Ecology and Evolution of the Human Microbiota: Fire, Farming and Antibiotics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The History of the Human Microbiome
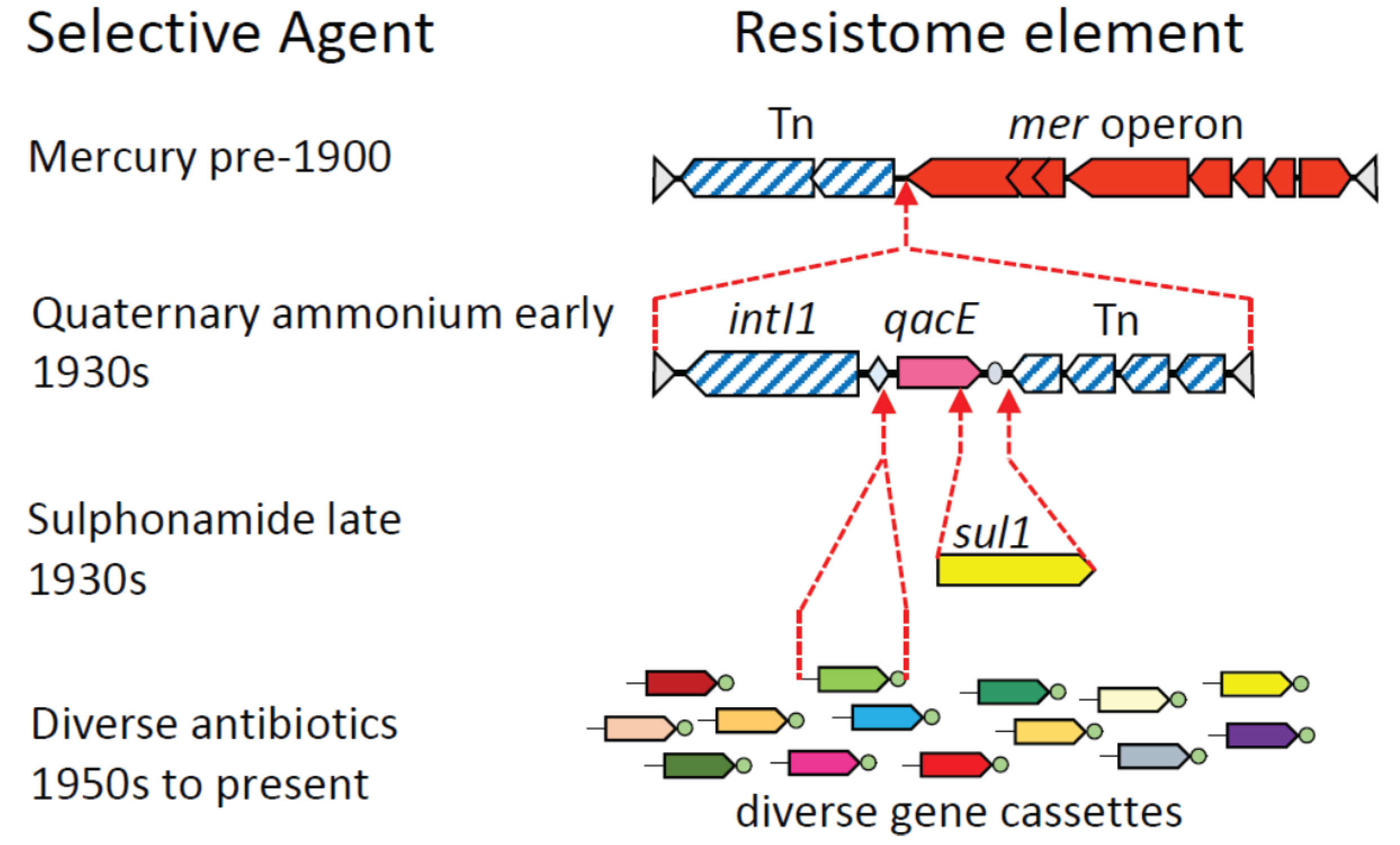
3. Assembly of Multi-Resistance DNA Elements within the Microbiome
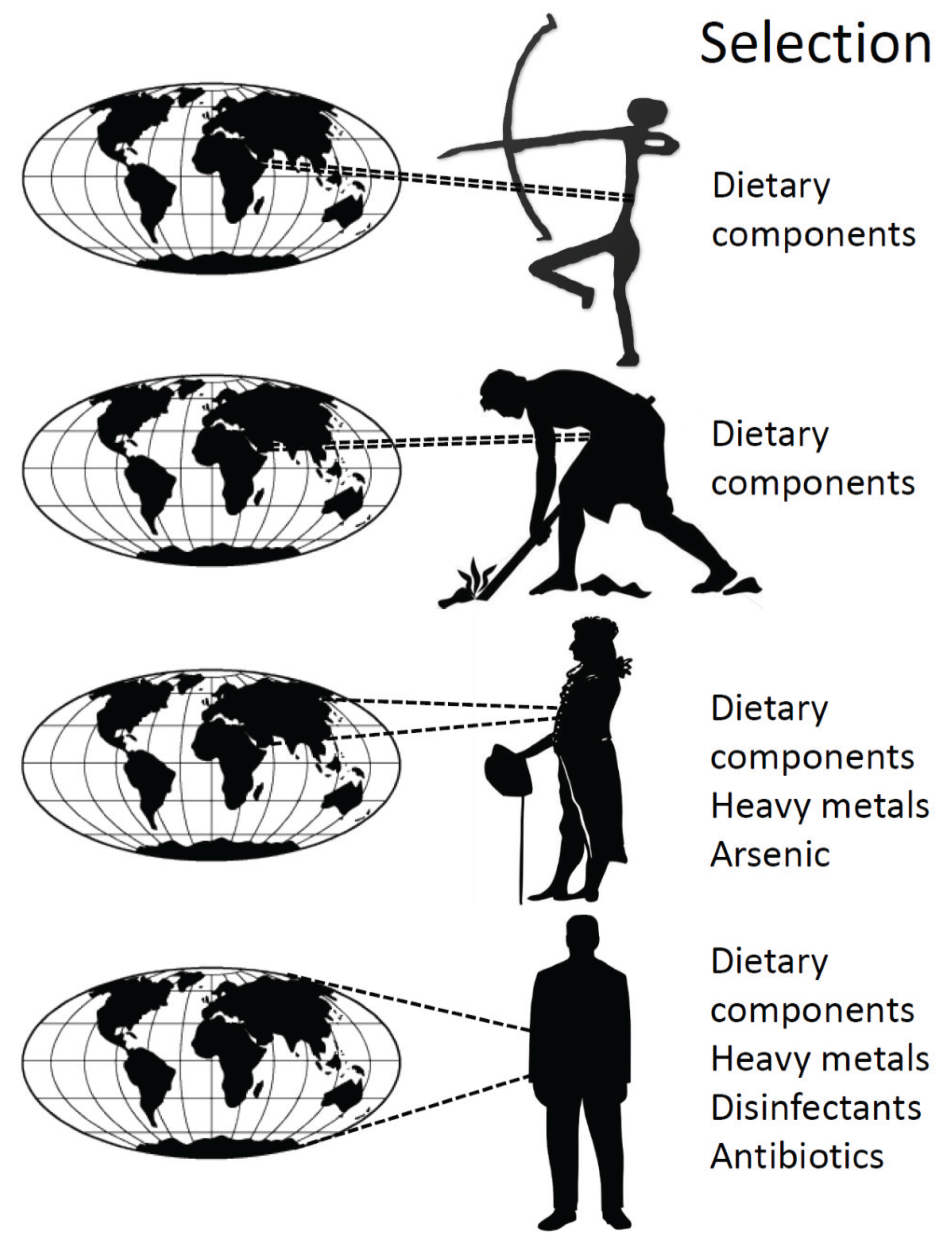
4. History of the Human Microbiota
5. Conclusions
| Timeframe | Ecological or Evolutionary driver | Possible effect on microbiota | Possible effect on microbiome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-350,000 bp A | fire & diet gut vs. brain investment | ↓ α-diversity | speeds molecular clock |
| Neolithic 10,000 bp | farming & diet | ↓ α-diversity zoonotic exchanges | ↓ gene functions |
| Industrial revolution 18th century | processed foods pollutants, heavy metals globalization | ↓ α-diversity selection ↑ dispersal | selection for mer operon |
| Modern era 1930’s | disinfectants sanitation | ↓ α-diversity ↑ β-diversity? | selection for qacE, spread of class 1 integron |
| First antibiotic 1930’s | sulphonamides | ↓ α-diversity selection | selection for sul1 |
| Antibiotic era 1950’s on | diverse antibiotics caesarean section bottle feeding globalization sanitation | ↓ α-diversity ↓ transmission ↓ transmission ↑ dispersal ↑ β-diversity | selection for resistance genes ↓ intra-species genetic diversity |
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palumbi, S.R. Humans as the world’s greatest evolutionary force. Science 2001, 293, 1786–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockstrom, J.; Steffen, W.; Noone, K.; Persson, A.; Chapin, F.S.; Lambin, E.F.; Lenton, T.M.; Scheffer, M.; Folke, C.; Schellnhuber, H.J.; et al. A safe operating space for humanity. Nature 2009, 461, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; Zalasiewicz, J.; Haff, P.; Schwagerl, C.; Barnosky, A.D.; Ellis, E.C. The Anthropocene biosphere. Anthr. Rev. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillings, M.R.; Westoby, M. DNA technology and evolution of the central dogma. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2014, 29, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkowski, P.G.; Fenchel, T.; Delong, E.F. The microbial engines that drive Earth’s biogeochemical cycles. Science 2008, 320, 1034–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, D.M. Have we underestimated the importance of humans in the biogeography of free-living terrestrial microorganisms? J. Biogeogr. 2010, 37, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillings, M.R.; Paulsen, I.T. Microbiology of the Anthropocene. Anthropocene 2014, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, X.C.; Segata, N.; Huttenhower, C. Biodiversity and functional genomics in the human microbiome. Trends Genet. 2013, 29, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.R.; Pop, M.; DeBoy, R.T.; Eckburg, P.B.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Samuel, B.S.; Gordon, J.I.; Relman, D.A.; Fraser-Liggett, C.M.; Nelson, K.E. Metagenomic analysis of the human distal gut microbiome. Science 2006, 312, 1355–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.; Blaser, M.J. The human microbiome: At the interface of health and disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, J.C.; Pehrsson, E.C.; Blaser, M.J.; Sandhu, K.; Gao, Z.; Wang, B.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Contreras, M.; Noya-Alarcón, Ó. The microbiome of uncontacted Amerindians. Sci. Adv. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, E.K.; Stagaman, K.; Dethlefsen, L.; Bohannan, B.J.; Relman, D.A. The application of ecological theory toward an understanding of the human microbiome. Science 2012, 336, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Knight, R. Dietary effects on human gut microbiome diversity. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, S1–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, H.W.; Gillings, M.R. Gene flow, mobile genetic elements and the recruitment of antibiotic resistance genes into Gram-negative pathogens. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 790–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillings, M.R. Evolutionary consequences of antibiotic use for the resistome, mobilome and microbial pangenome. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, O.; Dagan, T. Trends and barriers to lateral gene transfer in prokaryotes. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.M.; Nielsen, K.M. Mechanisms of, and barriers to, horizontal gene transfer between bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloesges, T.; Popa, O.; Martin, W.; Dagan, T. Networks of gene sharing among 329 proteobacterial genomes reveal differences in lateral gene transfer frequency at different phylogenetic depths. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 28, 1057–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skippington, E.; Ragan, M.A. Lateral genetic transfer and the construction of genetic exchange communities. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 707–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, S.J.; Bailey, M.; Hansen, L.H.; Kroer, N.; Wuertz, S. Studying plasmid horizontal transfer in situ: A critical review. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smillie, C.S.; Smith, M.B.; Friedman, J.; Cordero, O.X.; David, L.A.; Alm, E.J. Ecology drives a global network of gene exchange connecting the human microbiome. Nature 2011, 480, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, K.; Itoh, T.; Kuwahara, T.; Oshima, K.; Toh, H.; Toyoda, A.; Takami, H.; Morita, H.; Sharma, V.K.; Srivastava, T.P. Comparative metagenomics revealed commonly enriched gene sets in human gut microbiomes. DNA Res. 2007, 14, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, F.; Hehemann, J.-H.; Rebuffet, E.; Czjzek, M.; Michel, G. Environmental and gut Bacteroidetes: The food connection. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnorr, S.L.; Candela, M.; Rampelli, S.; Centanni, M.; Consolandi, C.; Basaglia, G.; Turroni, S.; Biagi, E.; Peano, C.; Severgnini, M. Gut microbiome of the Hadza hunter-gatherers. Nat. Commun. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippo, C.; Cavalieri, D.; Di Paola, M.; Ramazzotti, M.; Poullet, J.B.; Massart, S.; Collini, S.; Pieraccini, G.; Lionetti, P. Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14691–14696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsunenko, T.; Rey, F.E.; Manary, M.J.; Trehan, I.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Baldassano, R.N.; Anokhin, A.P.; et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 2012, 486, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehemann, J.-H.; Correc, G.; Barbeyron, T.; Helbert, W.; Czjzek, M.; Michel, G. Transfer of carbohydrate-active enzymes from marine bacteria to Japanese gut microbiota. Nature 2010, 464, 908–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, C.J.; Dobney, K.; Weyrich, L.S.; Kaidonis, J.; Walker, A.W.; Haak, W.; Bradshaw, C.J.A.; Townsend, G.; Soltysiak, A.; Alt, K.W.; et al. Sequencing ancient calcified dental plaque shows changes in oral microbiota with dietary shifts of the Neolithic and Industrial Revolutions. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Bij, A.K.; Pitout, J.D. The role of international travel in the worldwide spread of multiresistant Enterobacteriaceae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2090–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.; Davies, D. Origins and evolution of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussaint, A.; Chandler, M. Prokaryote genome fluidity: Toward a system approach of the mobilome. In Bacterial Molecular Networks; Helden, J., Toussaint, A., Thieffry, D., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 804, pp. 57–80. [Google Scholar]
- D’Costa, V.M.; McGrann, K.M.; Hughes, D.W.; Wright, G.D. Sampling the antibiotic resistome. Science 2006, 311, 374–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsberg, K.J.; Reyes, A.; Wang, B.; Selleck, E.M.; Sommer, M.O.A.; Dantas, G. The shared antibiotic resistome of soil bacteria and human pathogens. Science 2012, 337, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.D. The antibiotic resistome. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2010, 5, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, G.; Sommer, M.O.A. Context matters—The complex interplay between resistome genotypes and resistance phenotypes. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2012, 15, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, H.K.; Donato, J.; Wang, H.H.; Cloud-Hansen, K.A.; Davies, J.; Handelsman, J. Call of the wild: Antibiotic resistance genes in natural environments. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riesenfeld, C.S.; Goodman, R.M.; Handelsman, J. Uncultured soil bacteria are a reservoir of new antibiotic resistance genes. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, J.A.; Westman, E.L.; Wright, G.D. The antibiotic resistome: What’s new? Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2014, 21, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, M.O.A.; Dantas, G.; Church, G.M. Functional characterization of the antibiotic resistance reservoir in the human microflora. Science 2009, 325, 1128–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, M.O.; Church, G.M.; Dantas, G. The human microbiome harbors a diverse reservoir of antibiotic resistance genes. Virulence 2010, 1, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, N.; Hughes, V.M. Plasmids of the same Inc groups in enterobacteria before and after the medical use of antibiotics. Nature 1983, 306, 616–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulain, A.J.; Aris-Brosou, S.; Blais, J.M.; Brazeau, M.; Keller, W.B.; Paterson, A.M. Microbial DNA records historical delivery of anthropogenic mercury. ISME J. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebert, C.A.; Hall, R.M.; Summers, A.O. Transposon Tn21, flagship of the floating genome. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1999, 63, 507–522. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, H.K.; Moe, L.A.; Rodbumrer, J.; Gaarder, A.; Handelsman, J. Functional metagenomics reveals diverse β-lactamases in a remote Alaskan soil. ISME J. 2008, 3, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Costa, V.M.; King, C.E.; Kalan, L.; Morar, M.; Sung, W.W.L.; Schwarz, C.; Froese, D.; Zazula, G.; Calmels, F.; Debruyne, R.; et al. Antibiotic resistance is ancient. Nature 2011, 477, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaze, W.H.; Abdouslam, N.; Hawkey, P.M.; Wellington, E.M.H. Incidence of class 1 integrons in a quaternary ammonium compound-polluted environment. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 1802–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosewarne, C.P.; Pettigrove, V.; Stokes, H.W.; Parsons, Y.M. Class 1 integrons in benthic bacterial communities: Abundance, association with Tn402-like transposition modules and evidence for coselection with heavy-metal resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 72, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, M.S.; Baker-Austin, C.; Lindell, A.H.; Stepanauskas, R.; Stokes, H.W.; McArthur, J.V. Influence of industrial contamination on mobile genetic elements: Class 1 integron abundance and gene cassette structure in aquatic bacterial communities. ISME J. 2008, 2, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillings, M.; Boucher, Y.; Labbate, M.; Holmes, A.; Krishnan, S.; Holley, M.; Stokes, H.W. The evolution of class 1 integrons and the rise of antibiotic resistance. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 5095–5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholodii, G.Y.; Mindlin, S.; Bass, I.; Yurieva, O.; Minakhina, S.; Nikiforov, V. Four genes, two ends, and a res region are involved in transposition of Tn5053: A paradigm for a novel family of transposons carrying either a mer operon or an integron. Mol. Microbiol. 1995, 17, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillings, M.R. Integrons: Past, present, and future. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2014, 78, 257–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, A. Introduction of biocides into clinical practice and the impact on antibiotic-resistant bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 92, S121–S135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, S.R.; Brown, H.J.; Stokes, H.; Hall, R.M. Transposons Tn1696 and Tn21 and their integrons In4 and In2 have independent origins. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sköld, O. Sulfonamide resistance: Mechanisms and trends. Drug Resist. Updates 2000, 3, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, S.R.; Tsafnat, G.; Coiera, E.; Iredell, J.R. Gene cassettes and cassette arrays in mobile resistance integrons. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 33, 757–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Freijo, P.; Fluit, A.; Schmitz, F.; Grek, V.; Verhoef, J.; Jones, M. Class 1 integrons in gram-negative isolates from different European hospitals and association with decreased susceptibility to multiple antibiotic compounds. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1998, 42, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Essen-Zandbergen, A.; Smith, H.; Veldman, K.; Mevius, D. Occurrence and characteristics of class 1, 2 and 3 integrons in Escherichia coli, Salmonella and Campylobacter spp. in the Netherlands. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 59, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, C.; Lee, M.D.; Sanchez, S.; Hudson, C.; Phillips, B.; Register, B.; Grady, M.; Liebert, C.; Summers, A.O.; White, D.G. Incidence of class 1 and 2 integrases in clinical and commensal bacteria from livestock, companion animals, and exotics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 723–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillings, M.R.; Stokes, H.W. Are humans increasing bacterial evolvability? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillings, M.R.; Xuejun, D.; Hardwick, S.A.; Holley, M.P.; Stokes, H.W. Gene cassettes encoding resistance to quaternary ammonium compounds: A role in the origin of clinical class 1 integrons? ISME J. 2009, 3, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garriss, G.; Waldor, M.K.; Burrus, V. Mobile antibiotic resistance encoding elements promote their own diversity. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillings, M.R.; Labbate, M.; Sajjad, A.; Giguere, N.J.; Holley, M.P.; Stokes, H.W. Mobilization of a Tn402-like class 1 integron with a novel cassette array via flanking miniature inverted-repeat transposable element-like structures. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 6002–6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmer, C.J.; Moran, R.A.; Hall, R.M. Movement of IS26-associated antibiotic resistance genes occurs via a translocatable unit that includes a single IS26 and preferentially inserts adjacent to another IS26. MBio 2014, 5, e01801–e01814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, C.; Chowdhury, P.R.; Djordjevic, S.P. Tn6026 and Tn6029 are found in complex resistance regions mobilised by diverse plasmids and chromosomal islands in multiple antibiotic resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Plasmid 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dethlefsen, L.; McFall-Ngai, M.; Relman, D.A. An ecological and evolutionary perspective on human–microbe mutualism and disease. Nature 2007, 449, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.L.; Maslin, M.A. Defining the Anthropocene. Nature 2015, 519, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, A.H.; Li, Y.; Ngole, E.M.; Ahuka-Mundeke, S.; Lonsdorf, E.V.; Pusey, A.E.; Peeters, M.; Hahn, B.H.; Ochman, H. Rapid changes in the gut microbiome during human evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16431–16435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Rodriguez, T.M.; Narganes-Storde, Y.M.; Chanlatte, L.; Crespo-Torres, E.; Toranzos, G.A.; Jimenez-Flores, R.; Hamrick, A.; Cano, R.J. Microbial communities in pre-Columbian coprolites. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warinner, C.; Speller, C.; Collins, M.J.; Lewis, C.M. Ancient human microbiomes. J. Hum. Evol. 2015, 79, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimelmitz, R.; Kuhn, S.L.; Jelinek, A.J.; Ronen, A.; Clark, A.E.; Weinstein-Evron, M. “Fire at will”: The emergence of habitual fire use 350,000 years ago. J. Hum. Evol. 2014, 77, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, L.C.; Wheeler, P. The expensive-tissue hypothesis: The brain and the digestive system in human and primate evolution. Curr. Anthropol. 1995, 36, 199–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milton, K. A hypothesis to explain the role of meat-eating in human evolution. Evol. Anthropol. Issues News Rev. 1999, 8, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tito, R.Y.; Knights, D.; Metcalf, J.; Obregon-Tito, A.J.; Cleeland, L.; Najar, F.; Roe, B.; Reinhard, K.; Sobolik, K.; Belknap, S. Insights from characterizing extinct human gut microbiomes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, I.; Stegen, J.C.; Maldonado-Gómez, M.X.; Eren, A.M.; Siba, P.M.; Greenhill, A.R.; Walter, J. The gut microbiota of rural Papua New Guineans: Composition, diversity patterns, and ecological processes. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzosa, E.A.; Huang, K.; Meadow, J.F.; Gevers, D.; Lemon, K.P.; Bohannan, B.J.; Huttenhower, C. Identifying personal microbiomes using metagenomic codes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E2930–E2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molton, J.S.; Tambyah, P.A.; Ang, B.S.P.; Ling, M.L.; Fisher, D.A. The global spread of healthcare-associated multidrug-resistant bacteria: A perspective from Asia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, 1310–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantón, R.; Akóva, M.; Carmeli, Y.; Giske, C.G.; Glupczynski, Y.; Gniadkowski, M.; Livermore, D.M.; Miriagou, V.; Naas, T.; Rossolini, G. Rapid evolution and spread of carbapenemases among Enterobacteriaceae in Europe. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.P.; Woodford, N. Global spread of antibiotic resistance: The example of New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase (Ndm)-mediated carbapenem resistance. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 62, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jernberg, C.; Löfmark, S.; Edlund, C.; Jansson, J.K. Long-term ecological impacts of antibiotic administration on the human intestinal microbiota. ISME J. 2007, 1, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsson, H.E.; Jernberg, C.; Andersson, A.F.; Sjölund-Karlsson, M.; Jansson, J.K.; Engstrand, L. Short-term antibiotic treatment has differing long-term impacts on the human throat and gut microbiome. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, H.; Ferech, M.; Vander Stichele, R.; Elseviers, M.; Group, E.P. Outpatient antibiotic use in Europe and association with resistance: A cross-national database study. Lancet 2005, 365, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dethlefsen, L.; Relman, D.A. Incomplete recovery and individualized responses of the human distal gut microbiota to repeated antibiotic perturbation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4554–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjölund, M.; Tano, E.; Blaser, M.J.; Andersson, D.I.; Engstrand, L. Persistence of resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis after single course of clarithromycin. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1389–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjölund, M.; Wreiber, K.; Andersson, D.I.; Blaser, M.J.; Engstrand, L. Long-term persistence of resistant Enterococcus species after antibiotics to eradicate Helicobacter pylori. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 139, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloissnig, S.; Arumugam, M.; Sunagawa, S.; Mitreva, M.; Tap, J.; Zhu, A.; Waller, A.; Mende, D.R.; Kultima, J.R.; Martin, J. Genomic variation landscape of the human gut microbiome. Nature 2013, 493, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morowitz, M.J.; Denef, V.J.; Costello, E.K.; Thomas, B.C.; Poroyko, V.; Relman, D.A.; Banfield, J.F. Strain-resolved community genomic analysis of gut microbial colonization in a premature infant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1128–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, M.J.; Falkow, S. What are the consequences of the disappearing human microbiota? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, J.E.; Spor, A.; Scalfone, N.; Fricker, A.D.; Stombaugh, J.; Knight, R.; Angenent, L.T.; Ley, R.E. Succession of microbial consortia in the developing infant gut microbiome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4578–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, O.; Knights, D.; Gonzalez, A.; Waldron, L.; Segata, N.; Knight, R.; Huttenhower, C.; Ley, R.E. A guide to enterotypes across the human body: Meta-analysis of microbial community structures in human microbiome datasets. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2013, 9, e1002863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jernberg, C.; Löfmark, S.; Edlund, C.; Jansson, J.K. Long-term impacts of antibiotic exposure on the human intestinal microbiota. Microbiology 2010, 156, 3216–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahti, L.; Salojärvi, J.; Salonen, A.; Scheffer, M.; de Vos, W.M. Tipping elements in the human intestinal ecosystem. Nat. Commun. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlers, S.; Kaufmann, S.H. Infection, inflammation, and chronic diseases: Consequences of a modern lifestyle. Trends Immunol. 2010, 31, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, J.A.; Forsythe, P.; Chew, M.V.; Escaravage, E.; Savignac, H.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Bienenstock, J.; Cryan, J.F. Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16050–16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijtz, R.D.; Wang, S.; Anuar, F.; Qian, Y.; Björkholm, B.; Samuelsson, A.; Hibberd, M.L.; Forssberg, H.; Pettersson, S. Normal gut microbiota modulates brain development and behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3047–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.A.; McVey Neufeld, K.-A. Gut–brain axis: How the microbiome influences anxiety and depression. Trends Neurosci. 2013, 36, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurice, C.F.; Haiser, H.J.; Turnbaugh, P.J. Xenobiotics shape the physiology and gene expression of the active human gut microbiome. Cell 2013, 152, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, L.M.; Yamanishi, S.; Sohn, J.; Alekseyenko, A.V.; Leung, J.M.; Cho, I.; Kim, S.G.; Li, H.; Gao, Z.; Mahana, D. Altering the intestinal microbiota during a critical developmental window has lasting metabolic consequences. Cell 2014, 158, 705–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nood, E.; Vrieze, A.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Fuentes, S.; Zoetendal, E.G.; de Vos, W.M.; Visser, C.E.; Kuijper, E.J.; Bartelsman, J.F.; Tijssen, J.G. Duodenal infusion of donor feces for recurrent Clostridium difficile. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gillings, M.R.; Paulsen, I.T.; Tetu, S.G. Ecology and Evolution of the Human Microbiota: Fire, Farming and Antibiotics. Genes 2015, 6, 841-857. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes6030841
Gillings MR, Paulsen IT, Tetu SG. Ecology and Evolution of the Human Microbiota: Fire, Farming and Antibiotics. Genes. 2015; 6(3):841-857. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes6030841
Chicago/Turabian StyleGillings, Michael R., Ian T. Paulsen, and Sasha G. Tetu. 2015. "Ecology and Evolution of the Human Microbiota: Fire, Farming and Antibiotics" Genes 6, no. 3: 841-857. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes6030841
APA StyleGillings, M. R., Paulsen, I. T., & Tetu, S. G. (2015). Ecology and Evolution of the Human Microbiota: Fire, Farming and Antibiotics. Genes, 6(3), 841-857. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes6030841