Catalytic Oxidation of Propene over Pd Catalysts Supported on CeO2, TiO2, Al2O3 and M/Al2O3 Oxides (M = Ce, Ti, Fe, Mn)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
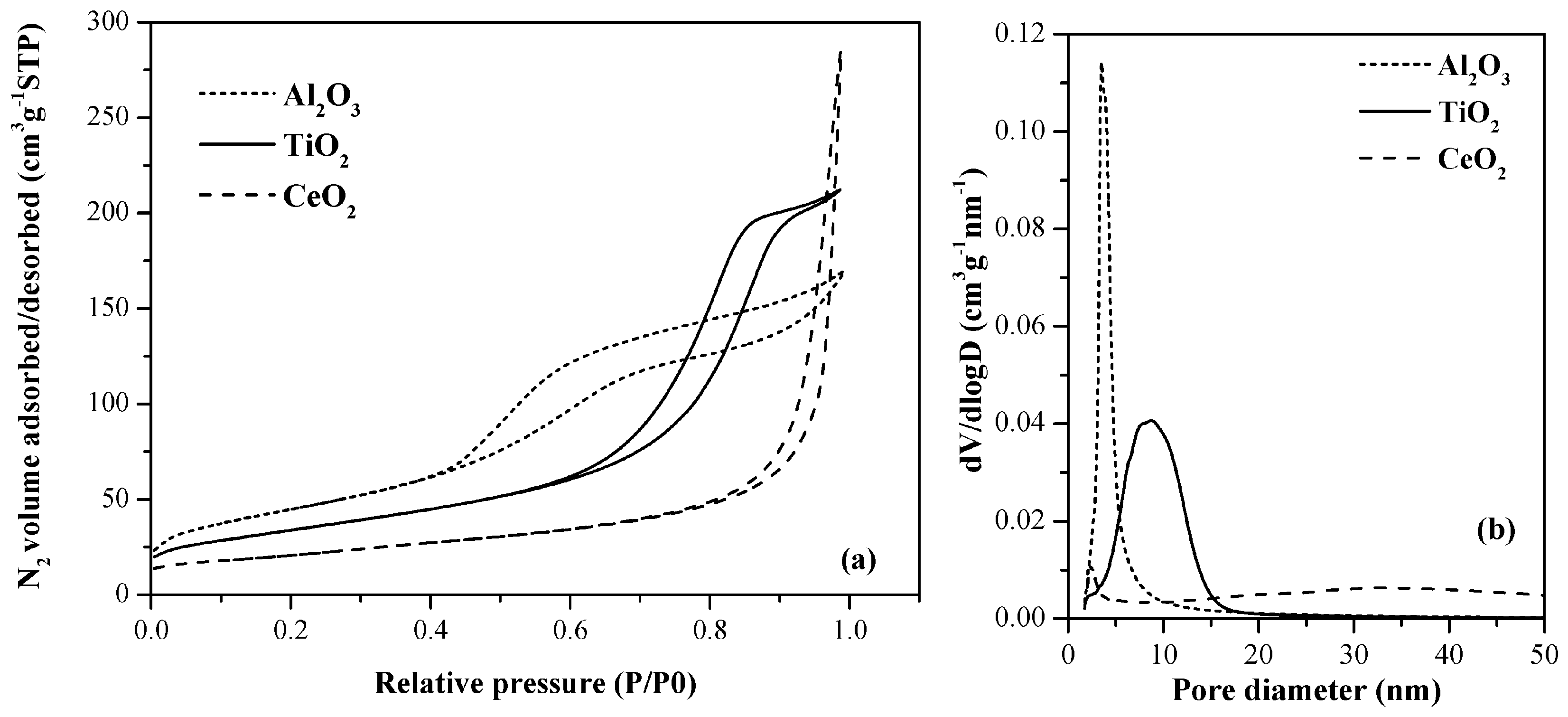
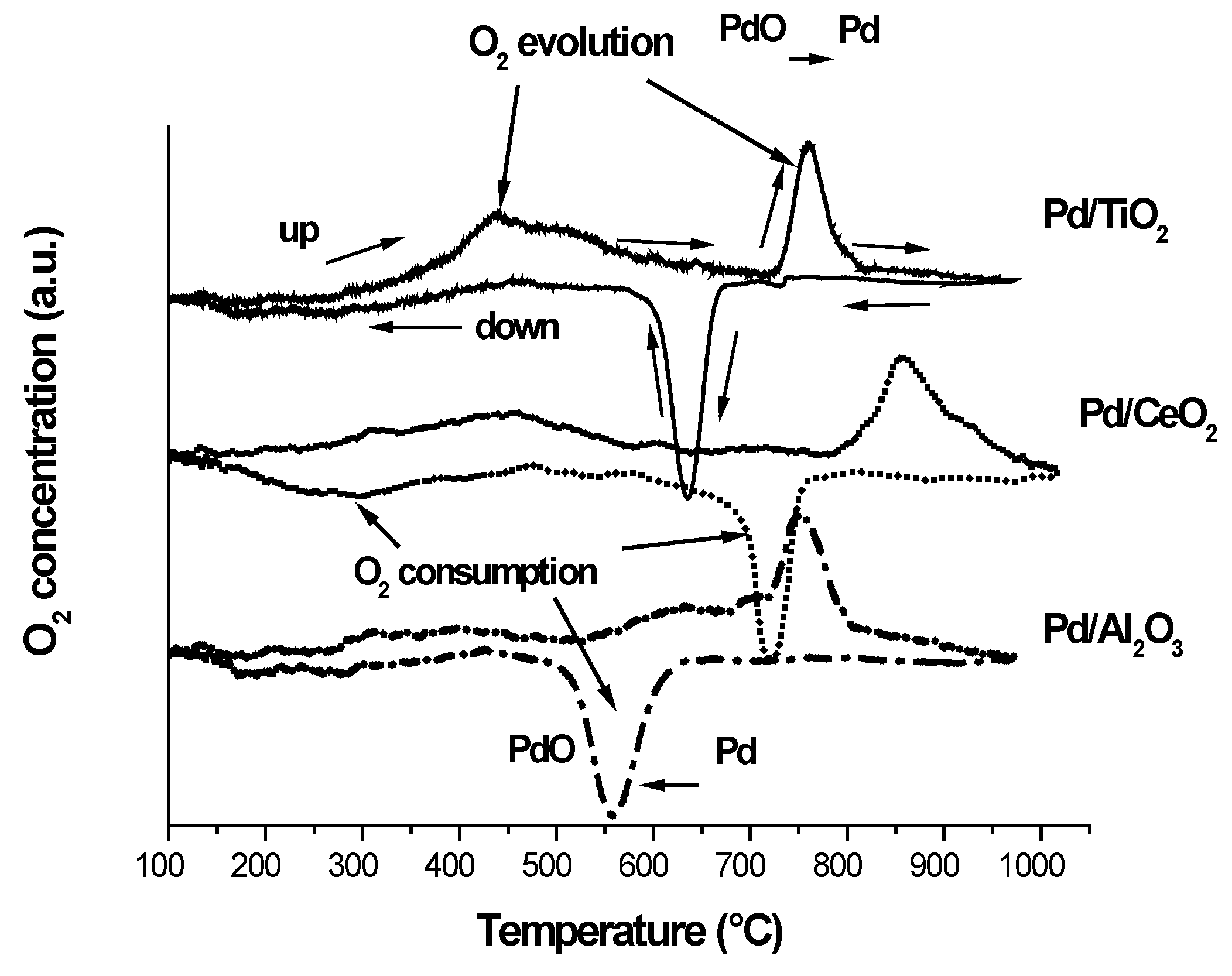
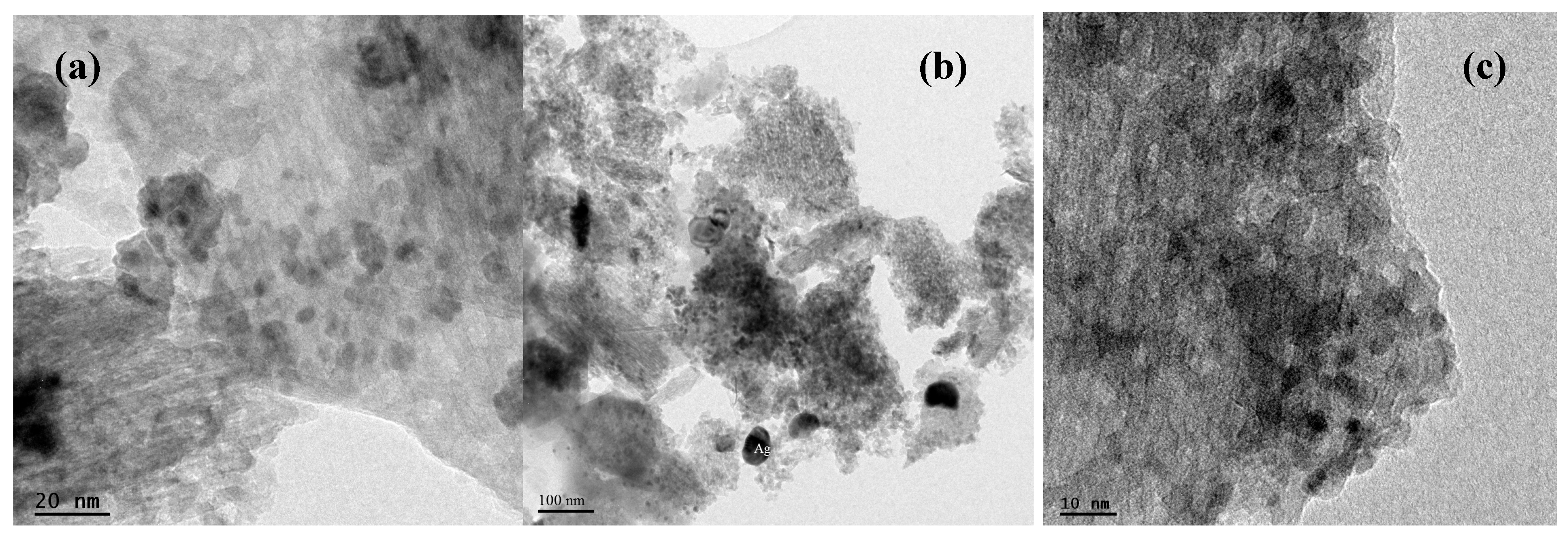
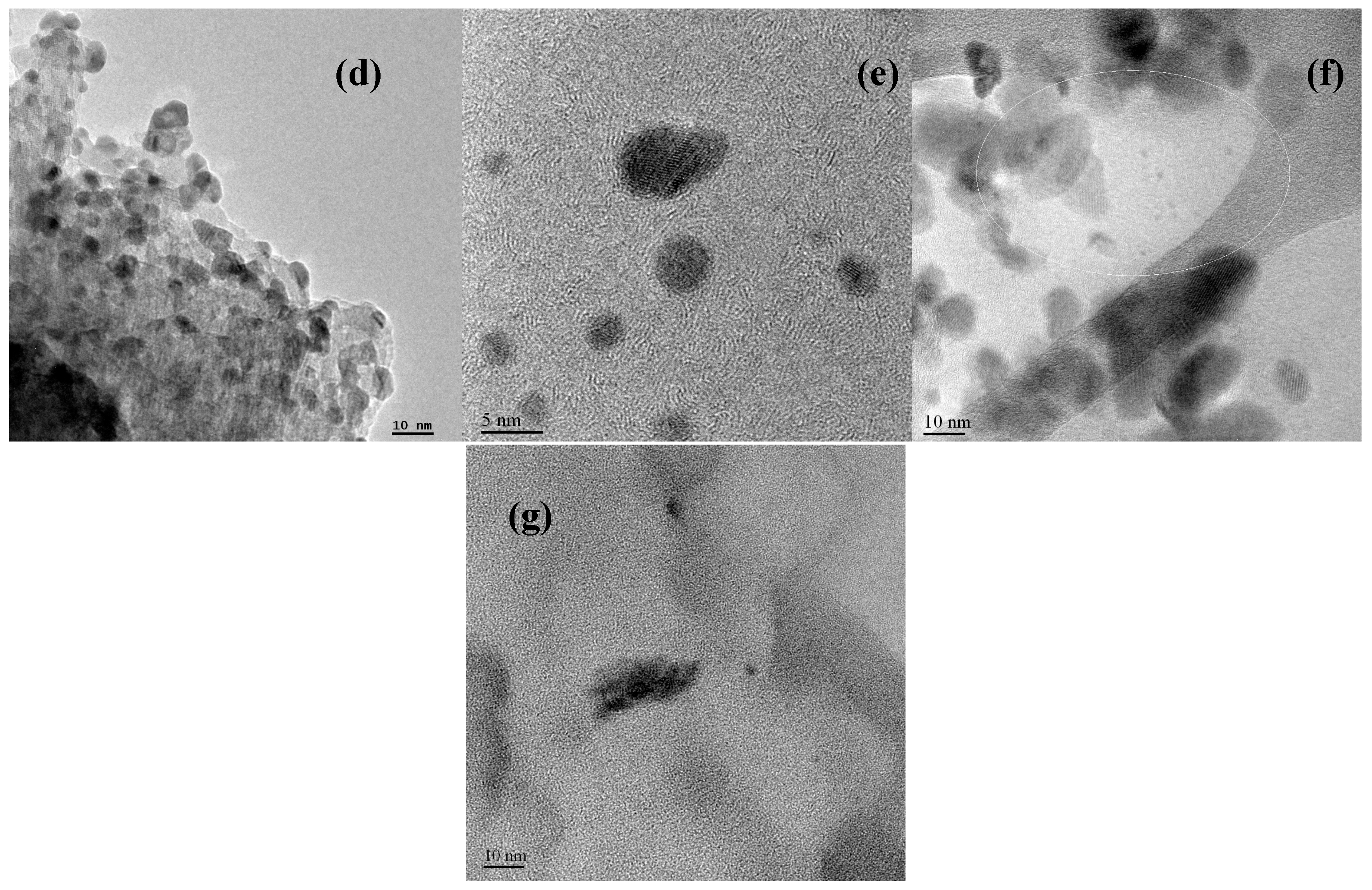
2.1. Support and Catalysts Characterization
| Supports | BET surface area (m2·g−1) | BET surface area APT1 (m2·g−1) | Total pore volume (cm3·g−1) | Mean pore diameter (nm) 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2 | 115 | - | 0.3 | 8.1 |
| CeO2 | 79 | - | 0.4 | 15.0–50.0 (broad curve) |
| Al2O3 | 157 | - | 0.2 | 4.6 |
| Ce/Al2O3 | 140 | 128 | 0.2 | 5.0 |
| Ti/Al2O3 | 155 | 150 | 0.2 | 4.5 |
| Fe/Al2O3 | 145 | 143 | 0.2 | 5.0 |
| Mn/Al2O3 | 146 | 145 | 0.2 | 5.0 |
| Catalysts | BET surface area (m2·g−1) | BET surface area APT1 (m2·g−1) | Pd loading (wt%) 2 | dCeO2 (nm) 3 | p-Value 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd/TiO2 | 102 | 99 | 0.8 | - | 0.64 |
| Pd/CeO2 | 77 | 77 | 0.5 | 105 | 0.86 |
| Pd/Al2O3 | 148 | 144 | 0.8 | - | 1.04 |
| Pd/Ce/Al2O3 | 137 | 132 | 0.8 | 13 | - |
| Pd/Ti/Al2O3 | 154 | 142 | 0.8 | - | - |
| Pd/Fe/Al2O3 | 138 | 130 | 0.8 | - | - |
| Pd/Mn/Al2O3 | 135 | 138 | 0.8 | - | - |


| Catalysts | Binding Energies (eV) | Atomic Surface Ratio | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al 2p | 1 Pd 3d5/2. Bulk PdO | 1 Pd 3d5/2. PdO2 | O 1s | Ti 2p3/2 | Ce 3d5/2 | 2 Ce4+ | 2 Ce3+ | Fe 2p3/2 | Mn 2p3/2 | O/Al | M/Al | |
| Pd/TiO2 | - | 336.1 (100) | - | 529.7 | 458.4 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Pd/CeO2 | - | - | 337.4 (100) | 529.1 | - | 881.9 | 83 | 17 | - | - | - | |
| Pd/Al2O3 | 74.1 | 336.4 (100) | - | 530.8 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.66 | |
| Pd/Ce/Al2O3 | 74.2 | 336.1 (83.2) | 338.1 (16.4) | 530.9 | - | 882.1 | 69 | 31 | - | - | 1.92 | 0.025 |
| Pd/Ti/Al2O3 | 74 | 336.3 (100) | - | 530.8 | 458.5 | - | - | - | - | - | 1.79 | 0.052 |
| Pd/Fe/Al2O3 | 74 | 336.1 (100) | - | 530.5 | - | - | - | - | 710 | - | 1.90 | 0.09 |
| Pd/Mn/Al2O3 | 74 | 336.7 (100) | - | 530.9 | - | - | - | - | - | 641.9 | 1.74 | 0.04 |
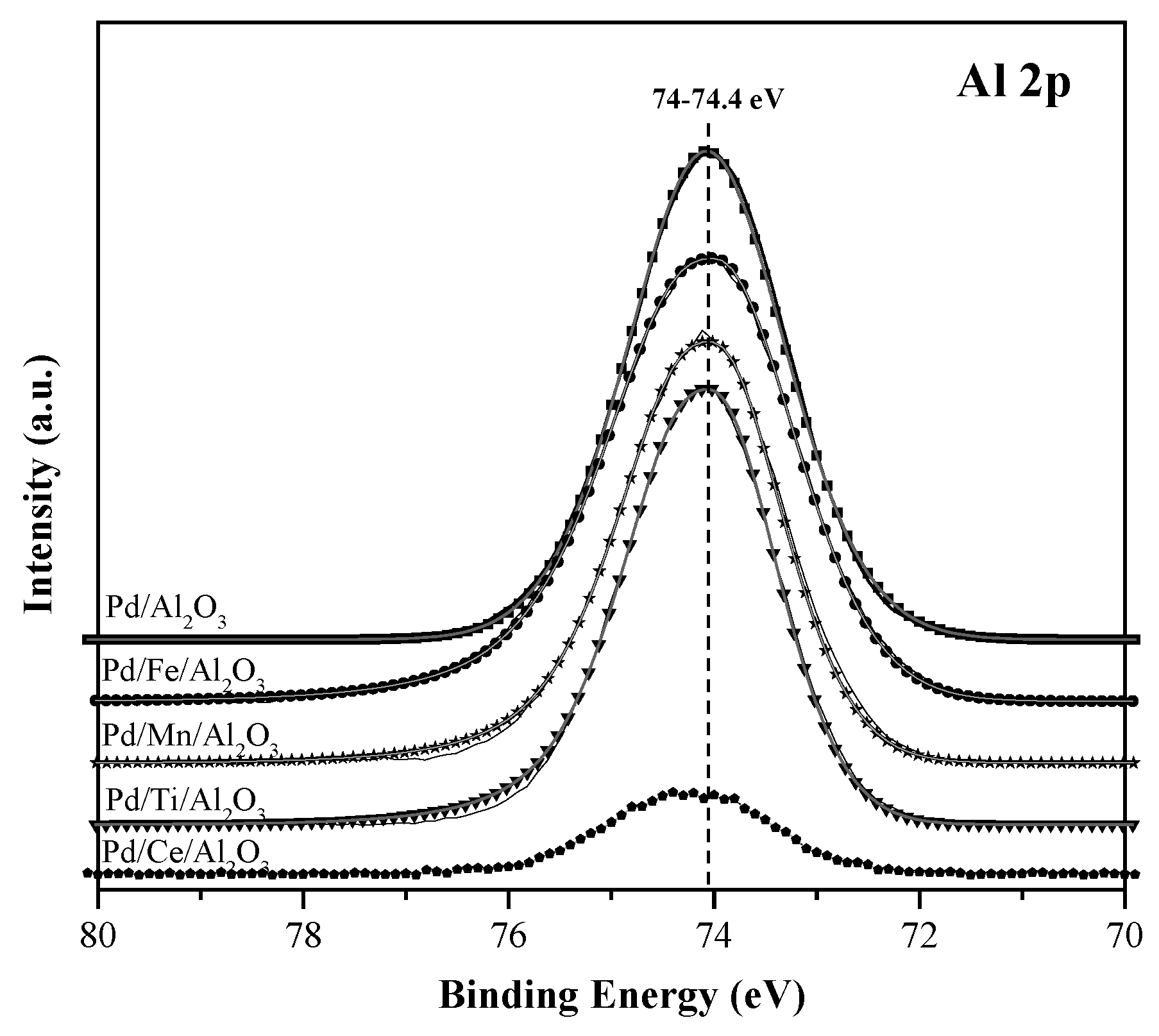
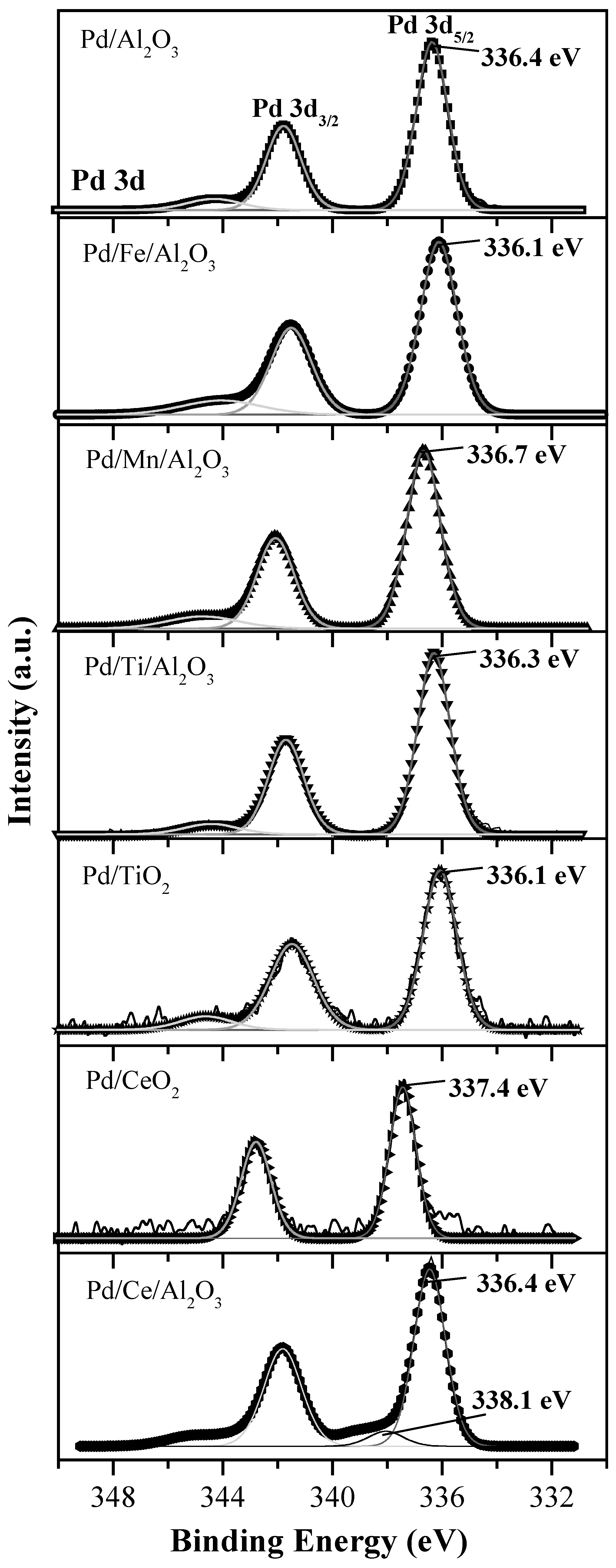
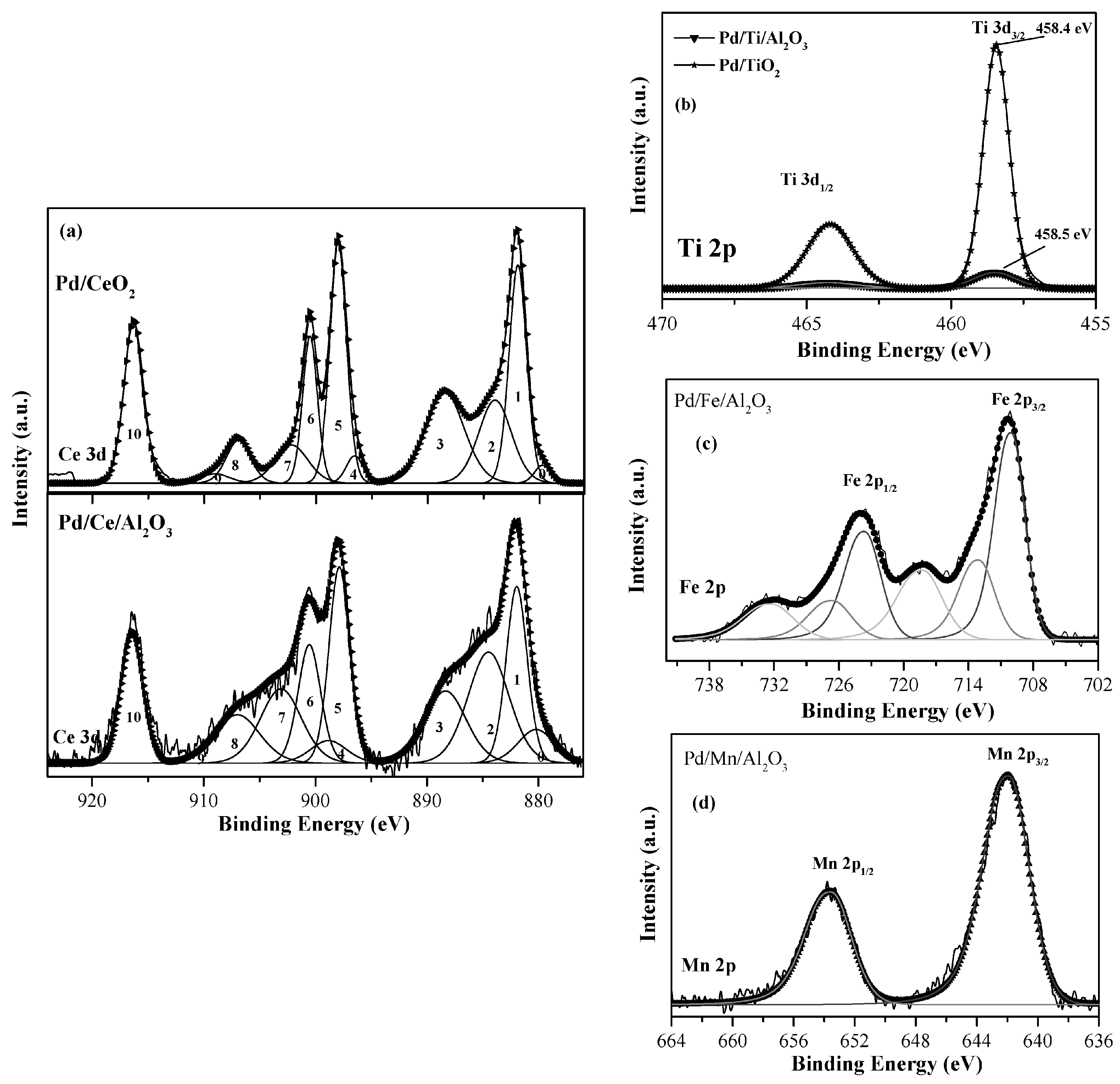
2.2. Catalytic Tests: Oxidation of Propene

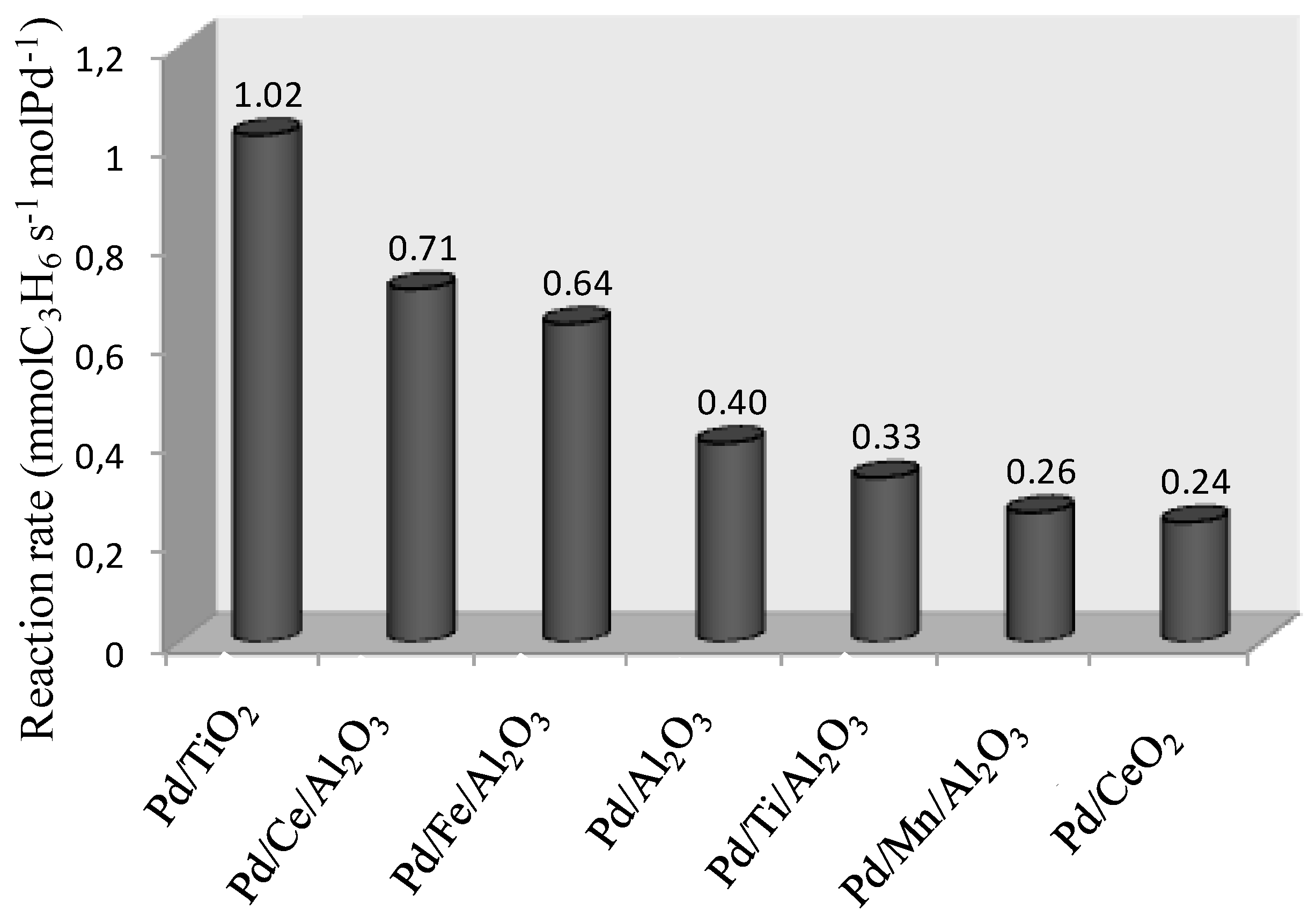
| Catalysts | T20 (°C) 1 | T50 (°C) 1 | T80 (°C) 1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I run | II run | III run | I run | II run | III run | I run | II run | III run | |
| Pd/TiO2 | 136 | 139 | 142 | 150 | 154 | 157 | 158 | 163 | 166 |
| Pd/CeO2 | 162 | 162 | 166 | 189 | 190 | 192 | 213 | 214 | 217 |
| Pd/Al2O3 | 149 | 152 | 155 | 160 | 164 | 170 | 172 | 175 | 182 |
| Pd/Ce/Al2O3 | 141 | 144 | 148 | 150 | 153 | 159 | 161 | 164 | 169 |
| Pd/Fe/Al2O3 | 142 | 145 | 153 | 154 | 157 | 165 | 170 | 172 | 174 |
| Pd/Mn/Al2O3 | 153 | 155 | 159 | 166 | 169 | 175 | 180 | 183 | 189 |
| Pd/Ti/Al2O3 | 150 | 152 | 158 | 163 | 166 | 170 | 183 | 186 | 187 |
| Catalysts | Eact (KJ·mol−1) | LnA |
|---|---|---|
| Pd/CeO2 | 93.7 | 26.7 |
| Pd/Al2O3 | 132 | 38.4 |
| Pd/TiO2 | 95.3 | 28.7 |
| Pd/Ce/Al2O3 | 162.6 | 48.1 |
| Pd/Fe/Al2O3 | 161.1 | 47.4 |
| Pd/Ti/Al2O3 | 135.1 | 39.1 |
| Pd/Mn/Al2O3 | 130.7 | 37.6 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Catalyst Preparation
3.2. Catalysts Characterization
3.3. Catalytic Tests
3.4. Analysis of Products
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amann, M.; Lutz, M. The revision of the air quality legislation in the European Union related to ground-level ozone. J. Hazard. Mater. 2000, 78, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liotta, L.F.; Ousmane, M.; Di Carlo, G.; Pantaleo, G.; Deganello, G.; Marcì, G.; Retailleau, L.; Giroir-Fendler, A. Total oxidation of propene at low temperature over Co3O4–CeO2 mixed oxides: Role of surface oxygen vacancies and bulk oxygen mobility in the catalytic activity. Appl. Catal. A 2008, 347, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez, A.; Molina, R.; Moreno, S. Enhanced voc oxidation over Ce/CoMgAl mixed oxides using a reconstruction method with edta precursors. Appl. Catal. A 2014, 477, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahousse, C.; Bernier, A.; Grange, P.; Delmon, B.; Papaefthimiou, P.; Ioannides, T.; Verykios, X. Evaluation of γ-MnO2 as a VOC removal catalyst: Comparison with a noble metal catalyst. J. Catal. 1998, 178, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloirec, P.L. Les Composés Organiques Volatils Dans L’environnement; Lavoisier, Tec et Doc: Paris, France, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, M.; Barakat, T.; Cousin, R.; Aboukaïs, A.; Su, B.L.; De Weireld, G.; Siffert, S. Catalytic performance of core-shell and alloy Pd-Au nanoparticles for total oxidation of VOC: The effect of metal deposition. Appl. Catal. B 2012, 111–112, 218–224. [Google Scholar]
- Derwent, R.G.; Jenkin, M.E.; Saunders, S.M.; Pilling, M.J. Photochemical ozone creation potentials for organic compounds in northwest europe calculated with a master chemical mechanism. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 2429–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevenin, P.O.; Ersson, A.G.; Kušar, H.; Menon, P.; Järås, S.G. Deactivation of high temperature combustion catalysts. Appl. Catal. A 2001, 212, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, W.B.; Lewis, D.; Perry, J.; Gandhi, H.S. Durability of palladium automotive catalysts: Effects of trace lead levels, exhaust composition, and misfueling. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 1984, 23, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, A. Platinum 2013. Interim Review; Johnson Matthey: Hertfordshire, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Okumura, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Tanaka, H.; Niwa, M. Toluene combustion over palladium supported on various metal oxide supports. Appl. Catal. B 2003, 44, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venezia, A.M.; Di Carlo, G.; Liotta, L.F.; Pantaleo, G.; Kantcheva, M. Effect of Ti(IV) loading on CH4 oxidation activity and SO2 tolerance of Pd catalysts supported on silica SBA-15 and HMS. Appl. Catal. B 2011, 106, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simplício, L.M.; Brandao, S.T.; Domingos, D.; Bozon-Verduraz, F.; Sales, E.A. Catalytic combustion of methane at high temperatures: Cerium effect on PdO/Al2O3 catalysts. Appl. Catal. A 2009, 360, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooke, J.C.; Barakat, T.; Siffert, S.; Su, B.L. Total catalytic oxidation of toluene using Pd impregnated on hierarchically porous Nb2O5 and Ta2O5 supports. Catal. Today 2012, 192, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, M.G.; Gazquez, J.L. Oxygen vacancy model in strong metal-support interaction. J. Catal. 1987, 104, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Chu, W.; Chen, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T. Preparation of novel titania supported palladium catalysts for selective hydrogenation of acetylene to ethylene. Catal. Commun. 2007, 8, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marécot, P.; Fakche, A.; Kellali, B.; Mabilon, G.; Prigent, P.; Barbier, J. Propane and propene oxidation over platinum and palladium on alumina: Effects of chloride and water. Appl. Catal. B 1994, 3, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillet, T.; Solleau, C.; Barbier, J.; Duprez, D. Oxidation of carbon monoxide, propene, propane and methane over a Pd/Al2O3 catalyst. Effect of the chemical state of pd. Appl. Catal. B 1997, 14, 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, A.; Korneeva, E.; Slavinskaya, E.; Zyuzin, D.; Moroz, E.; Danilova, I.; Gulyaev, R.; Boronin, A.; Stonkus, O.; Zaikovskii, V. Role of the support in the formation of the properties of a Pd/Al2O3 catalyst for the low-temperature oxidation of carbon monoxide. Kinet. Catal. 2014, 55, 748–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cheng, Y.; Seo, C.Y.; Schwank, J.W.; McCabe, R.W. Aging, re-dispersion, and catalytic oxidation characteristics of model Pd/Al2O3 automotive three-way catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 2015, 163, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Angel, G.; Padilla, J.; Cuauhtemoc, I.; Navarrete, J. Toluene combustion on γ-Al2O3-CeO2 catalysts prepared from boehmite and cerium nitrate. J. Mol. Catal. A 2008, 281, 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- Saitzek, S.; Blach, J.F.; Villain, S.; Gavarri, J.R. Nanostructured ceria: A comparative study from X-ray diffraction, raman spectroscopy and bet specific surface measurements. Phys. Status Solidi (a) 2008, 205, 1534–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, B.; Zhou, R.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, X. Study of the methane combustion and TPR/TPO properties of Pd/Ce-Zr-M/Al2O3 catalysts with M = Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba. J. Mol. Catal. A 2005, 238, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, K.; Thevenin, P.; Jansson, K.; Agrell, J.; Järås, S.G.; Pettersson, L.J. Preparation of alumina-supported palladium catalysts for complete oxidation of methane. Appl. Catal. A 2003, 249, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groppi, G.; Cristiani, C.; Lietti, L.; Forzatti, P. Study of PdO/Pd transformation over alumina supported catalysts for natural gas combustion. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2000, 130, 3801–3806. [Google Scholar]
- Tidahy, H.; Siffert, S.; Lamonier, J.-F.; Zhilinskaya, E.; Aboukaïs, A.; Yuan, Z.-Y.; Vantomme, A.; Su, B.-L.; Canet, X.; de Weireld, G. New Pd/hierarchical macro-mesoporous ZrO2, TiO2 and ZrO2-TiO2 catalysts for vocs total oxidation. Appl. Catal. A 2006, 310, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Peña O’Shea, V.; Alvarez-Galvan, M.; Fierro, J.; Arias, P. Influence of feed composition on the activity of Mn and PdMn/Al2O3 catalysts for combustion of formaldehyde/methanol. Appl. Catal. B 2005, 57, 191–199. [Google Scholar]
- Gaya, U.I.; Abdullah, A.H. Heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of organic contaminants over titanium dioxide: A review of fundamentals, progress and problems. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C: Photochem. Rev. 2008, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Ye, X.; Zhang, L.; Leung, D.Y.C. Mechanistic study on formaldehyde removal over Pd/TiO2 catalysts: Oxygen transfer and role of water vapor. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 230, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihm, S.-K.; Jun, Y.-D.; Kim, D.-C.; Jeong, K.-E. Low-temperature deactivation and oxidation state of Pd/γ-Al2O3 catalysts for total oxidation of n-hexane. Catal. Today 2004, 93, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznárez, A.; Korili, S.A.; Gil, A. The promoting effect of cerium on the characteristics and catalytic performance of palladium supported on alumina pillared clays for the combustion of propene. Appl. Catal. A 2014, 474, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Lu, G. Catalytic CO oxidation over palladium supported NaZSM-5 catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 2003, 41, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, R.S.; Dieguez, L.C.; Schmal, M. The role of pd precursors in the oxidation of carbon monoxide over Pd/Al2O3 and Pd/CeO2/Al2O3 catalysts. Catal. Today 2001, 65, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ousmane, M.; Liotta, L.F.; di Carlo, G.; Pantaleo, G.; Venezia, A.; Deganello, G.; Retailleau, L.; Boreave, A.; Giroir-Fendler, A. Supported au catalysts for low-temperature abatement of propene and toluene, as model VOCs: Support effect. Appl. Catal. B 2011, 101, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfau, A.; Schierbaum, K. The electronic structure of stoichiometric and reduced CeO2 surfaces: An XPS, UPS and HREELS study. Surf. Sci. 1994, 321, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burroughs, P.; Hamnett, A.; Orchard, A.F.; Thornton, G. Satellite structure in the X-Ray Photoelectron Spectra of some binary and mixed oxides of lanthanum and cerium. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1976, 1686–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosvenor, A.P.; Kobe, B.A.; Biesinger, M.C.; McIntyre, N.S. Investigation of multiplet splitting of Fe 2p XPS spectra and bonding in iron compounds. Surf. Interface Anal. 2004, 36, 1564–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrandon, M.; Carnö, J.; Järås, S.; Björnbom, E. Total oxidation catalysts based on manganese or copper oxides and platinum or palladium I: Characterisation. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 1999, 180, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, K.-I.; Ribeiro, F.H.; Avalos-Borja, M.; Iglesia, E. Structure and reactivity of PdOx/ZrO2 catalysts for methane oxidation at low temperatures. J. Catal. 1998, 179, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulos, K.; Reyniers, M.-F.; Marin, G.B. Reaction path analysis of propene selective oxidation over V2O5 and V2O5/TiO2. J. Catal. 2012, 295, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.; Bell, A.T. The kinetics of selective oxidation of propene on bismuth vanadium molybdenum oxide catalysts. J. Catal. 2013, 308, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Kanno, T.; Takeda, H.; Fujisaki, S. Reaction pathway design and optimization in heterogeneous catalysis: Ii. Oscillating partial oxidation of propene on Pt/SiO2 designed by widely varying dispersion. Appl. Catal. A 1997, 151, 207–221. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gil, S.; Garcia-Vargas, J.M.; Liotta, L.F.; Pantaleo, G.; Ousmane, M.; Retailleau, L.; Giroir-Fendler, A. Catalytic Oxidation of Propene over Pd Catalysts Supported on CeO2, TiO2, Al2O3 and M/Al2O3 Oxides (M = Ce, Ti, Fe, Mn). Catalysts 2015, 5, 671-689. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal5020671
Gil S, Garcia-Vargas JM, Liotta LF, Pantaleo G, Ousmane M, Retailleau L, Giroir-Fendler A. Catalytic Oxidation of Propene over Pd Catalysts Supported on CeO2, TiO2, Al2O3 and M/Al2O3 Oxides (M = Ce, Ti, Fe, Mn). Catalysts. 2015; 5(2):671-689. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal5020671
Chicago/Turabian StyleGil, Sonia, Jesus Manuel Garcia-Vargas, Leonarda Francesca Liotta, Giuseppe Pantaleo, Mohamed Ousmane, Laurence Retailleau, and Anne Giroir-Fendler. 2015. "Catalytic Oxidation of Propene over Pd Catalysts Supported on CeO2, TiO2, Al2O3 and M/Al2O3 Oxides (M = Ce, Ti, Fe, Mn)" Catalysts 5, no. 2: 671-689. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal5020671






