A Study on the Comparison of Corrosion in Water Supply Pipes Due to Tap Water (TW) and Reclaimed Water (RW)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Preparation of Tested Water
2.3. Analytical Method
2.3.1. Water Quality Analysis
2.3.2. Assessment of Corrosion Rate
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Tested Water
3.1.1. Quality of the Initial Influent
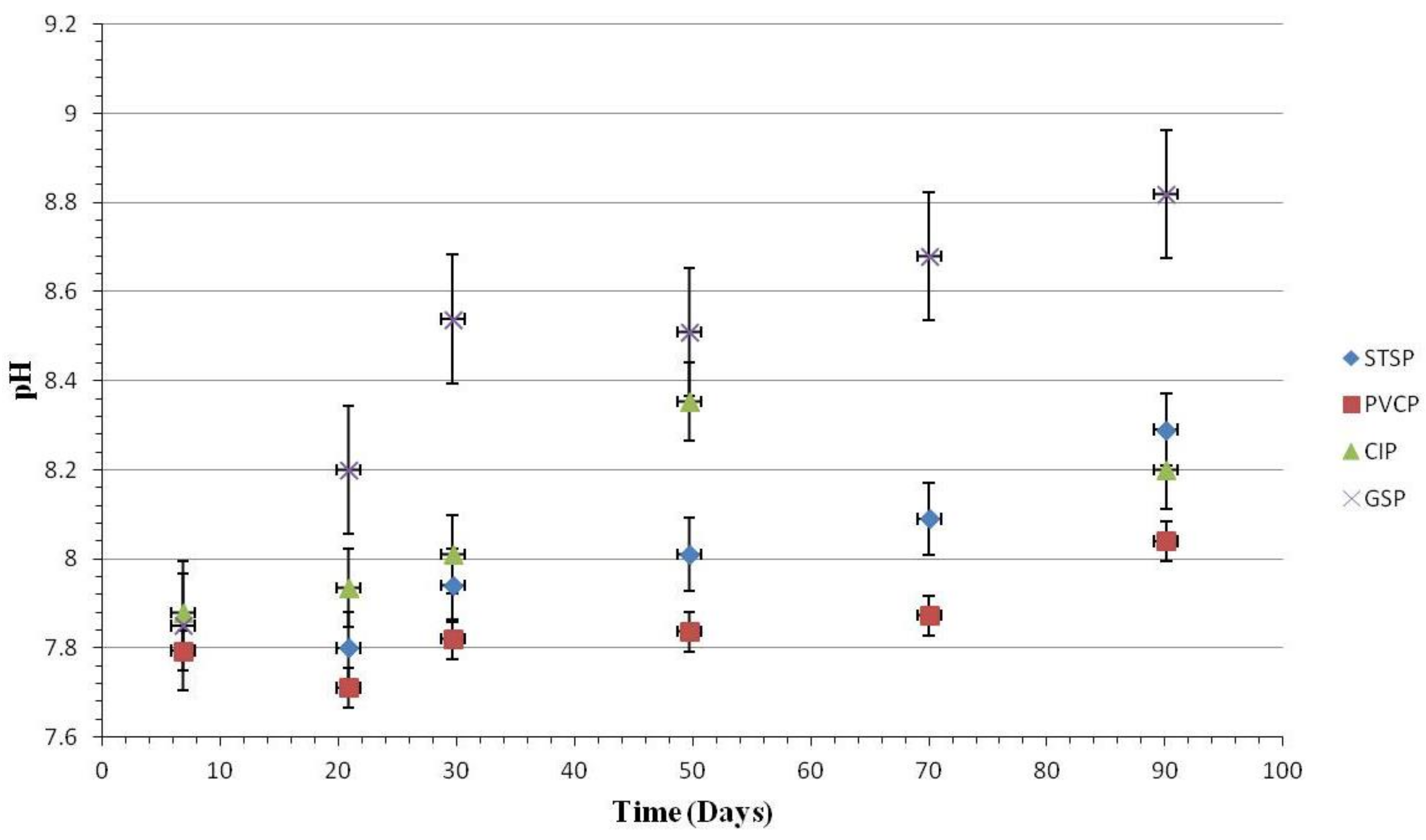
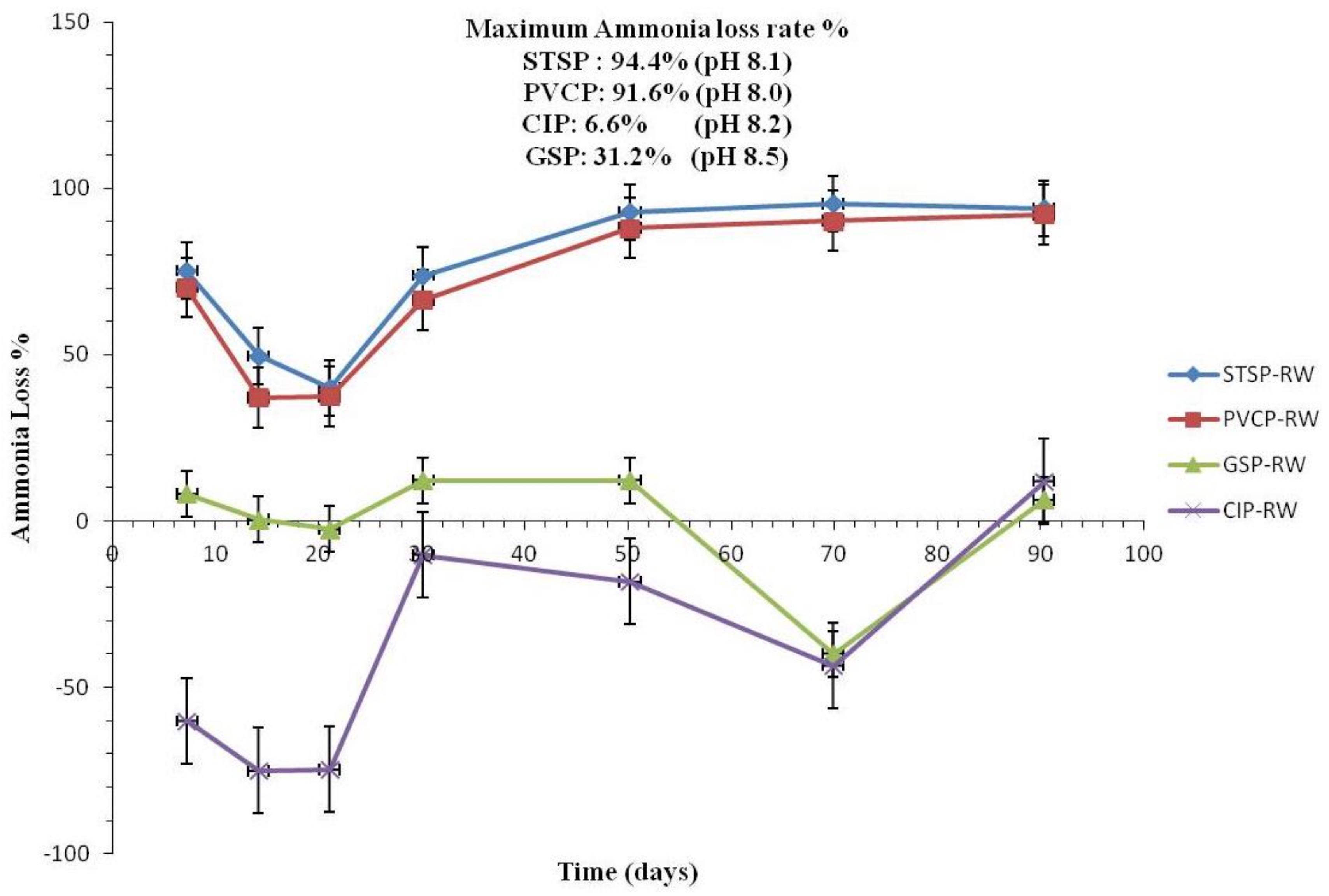
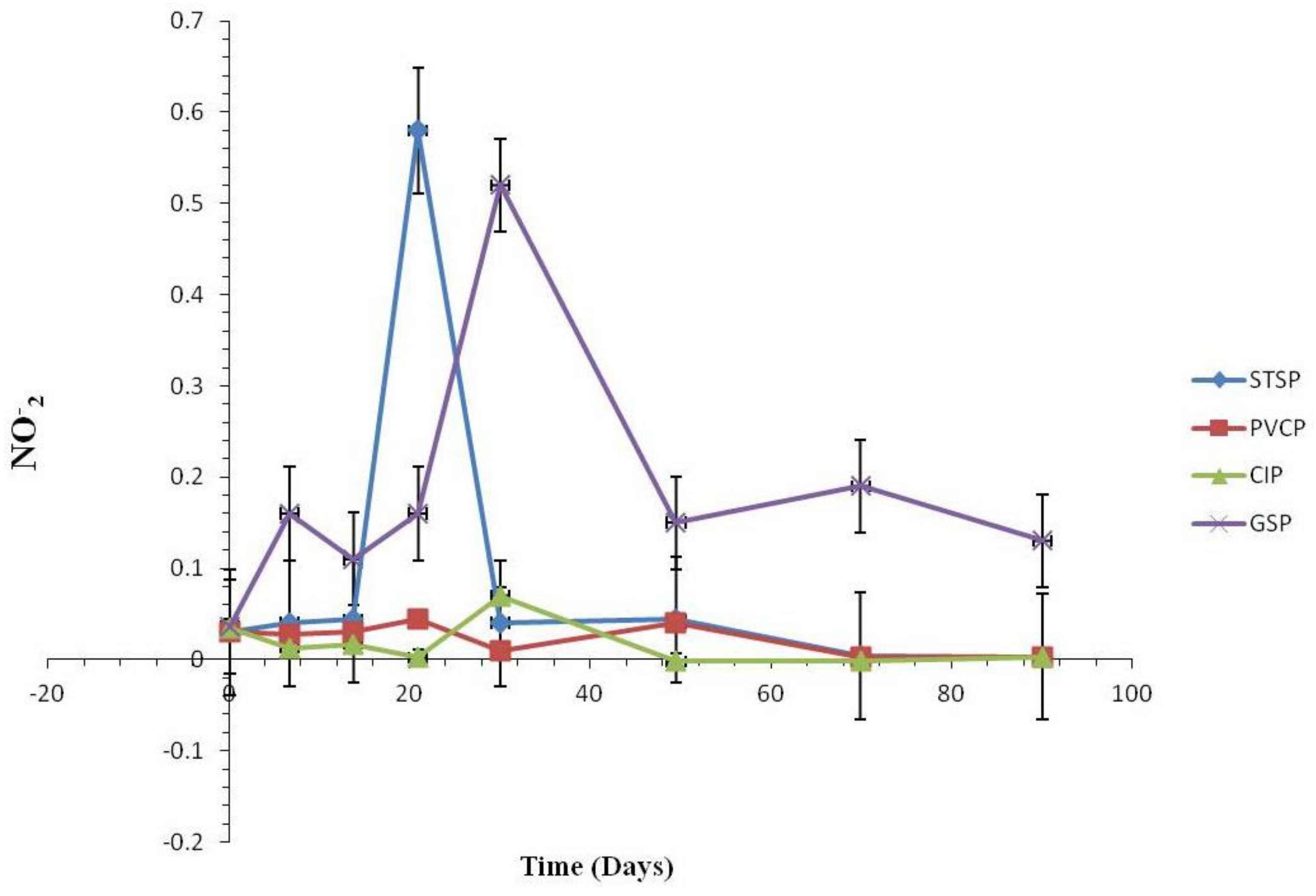
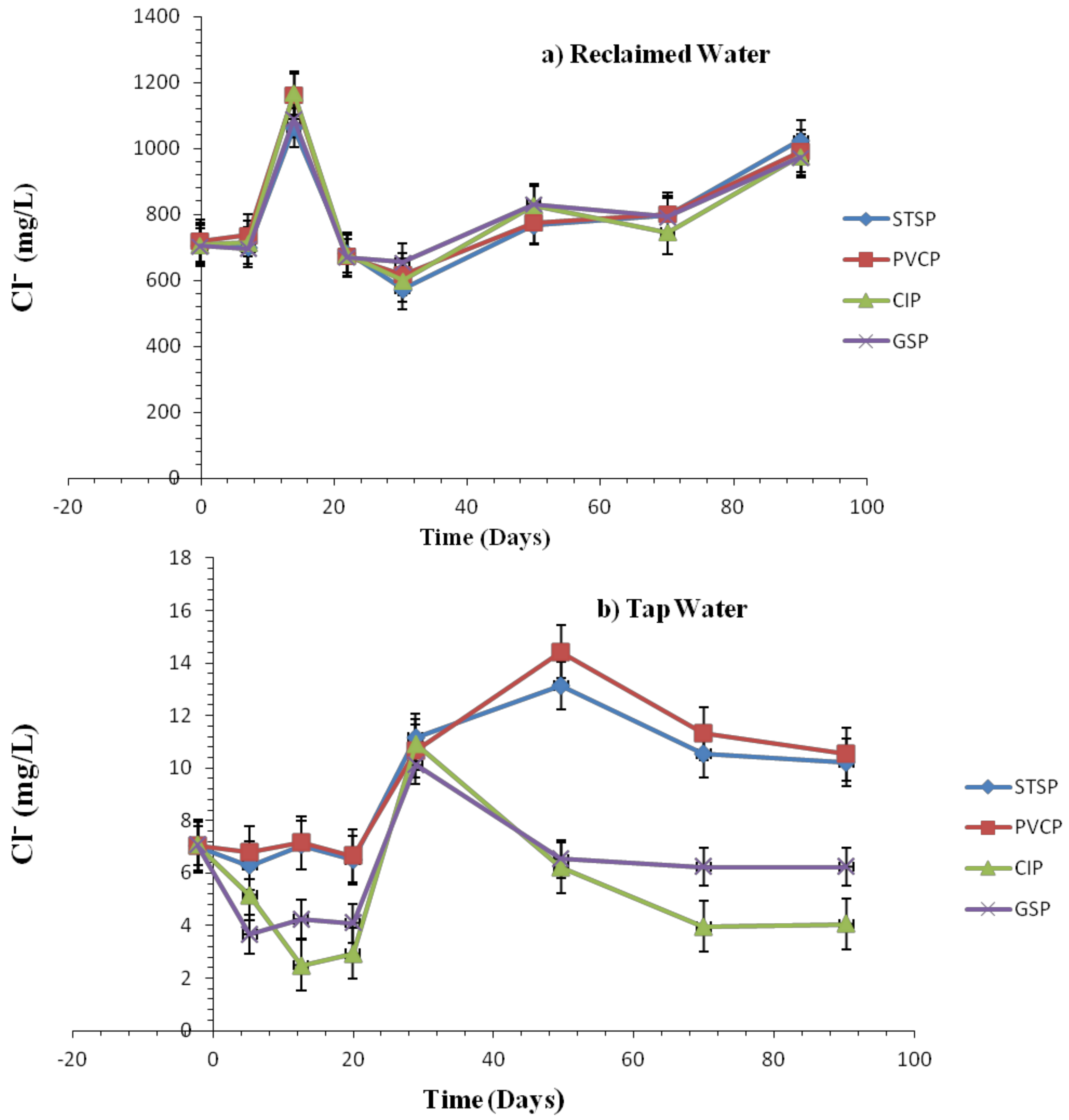
3.1.2. Water Quality Change
Water Quality Change
Effect of Nitrification and Denitrification
Effect of Chlorite Ions and Sulfate Ions
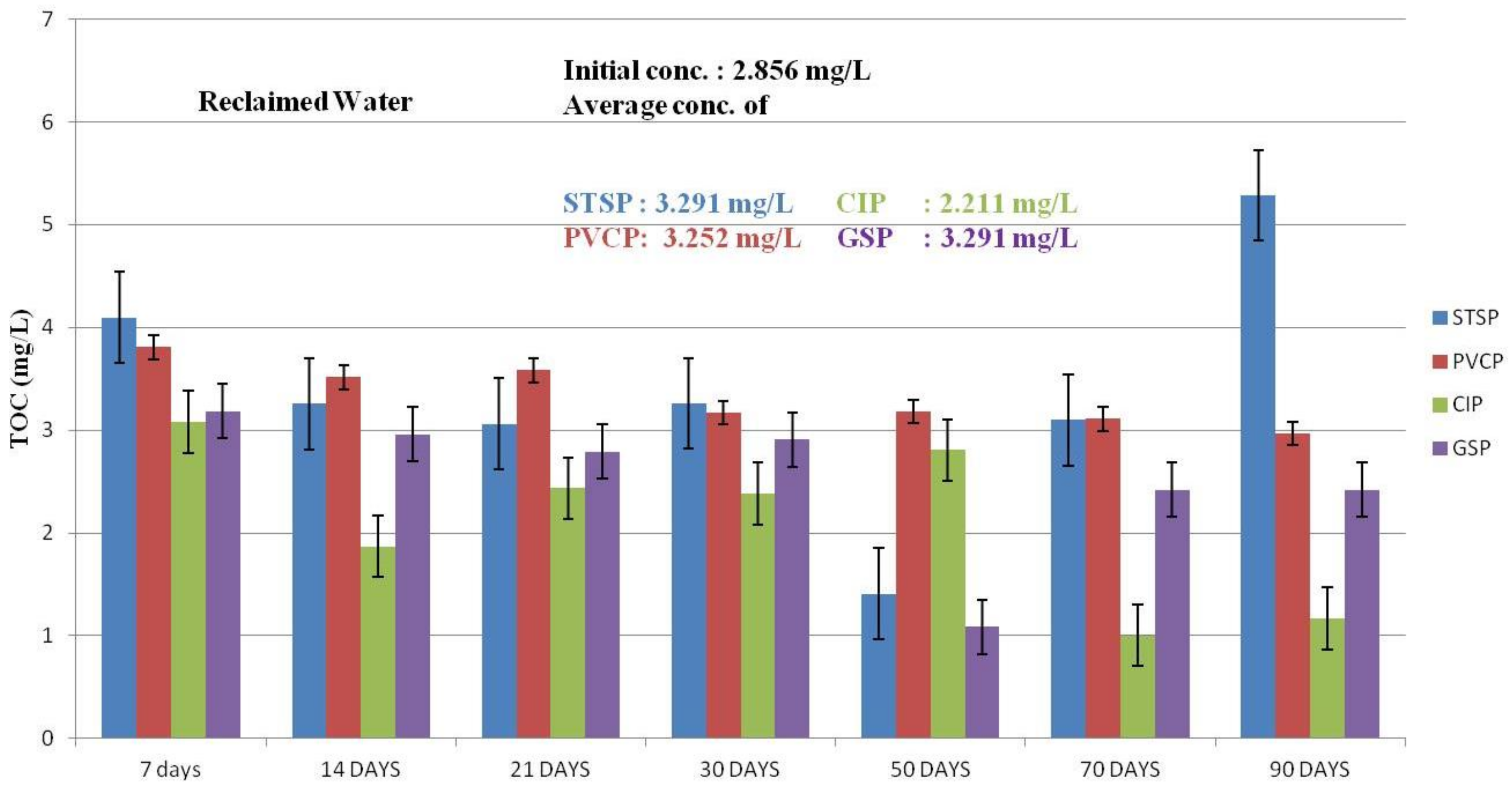
Effect of TOC
3.2. Corrosion Rate by Tested Water
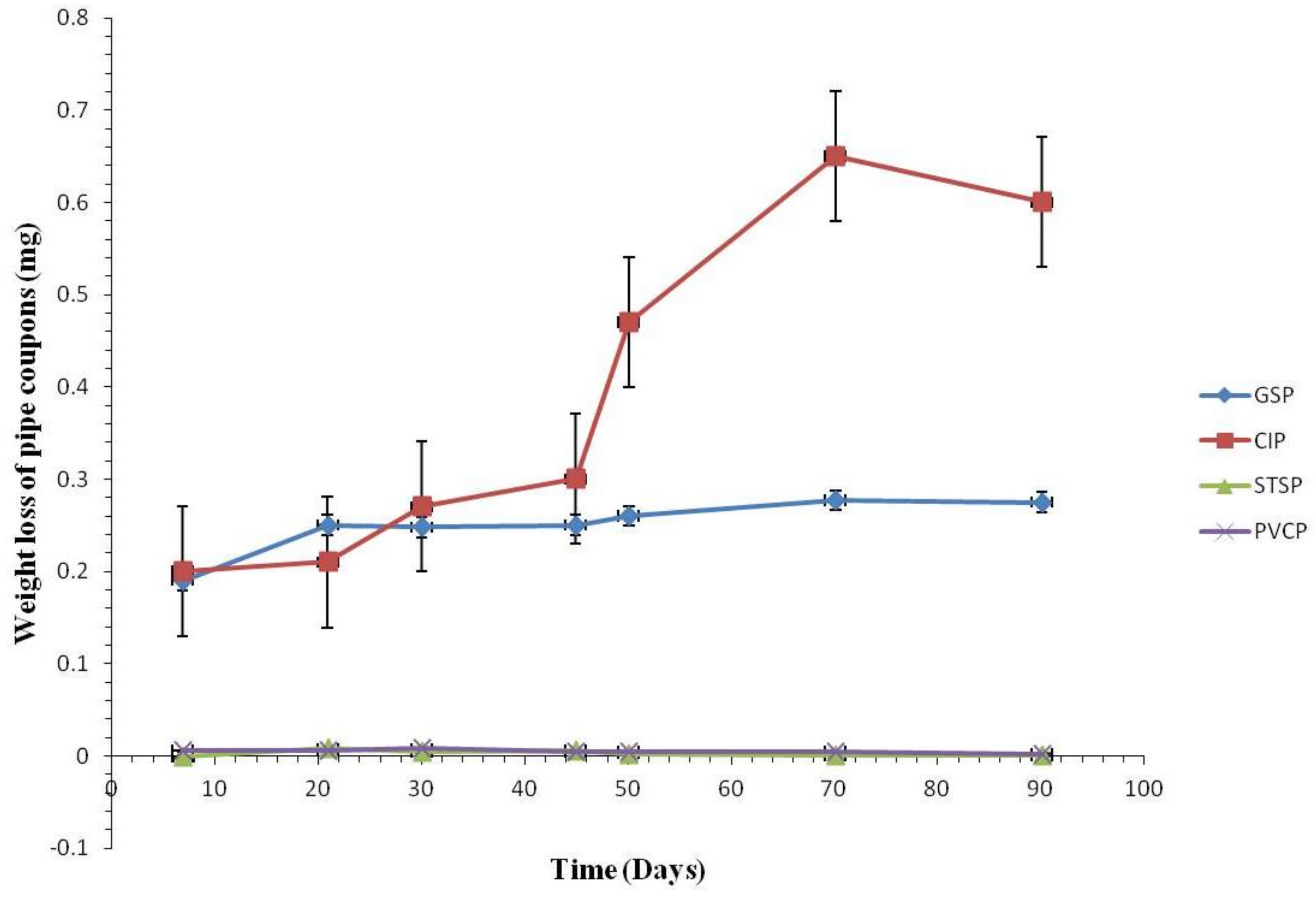
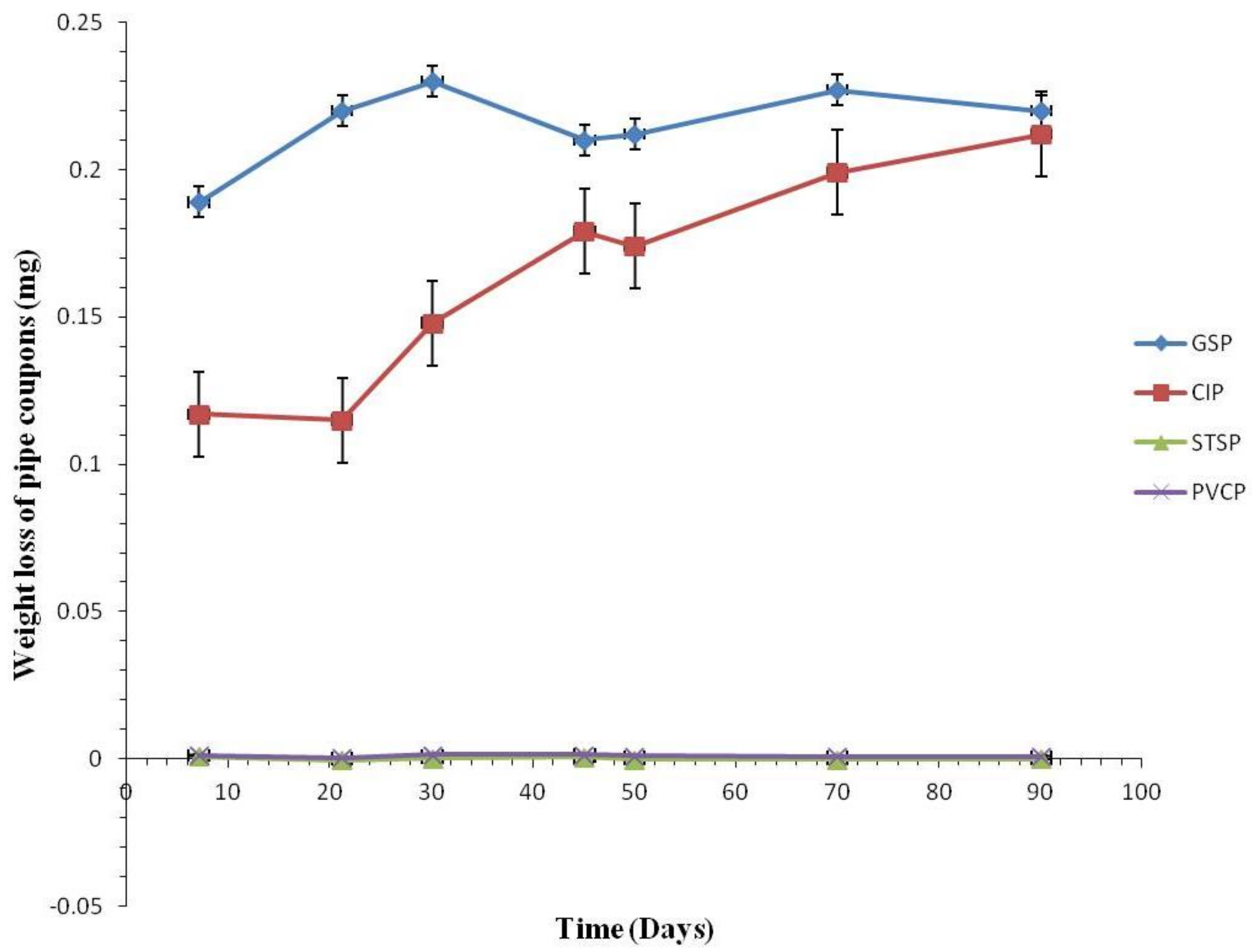
3.2.1. Coupon Weight Loss by Pipe Materials
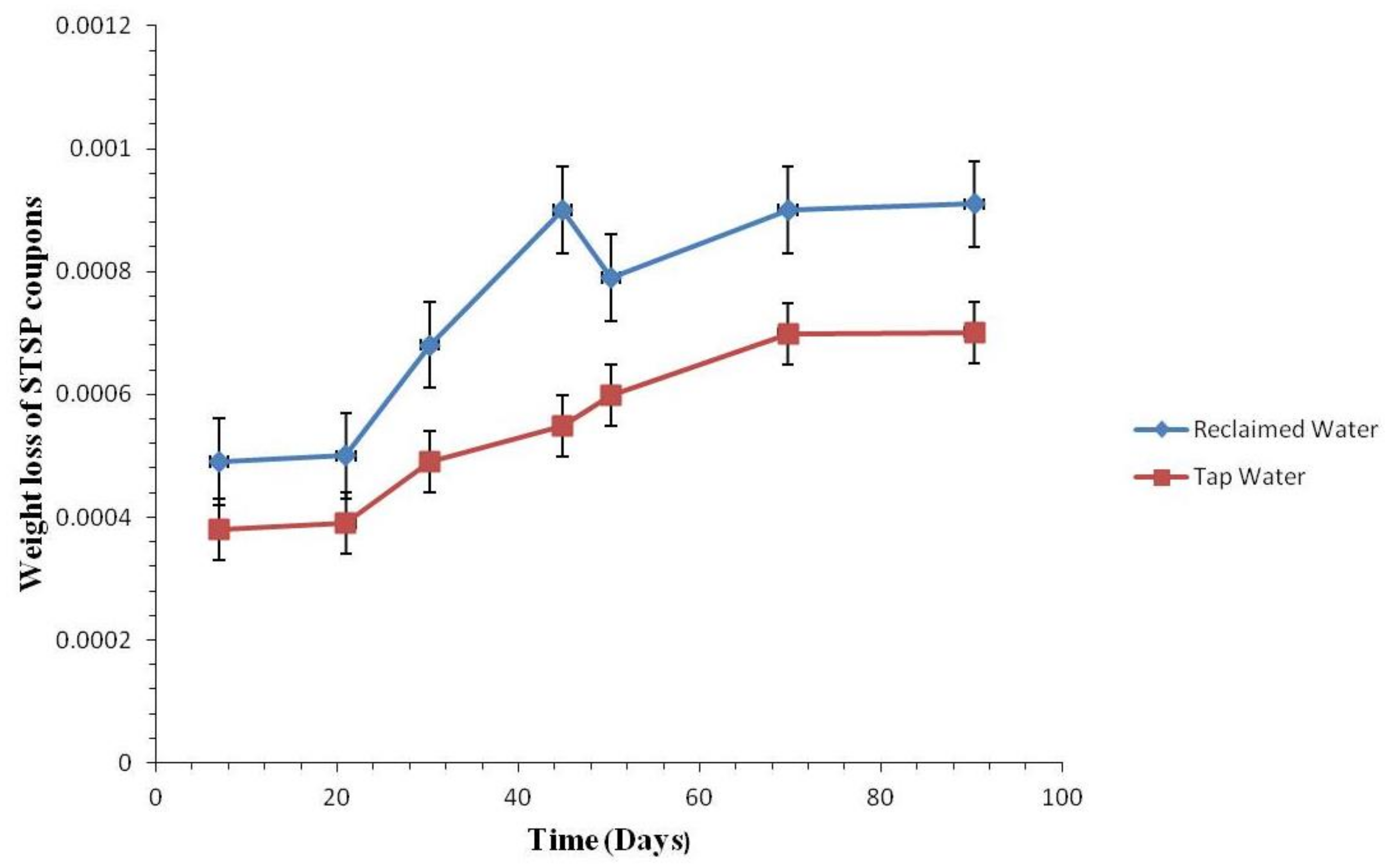
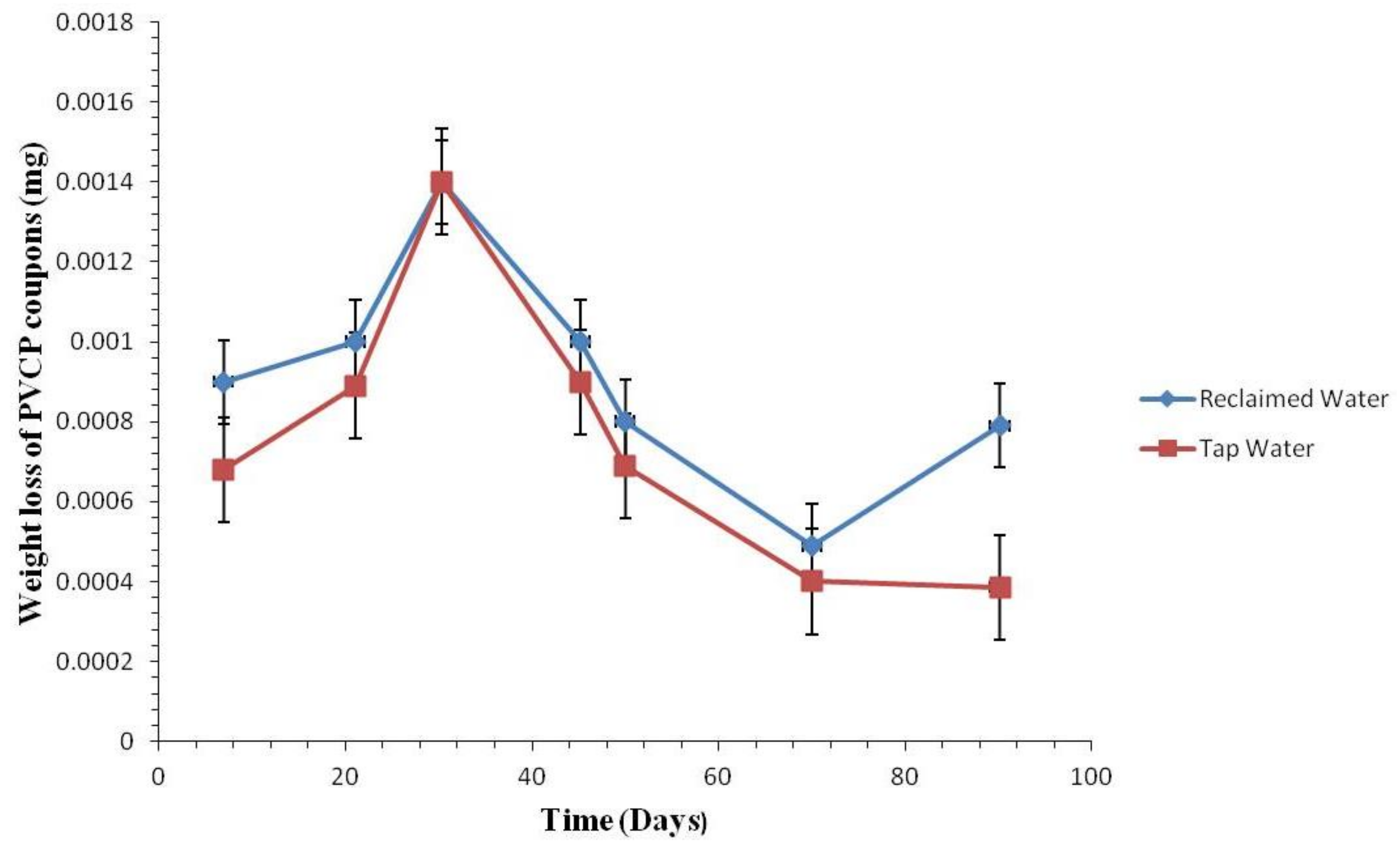
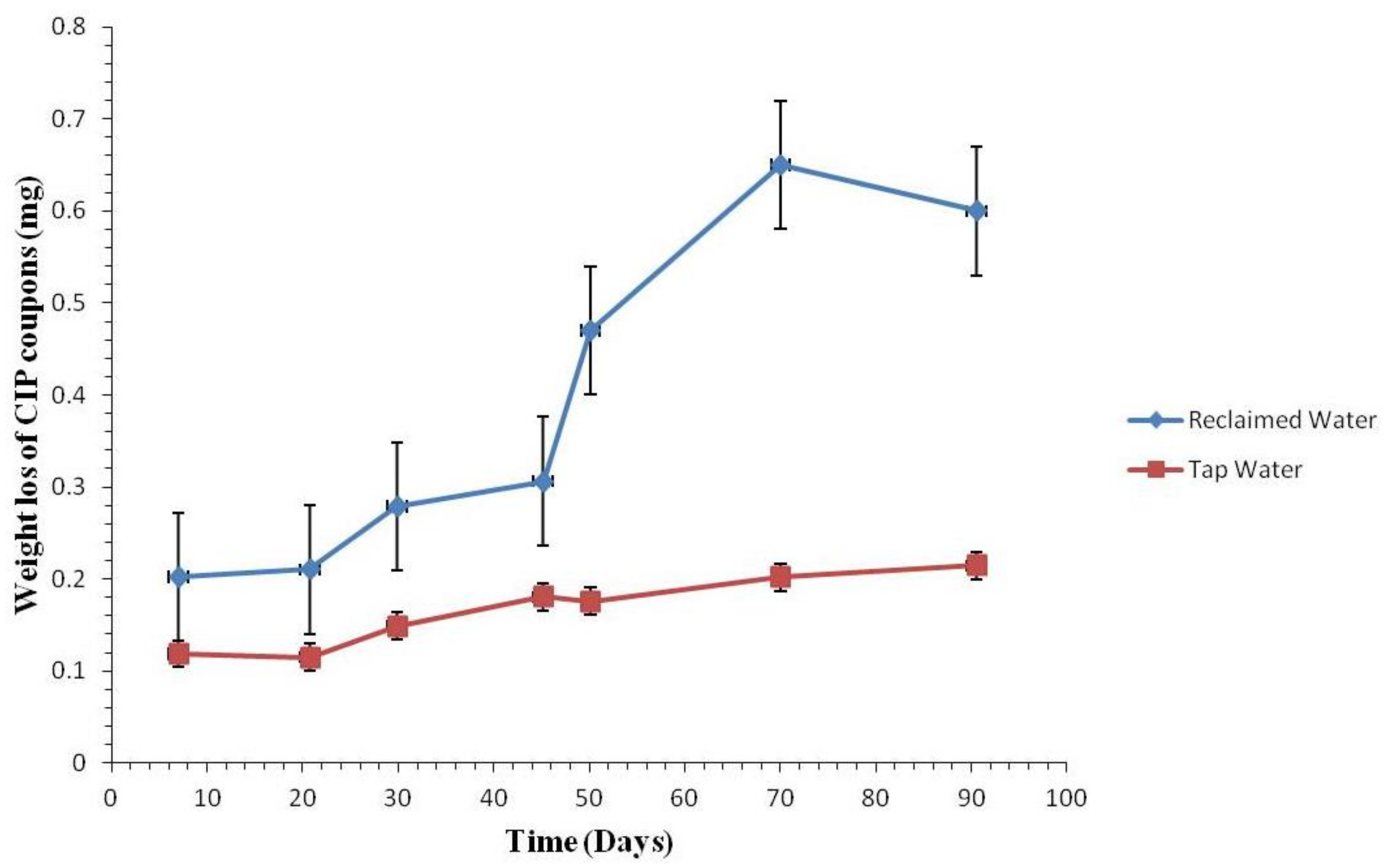
3.2.2. Weight Loss of the Coupons
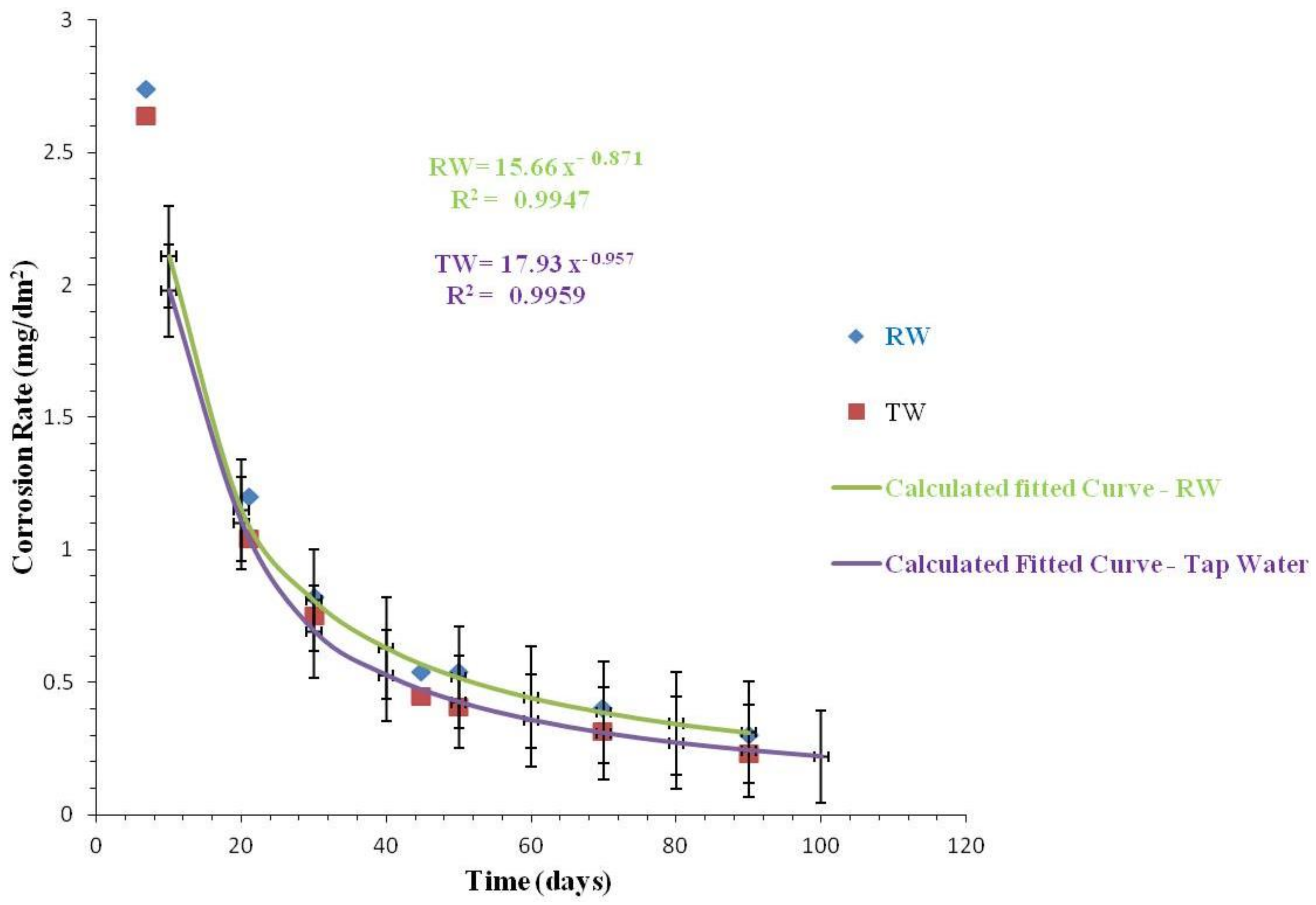
3.2.3. Comparison of Corrosion Rates
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- KCID-ICID. Overview of National Policies and Development Plans; Korean National Committee on Irrigation and Drainage-The International Commission on Irrigation and Drainage (KCID-ICID): Seoul, South Korea, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Bae, C.; Park, J.; Chung, W.; Kwak, P. Evaluation of water quality characteristics effects on the internal corrosion of galvanized steel service pipe in the building. J. Korean Soc. Water Qual. 2001, 17, 627–635. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, G.H.; Kim, T.W.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.H. Optimization of water reuse system under uncertainty. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2010, 43, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davil, M.F.; Mahvi, A.H.; Norouzi, M.; Mazloomi, S.; Amarluie, A.; Tardast, A.; Karamitabar, Y. Survey of corrosion and scaling potential produced water from Ilam water treatment plant. Appl. Sci. 2009, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell, S.A.; Rippey, S.R.; Watkins, W.D. Inactivation of bacterial and viral indicators in secondary sewage effluents, using chlorine and ozone. Water Res. 1995, 29, 2483–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). Standard practice for preparing, cleaning and evaluating corrosion test specimens. In Annual Book of ASTM Standards; American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM): West Conshohoken, PA, USA, 1985; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Sanusi, K.O.; Okoro, H.K. Investigation of corrosion effect of mild steel on orange juice. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orubite, O.K.; Oforka, N.C. Corrosion inhibition of Zinc on HCl using Nypa fruticans Wurmb Extract and 1, 5 Diphenel Carbazone. J. Appl. Sci. 2004, 8, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environment. Environmental Statistics Yearbook 2009; Ministry of Environment: Seoul, South Korea, 2009.
- AWWARF (American Water Works Association Research Foundation). Internal Corrosion of Water Distribution Systems; AWWARF-DVGW-TZW Cooperative Research Report; AWWARF (American Water Works Association Research Foundation): Denver, CO, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Caroline, K.N.; Kendall, R.S.; Marc, A.E. Nitrate accelerated corrosion of lead solder in potable water systems. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 1044–1049. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y. Study on Corrosion Characteristics in the Water Distribution Pipeline Depending on Water Quality. Master’s Thesis, University of Seoul, Seoul, Korea, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.; Lee, Y.; Lee, H.; Lee, C.; Ahn, K.; Lee, W. Influence of pipe materials on corrosion and bacteria regrowth in a model home plumbing system. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 16, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridgway, H.F.; Olson, B.H. Scanning electron microscope evidence for bacterial colonization of a drinking-water distribution system. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1982, 41, 274–287. [Google Scholar]
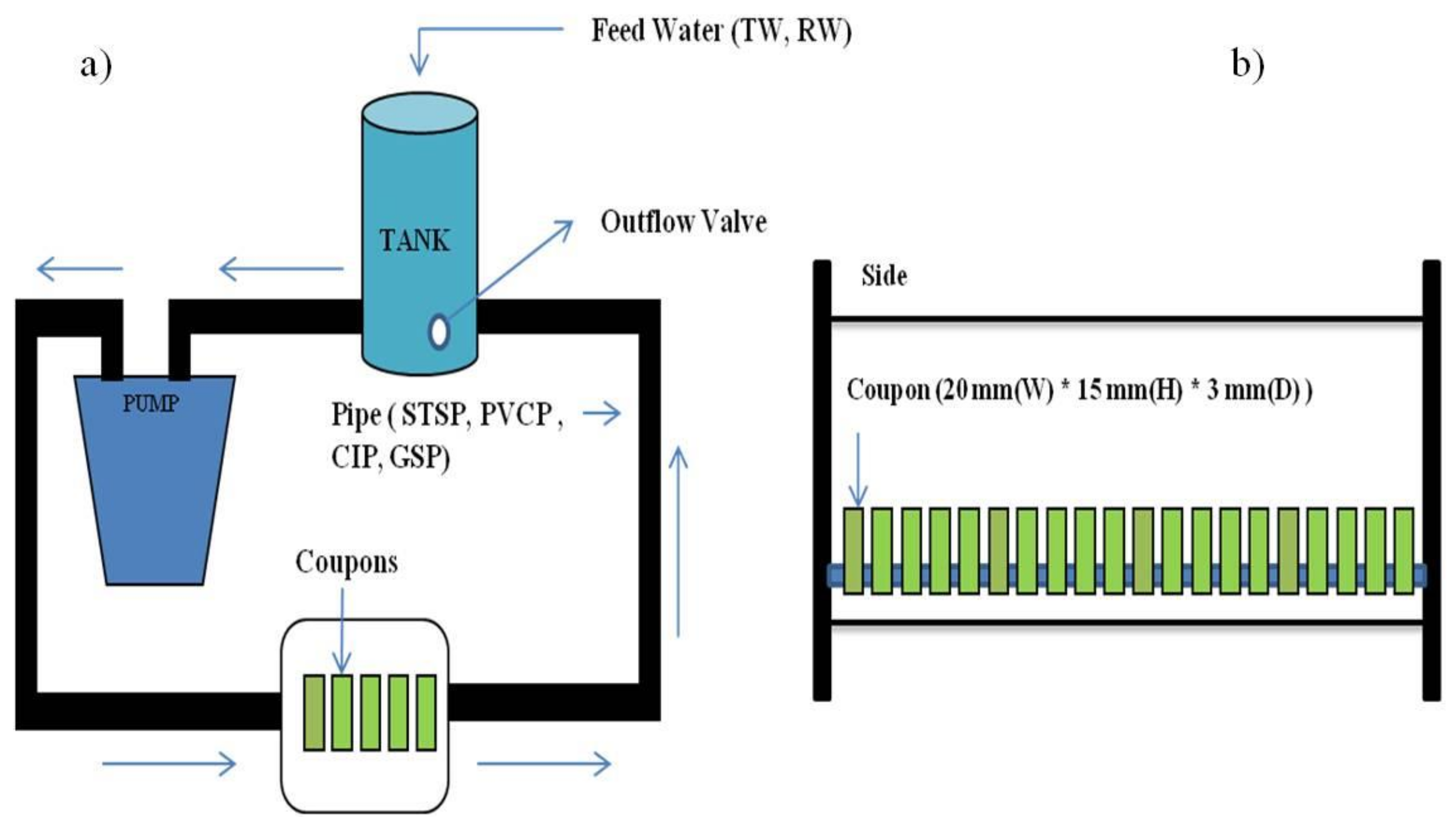





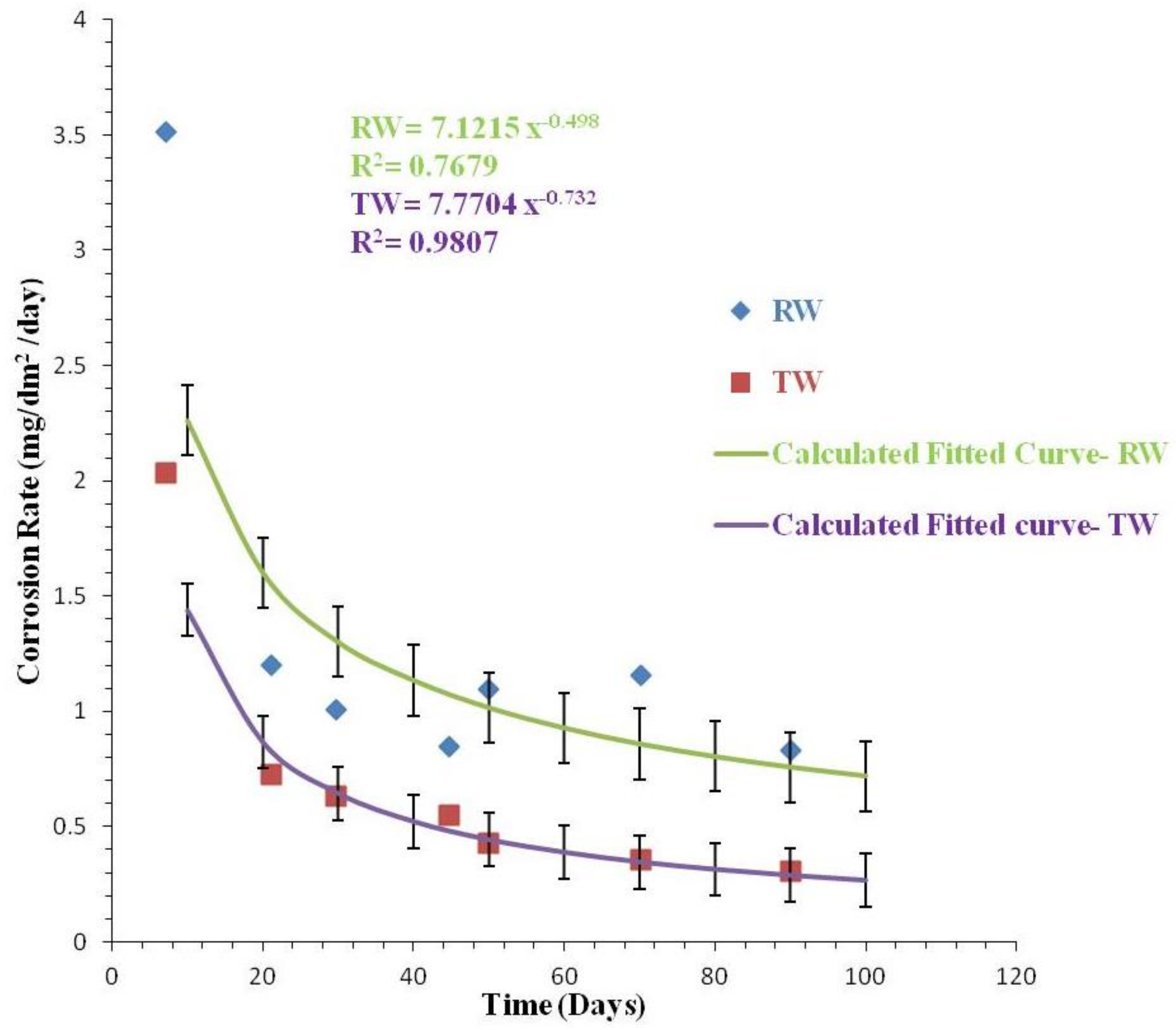
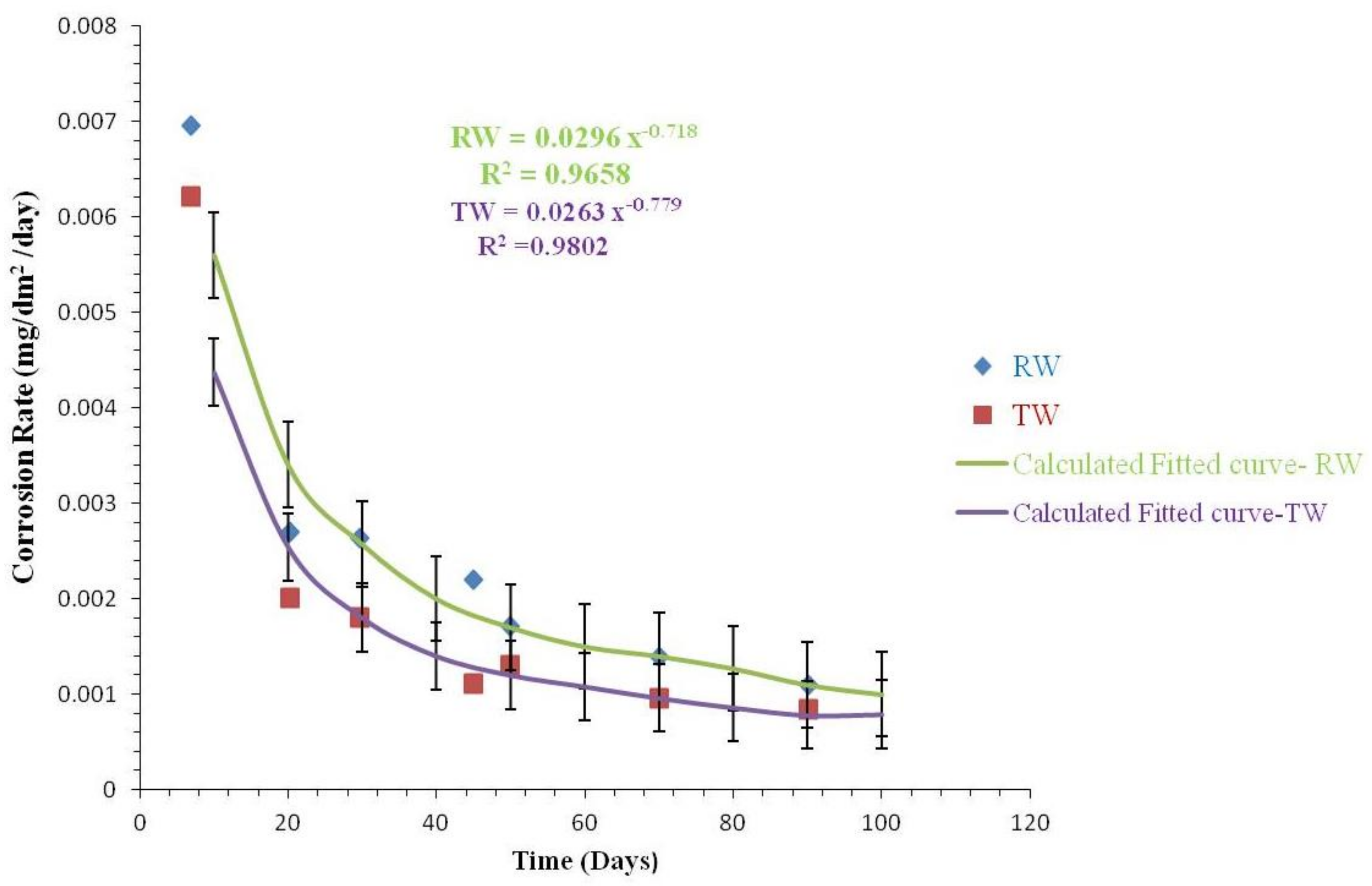
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Type of Experiments | Loop Test |
| Coupon Size | 20 mm (W) × 3 mm (D) × 15 mm (H) |
| Source of Water | TW (Tap Water) RW (Reclaimed Water) |
| Running Time | 24 h |
| Flow Rate | 1.5 m/s |
| Type of Coupon | PVCP (Polyvinyl chloride pipe) GSP (Galvanized steel pipe) CIP (Cast iron pipe) STSP (Stainless steel pipe 304) |
| Volume of Water | 4 L |
| Measurement Parameters | Temperature, Dissolved Oxygen (DO), pH, Alkalinity, Turbidity, NO3−-N, Hardness, Total Organic Carbon (TOC), Cl−, Fe2+, Hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC), NO2−-N, PO43−-P, SO42−, NH4+-N, Zn2+, Conductivity |
| Classification | pH | BOD (mg/L) | COD (mg/L) | SS (mg/L) | T-N (mg/L) | T-P (mg/L) | Chromaticity (Degree) | Chloride (mg/L) | Coliform (ea/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supplied water quantity | Toilet | - | 1.5 | 5.3 | 3.4 | 3.361 | 0.380 | 2 | 620 | ND |
| Landscape | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Recreation | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Treatment plant | Treated Water | - | 16.9 | 8.4 | 7.7 | 7.7 | 0.57 | - | - | 259 |
| Inflow | - | 66.8 | 66.3 | 131.7 | 31.0 | 4.57 | - | - | - | |
| Recommendation standards of reclaimed water quantity | Toilet | 5.8~8.5 | Less 10 | Less 20 | - | - | - | Less 20 | - | ND |
| Landscape | 5.8~8.5 | Less 10 | Less 20 | - | - | - | Less 20 | Less 250 | ND | |
| Parameter | Unit | Method |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | μs/cm | Conductivity meter, Model 115A Plus, Expotech, Houstan, TX, USA |
| Total organic carbon (TOC) | mg/L | Standard method |
| Temperature | °C | - |
| Hardness | mg/L CaCO3− | DR 4000, HACH, Loveland, CO, USA |
| Dissolved Oxygen (DO) | mg/L | DO meter, YSI 550A, Istek, Seoul, South Korea |
| Cl− | mg/L | DR 4000, HACH, Loveland, CO, USA |
| pH | pH meter, Istek pH-250L, Seoul, South Korea | |
| Fe2+ | mg/L | DR 4000, HACH, Loveland, CO, USA |
| NO3−-N, NO2−-N NH4+-N, PO43−-P | mg/L | DR 4000, HACH, Loveland, CO, USA |
| Zn2+ | mg/L | DR 4000, HACH, Loveland, CO, USA |
| Material | Time | Temperature | Chemical | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper and copper alloys | 20 min | 20∼25 °C | 50% HCl | followed by light scrub |
| Stainless steel | 20 min | 60 °C | 10% HNO3 | followed by light scrub |
| Iron and steel | 20 min | 20∼25 °C | Concentrated HCl + 50 g/L SnCl2 + 20 g/L SbCl3 | followed by light scrub |
| Analysis Item | Unit | Sewage Reuse Water | Tap Water |
|---|---|---|---|
| Turbidity | NTU | 0.791 | 0.088 |
| Electrical conductivity | μs/cm | 3700 | 177.45 |
| DO | mg/L | 4.94 | 4.86 |
| Alkalinity | mg/L as CaCO3 | 96 | 34 |
| Free residual chlorine | mg/L | 0.03 | 0.1 |
| SO42− | mg/L | 191.5 | 12.0 |
| Hardness | mg/L as CaCO3 | 743 | 82 |
| Bonded residual chlorine | mg/L | 0.010 | 0.20 |
| pH | - | 7.42 | 7.86 |
| Zn2+ | mg/L | 0.010 | 0.068 |
| Fe2+ | mg/L | 0.006 | 0.010 |
| NO2−-N | mg/L | 0.0365 | 0.0093 |
| NO3−-N | mg/L | 4.9 | 1.1 |
| NH4+-N | mg/L | 0.578 | 0.072 |
| TOC | mg/L | 2.86 | 1.29 |
| PO43−-P | mg/L | 0.406 | 0.0492 |
| Suspended HPC | CFU/mL | 1672 | 10 |
| Chlorine | mg/L | 704.75 | 7.04 |
| Water temperature | °C | 26.1 | 25.9 |
| Water Quality | Effect |
|---|---|
| Temperature | High water temperature promotes the rate of oxidation. Experience shows that corrosion is more pronounced in hot water lines. |
| pH | Low pH may increase corrosion. High pH may protect pipes and decrease corrosion rates or could cause dezincification of brasses or soft blue hydroxide deposits on copper pipe. |
| Alkalinity | May help form protective coating; helps control pH changes. Low to moderate alkalinity reduces corrosion of most materials. High alkalinity increases corrosion of copper, lead, and zinc. |
| Calcium Hardness | Calcium may precipitate as CaCO3 and may provide protection and reduce corrosion rates, but may cause turbidity or excessive scaling. |
| Magnesium | May inhibit the precipitation of calcite in the form of CaCO3 on pipe surface and favor the deposition of the more soluble aragonite form of CaCO3. |
| DO | High DO increases many corrosion rates. |
| Conductivity | High conductivity tends to increase corrosion rate. |
| Chlorine residual | Increases corrosion, particularly for copper, iron, and steel. |
| Acidity | High acidity increases corrosion rate and release rate of metal. |
| Chloride, sulfate | High levels increase corrosion of iron, copper, and galvanized steel. |
| TOC | Low TOC may decrease microbial activity. |
| Material | Corrosion Type | Tap Water Quality Deterioration |
|---|---|---|
| Cast | - | - |
| Iron | Uniform | Rust tubercles (blockage of pipe) |
| Ductile | Graphitization Pitting under unprotective scale | Iron and suspended particles release |
| Steel | Pitting | Rust tubercles (blockage of pipe), iron, and suspended particles release |
| Galvanized steel | General pitting | Excessive zinc, lead, cadmium, and iron release and blockage of pipe |
| Copper | Uniform | Copper release |
| Localized attack Cold water Hot water | Pipe perforation and subsequent leakage from pipes | |
| Corrosion fatigue | Rupture of pipes and fittings and consequent leakage | |
| Erosion | Leakage from pipes. |
| Inhibition Factor | Value | Acceleration Factor | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.5 | Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) (mg/L) | 85 |
| Alkalinity (mg/L as CaCO3) | 60 | Cl− (mg/L) | 10 |
| Hardness (mg/L as CaCO3) | 80 | SO42− | 10 |
| Inhibition Factor | Value | Acceleration Factor | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.5 (5.8~8.5) | TDS | 500 |
| Hardness | 650 | NH4+ | 1.0 |
| Alkalinity | 350 | PO43− | 0.5 |
| Chlorine | 0.2 | Cl−, SO42− | 200~500 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.; Rasheed, U.; Kong, M. A Study on the Comparison of Corrosion in Water Supply Pipes Due to Tap Water (TW) and Reclaimed Water (RW). Water 2018, 10, 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10040496
Lee H, Rasheed U, Kong M. A Study on the Comparison of Corrosion in Water Supply Pipes Due to Tap Water (TW) and Reclaimed Water (RW). Water. 2018; 10(4):496. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10040496
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hyundong, Usman Rasheed, and Myeongsik Kong. 2018. "A Study on the Comparison of Corrosion in Water Supply Pipes Due to Tap Water (TW) and Reclaimed Water (RW)" Water 10, no. 4: 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10040496




