Combustion Characteristics of Single Particles from Bituminous Coal and Pine Sawdust in O2/N2, O2/CO2, and O2/H2O Atmospheres
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fuel Samples
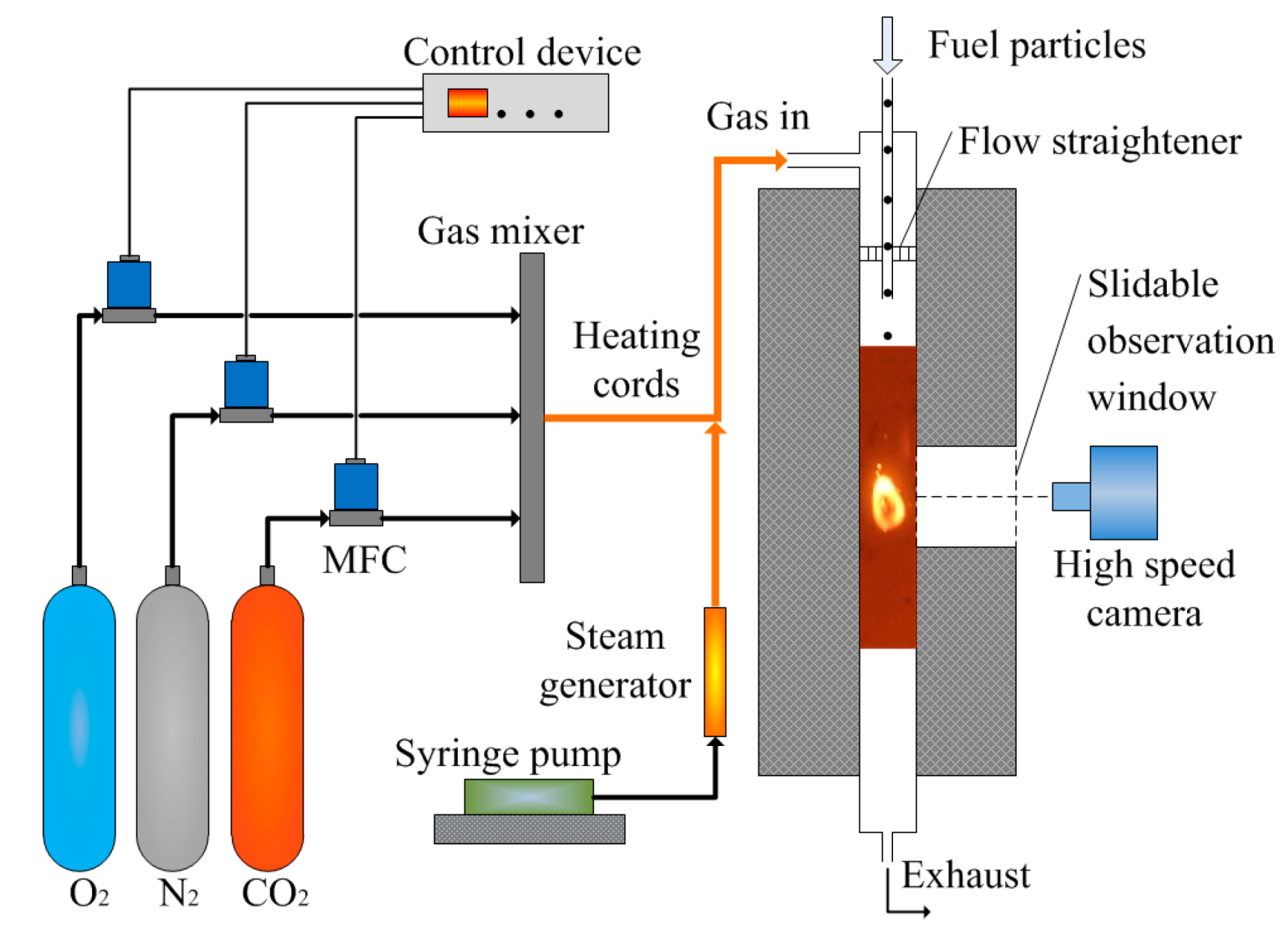
2.2. Experimental Method
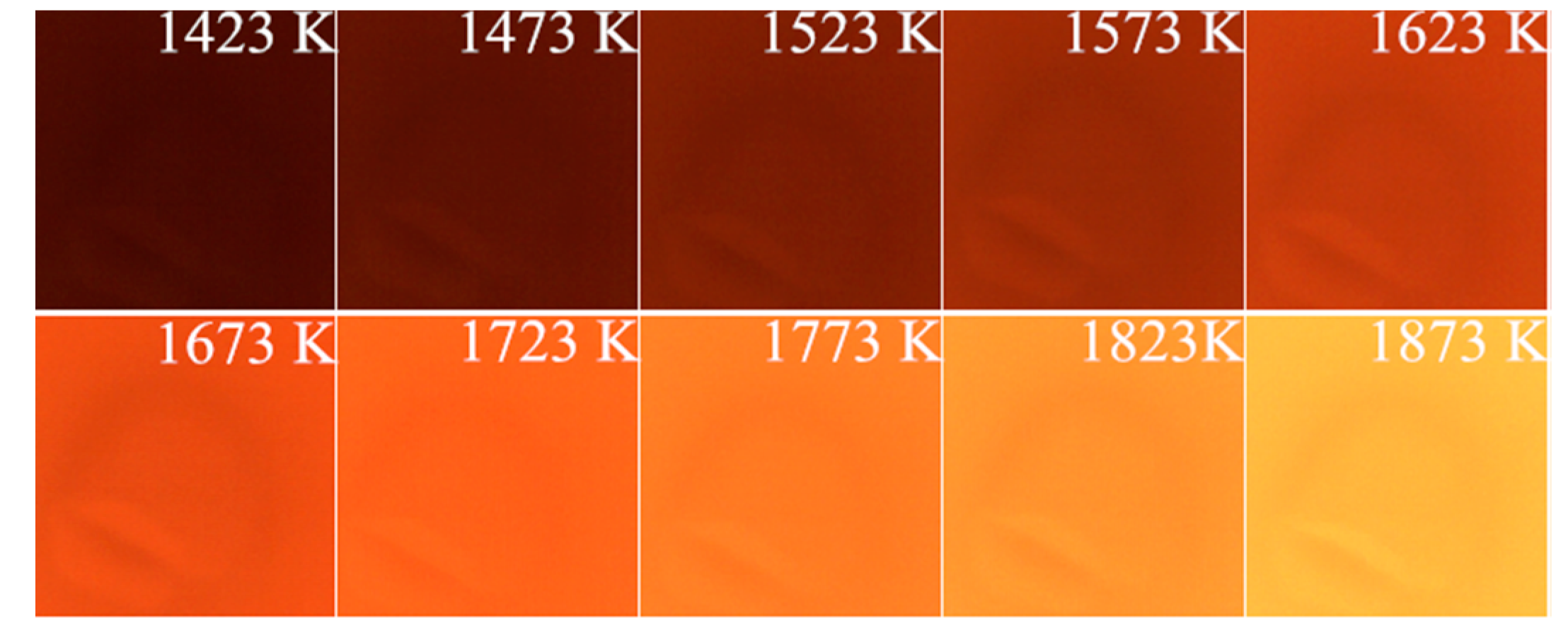
2.3. Measurement of Temperature
3. Results and Discussion
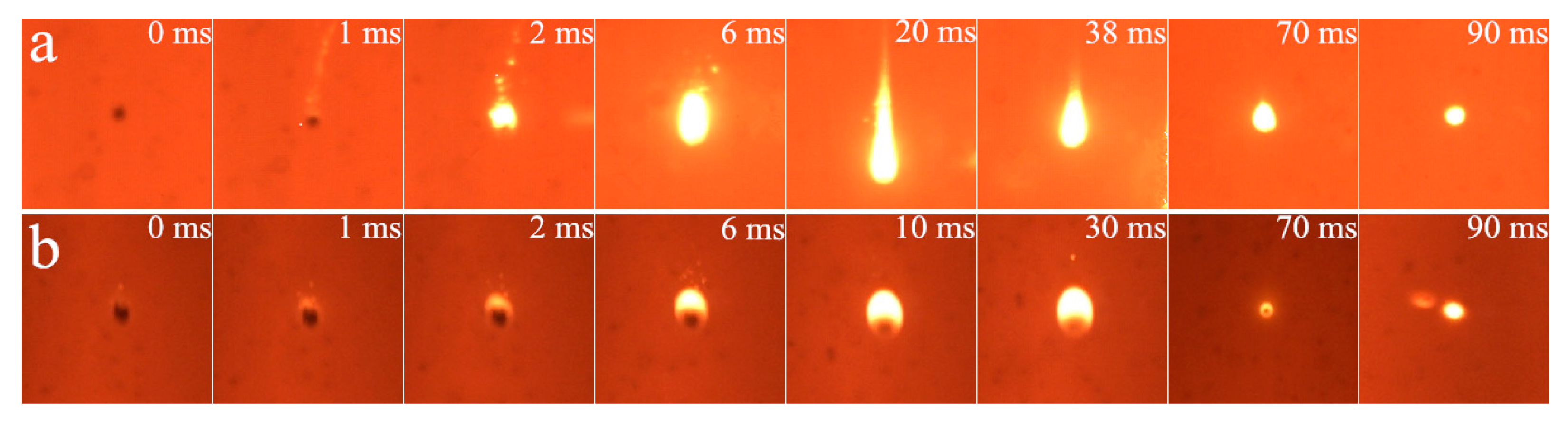
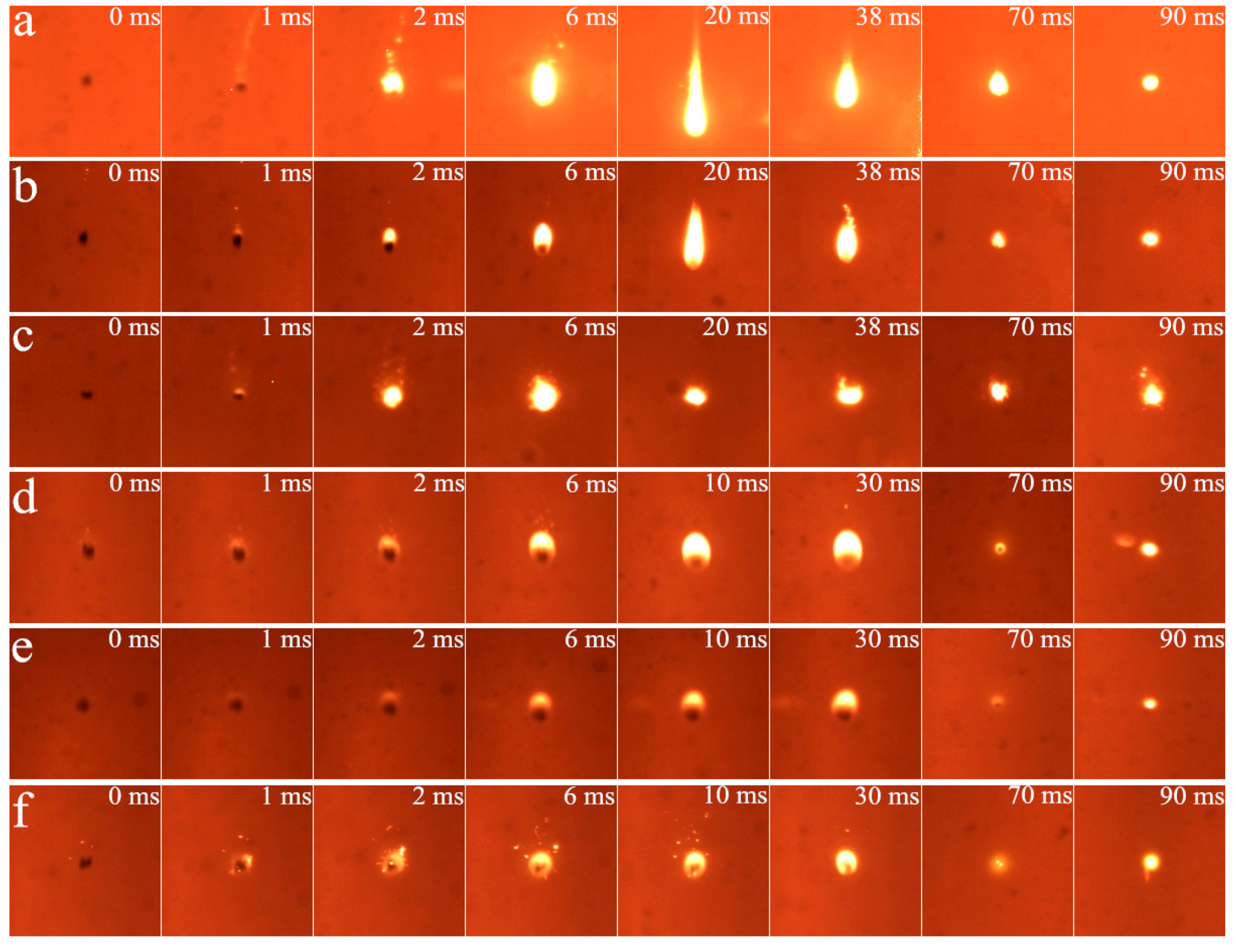
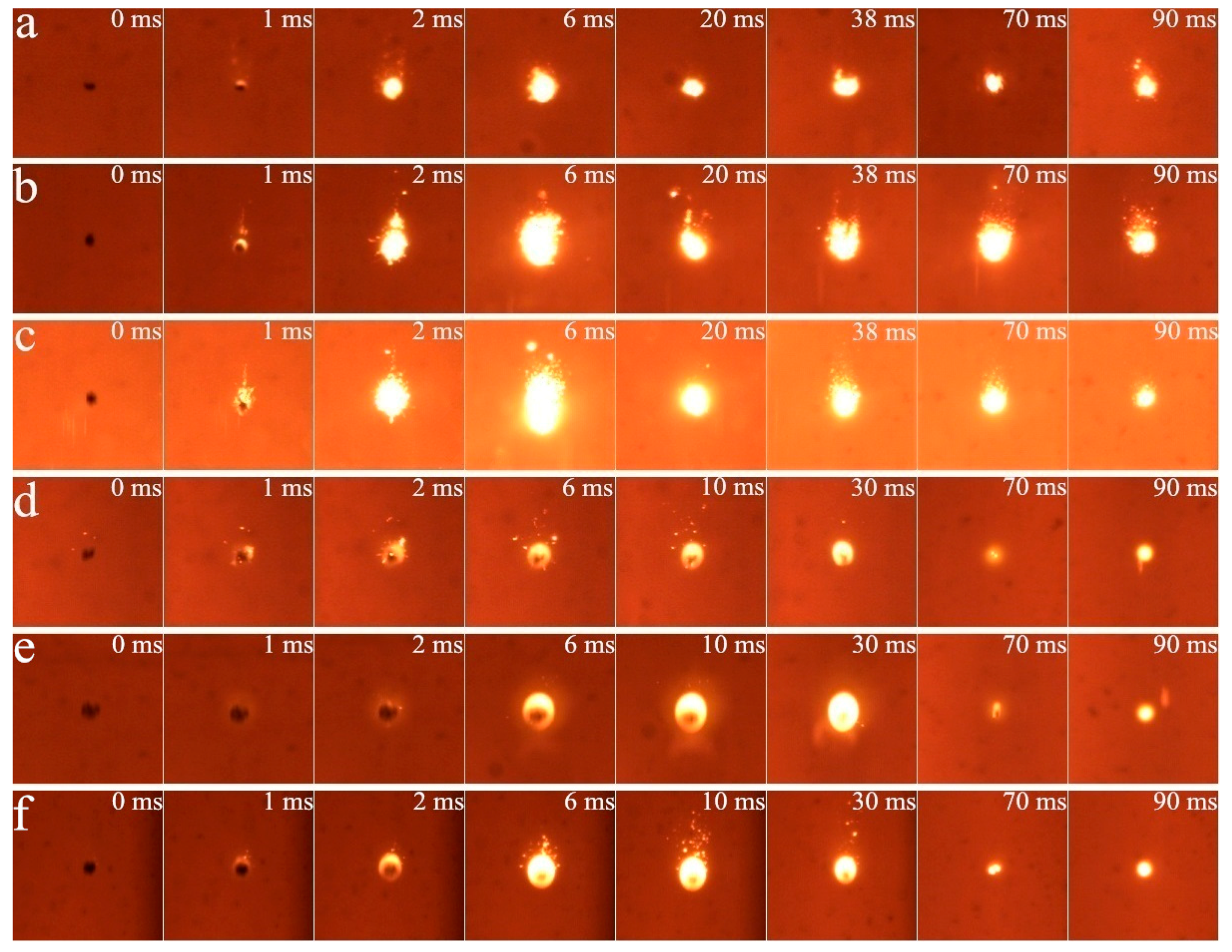
3.1. Cinematographic Observations Analysis
3.1.1. Ignition Mode and Combustion Process
3.1.2. Effect of Diluent Gas (N2, CO2 and H2O)
3.1.3. Effect of O2 Mole Fraction
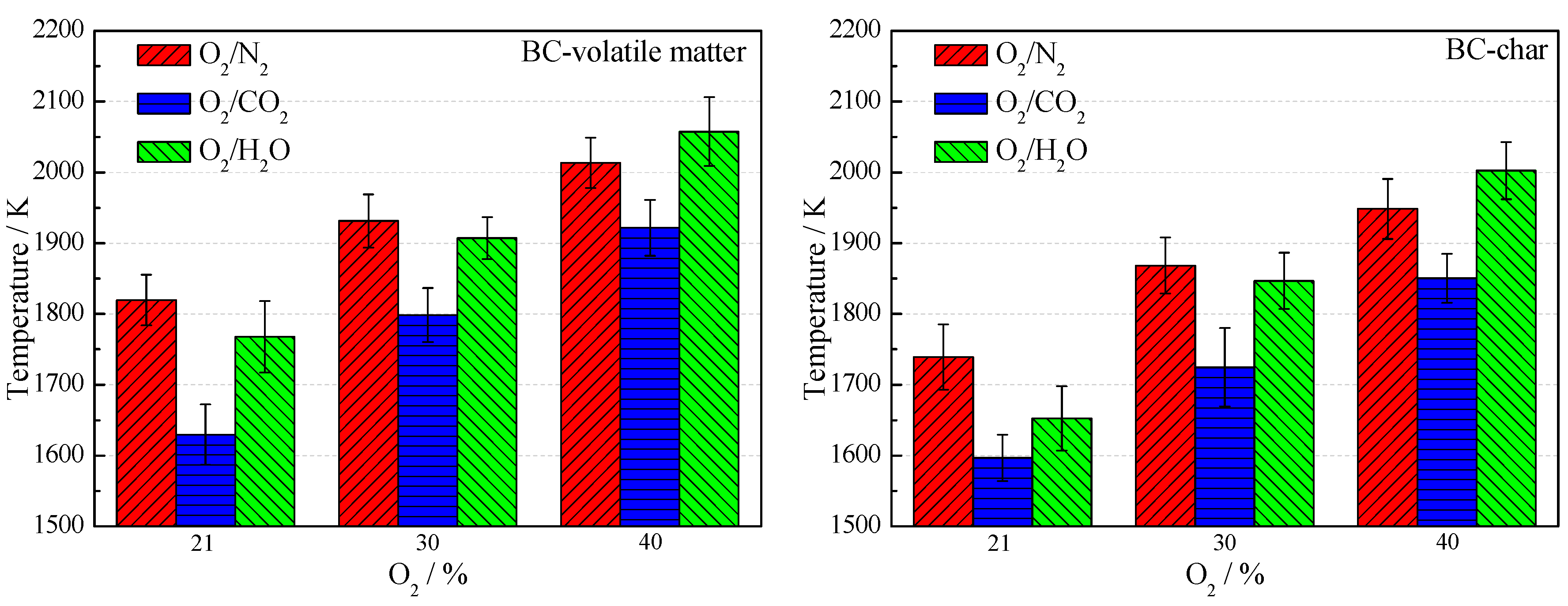
3.2. Combustion Temperature
3.3. Ignition Delay Time
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- British Petroleum. Statistical Review of World Energy; BP: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Niu, D.; Cao, Y.; Hong, W. Analysis and Modeling for China’s Electricity Demand Forecasting Using a Hybrid Method Based on Multiple Regression and Extreme Learning Machine: A View from Carbon Emission. Energies 2016, 9, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, K.J.; Jones, G.A. The Climate-Independent Need for Renewable Energy in the 21st Century. Energies 2017, 10, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondino, G.; Grande, C.A.; Blom, R. Effect of Gas Recycling on the Performance of a Moving Bed Temperature-Swing (MBTSA) Process for CO2 Capture in a Coal Fired Power Plant Context. Energies 2017, 10, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnam, R.K.; Elliott, L.K.; Wall, T.F.; Liu, Y.; Moghtaderi, B. Differences in reactivity of pulverised coal in air (O2/N2) and oxy-fuel (O2/CO2) conditions. Fuel Process. Technol. 2009, 90, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, R.; Stivers, C.; Levendis, Y.A. Ignition characteristics of single coal particles from three different ranks in O2/N2 and O2/CO2 atmospheres. Combust. Flame 2012, 159, 3554–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, R.; Stivers, C.; Joshi, K.; Levendis, Y.A.; Sarofim, A.F. Combustion behavior of single particles from three different coal ranks and from sugar cane bagasse in O2/N2 and O2/CO2 atmospheres. Combust. Flame 2012, 159, 1253–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Binner, E.; Qiao, Y.; Li, C. In situ diagnostics of Victorian brown coal combustion in O2/N2 and O2/CO2 mixtures in drop-tube furnace. Fuel 2010, 89, 2703–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejarano, P.A.; Levendis, Y.A. Single-coal-particle combustion in O2/N2 and O2/CO2 environments. Combust. Flame 2008, 153, 270–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seepana, S.; Jayanti, S. Steam-moderated oxy-fuel combustion. Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 1981–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Cai, L.; Wu, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zheng, C. Ignition behaviors of pulverized coal particles in O2/N2 and O2/H2O mixtures in a drop tube furnace using flame monitoring techniques. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2015, 35, 3629–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Zou, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, K.; Han, Q.; Zheng, C. Numerical and experimental studies on the ignition of pulverized coal in O2/H2O atmospheres. Fuel 2015, 139, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Zou, C.; Guan, Y.; Jia, H.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, C. Effect of steam on ignition of pulverized coal particles in oxy-fuel combustion in a drop tube furnace. Fuel 2016, 182, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prationo, W.; Zhang, L. Influence of steam on ignition of Victorian brown coal particle stream in oxy-fuel combustion: In-situ diagnosis and transient ignition modelling. Fuel 2016, 181, 1203–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.V.; Riaza, J.; Álvarez, L.; Pevida, C.; Pis, J.J.; Rubiera, F. A study of oxy-coal combustion with steam addition and biomass blending by thermogravimetric analysis. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012, 109, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, B.; Zhang, L.; Huang, F.; Mao, Z.; Zheng, C. Effect of H2O on the combustion characteristics of pulverized coal in O2/CO2 atmosphere. Appl. Energy 2014, 132, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Zhang, L.; Cao, S.; Zheng, C. A study of combustion characteristics of pulverized coal in O2/H2O atmosphere. Fuel 2014, 115, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuellar, A.D.; Herzog, H. A Path Forward for Low Carbon Power from Biomass. Energies 2015, 8, 1701–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arce, M.E.; Saavedra, A.; Míguez, J.L.; Granada, E.; Cacabelos, A. Biomass Fuel and Combustion Conditions Selection in a Fixed Bed Combustor. Energies 2013, 6, 5973–5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Yang, S.; Pang, M. A Hybrid Life-Cycle Assessment of Nonrenewable Energy and Greenhouse-Gas Emissions of a Village-Level Biomass Gasification Project in China. Energies 2012, 5, 2708–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaza, J.; Khatami, R.; Levendis, Y.A.; Álvarez, L.; Gil, M.V.; Pevida, C.; Rubiera, F.; Pis, J.J. Combustion of single biomass particles in air and in oxy-fuel conditions. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 64, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Kai, X.; Yang, T.; Sun, Y.; He, Y.; Shen, S. Release and transformation of alkali metals during co-combustion of coal and sulfur-rich wheat straw. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 83, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillman, D.A. Biomass cofring: The technology, the experience, the combustion consequences. Biomass Bioenergy 2000, 19, 365–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, L. Biomass-coal co-combustion: Opportunity for affordable renewable energy. Fuel 2005, 84, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaza, J.; Gil, M.V.; Pevida, C.; Pis, J.J.; Rubiera, F. Oxy-fuel combustion of coal and biomass blends. Energy 2012, 41, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Li, Y.; Li, N.; Qiu, R.; Cen, K. NO and N2O Emissions during Devolatilization and Char Combustion of a Single Biomass Particle under Oxy-fuel Conditions at Fluidized Bed Temperature. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 7157–7165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, A.; Shaddix, C.R. Ignition and devolatilization of pulverized bituminous coal particles during oxygen/carbon dioxide coal combustion. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2007, 31, 1905–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guizani, C.; Jeguirim, M.; Valin, S.; Limousy, L.; Salvador, S. Biomass Chars: The Effects of Pyrolysis Conditions on Their Morphology, Structure, Chemical Properties and Reactivity. Energies 2017, 10, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Shao, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Xu, T.; Guo, J.; Wang, H.; Xu, R.; Lin, H. Thermal behavior and kinetic analysis of co-combustion of waste biomass/low rank coal blends. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 124, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.X.; Zhou, H.C. A Combustion-Monitoring System with 3-D Temperature Reconstruction Based on Flame-Image Processing Technique. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2007, 56, 1877–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.C.; Lou, C.; Cheng, Q.; Jiang, Z.W.; He, J.; Huang, B.Y.; Pei, Z.L.; Lu, C.X. Experimental investigations on visualization of three-dimensional temperature distributions in a large-scale pulverized-coal-fired boiler furnace. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2005, 30, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, D.C. Quantitative Chemical Analysis; WH Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Khatami, R.; Levendis, Y.A. On the deduction of single coal particle combustion temperature from three-color optical pyrometry. Combust. Flame 2011, 158, 1822–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Fuels | Proximate Analysis (wt %) | Ultimate Analysis (wt %) | HHV (MJ/Kg) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mad | Vad | FCad | Aad | Cdaf | Hdaf | Odaf | Ndaf | Sdaf | ||
| BC | 7.99 | 32.68 | 50.07 | 9.26 | 67.77 | 4.14 | 25.35 | 1.01 | 1.73 | 25.74 |
| PS | 4.76 | 80.61 | 14.13 | 0.50 | 48.74 | 6.88 | 44.30 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 18.73 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, K.; Ye, B.; Cao, J.; Zhang, R.; Liu, D. Combustion Characteristics of Single Particles from Bituminous Coal and Pine Sawdust in O2/N2, O2/CO2, and O2/H2O Atmospheres. Energies 2017, 10, 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111695
Lei K, Ye B, Cao J, Zhang R, Liu D. Combustion Characteristics of Single Particles from Bituminous Coal and Pine Sawdust in O2/N2, O2/CO2, and O2/H2O Atmospheres. Energies. 2017; 10(11):1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111695
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Kai, Buqing Ye, Jin Cao, Rui Zhang, and Dong Liu. 2017. "Combustion Characteristics of Single Particles from Bituminous Coal and Pine Sawdust in O2/N2, O2/CO2, and O2/H2O Atmospheres" Energies 10, no. 11: 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111695




