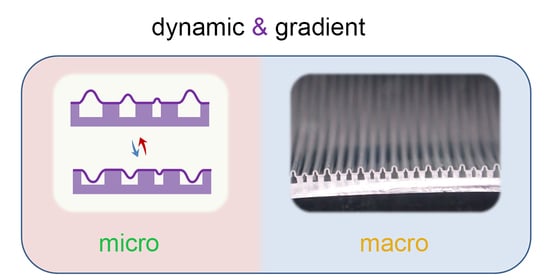
Active Surface with Dynamic Microstructures and Hierarchical Gradient Enabled by in situ Pneumatic Control
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, S.; Wei, W.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Feng, S.; Guo, H.; Li, J. Reconfigurable nano-kirigami metasurfaces by pneumatic pressure. Photonics Res. 2020, 8, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, L.; Pitchappa, P.; Lee, C.; Singh, R. Active phase transition via loss engineering in a terahertz MEMS metamaterial. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, A.; Zhang, S.; Shian, S.; Clarke, D.R.; Cappasso, F. Adaptive metalenses with simultaneous electrical control of focal length, astigmatism, and shift. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaap9957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallin, T.J.; Pikul, J.; Shepherd, R.F. 3D printing of soft robotic systems. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-N.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Feng, J.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y.-H.; Sun, H.-B. Wearable superhydrophobic elastomer skin with switchable wettability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Feng, J.; Ma, R.; Liu, Y.-F.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Zhang, X.-L.; Bi, Y.-G.; Chen, Q.-D.; Sun, H.-B. Efficient and mechanically robust stretchable organic light-emitting devices by a laser-programmable buckling process. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Song, X.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, Y. Recent progress in biomimetic additive manufacturing technology: From materials to functional structures. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706539. [Google Scholar]
- Gladman, A.S.; Matsumoto, E.A.; Nuzzo, R.G.; Mahadevan, L.; Lewis, J.A. Biomimetic 4D printing. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhang, D.; Lv, T.; Lai, H.; Zhang, E.; Kang, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Liu, Y.; Du, Y.; et al. Superhydrophobic shape memory polymer arrays with switchable isotropic/anisotropic wetting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Liu, K.; Yao, X.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired Surfaces with superwettability: New insight on theory, design, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 8230–8293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overvelde, J.T.B.; de Jong, T.A.; Shevchenko, Y.; Becerra, S.A.; Whitesides, G.M.; Weaver, J.C.; Hoberman, C.; Bertoldi, K. A three-dimensional actuated origami-inspired transformable metamaterial with multiple degrees of freedom. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.-Y.; Li, J. Kirigami/origami: Unfolding the new regime of advanced 3D microfabrication/nanofabrication with “folding”. Light Sci. Appl. 2020, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.S.Y.; Gutruf, P.; Sriram, S.; Bhaskaran, M.; Wang, Z.; Tricoli, A. Strain engineering of wave-like nanofibers for dynamically switchable adhesive/repulsive surfaces. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.M.; Liu, A.Q.; Zhang, X.M.; Tsai, D.P.; Bourouina, T.; Teng, J.H.; Zhang, X.H.; Guo, H.C.; Tanoto, H.; Mei, T.; et al. Switchable magnetic metamaterials using micromachining processes. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 1792–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshita, M.; Takahashi, H.; Ajiki, Y.; Kan, T. Reconfigurable surface plasmon resonance photodetector with a MEMS deformable cantilever. ACS Photonics 2020, 7, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Mcadams, D.A.; Grunlan, J.C. Nano/micro-manufacturing of bioinspired materials: A review of methods to mimic natural structures. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 6292–6321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Hogan, A.; Xu, J.; Meyers, M.A. Additive manufacturing as a method to design and optimize bioinspired structures. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C.; Arribart, H.; Guille, M.M.G. Biomimetism and bioinspiration as tools for the design of innovative materials and systems. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Gao, X.; Jiang, L. Directional adhesion of superhydrophobic butterfly wings. Soft Matter 2007, 3, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Ran, T.; Gan, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, L. Ultrafast water harvesting and transport in hierarchical microchannels. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-N.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Feng, J.; Sun, H.-B. Pneumatic smart surfaces with rapidly switchable dominant and latent superhydrophobicity. NPG Asia Mater. 2018, 10, e470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehner, M.; Truby, R.L.; Fitzgerald, D.J.; Mosadegh, B.; Whitesides, G.M.; Lewis, J.A.; Wood, R.J. An integrated design and fabrication strategy for entirely soft, autonomous robots. Nature 2016, 536, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llobera, A.; Juvert, J.; Gonzalez-Fernandez, A.; Ibarlucea, B.; Carregal-Romero, E.; Buttgenbach, S.; Fernandez-Sanchez, C. Biofunctionalized all-polymer photonic lab on a chip with integrated solid-state light emitter. Light Sci. Appl. 2015, 4, e271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eddings, M.A.; Johnson, M.A.; Gale, B.K. Determining the optimal PDMS–PDMS bonding technique for microfluidic devices. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2008, 18, 067001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, D.C.; McDonald, J.C.; Schueller, O.J.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Rapid prototyping of microfluidic systems in poly (dimethylsiloxane). Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 4974–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariga, K.; Li, J.; Fei, J.; Ji, Q.; Hill, J.P. Nanoarchitectonics for dynamic functional materials from atomic-/molecular-level manipulation to macroscopic action. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 1251–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Altenried, S.; Liu, M.; Hegemann, D.; Bulbul, E.; Moeller, J.; Schmahl, W.W.; Maniura-Weber, K.; Ren, Q. A nanolayer coating on polydimethylsiloxane surfaces enables a mechanistic study of bacterial adhesion influenced by material surface physicochemistry. Mater. Horiz. 2020, 7, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Ma, C.; Shen, S.; Tian, C.; Xu, J.; Tu, Q.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Pneumatic microfluidics-based multiplex single-cell array. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 78, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, C.; Dong, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhuo, S.; Zhou, X.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Liu, M. Adaptive superamphiphilic organohydrogels with reconfigurable surface topography for programming unidirectional liquid transport. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1807858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, T.; Isozaki, A.; Kanda, N.; Nemoto, N.; Konishi, K.; Takahashi, H.; Kuwata-Gonokami, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Shimoyama, I. Enantiomeric switching of chiral metamaterial for terahertz polarization modulation employing vertically deformable MEMS spiral. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siefert, E.; Reyssat, E.; Bico, J.; Roman, B. Bio-inspired pneumatic shape-morphing elastomers. Nat. Mater. 2019, 18, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivapooja, P.; Wang, Q.; Orihuela, B.; Rittschof, D.; Lopez, G.P.; Zhao, X. Bioinspired surfaces with dynamic topography for active control of biofouling. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1430–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.-N.; Bai, B.; Chen, Q.-D.; Sun, H.-B. Active Surface with Dynamic Microstructures and Hierarchical Gradient Enabled by in situ Pneumatic Control. Micromachines 2020, 11, 992. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11110992
Wang J-N, Bai B, Chen Q-D, Sun H-B. Active Surface with Dynamic Microstructures and Hierarchical Gradient Enabled by in situ Pneumatic Control. Micromachines. 2020; 11(11):992. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11110992
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jian-Nan, Benfeng Bai, Qi-Dai Chen, and Hong-Bo Sun. 2020. "Active Surface with Dynamic Microstructures and Hierarchical Gradient Enabled by in situ Pneumatic Control" Micromachines 11, no. 11: 992. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11110992
APA StyleWang, J.-N., Bai, B., Chen, Q.-D., & Sun, H.-B. (2020). Active Surface with Dynamic Microstructures and Hierarchical Gradient Enabled by in situ Pneumatic Control. Micromachines, 11(11), 992. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11110992