Fuel Economy Improvement of a Heavy-Duty Powertrain by Using Hardware-in-Loop Simulation and Calibration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Virtual Calibration Platform
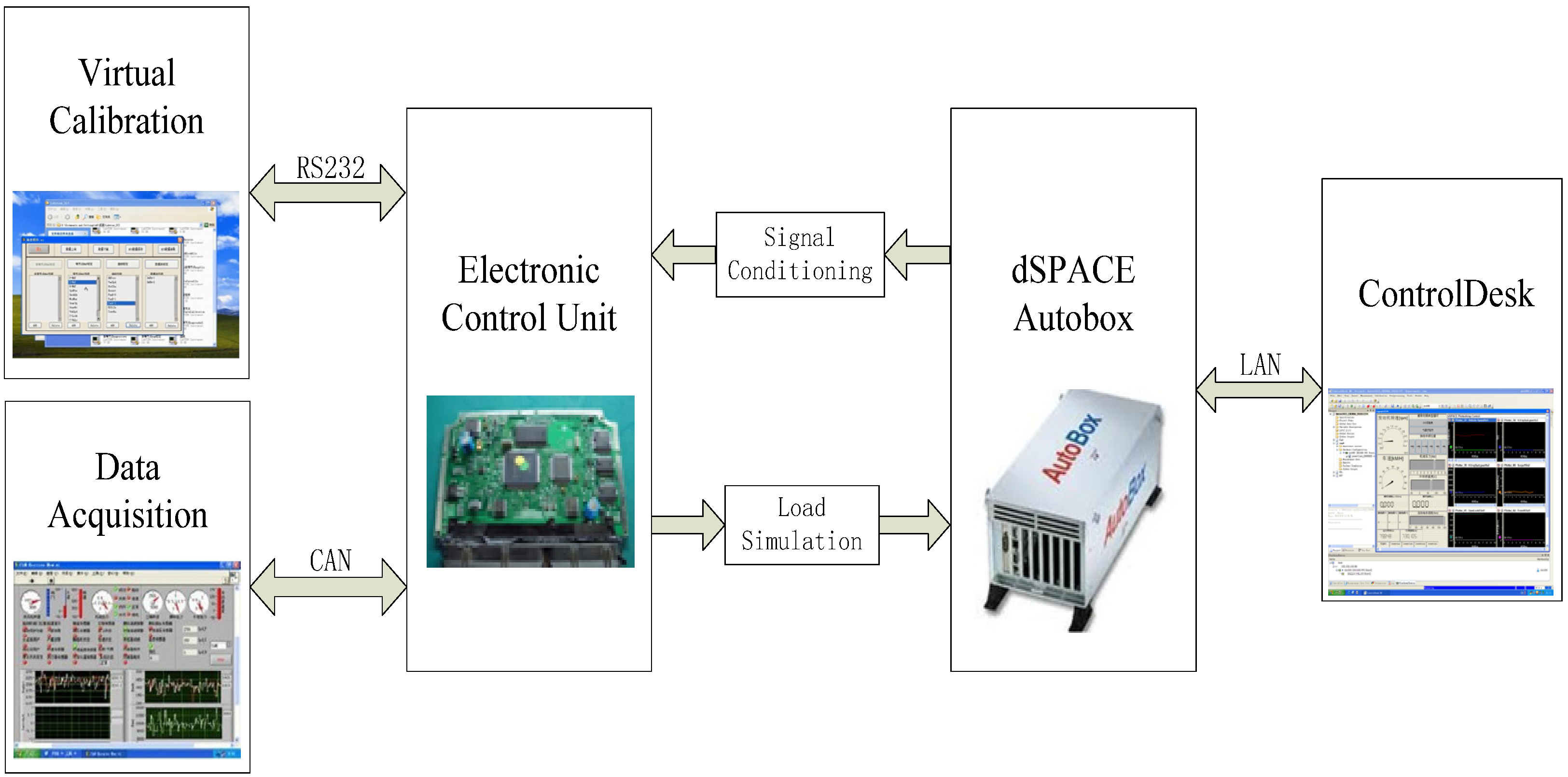

2.2. Real-Time Dynamic Model of Powertrain

2.2.1. Diesel Model
2.2.2. Torque Converter Model
2.2.3. Gearbox Model
| Gear Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL | √ | √ | ||
| CH | √ | √ | ||
| C1 | √ | √ | ||
| C2 | √ | √ |
2.2.4. Driver Model
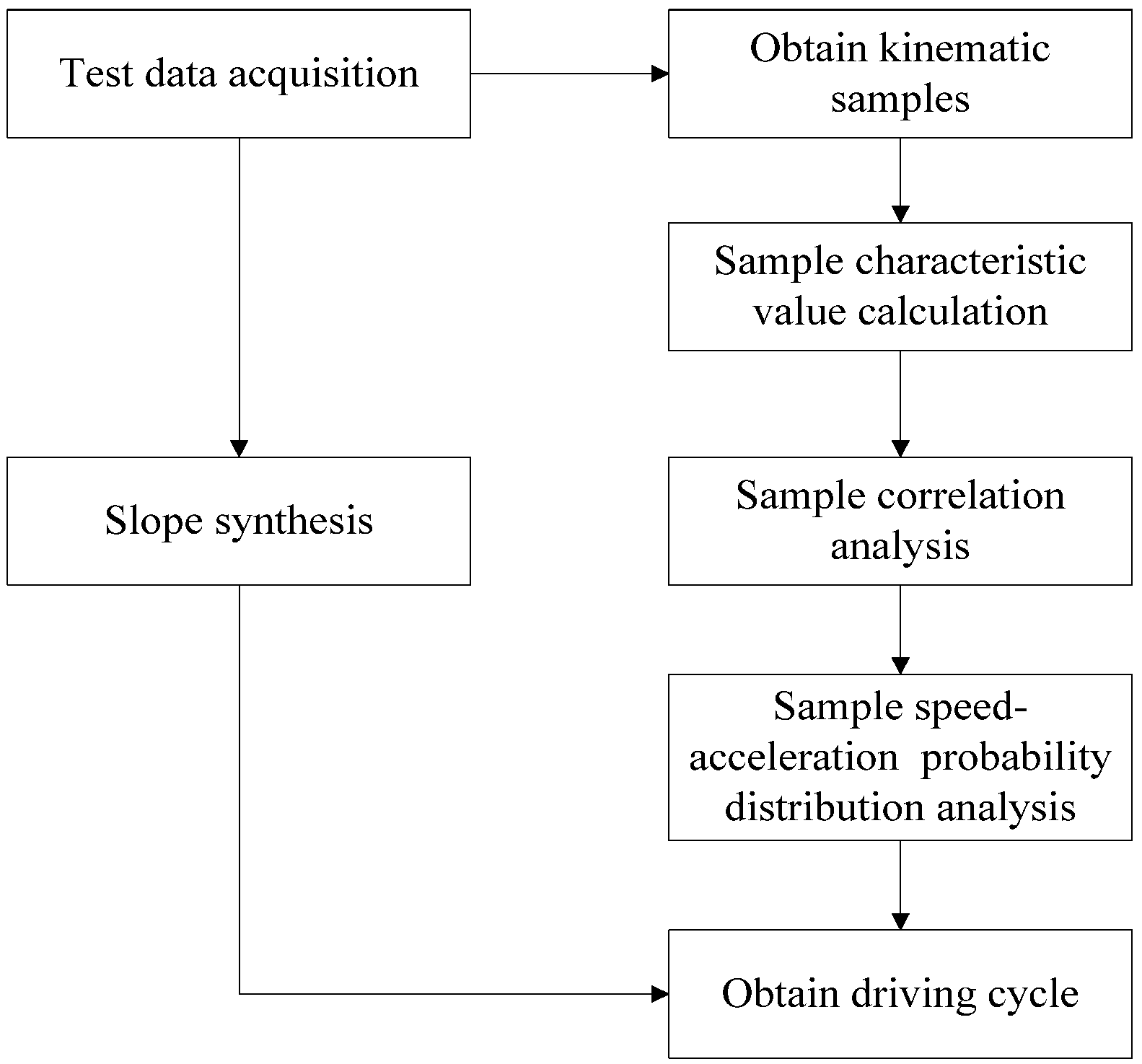
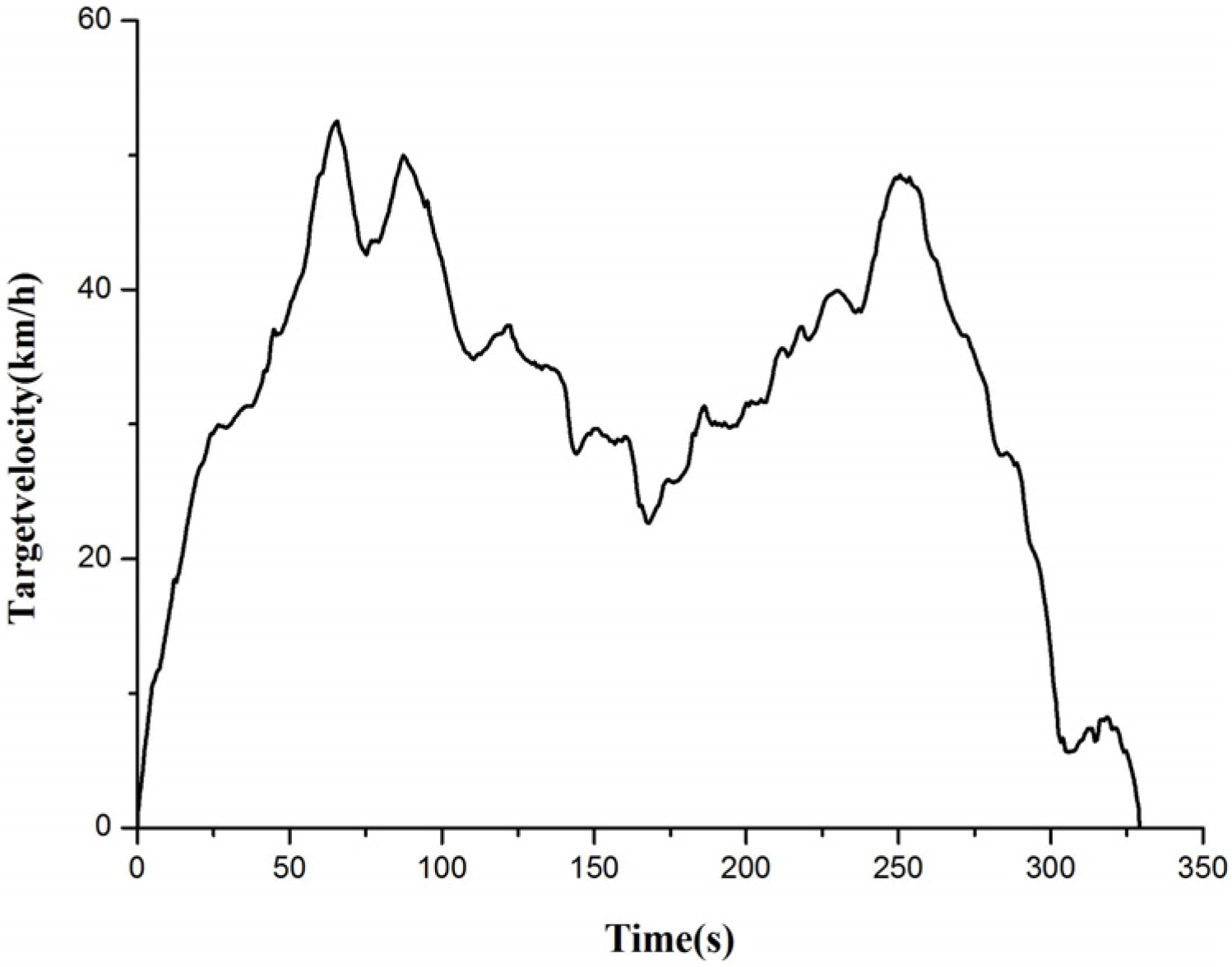
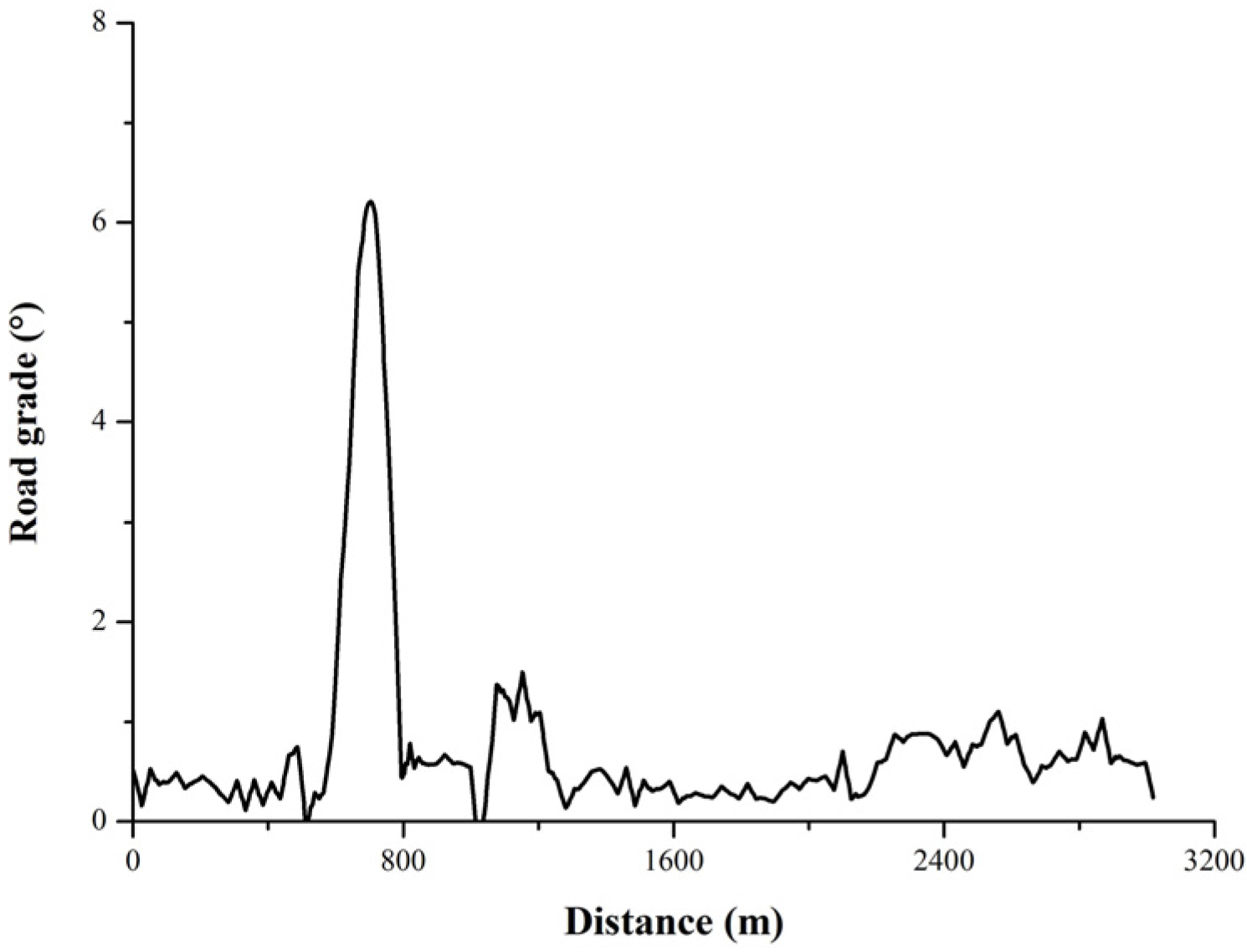
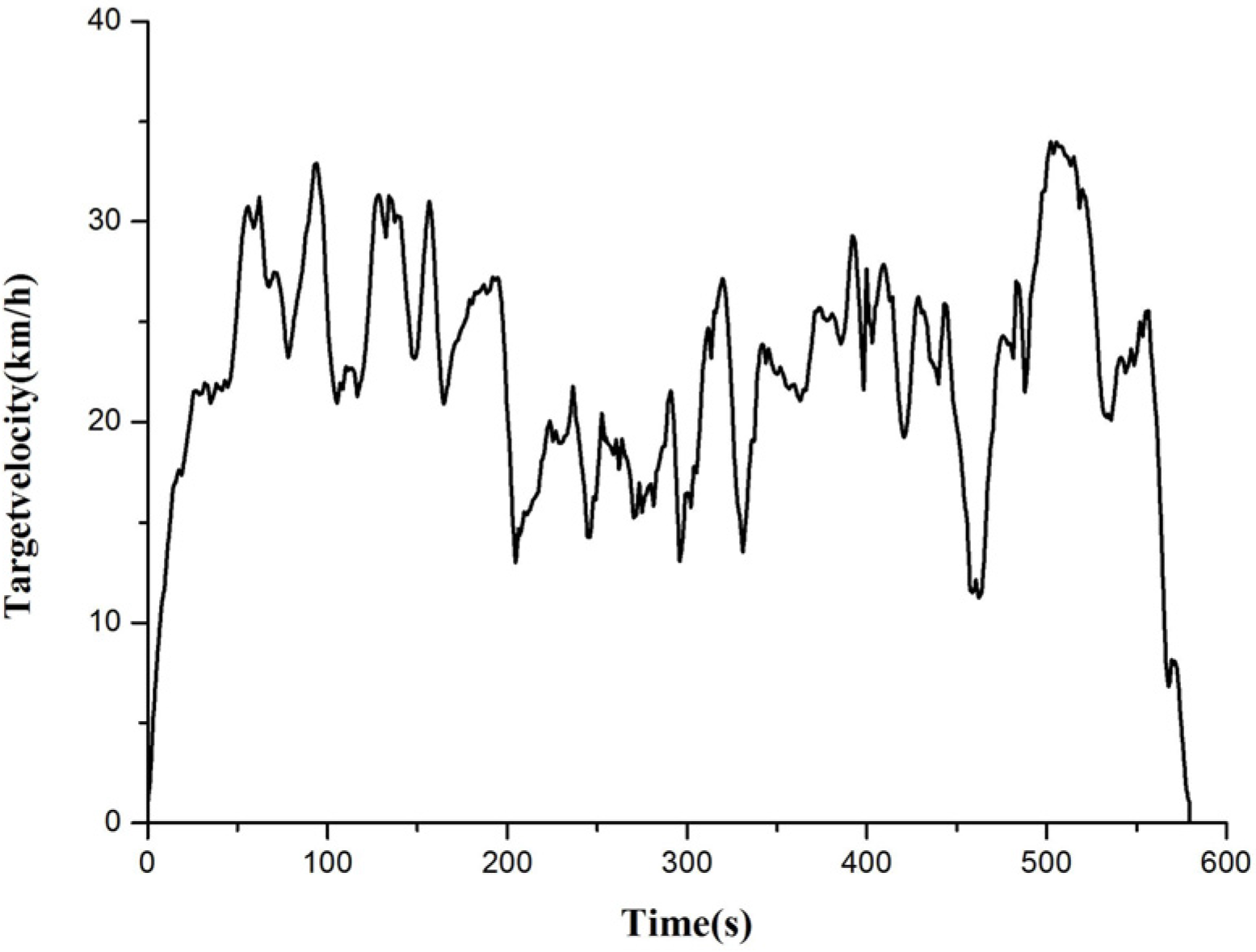
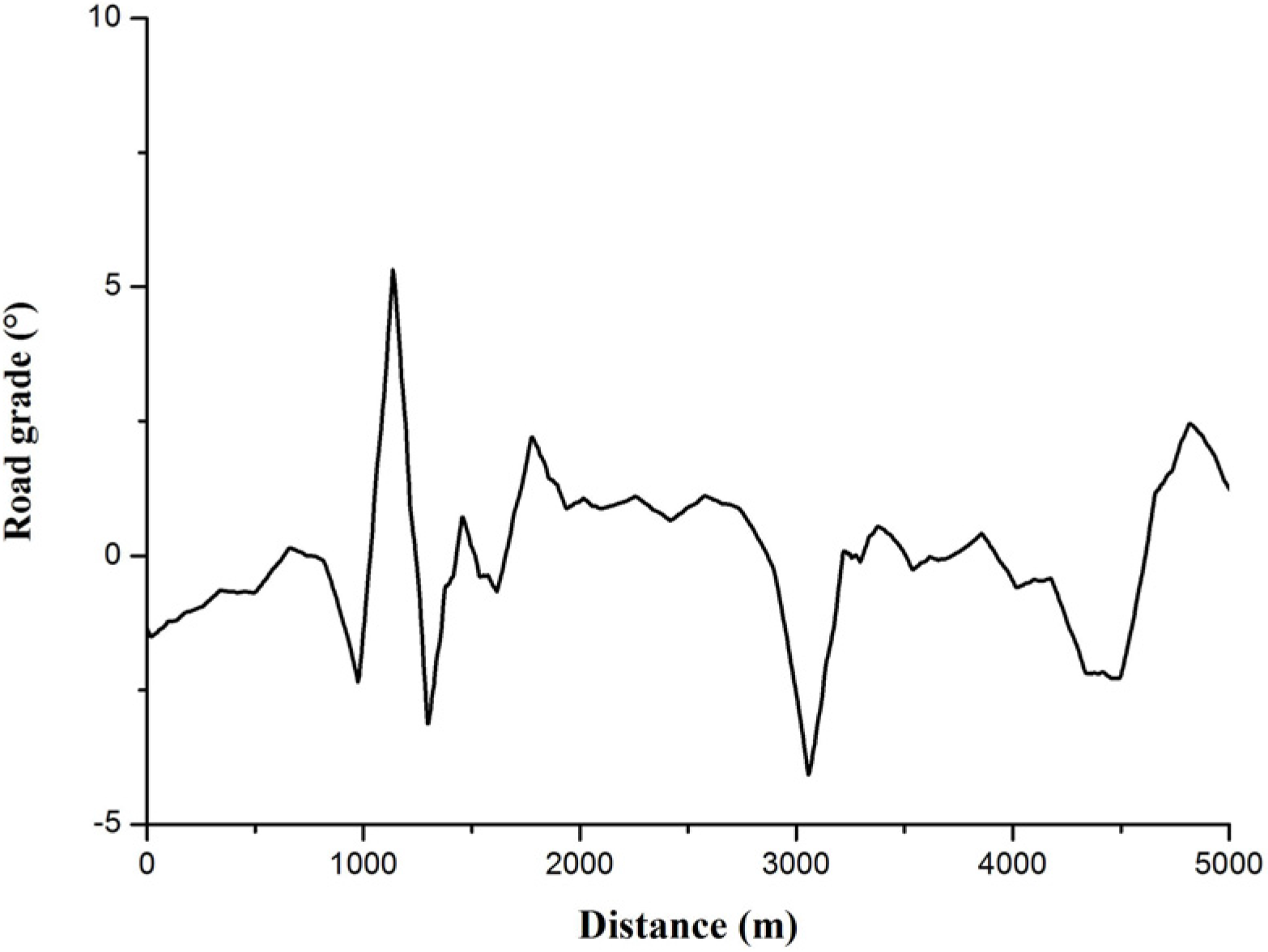
2.2.5. Vehicle Dynamic Model
3. Results
3.1. Certifying the Virtual Calibration Platform
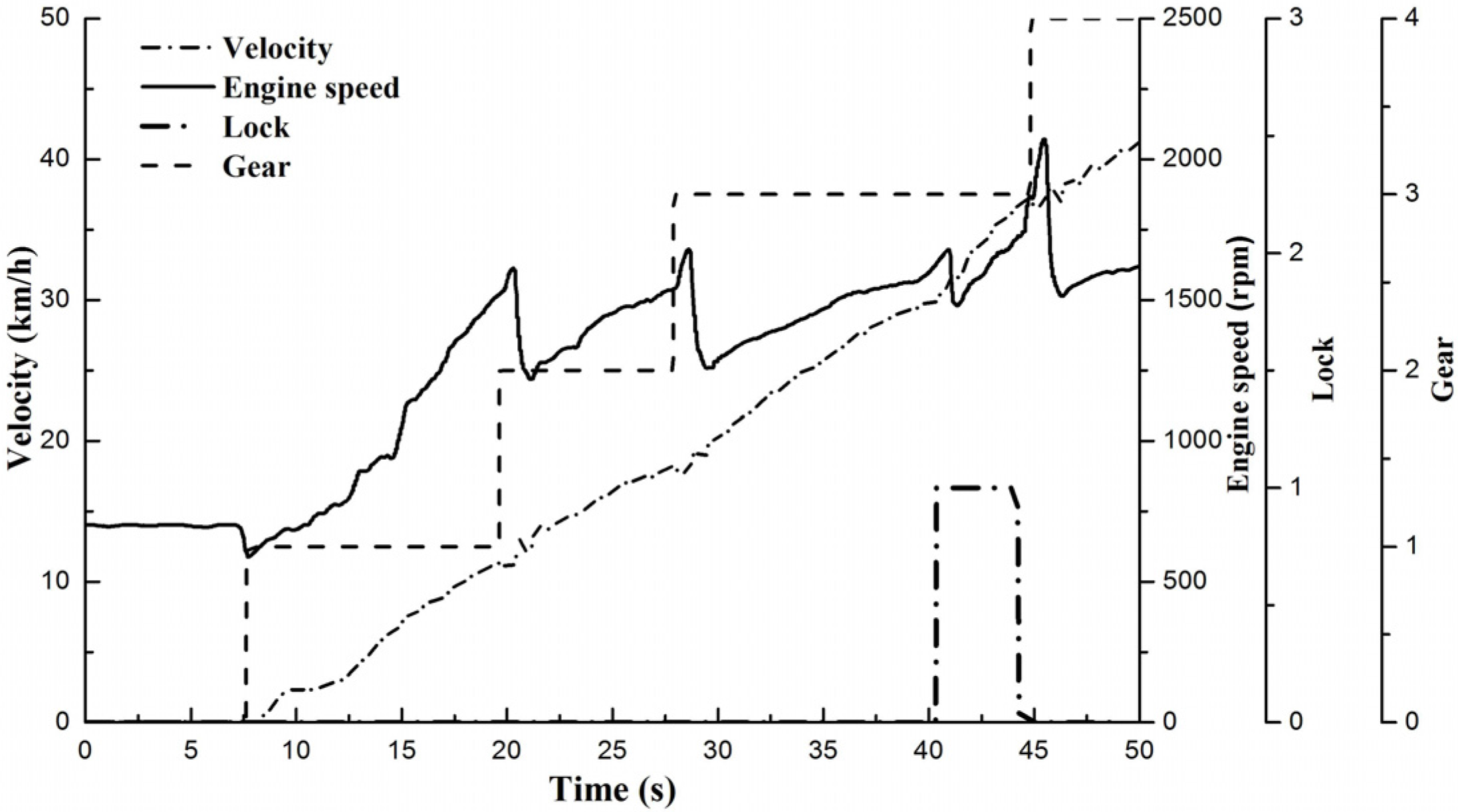

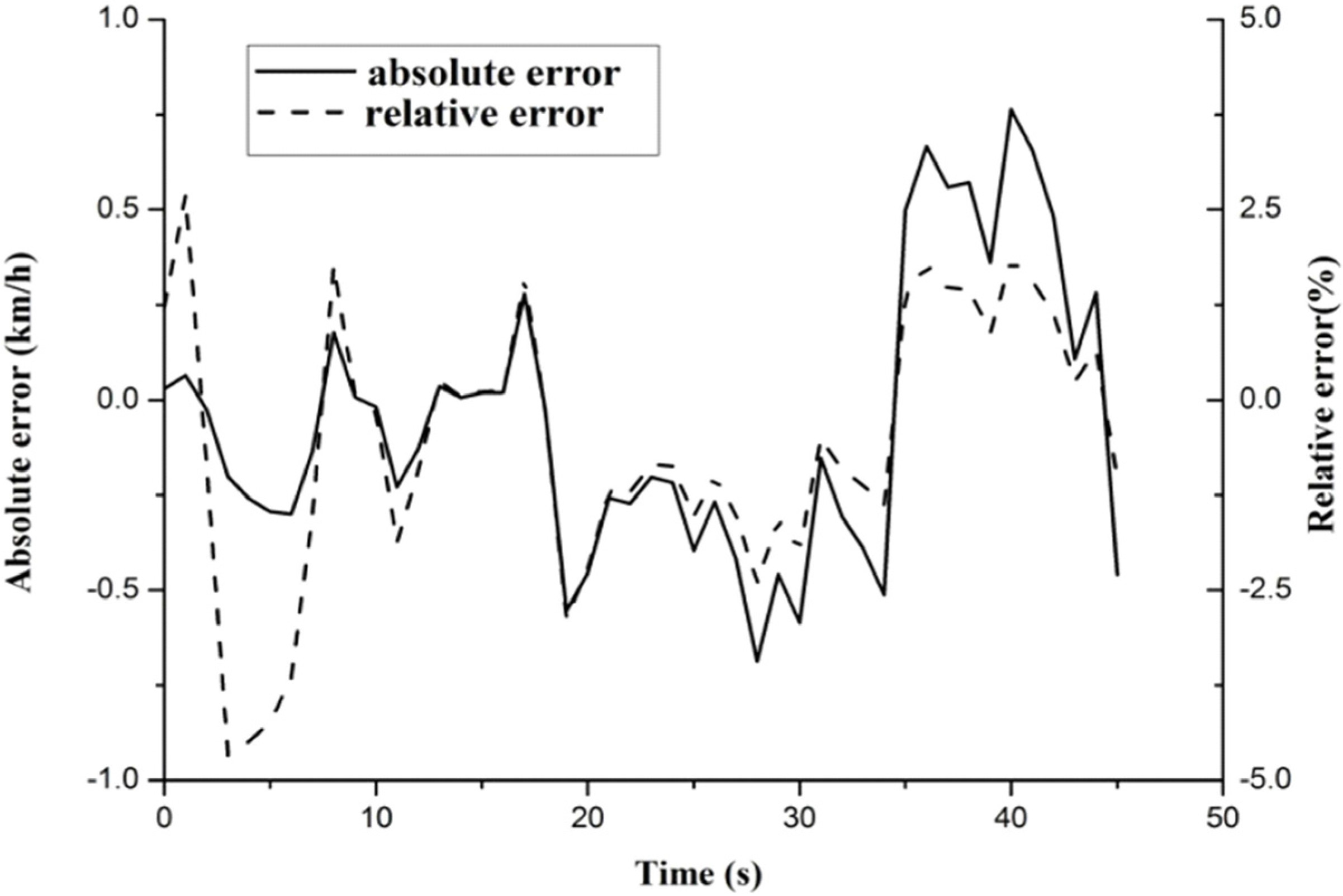
3.2. Economic Shift Schedule

3.3. Virtual Calibration of Economic Shift Schedule Based on Driving Cycles
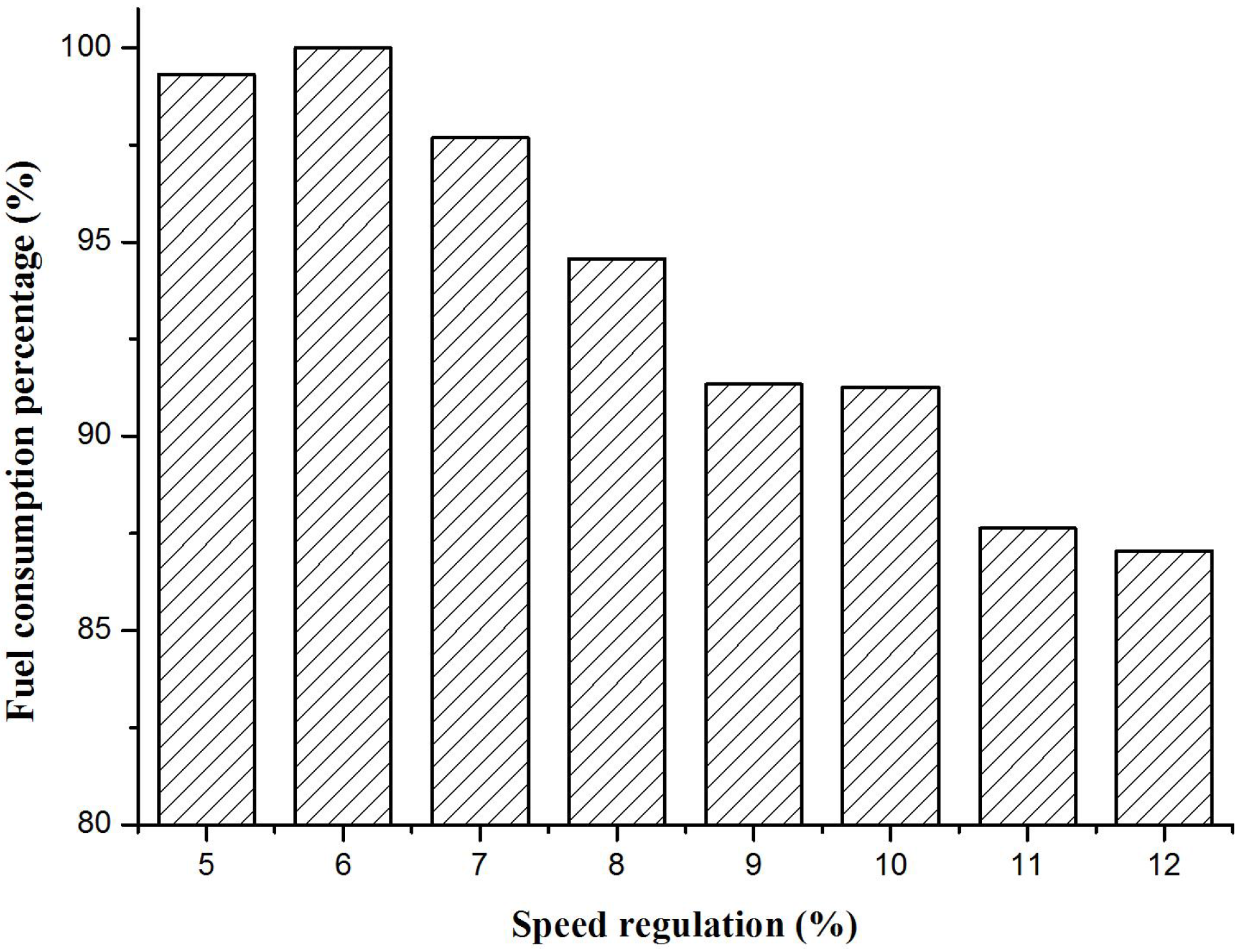
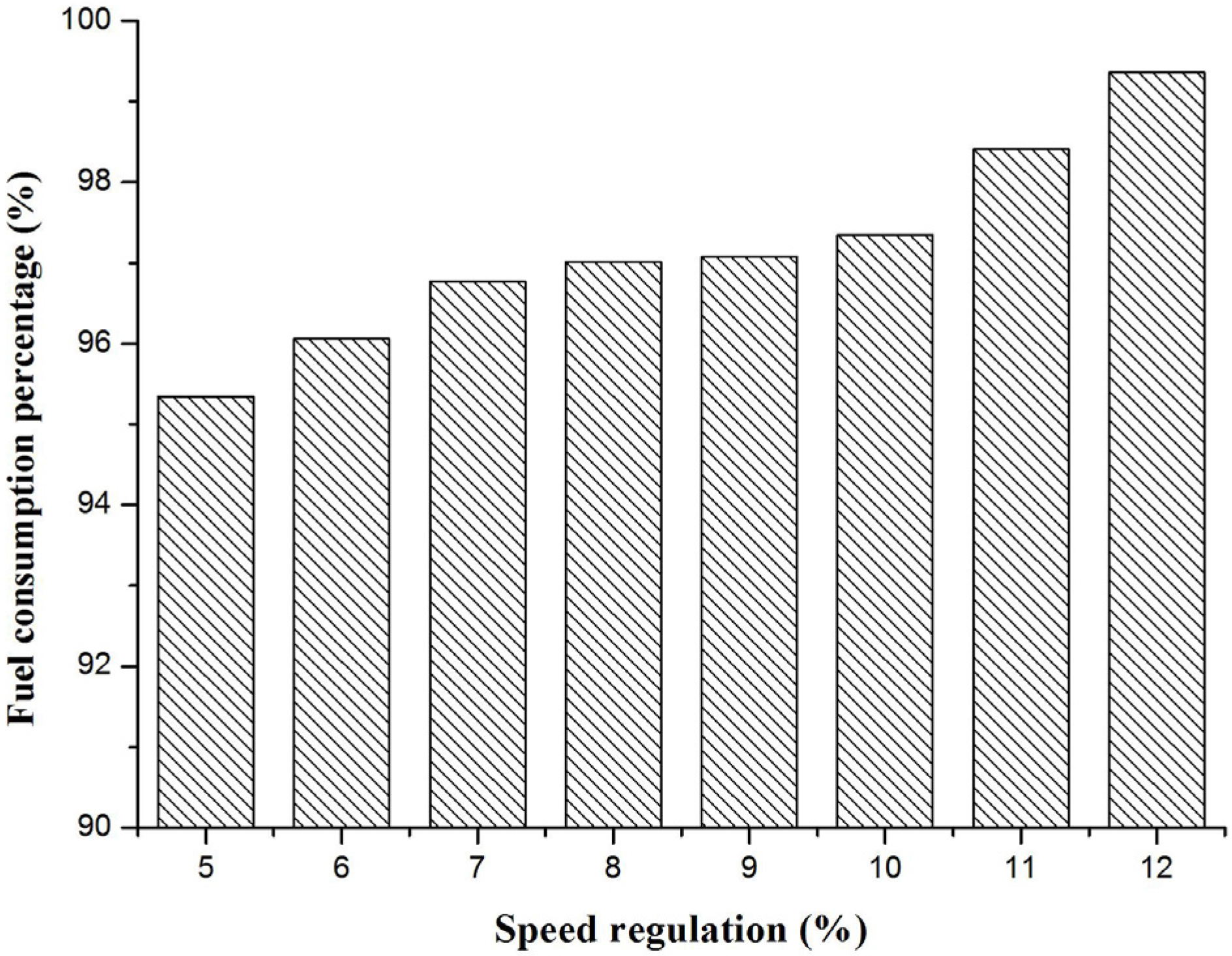
3.4. Real Vehicle Confirmatory Experiment
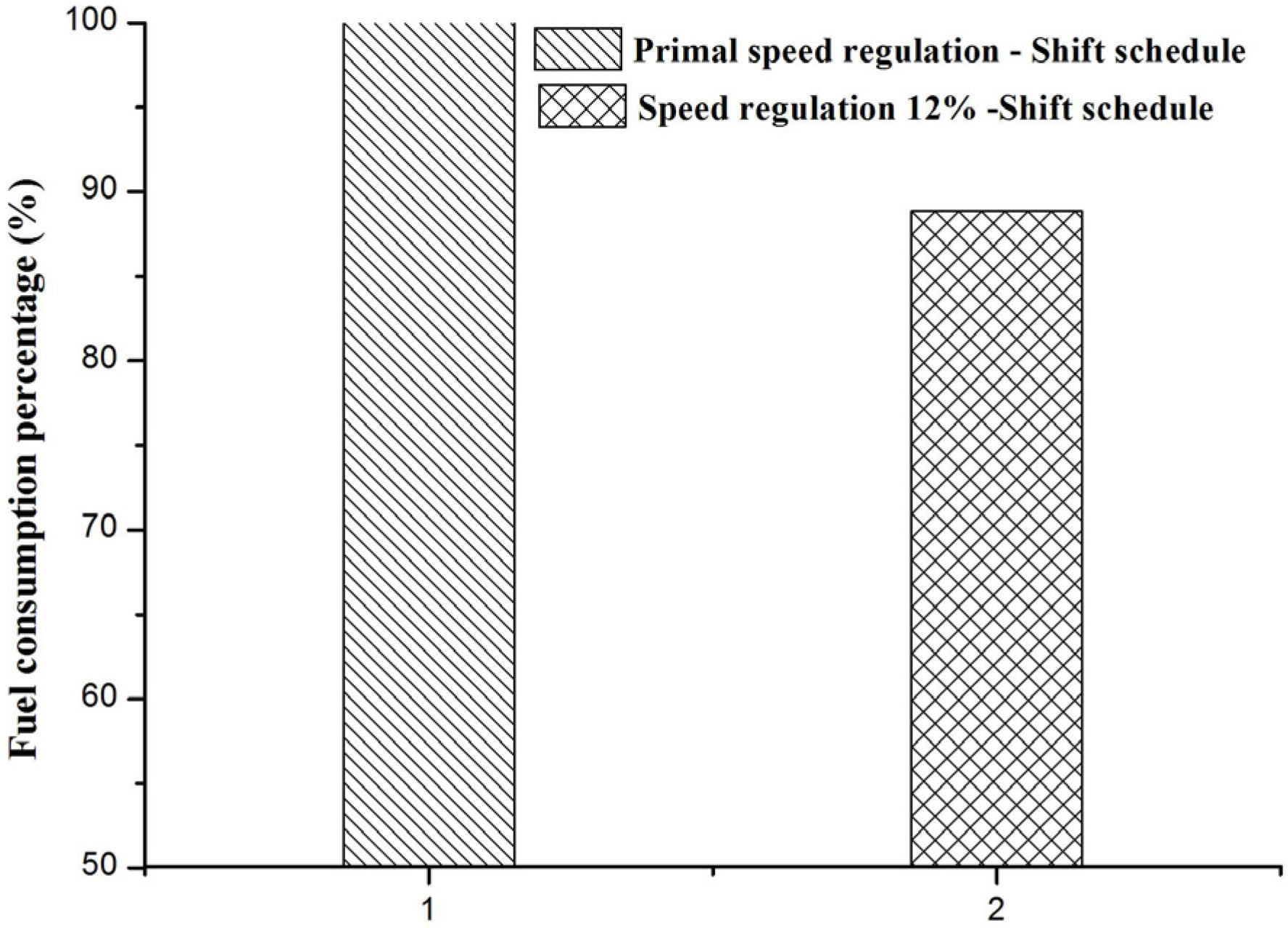

4. Conclusions
- Fuel economy improvement for a heavy-duty powertrain was performed on a dSPACE hardware-in-loop simulation and calibration test bench, which is valuable for a more efficient and easier shift schedule calibration for an off-road heavy-duty powertrain.
- For diesel powertrains, especially when an all-speed governor is employed, optimization of the speed governing rate and shift schedule should be conducted. For the first time, by using the s virtual calibration platform, the corresponding work was successfully performed.
- A real road test which corresponds to the smooth and complex driving cycles was performed in order to verify the results of the virtual calibration platform. As the results show, it is reasonable and effective to carry out virtual calibration of economic shift schedules for heavy-duty vehicles. This is proved conclusively to be instructive for calibrating a real heavy-duty vehicle’s economic performance.
- By virtual calibration, it is shown that in the smooth driving cycle, when the powertrain applies a larger speed regulation such as 12% and the corresponding shift schedule is used, the fuel consumption is smaller and reduced by 13%. In the complex driving cycle, when the powertrain applies a smaller speed regulation such as 5% and the corresponding shift schedule, the fuel consumption is smaller and reduced by 5%. By matching the best regulation of economic shift schedule under different road conditions, the fuel economy of vehicles can be improved.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pelkmans, L.; de Keukeleere, D.; Bruneel, H.; Lenaers, G. Influence of Vehicle Test Cycle Characteristics on Fuel Consumption and Emissions of City Buses; SAE Technical Paper No.2001-01-2002; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.S. Automobile Theory; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2009. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bruneel, H. Heavy Duty Testing Cycles Development: A New Methodology; SAE Technical Paper No.2000-01-1860; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.X. Study on Urban Vehicle Conditions. Master’s Thesis, Wuhan Polytechnics University, Wuhan, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.W.; Li, M.L.; Ai, G.H.; Zhang, F.X.; Zhu, X.C. Study on vehicle driving cycles and performances. Automot. Eng. 2005, 27, 220–224. [Google Scholar]
- Song, B.Z. Study on Real Driving Cycles in Xi’an. Master’s Thesis, Traffic Environment and Safety Technology of Changan University, Xi’an, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Z.Y. Study on Driving Cycles of Urban Buses. Master’s Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.G.; Zhao, C.L.; Liu, B.L.; Zhang, F.J. Active control technology of engine forpowertrain plant during upshifting. Acta Armamentarii 2014, 35, 312–317. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.M. An Investigation on Model-Based Virtual Calibration System of Engines with EFI. Master’s Thesis, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.Y. An Investigation on Model-Based Virtual Calibration System of High Pressure Common Rail Diesel Engine. Master’s Thesis, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Catania, A.E.; Finesso, R.; Spessa, E. Predictive zero-dimensional combustion model for DI diesel engine feed-forward control. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 3159–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finesso, R.; Spessa, E. A real time zero-dimensional diagnostic model for the calculation of in-cylinder temperatures, HRR and nitrogen oxides in diesel engines. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 79, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Ambrosio, S.; Finesso, R.; Fu, L.; Mittica, A.; Spessa, E. A control-oriented real-time semi-empirical model for the prediction of NOx emissions in diesel engines. Appl. Energy 2014, 130, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.W.; Zhang, H.B.; Zhao, C.L.; Zhang, F.J.; Huang, Y.; Sun, Y.B. Study on electronic control unit hardwares in the loop simulation platform of engine control systems based on dSPACEsystem. Acta Armamentarii 2004, 25, 402–406. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hanselmann, H. Hardware-in-the-loop Simulation as a Standard Approach for Development, Customization and Production Test; SAE 931953; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith, S. A Practical Guide to Real-Time Systems Development; Prentice-Hall, Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Isermann, R.; Sinsel, S.; Schaffnit, J. Modeling and Real-Time Simulation of Diesel Engines for Control; SAE 980796; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C. Study on Locking Control of Lock-up Torque Converter. Master’s Thesis, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Q.D.; Zhang, L.D.; Zhao, Y.Q. Structure and Design of Tank (Part II); Beijing Institute of Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2007. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.B.; Yan, Q.D.; Li, H.C. Road roughness research of tracked vehicle compliance simulation experiment. J. Syst. Simul. 2006, 18, 95–97. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.J.; Zhang, F.J. Simulation about power performance of tracked vehicles and analysis of parameters of the law. Veh. Power Technol. 2010, 1, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.Z.; Zhang, F.J.; Zhao, C.L.; Shi, Y.; Yuan, H.J. Investigation on a construction method of driving cycle for tracked vehicle. Acta Armamentarii 2011, 32, 1041–1046. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, B.; Ai, X.; Liu, P.; Zhang, C.; Hu, X.; Dong, T. Fuel Economy Improvement of a Heavy-Duty Powertrain by Using Hardware-in-Loop Simulation and Calibration. Energies 2015, 8, 9878-9891. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8099878
Liu B, Ai X, Liu P, Zhang C, Hu X, Dong T. Fuel Economy Improvement of a Heavy-Duty Powertrain by Using Hardware-in-Loop Simulation and Calibration. Energies. 2015; 8(9):9878-9891. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8099878
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Bolan, Xiaowei Ai, Pan Liu, Chuang Zhang, Xingqi Hu, and Tianpu Dong. 2015. "Fuel Economy Improvement of a Heavy-Duty Powertrain by Using Hardware-in-Loop Simulation and Calibration" Energies 8, no. 9: 9878-9891. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8099878
APA StyleLiu, B., Ai, X., Liu, P., Zhang, C., Hu, X., & Dong, T. (2015). Fuel Economy Improvement of a Heavy-Duty Powertrain by Using Hardware-in-Loop Simulation and Calibration. Energies, 8(9), 9878-9891. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8099878






