Detection of Acidic Pharmaceutical Compounds Using Virus-Based Molecularly Imprinted Polymers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Amplification and Purification of Phage
2.3. Electrochemical Polymerization of MIP and MIP with Filamentous Bacteriophage (MIP-Phage)
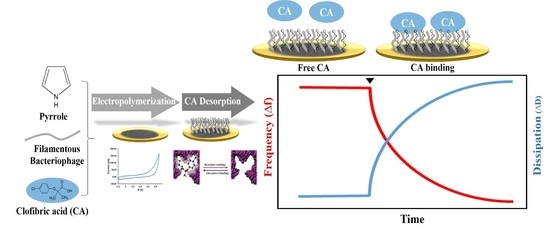
2.4. Analysis of the Viscoelastic Properties and Topography of the Polypyrrole Matrix
2.5. UV/VIS Spectroscopy Measurement
2.6. Liquid Chromatography—Tandem Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.7. Selectivity of MIP and MIP-Phage
2.8. Reusability of MIP and MIP-Phage
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electropolymerization of Polypyrrole—Phage Biocomposites
3.2. UV/VIS Characterization of Pyrrole, Phage, and CA Complexes
3.3. SEM Analysis of Polypyrrole Matrix Topography
3.4. Interaction of CA with the Polypyrrole Matrix on a Microbalance Sensor
3.5. Binding Efficiency and Capacity of CA to Polypyrrole Matrix on Microbalance Sensor
3.6. Binding Selectivity of NIP, MIP, and MIP-Phage
3.7. Reusability of MIP and MIP-Phage
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Larsson, D.G. Pollution from drug manufacturing: Review and perspectives. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, R.E.; Puri, V.; Dominguez, M.; Marks, D.L. Membrane traffic in sphingolipid storage diseases. Traffic 2000, 1, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esplugas, S.; Bila, D.M.; Krause, L.G.; Dezotti, M. Ozonation and advanced oxidation technologies to remove endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in water effluents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 149, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viruna, N.; Alex, D.; Luke, W.; Iain, P.H. Statin and fibrate-induced dichotomy of mitochondrial function. In Mitochondrial Dysfunction Caused by Drugs and Environmental Toxicants; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 459–473. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, C.-M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Zhou, X.-F.; Duan, Y.-P.; Liu, S.-G. Selective removal of acidic pharmaceuticals from contaminated lake water using multi-templates molecularly imprinted polymer. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 211–212, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didaskalou, C.; Buyuktiryaki, S.; Kecili, R.; Fonte, C.P.; Szekely, G. Valorisation of agricultural waste with adsorption/nanofiltration hybrid process: From materials to sustainable process design. Green Chem. 2017, 13, 3116–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, A.I.; Esteves, T.; Afonso, C.A.; Ferreira, F.C. Solvent compatible polymer functionalization with adenine, a DNA base, for api degenotoxification: Preparation and characterization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 179, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Lu, W.; Wu, X.; Li, J. Molecular imprinting: Perspectives and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2137–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirsch, N.; Hedin-Dahlström, J.; Henschel, H.; Whitcombe, M.J.; Wikman, S.; Nicholls, I.A. Molecularly imprinted polymer catalysis of a diels-alder reaction. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2009, 58, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, S.; Liu, W.; Fu, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, L. Molecular imprinting based hybrid ratiometric fluorescence sensor for the visual determination of bovine hemoglobin. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Wu, X.; Fu, J.; Kang, Q.; Shen, D.; Li, J.; Chen, L. A molecular imprinting-based turn-on ratiometric fluorescence sensor for highly selective and sensitive detection of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 81, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Sharma, R.C. Advances in conductive polymers. Eur. Polym. J. 1998, 34, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.J.; Tong, Y.W. The effect of protein structural conformation on nanoparticle molecular imprinting of ribonuclease a using miniemulsion polymerization. Langmuir 2007, 23, 2722–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanazawa, K.K.; Diaz, A.F.; Geiss, R.H.; Gill, W.D.; Kwak, J.F.; Logan, J.A.; Rabolt, J.F.; Street, G.B. Organic metals—Polypyrrole, a stable synthetic metallic polymer. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1979, 19, 854–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.W.; Bruckman, M.A.; Harp, B.; Mello, C.M.; Wang, Q. Bacteriophage m13 as a scaffold for preparing conductive polymeric composite fibers. Nano Res. 2008, 1, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, R.J.; Tsai, C.L.; Ma, L.P.; Ouyang, J.Y. Digital memory device based on tobacco mosaic virus conjugated with nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2006, 1, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeel, A.; Adnan, M.; Romana, S.; Sadia Zafar, B.; Usman, L.; Saima, F. Gravimetric viral diagnostics: Qcm based biosensors for early detection of viruses. Chemosensors 2017, 5, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Arter, J.A.; Taggart, D.K.; McIntire, T.M.; Penner, R.M.; Weiss, G.A. Virus-pedot nanowires for biosensing. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 4858–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhou, X.F.; Liu, S.G. Application of molecularly imprinted polymers to selective removal of clofibric acid from water. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupai, J.; Razali, M.; Buyuktiryaki, S.; Kecili, R.; Szekely, G. Long-term stability and reusability of molecularly imprinted polymers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarafraz-Yazdi, A.; Razavi, N. Application of molecularly-imprinted polymers in solid-phase microextraction techniques. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 73, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Shinde, S.; Yeung, S.Y.; Jakštaitė, M.; Li, Q.; Wingren, A.G.; Sellergren, B. An epitope-imprinted biointerface with dynamic bioactivity for modulating cell–biomaterial interactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2017, 56, 15959–15963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, S.P.; Kougianos, E. Biosensors: A tutorial review. IEEE Potentials 2006, 25, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodahl, M.; Hook, F.; Fredriksson, C.; Keller, C.A.; Krozer, A.; Brzezinski, P.; Voinova, M.; Kasemo, B. Simultaneous frequency and dissipation factor qcm measurements of biomolecular adsorption and cell adhesion. Faraday Discuss. 1997, 107, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehoe, J.W.; Kay, B.K. Filamentous phage display in the new millennium. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 4056–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Glucksman, M.J.; Makowski, L. Structural polymorphism correlated to surface-charge in filamentous bacteriophages. Biophys. J. 1992, 61, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoylova, T.I.; Braden, T.D.; Spencer, J.A.; Bartol, F.F. Immunocontraception: Filamentous bacteriophage as a platform for vaccine development. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 3907–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, C.M.; Barker, N.; Lee, S.W.; Perkins, E.J. M13 bacteriophage production for large-scale applications. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 37, 2067–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Song, J.; Hwang, M.P.; Lee, K.H. Nanoscale bacteriophage biosensors beyond phage display. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 3917–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Arutyunov, D.; Szymanski, C.M.; Evoy, S. Bacteriophage based probes for pathogen detection. Analyst 2012, 137, 3405–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.H.; Alcaine, S.D.; Jiang, Z.W.; Rotello, V.M.; Nugen, S.R. Detection of Escherichia coli in drinking water using t7 bacteriophage-conjugated magnetic probe. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 8977–8984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Qiu, H.; Shen, H.; Pan, J.; Dai, X.; Yan, Y.; Pan, G.; Sellergren, B. Molecularly imprinted fluorescent hollow nanoparticles as sensors for rapid and efficient detection lambda-cyhalothrin in environmental water. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorokulova, I.; Olsen, E.; Vodyanoy, V. Bacteriophage biosensors for antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2014, 11, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirale, D.J.; Bangar, M.A.; Park, M.; Yates, M.V.; Chen, W.; Myung, N.V.; Mulchandani, A. Label-free chemiresistive immunosensors for viruses. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 9030–9035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.K.; Yun, D.S.; Belcher, A.M. Cobalt ion mediated self-assembly of genetically engineered bacteriophage for biomimetic co-pt hybrid material. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yacoby, I.; Shamis, M.; Bar, H.; Shabat, D.; Benhar, I. Targeting antibacterial agents by using drug-carrying filamentous bacteriophages. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 2087–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrico, Z.M.; Farkas, M.E.; Zhou, Y.; Hsiao, S.C.; Marks, J.D.; Chokhawala, H.; Clark, D.S.; Francis, M.B. N-terminal labeling of filamentous phage to create cancer marker imaging agents. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 6675–6680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merzlyak, A.; Indrakanti, S.; Lee, S.W. Genetically engineered nanofiber-like viruses for tissue regenerating materials. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, D.Y.; Dang, X.N.; Yi, H.J.; Allen, M.A.; Xu, K.; Lee, Y.J.; Belcher, A.M. Graphene sheets stabilized on genetically engineered m13 viral templates as conducting frameworks for hybrid energy-storage materials. Small 2012, 8, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.L.; Wang, R.Z.; Liu, Y.G.; Zeng, G.M.; Lai, C.; Xu, P.; Lu, B.A.; Xu, J.J.; Wang, C.; Huang, C. Application of molecularly imprinted polymers in wastewater treatment: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 963–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkmaz, N.; Kim, Y.J.; Nam, C.H. Bacteriophages as templates for manufacturing supramolecular structures. Macromol. Biosci. 2013, 13, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweiger, B.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Ulbricht, M. Electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polypyrrole film for sensing of clofibric acid. Sensors 2015, 15, 4870–4889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, B.K.; Sathyamurthy, N. Pi-pi interaction in pyridine. J. Phys. Chem. A 2005, 109, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Song, T.; Yin, X.; Jin, P.; Xiao, J. Synthesis, crystal analysis, and optoelectronic properties of diazole-functionalized acenes and azaacenes. Chemistry 2018, 24, 6572–6579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, D.J.; Rosenstein, R.D. The structure elucidation of rhazinilam, a new class of alkaloids from the apocynaceae, by X-ray analysis. Tetrahedron Lett. 1972, 13, 909–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadari, R. A study on the interactions of amino acids with nitrogen doped graphene; docking, md simulation, and qm/mm studies. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 4352–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janaky, C.; Endrodi, B.; Hajdu, A.; Visy, C. Synthesis and characterization of polypyrrole–magnetite–vitamin b12 hybrid composite electrodes. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2010, 14, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, C.A.; Lawson, K.R.; Perkins, J.; Urch, C.J. Aromatic interactions. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2 2001, 651–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modin, C.; Stranne, A.L.; Foss, M.; Duch, M.; Justesen, J.; Chevallier, J.; Andersen, L.K.; Hemmersam, A.G.; Pedersen, F.S.; Besenbacher, F. QCM-D studies of attachment and differential spreading of pre-osteoblastic cells on Ta and Cr surfaces. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1346–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duner, G.; Thormann, E.; Dedinaite, A. Quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation (Qcm-D) studies of the viscoelastic response from a continuously growing grafted polyelectrolyte layer. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 408, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emudianughe, T.S.; Caldwell, J.; Sinclair, K.A.; Smith, R.L. Species differences in the metabolic conjugation of clofibric acid and clofibrate in laboratory animals and man. Drug Metab. Dispos. Biol. Fate Chem. 1983, 11, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weigel, S.; Kuhlmann, J.; Huhnerfuss, H. Drugs and personal care products as ubiquitous pollutants: Occurrence and distribution of clofibric acid, caffeine and deet in the North Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 295, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heberer, T.; Schmidt-Baumler, K.; Stan, H.J. Occurrence and distribution of organic contaminants in the aquatic system in berlin. Part 1: Drug residues and other polar contaminants in berlin surface and groundwater. Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 1998, 26, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svenson, J.; Andersson, H.S.; Piletsky, S.A.; Nicholls, I.A. Spectroscopic studies of the molecular imprinting self-assembly process. J. Mol. Recognit. 1998, 11, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Regression Model | Function |
|---|---|
| Hill (H) | |
| Binding efficiency (%) |
| Imprinted Polymers | RM 1 | R 2 | Model Parameter | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A 2 | Β 3 | Γ 4 | |||
| NIP | H | 0.982 | −13.7500 | 24.6453 | 46.2427 |
| MIP | H | 0.987 | −68.7239 | 1.2715 | 142.6995 |
| MIP-phage | H | 0.995 | −99.0498 | 1.0592 | 143.4342 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baek, I.-H.; Han, H.-S.; Baik, S.; Helms, V.; Kim, Y. Detection of Acidic Pharmaceutical Compounds Using Virus-Based Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Polymers 2018, 10, 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10090974
Baek I-H, Han H-S, Baik S, Helms V, Kim Y. Detection of Acidic Pharmaceutical Compounds Using Virus-Based Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Polymers. 2018; 10(9):974. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10090974
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaek, In-Hyuk, Hyung-Seop Han, Seungyun Baik, Volkhard Helms, and Youngjun Kim. 2018. "Detection of Acidic Pharmaceutical Compounds Using Virus-Based Molecularly Imprinted Polymers" Polymers 10, no. 9: 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10090974
APA StyleBaek, I.-H., Han, H.-S., Baik, S., Helms, V., & Kim, Y. (2018). Detection of Acidic Pharmaceutical Compounds Using Virus-Based Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Polymers, 10(9), 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10090974