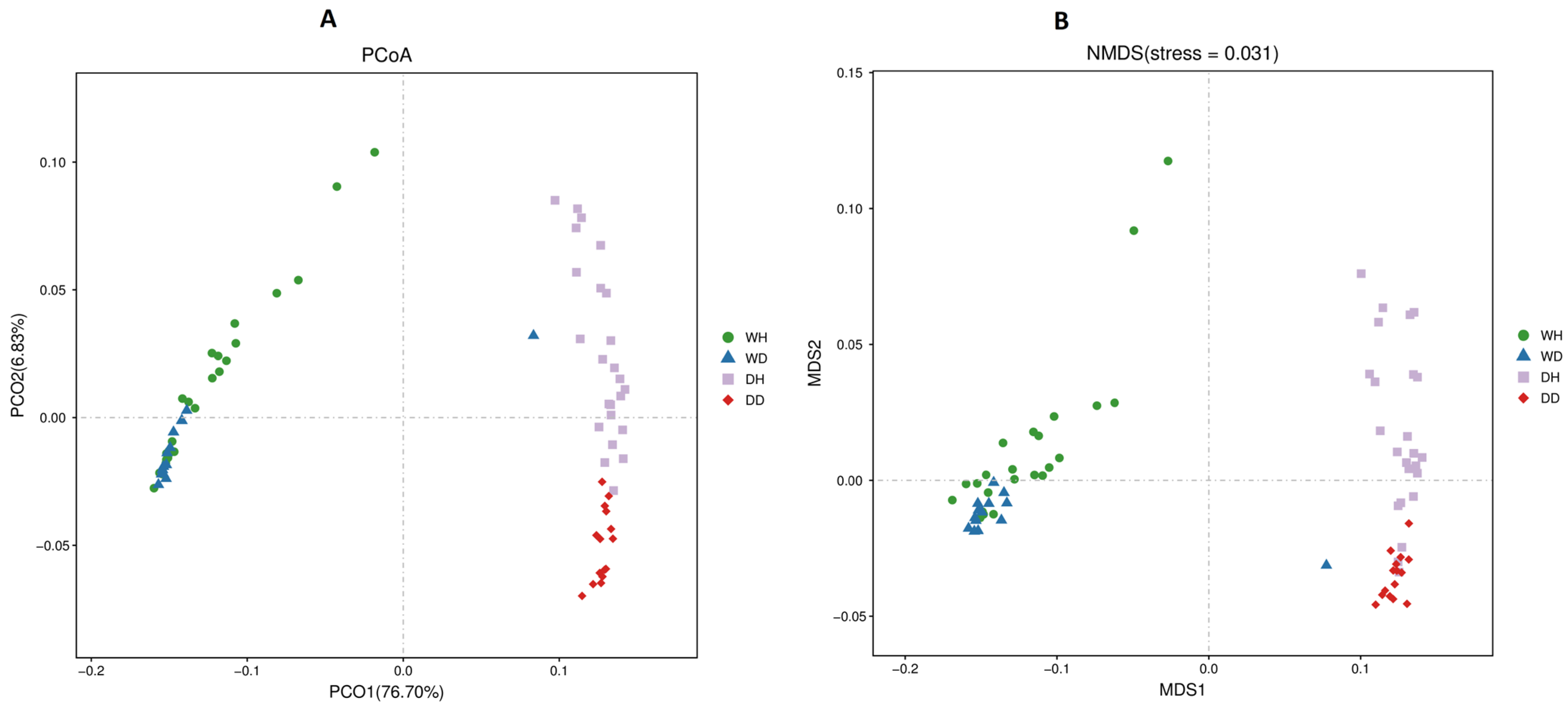
3.4. Beta Diversity Analysis
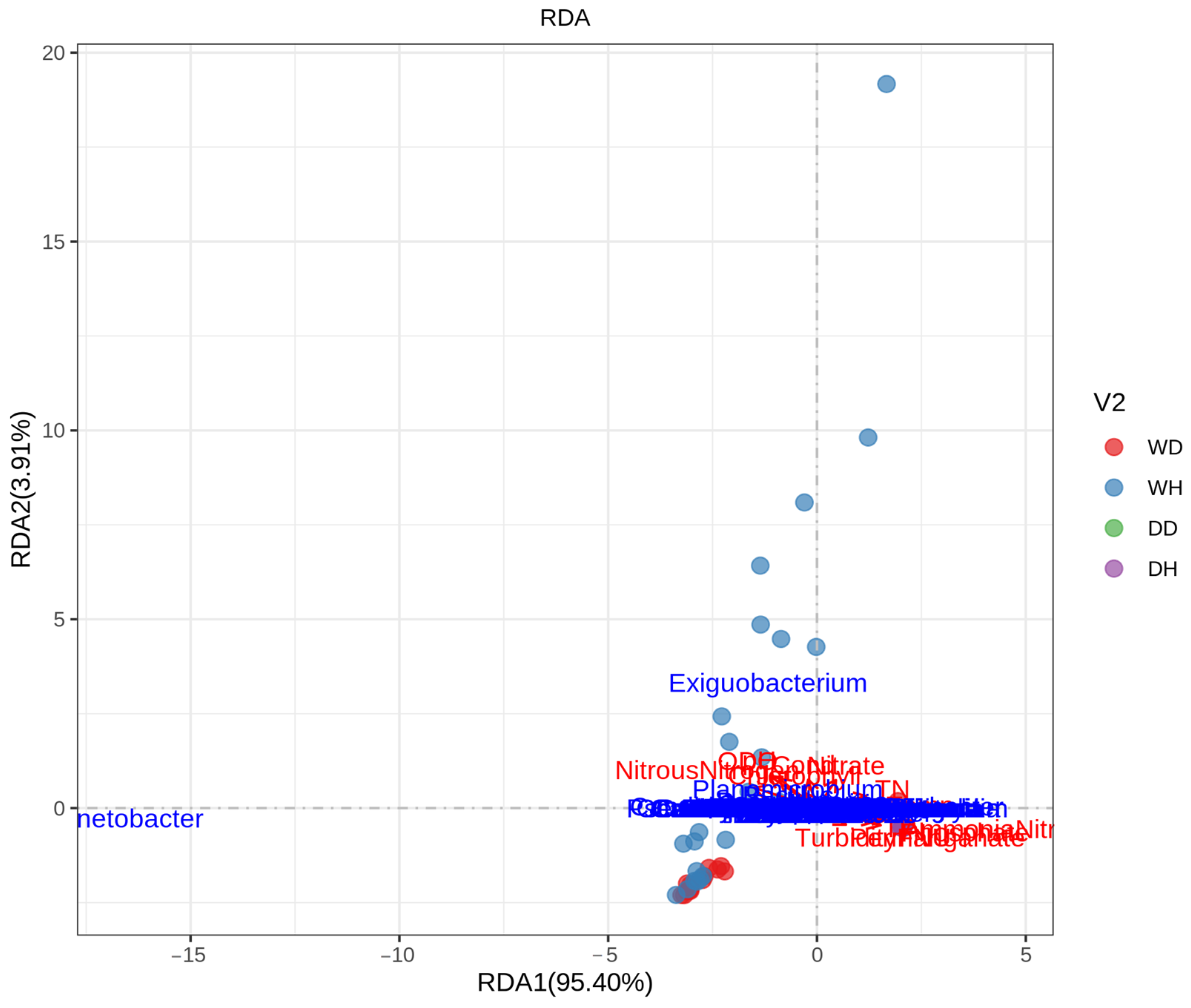
3.5. Correlation Analysis between Bacterial Communities and Environmental Parameters
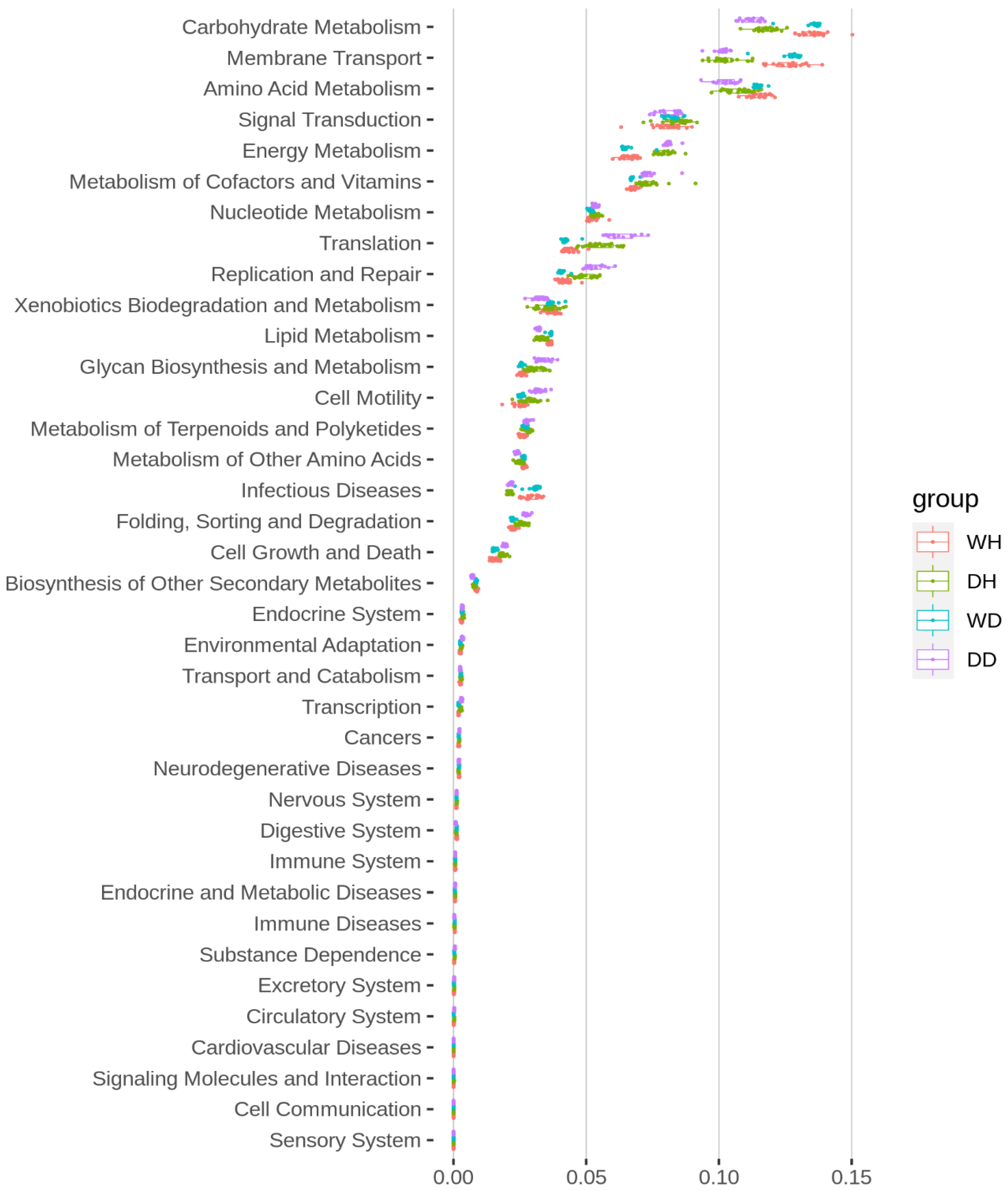
3.6. Bacterioplankton Functional Prediction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, P.; Li, Z.; Zhang, R.; Pan, J.; Liu, Y. Does water diversion project deteriorate the water quality of reservoir and downstream? A case-study in Danjiangkou reservoir. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 24, e01235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Li, K.; Finlayson, B.; Yin, W. Evaluation, prediction, and protection of water quality in Danjiangkou Reservoir, China. Water Sci. Eng. 2015, 8, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Cheng, X.; Xu, Z.; Han, H.; Zhang, Q. Spatial and temporal patterns of the water quality in the Danjiangkou Reservoir, China. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2009, 54, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, M.; Crow-Miller, B.; Rogers, S. The South–North water transfer project: Remaking the geography of China. Reg. Stud. 2017, 51, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, X. Dynamic change in the water-level fluctuation zone of the Danjiangkou reservoir and its influence on water quality. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W. Response of soil physico-chemical properties to restoration approaches and submergence in the water level fluctuation zone of the Danjiangkou Reservoir, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 145, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q. The South-to-North Water Transfer Project of China: Environmental Implications and Monitoring Strategy 1. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2009, 45, 1238–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.C.; Li, X.-Y.; Ma, Y.-J.; Smith, A.T.; Wu, J. A review of the economic, social, and environmental impacts of China’s South–North Water Transfer Project: A sustainability perspective. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Guo, S.; Li, Y.; Yin, W.; Qi, P.; Shi, J.; Hu, L.; Li, B.; Bi, S.; Zhu, J. Effects of water level increase on phytoplankton assemblages in a drinking water reservoir. Water 2018, 10, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Lv, H.; Yu, X.; Wilkinson, D.M.; Yang, J. Phytoplankton communities exhibit a stronger response to environmental changes than bacterioplankton in three subtropical reservoirs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10850–10858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, T.K.; Rawtani, D.; Agrawal, Y.K. Bioindicators: The natural indicator of environmental pollution. Front. Life Sci. 2016, 9, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, M.; Behera, P.; Kim, J.Y.; Rastogi, G. Seasonal and spatial dynamics of bacterioplankton communities in a brackish water coastal lagoon. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 134729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunse, C.; Pinhassi, J. Marine bacterioplankton seasonal succession dynamics. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Ju, F.; Hou, L.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Mulla, S.I.; Sun, Q.; Bürgmann, H.; Yu, C. Strong impact of anthropogenic contamination on the co-occurrence patterns of a riverine microbial community. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 4993–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Pan, Y.; Zhu, J.; Guo, S.; Hu, L.; Huang, J. Bioassessment of a drinking water reservoir using plankton: High throughput sequencing vs. traditional morphological method. Water 2018, 10, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, K.; Lahti, L.; Gonze, D.; De Vos, W.M.; Raes, J. Metagenomics meets time series analysis: Unraveling microbial community dynamics. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2015, 25, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stec, K.F.; Caputi, L.; Buttigieg, P.L.; D’Alelio, D.; Ibarbalz, F.M.; Sullivan, M.B.; Chaffron, S.; Bowler, C.; d’Alcala, M.R.; Iudicone, D. Modelling plankton ecosystems in the meta-omics era. Are we ready? Mar. Genom. 2017, 32, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.-J.; Xu, G.; Ding, C.-Y.; Zheng, B.-H.; Chen, Y.; Han, H.; Li, Y.-Y.; Shi, J.-W.; Hu, L.-Q. Illumina MiSeq sequencing and network analysis the distribution and co-occurrence of bacterioplankton in Danjiangkou Reservoir, China. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 859–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-J.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Li, Y.-Y.; Lin, L.-A.; Zheng, B.-H.; Ji, M.-F.; Li, B.L.; Han, X.-M. The Seasonal Patterns, Ecological Function and Assembly Processes of Bacterioplankton Communities in the Danjiangkou Reservoir, China. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 13, 884765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Q. Dissolved trace elements and heavy metals in the Danjiangkou Reservoir, China. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Xia, J.; Gippel, C.J.; Wang, R.; Zeng, S. Implications of modelled climate and land cover changes on runoff in the middle route of the south to north water transfer project in China. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 2563–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debroas, D.; Domaizon, I.; Humbert, J.-F.; Jardillier, L.; Lepère, C.; Oudart, A.; Taïb, N. Overview of freshwater microbial eukaryotes diversity: A first analysis of publicly available metabarcoding data. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fix023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žifčáková, L.; Větrovský, T.; Howe, A.; Baldrian, P. Microbial activity in forest soil reflects the changes in ecosystem properties between summer and winter. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, B.A.; Kwon, D.S. Efficient nucleic acid extraction and 16S rRNA gene sequencing for bacterial community characterization. JoVE J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 110, e53939. [Google Scholar]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y. China’s water security: Current status, emerging challenges and future prospects. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 106–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Jia, C.; Liu, Q.; Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Yang, M.; Zhao, M.; Li, W.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Q. Dynamics of bacterial community diversity and structure in the terminal reservoir of the south-to-north water diversion project in China. Water 2018, 10, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Lai, Z.; Wang, C.; Ni, J.; Gao, Y. Seasonal variation significantly affected bacterioplankton and eukaryoplankton community composition in Xijiang River, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Li, S.; Hou, K.; Ji, G. Spatial and seasonal bacterioplankton community dynamics in the main channel of the Middle Route of South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Res. Microbiol. 2019, 170, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, C.; Liu, W.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, M.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Q.; Ni, J. Dominant role of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in nitrification due to ammonia accumulation in sediments of Danjiangkou reservoir, China. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 3399–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Pan, B.; He, H.; Zhao, G.; Jiang, X.; Han, X.; Wang, H. Characterization of the bacterioplankton community and the influencing factors in the upper reaches of the Han River basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 61748–61759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milan, M.; Carraro, L.; Fariselli, P.; Martino, M.E.; Cavalieri, D.; Vitali, F.; Boffo, L.; Patarnello, T.; Bargelloni, L.; Cardazzo, B. Microbiota and environmental stress: How pollution affects microbial communities in Manila clams. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 194, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, C.; Wang, J.; He, Y.; Yang, S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, T.; Fu, J.; Chen, Q.; Ni, J. Rare biosphere regulates the planktonic and sedimentary bacteria by disparate ecological processes in a large source water reservoir. Water Res. 2022, 216, 118296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Bao, S.; Zhu, X.; Huang, X. Spatio-temporal variations of the bacterioplankton community composition in Chaohu Lake, China. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2008, 18, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, M. Spatial gradient and seasonal variation of trophic status in a large water supply reservoir for the South-to-North Water Diversion Project, China. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2015, 30, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Song, C.; Meng, S.; Qiu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, W.; Qu, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, C.; Hu, G. Spatial distribution of planktonic bacterial and archaeal communities in the upper section of the tidal reach in Yangtze River. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Z.; Wang, K.; Li, X.; Zhu, M.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J. Microbial characterization of aggregates within a one-stage nitritation–anammox system using high-throughput amplicon sequencing. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Ng, C.; Nshimyimana, J.P.; Loh, L.L.; Gin, K.Y.-H.; Thompson, J.R. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) for assessment of microbial water quality: Current progress, challenges, and future opportunities. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaki, H.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Hanada, S.; Nakamura, K.; Nomura, N.; Matsumura, M.; Kamagata, Y. Comparative analysis of bacterial diversity in freshwater sediment of a shallow eutrophic lake by molecular and improved cultivation-based techniques. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 2162–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Sun, C.; Liang, P. A Bayesian method for comprehensive water quality evaluation of the Danjiangkou Reservoir water source area, for the middle route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project in China. Front. Earth Sci. 2014, 8, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Qiao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, X.-H. Bacterial and archaeal communities in sediments of the north Chinese marginal seas. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 70, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.L.; Biggerstaff, J.; Eichhorn, A.; Ewing, E.; Shahan, R.; Soriano, D.; Stewart, S.; VanMol, K.; Walker, R.; Walters, P. Genomic characterization of three novel Desulfobacterota classes expand the metabolic and phylogenetic diversity of the phylum. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 4326–4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Su, C.; Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Liang, C.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Minggagud, H.; Feng, G.; Ma, W. Modern climate and soil properties explain functional structure better than phylogenetic structure of plant communities in Northern China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 531947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, H.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, X.; Ren, L.; Liu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Lv, L.; Che, Q. Screening of ecological impact assessment indicators in urban water body restoration process itle. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Bi, Y.; Deng, Y.; He, Z.; Wu, L.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Shi, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Hu, Z. Impacts of the Three Gorges Dam on microbial structure and potential function. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xie, P.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Q.; Fan, H.; Shen, H. Decrease of NH4+-N by bacterioplankton accelerated the removal of cyanobacterial blooms in aerated aquatic ecosystem. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 2223–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, T.; Liu, Y.; Fang, K.; Zhang, C. Microbial aerobic denitrification dominates nitrogen losses from reservoir ecosystem in the spring of Zhoucun reservoir. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 998–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.-X.; Liu, X.-G.; Lu, M.; Zhou, R.-F.; Sun, Z.-Y.; Xiao, S.-W. Characteristics of Bacterial Community in Pelteobagrus fulvidraco Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture System. Water 2022, 14, 3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beller, H.R.; Han, R.; Karaoz, U.; Lim, H.; Brodie, E.L. Genomic and physiological characterization of the chromate-reducing, aquifer-derived firmicute Pelosinus sp. strain HCF1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, P.; Niu, L.; Du, J.; Gao, Y. Bacterial community composition and function shift with the aggravation of water quality in a heavily polluted river. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 237, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, I.; Calisto, R.; Serra, C.R.; Lage, O.M.; Antunes, S.C. Bacterioplankton community as a biological element for reservoirs water quality assessment. Water 2021, 13, 2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Dai, T.; Tang, Y.; Tao, Y.; Huang, B.; Mu, Q.; Wen, D. Sediment bacterial community structures and their predicted functions implied the impacts from natural processes and anthropogenic activities in coastal area. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.L.; Hahn, M.W. Differences in structure and dynamics of Polynucleobacter communities in a temperate and a subtropical lake, revealed at three phylogenetic levels. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2006, 57, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, F.A.C.; Catão, E.C.P.; Santana, R.H.; de Souza Cabral, A.; Paranhos, R.; Rangel, T.P.; de Rezende, C.E.; Edwards, R.A.; Thompson, C.C.; Thompson, F.L.; et al. Microbial community profile and water quality in a protected area of the Caatinga biome. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.; Cai, L.; Yang, Y.; Ju, F.; Li, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, T. Metagenomic analysis reveals potential biodegradation pathways of persistent pesticides in freshwater and marine sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.J.; Rosenberg, R. Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems. Science 2008, 321, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spietz, R.L.; Williams, C.M.; Rocap, G.; Horner-Devine, M.C. A dissolved oxygen threshold for shifts in bacterial community structure in a seasonally hypoxic estuary. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, G.; Han, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, L. Spatial and temporal dynamics of microbial community composition and factors influencing the surface water and sediments of urban rivers. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 124, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hullar, M.A.J.; Kaplan, L.A.; Stahl, D.A. Recurring seasonal dynamics of microbial communities in stream habitats. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Stegen, J.C.; Yu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, S.; Dai, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, C. Nearly a decade-long repeatable seasonal diversity patterns of bacterioplankton communities in the eutrophic Lake Donghu (Wuhan, China). Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 3839–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, P.; Raghavan, R.V.; Jeon, C.O.; Lee, H.J.; Priya, P.V.; Dharani, G.; Kirubagaran, R. Complex bacterial communities in the deep-sea sediments of the Bay of Bengal and volcanic Barren Island in the Andaman Sea. Mar. Genom. 2017, 31, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, N.; Zheng, Q. The microbial carbon pump: From genes to ecosystems. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 7439–7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Q.; Li, D.; Chen, W.; Zhu, L.; Zou, X.; Hu, L.; Yuan, Y.; He, S.; Shi, F. Dynamics of Bacterioplankton Communities during Wet and Dry Seasons in the Danjiangkou Reservoir in Hubei, China. Life 2023, 13, 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13051206
Yang Q, Li D, Chen W, Zhu L, Zou X, Hu L, Yuan Y, He S, Shi F. Dynamics of Bacterioplankton Communities during Wet and Dry Seasons in the Danjiangkou Reservoir in Hubei, China. Life. 2023; 13(5):1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13051206
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Qing, Dewang Li, Wei Chen, Liming Zhu, Xi Zou, Lian Hu, Yujie Yuan, Shan He, and Fang Shi. 2023. "Dynamics of Bacterioplankton Communities during Wet and Dry Seasons in the Danjiangkou Reservoir in Hubei, China" Life 13, no. 5: 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13051206
APA StyleYang, Q., Li, D., Chen, W., Zhu, L., Zou, X., Hu, L., Yuan, Y., He, S., & Shi, F. (2023). Dynamics of Bacterioplankton Communities during Wet and Dry Seasons in the Danjiangkou Reservoir in Hubei, China. Life, 13(5), 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13051206





