NMR-Metabolic Methodology in the Study of GM Foods
Abstract
:Abbreviations
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Sample Production
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Sample Preparation for the NMR Analysis
2.4. Acquisition of NMR Spectra
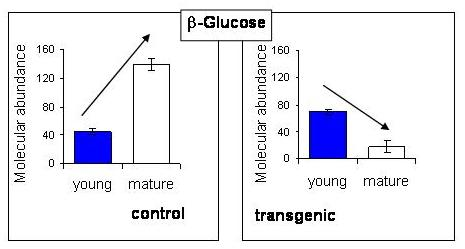
2.5. NMR - Metabolic Application: Characterization of Transgenic and Conventional Lettuce
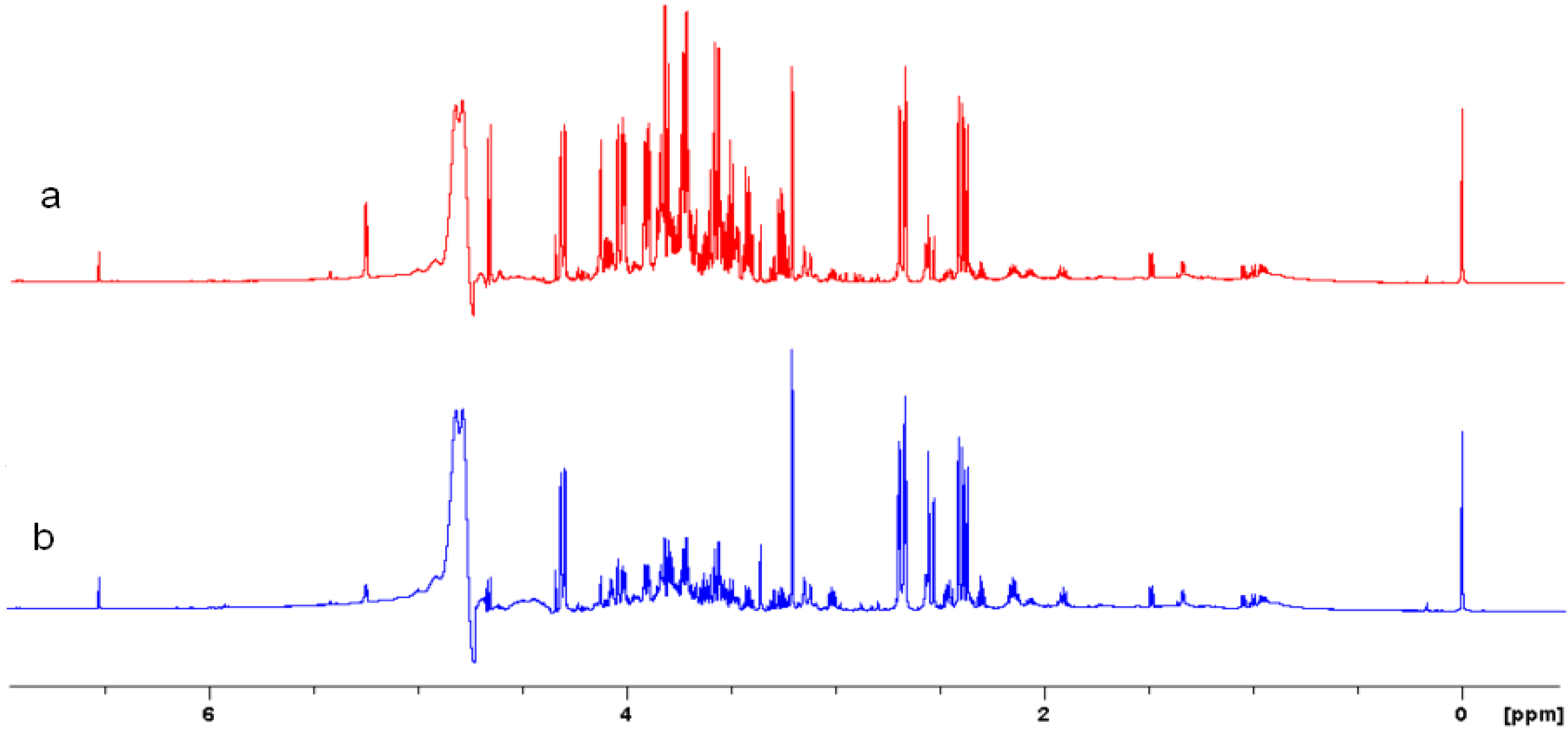
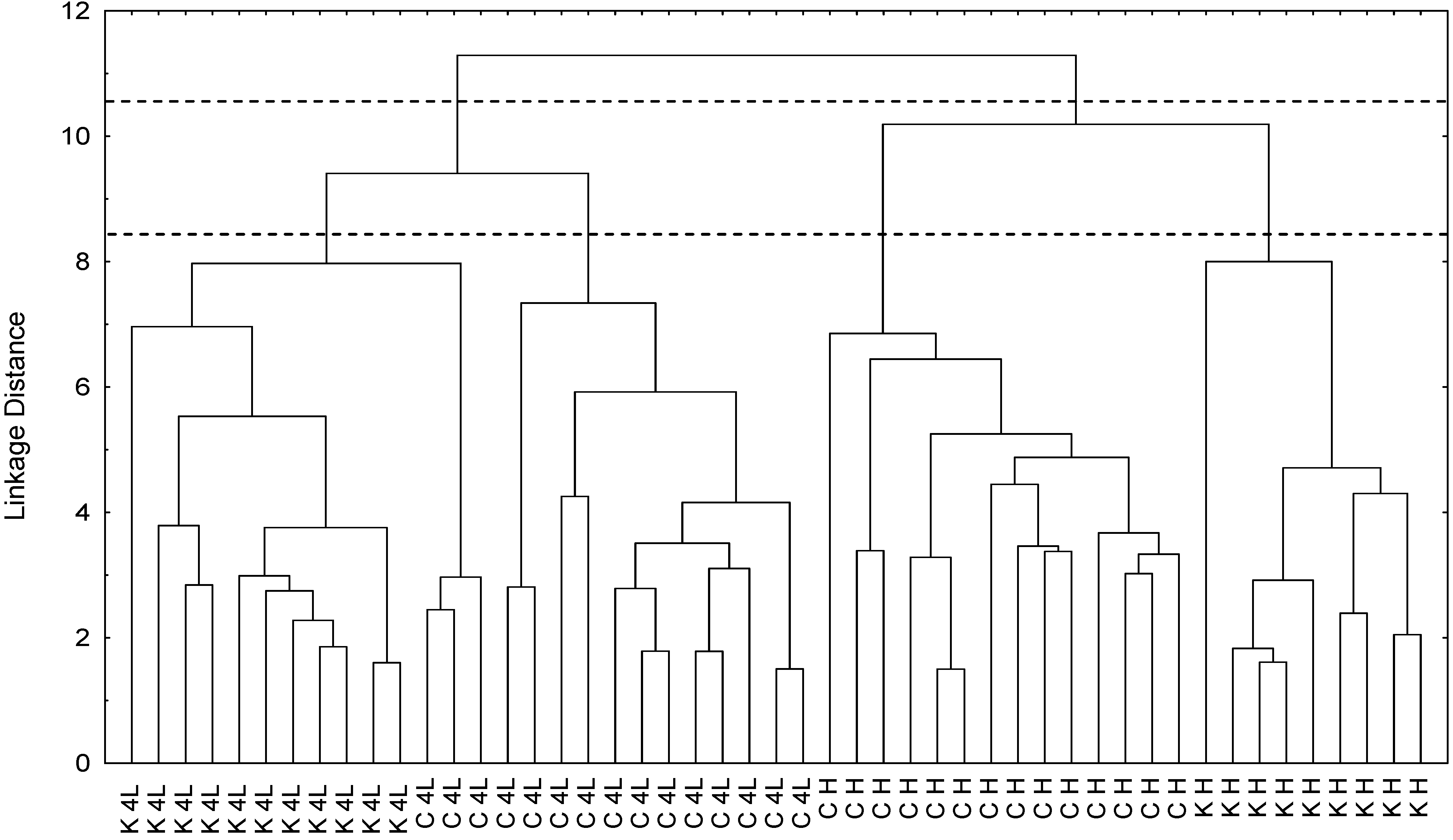
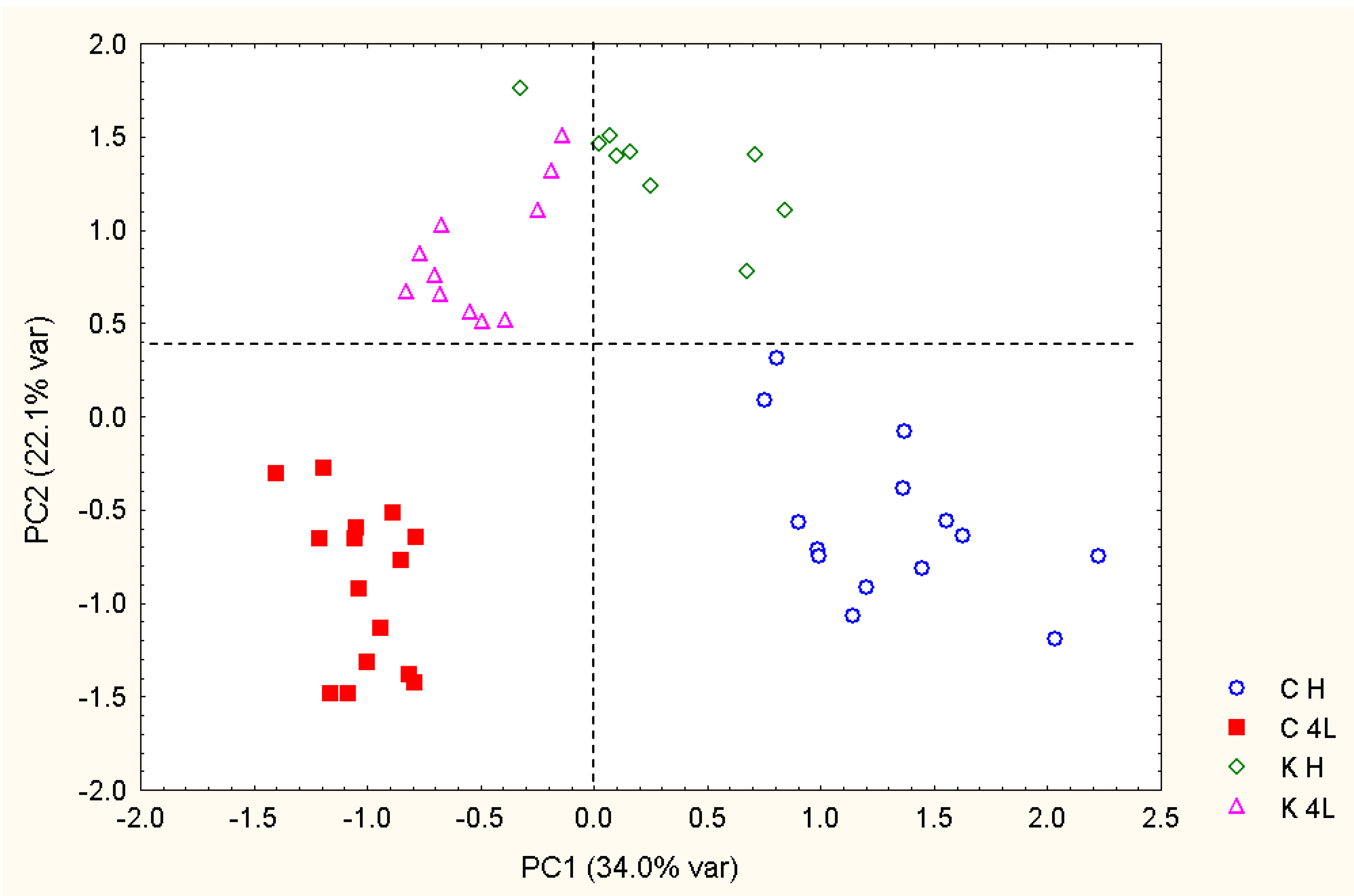
 |
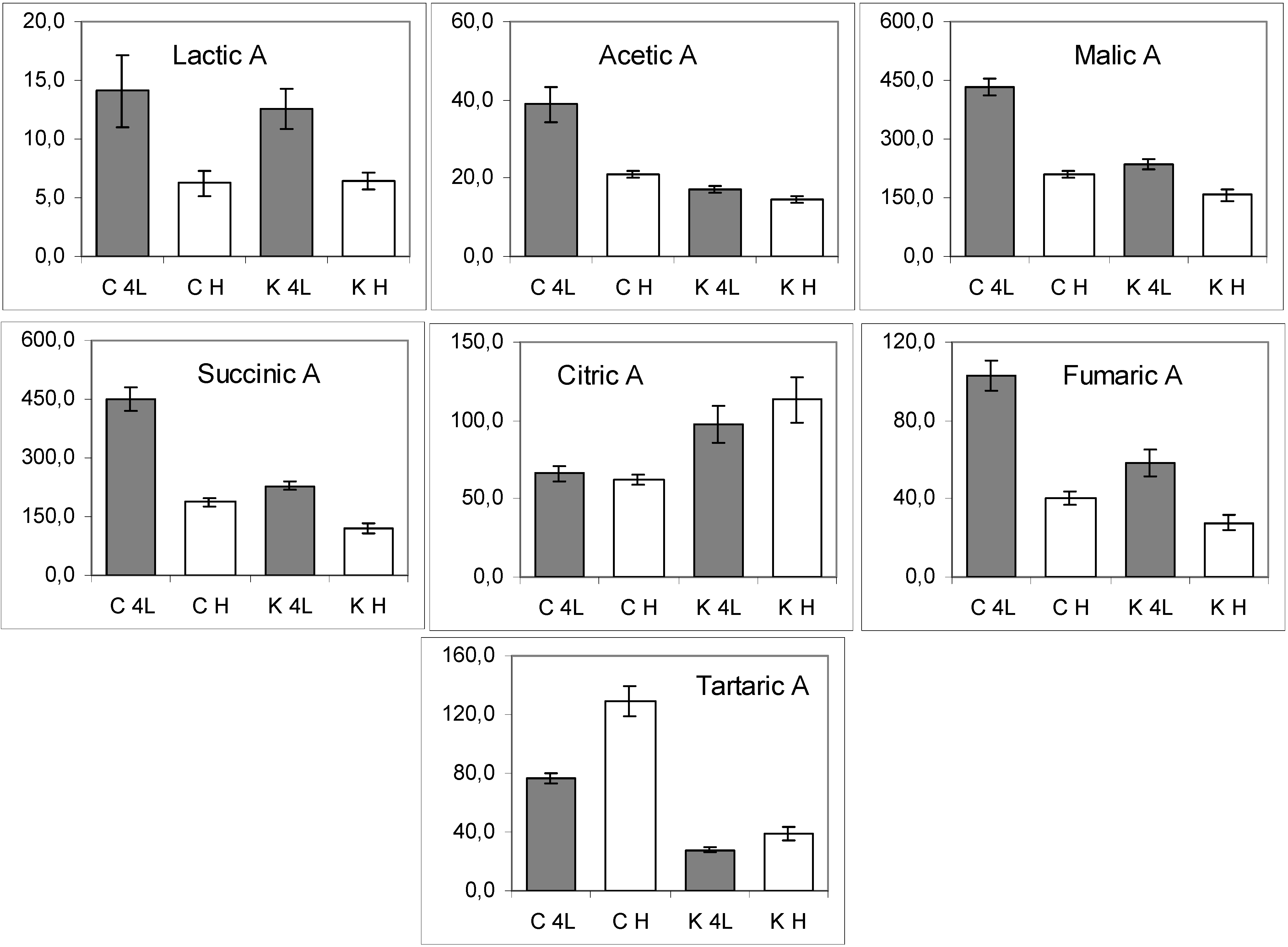
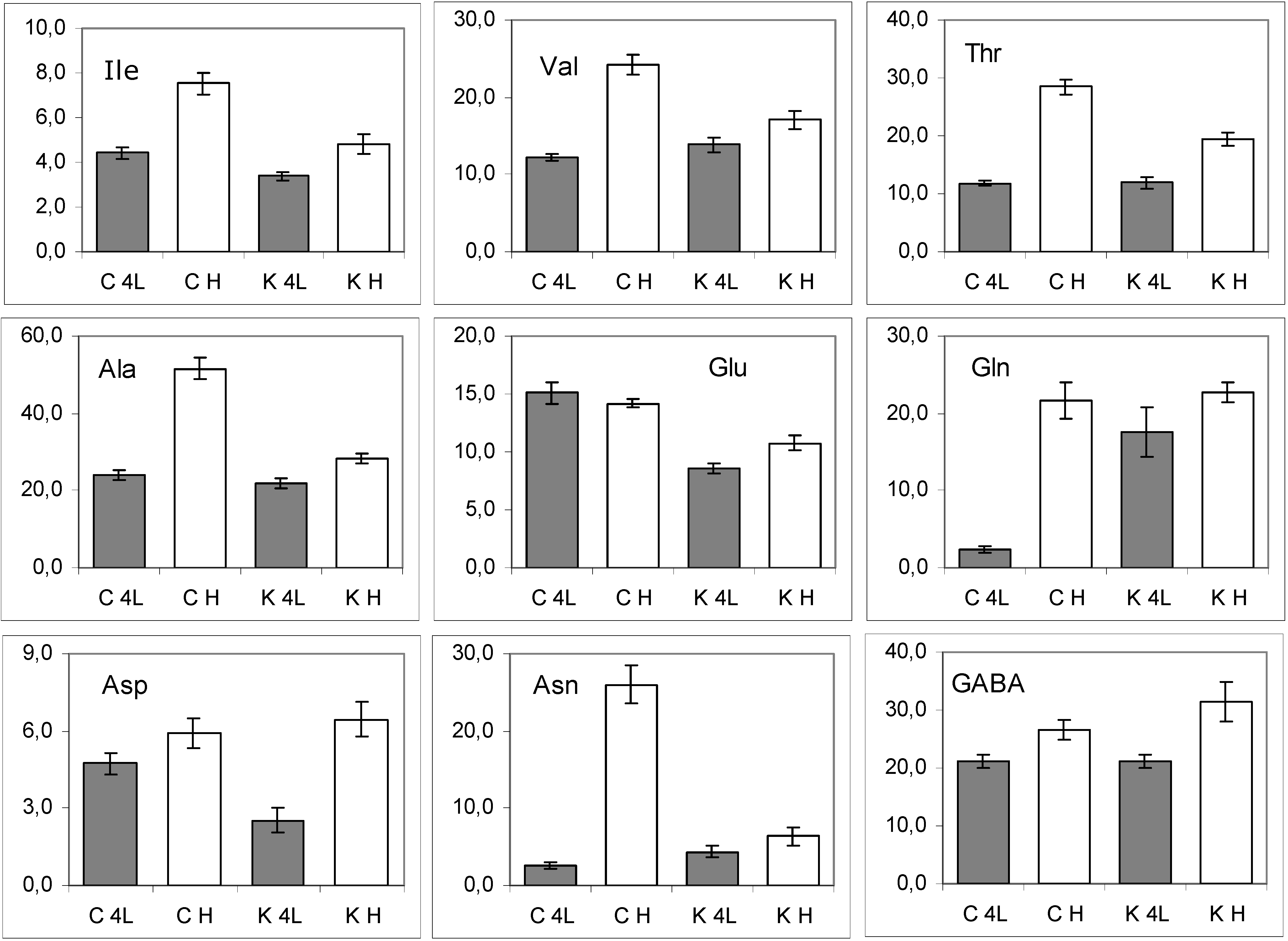

3. Experimental Section
3.1. Plant Material and Sampling
3.2. NMR Analysis
3.3. Measurement of the Metabolic Content in Aqueous Extract
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Fiehn, O. Metabolomics - the link between genotypes and phenotypes. Plant Mol. Biol. 2002, 48, 155–171. [Google Scholar]
- Fiehn, O.; Kopka, J.; Dörmann, P.; Altmann, T.; Trethewey, R.N.; Willmitzer, L. Metabolite profiling for plant functional genomics. Nature Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 1157–1161. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, T.W.-M. Metabolite profiling by one- and two-dimensional NMR analysis of complex mixtures. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 1996, 28, 161–219. [Google Scholar]
- Mannina, L.; Segre, A.L. High resolution NMR: from chemical structure to food authenticity. Grasas Aceites 2002, 53, 22–33. [Google Scholar]
- Sobolev, A.P.; Segre, A.L.; Lamanna, R. Proton high-field NMR study of tomato juice. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2003, 41, 237–245. [Google Scholar]
- Sobolev, A.P.; Brosio, E.; Gianferri, R.; Segre, A.L. Metabolic profile of lettuce leaves by high-field NMR spectra. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2005, 43, 625–638. [Google Scholar]
- Mannina, L.; Sobolev, A.P.; Capitani, D.; Iaffaldano, N.; Rosato, M.P.; Ragni, P.; Reale, A.; Sorrentino, E.; D'Amico, I.; Coppola, R. NMR metabolic profiling of organic and aqueous sea bass extracts: Implications in the discrimination of wild and cultured sea bass. Talanta 2008, 77, 433–444. [Google Scholar]
- Sobolev, A.P.; Segre, A.L.; Giannino, D.; Mariotti, D.; Nicolodi, C.; Brosio, E.; Amato, M.E. Strong increase of foliar inulin occurs in transgenic lettuce plants (Lactuca sativa L.) overexpressing the Asparagine Synthetase A gene from Escherichia coli. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2007, 55, 10827–10831. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mattoo, A.K.; Sobolev, A.P.; Neelam, A.; Goyal, R.K.; Handa, A.K.; Segre, A.L. NMR spectroscopy based metabolite profiling of transgenic tomato fruit engineered to accumulate spermidine and spermine reveals enhanced anabolic and nitrogen-carbon interactions. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 1759–1770. [Google Scholar]
- Piccioni, F.; Capitani, D.; Zolla, L.; Mannina, L. NMR metabolic profiling of transgenic maize with the Cry1A(b) gene. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2009, 57, 6041–6049. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, J.M.; Hawkins, N.D.; Ward, J.L.; Lovegrove, A.; Napier, J.A.; Shewry, P.R.; Beale, M.H. A metabolomic study of substantial equivalence of field-grown genetically modified wheat. Plant Biotech. J. 2006, 4, 381–392. [Google Scholar]
- Charlton, A.; Allnutt, T.; Holmes, S.; Chisholm, J.; Bean, S.; Ellis, N.; Mullineaux, P.; Oehlschlager, S. NMR profiling of transgenic peas. Plant Biotech. J. 2004, 2, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Frugis, G.; Giannino, D.; Mele, G.; Nicolodi, C.; Chiappetta, A.; Bitonti, M.B.; Innocenti, A.M.; Dewitte, W.; Van Onckelen, H.; Mariotti, D. Overexpression of KNAT1 in lettuce shifts leaf determinate growth to a shoot-like indeterminate growth associated with an accumulation of isopentenyl-type cytokinins. Plant Physiol. 2001, 126, 1370–1380. [Google Scholar]
- Giannino, D.; Nicolodi, C.; Testone, G.; Di Giacomo, E.; Iannelli, M.A.; Frugis, G.; Mariotti, D. Pollen-mediated transgene flow in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Plant Breed. 2008, 127, 308–314. [Google Scholar]
- Mou, B. Lettuce. In Vegetables I: Asteraceae, Brassicaceae, Chenopodicaceae, and Cucurbitaceae; Nuez, F., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 75–116. [Google Scholar]
- Neelam, A.; Cassol, T.; Mehta, R.A.; Abdul-Baki, A.A.; Sobolev, A.P.; Goyal, R.K.; Abbott, J.; Segre, A.L.; Handa, A.K.; Mattoo, A.K. A field-grown transgenic tomato line expressing higher levels of polyamines reveals legume cover crop mulch-specific perturbations in fruit phenotype at the levels of metabolite profiles, gene expression, and agronomic characteristic. J. Exp. Botany 2008, 59, 2337–2346. [Google Scholar]
- Gil, A.M.; Duarte, I.F.; Delgadillo, I.; Colquhoun, I.J.; Casuscelli, F.; Humpfer, E.; Spraul, M. Study of the compositional changes of mango during ripening by use of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2000, 48, 1524–1536. [Google Scholar]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar]
- Voehler, M.W.; Collier, G.; Young, J.K.; Stone, M.P.; Germann, M.W. Performance of cryogenic probes as a function of ionic strength and sample tube geometry. J. Magn. Reson. 2006, 183, 102–109. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen, N.E. NMR spectroscopy explained: simplified theory, applications and examples for organic chemistry and structural biology; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 109–110. [Google Scholar]
- Box, G.E.P.; Hunter, J.S.; Hunter, W.G. Factorial design at two levels. In Statistics for experimenters: design, discovery and innovation., 2; Box G.E.P.;, Hunter, J.S.; Hunter, W.G., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 173–222. [Google Scholar]
- Mele, G.; Ori, N.; Sato, Y.; Hake, S. The knotted1-like homeobox gene BREVIPEDICELLUS regulates cell differentiation by modulating metabolic pathways. Genes Develop. 2003, 17, 2088–2093. [Google Scholar]
- Frugis, G.; Giannino, D.; Nicolodi, C.; Innocenti, A.M.; Mariotti, D. Lettuce plants that overexpress the KNAT1 homeotic gene from Arabidopsis thaliana exhibit alteration in bolting and flower differentiation. Flower. Newslett. 2001, 32, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Sobolev, A.P.; Capitani, D.; Giannino, D.; Nicolodi, C.; Testone, G.; Santoro, F.; Frugis, G.; Iannelli, M.A.; Mattoo, A.K.; Brosio, E.; et al. NMR-Metabolic Methodology in the Study of GM Foods. Nutrients 2010, 2, 1-15. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu2010001
Sobolev AP, Capitani D, Giannino D, Nicolodi C, Testone G, Santoro F, Frugis G, Iannelli MA, Mattoo AK, Brosio E, et al. NMR-Metabolic Methodology in the Study of GM Foods. Nutrients. 2010; 2(1):1-15. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu2010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleSobolev, Anatoly P., Donatella Capitani, Donato Giannino, Chiara Nicolodi, Giulio Testone, Flavio Santoro, Giovanna Frugis, Maria A. Iannelli, Autar K. Mattoo, Elvino Brosio, and et al. 2010. "NMR-Metabolic Methodology in the Study of GM Foods" Nutrients 2, no. 1: 1-15. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu2010001
APA StyleSobolev, A. P., Capitani, D., Giannino, D., Nicolodi, C., Testone, G., Santoro, F., Frugis, G., Iannelli, M. A., Mattoo, A. K., Brosio, E., Gianferri, R., D’Amico, I., & Mannina, L. (2010). NMR-Metabolic Methodology in the Study of GM Foods. Nutrients, 2(1), 1-15. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu2010001