Evaluation of Pyridoacridine Alkaloids in a Zebrafish Phenotypic Assay
Abstract
:1. Introduction
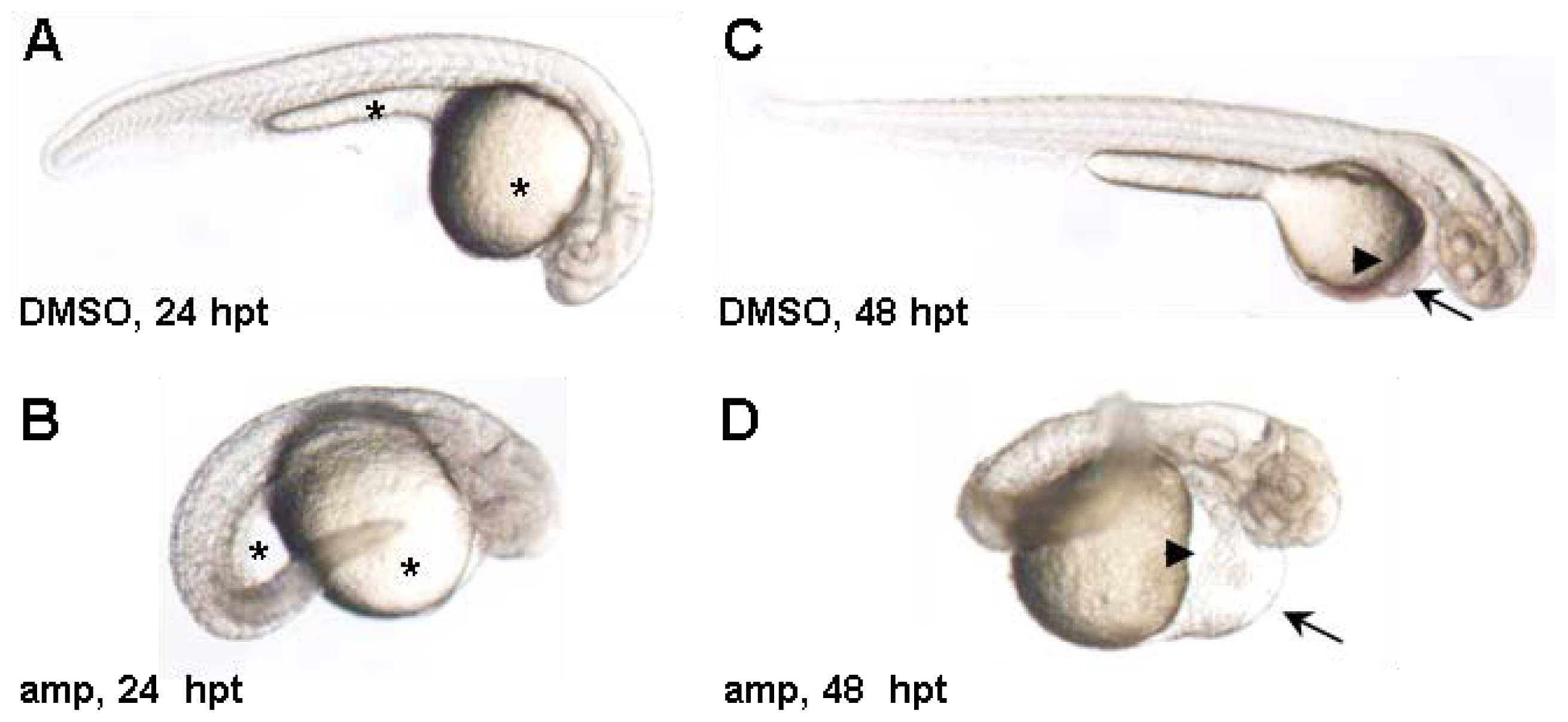
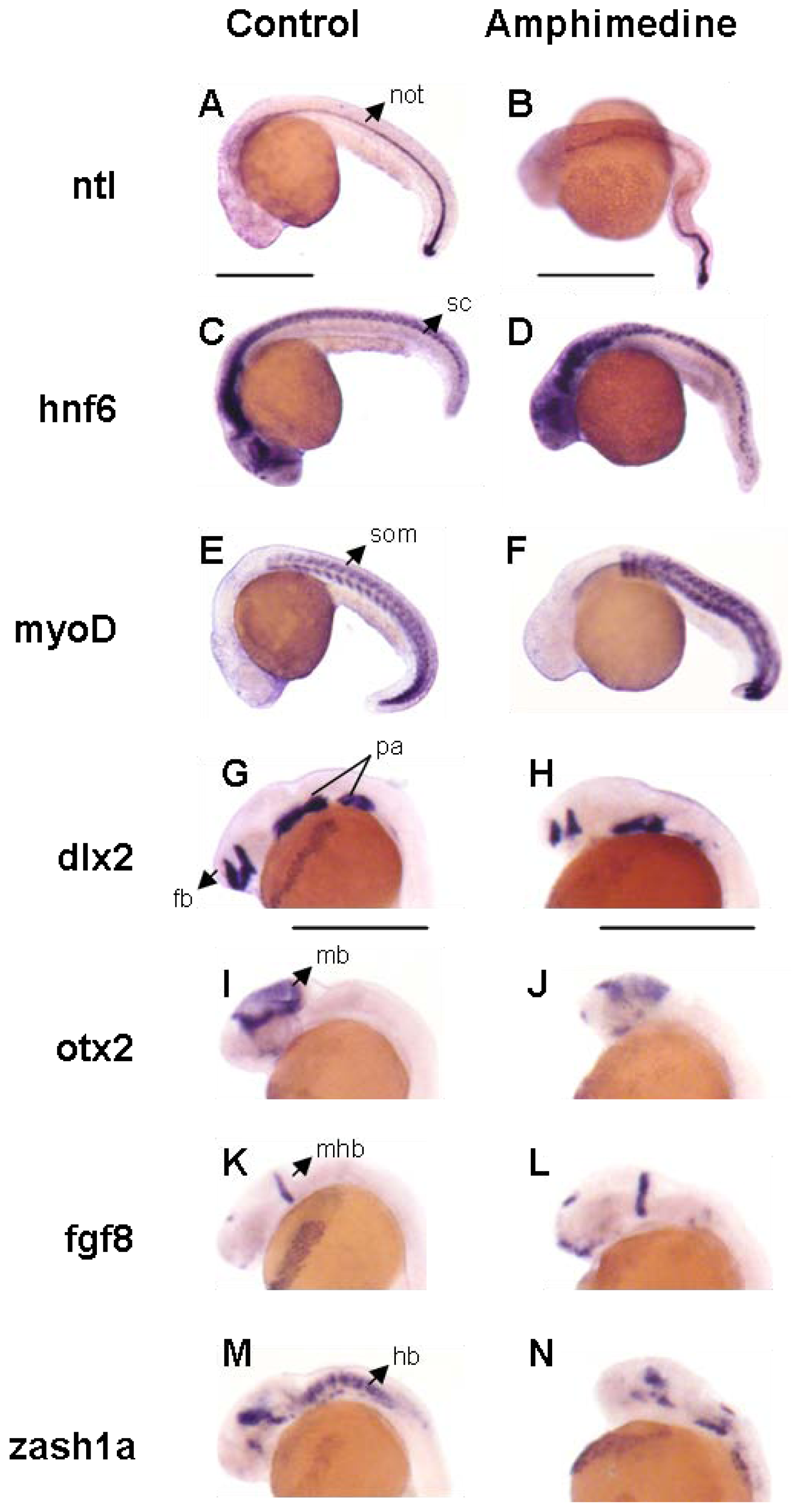
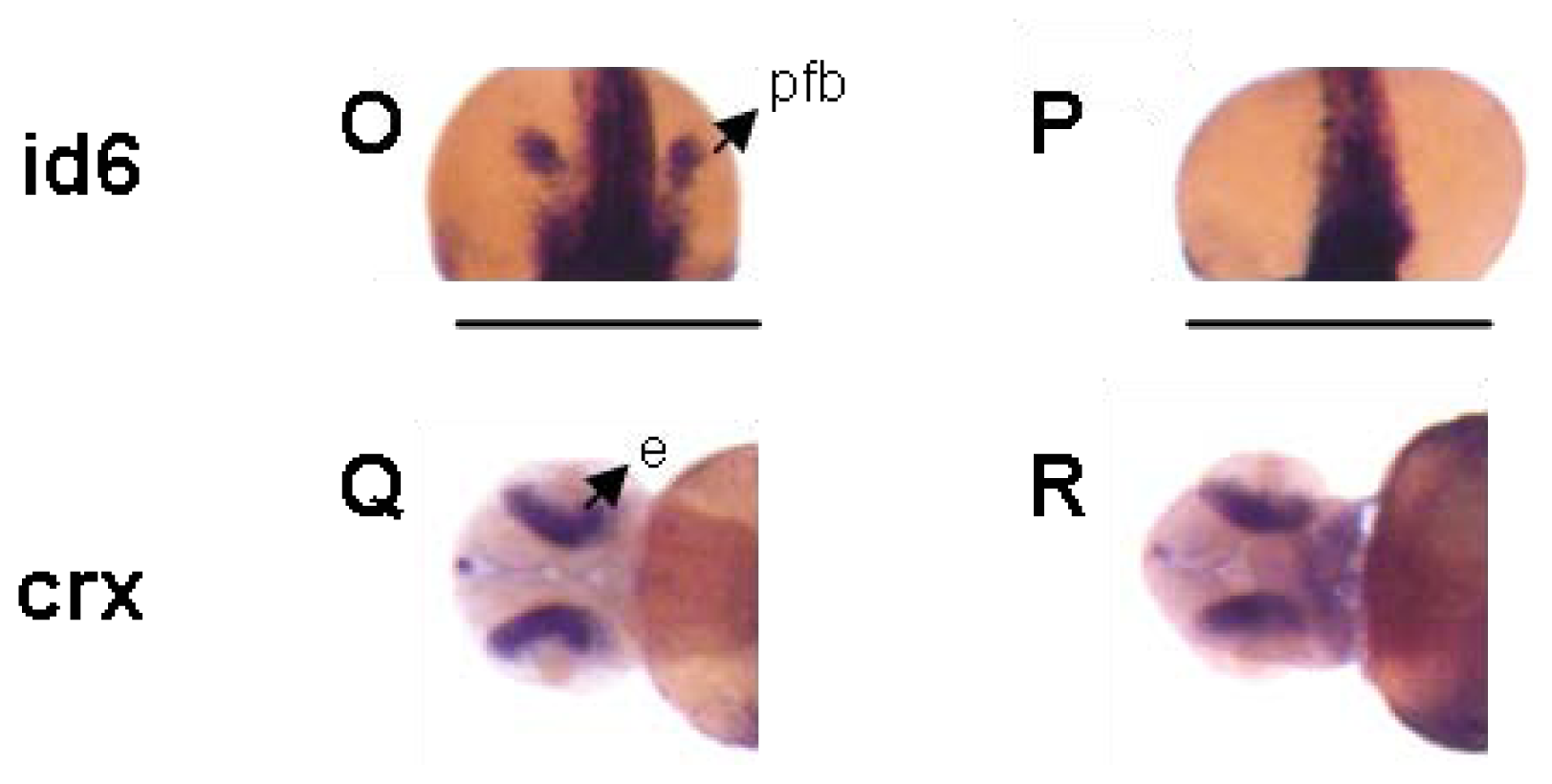
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Biological Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Zebrafish Screen
Acknowledgements
References
- Bowman, TV; Zon, LI. Swimming into the future of drug discovery: in vivo chemical screen in zebrafish. ACS Chem. Biol 2010, 5, 159–161. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, C; Hsu, CH; Wen, ZH; Lin, CS; Aqoramoorthy, G. Zebrafish: a complete animal model for in vivo drug discovery and development. Curr. Drug Metab 2009, 10, 116–124. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman, CK; White, RM; Zon, LI. Chemical genetic screening in the zebrafish embryo. Nat. Protoc 2009, 4, 1422–1432. [Google Scholar]
- Pichler, FB; Laurenson, S; Williams, LC; Dodd, A; Copp, BR; Love, DR. Chemical discovery and global gene expression analysis in zebrafish. Nat. Biotechnol 2003, 21, 879–883. [Google Scholar]
- Mandrekar, N; Thakur, NL. Significance of the zebrafish model in the discovery of bioactive molecules from nature. Biotechnol. Lett 2009, 31, 171–179. [Google Scholar]
- Crawford, AD; Esquerra, CV; de Witte, PA. Fishing for drugs from nature: zebrafish as a technology platform for natural product discovery. Planta Med 2008, 74, 624–632. [Google Scholar]
- He, MF; Liu, L; Ge, W; Shaw, PC; Liang, R; Wu, LW; But, PPH. Antiangiogenic activity of Tripterygium wilfordii and its terpenoids. J. Ethnopharm 2009, 121, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Suyama, TL; Cao, Z; Murray, TF; Gerwick, WH. Ichthyotoxic brominated diphenyl ethers from a mixed assemblage of a red alga and cyanobacterium: structure clarification and biological properties. Toxicon 2010, 55, 204–210. [Google Scholar]
- Kita, M; Roy, MC; Siwu, ER; Noma, I; Takiguchi, T; Itoh, M; Yamada, K; Koyama, T; Iwashita, T; Uemura, D. Durinskiol A: a long carbon-chain polyol compound from the symbiotic dinoflagellate Durinskia sp. Tetrahedron Lett 2007, 48, 3423–3427. [Google Scholar]
- Bugni, TS; Harper, MK; McCulloch, MW; Reppart, J; Ireland, CM. Fractionated marine invertebrate extract libraries for drug discovery. Molecules 2008, 13, 1372–1383. [Google Scholar]
- Bugni, TS; Richards, B; Bhoite, L; Cimbora, D; Harper, MK; Ireland, CM. Marine natural product libraries for high-throughput screening and rapid drug discovery. J. Nat. Prod 2008, 71, 1095–1098. [Google Scholar]
- Molinski, TF. Marine pyridoacridine alkaloids: structure, synthesis, and biological chemistry. Chem. Rev 1993, 93, 1825–1838. [Google Scholar]
- Molinski, TF; Fahy, E; Faulkner, JD; Van Duyne, GD; Clardy, J. Petrosamine, a novel pigment from the marine sponge Petrosia sp. J. Org. Chem 1988, 53, 1341–1343. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, AR; Ngo, AN; Quinn, RJ; Redburn, J; Hooper, JNA. Petrosamine B, an inhibitor of the Helicobacter pylori enzyme aspartyl semialdehyde dehydrogenase from the Australian sponge Oceanapia sp. J. Nat. Prod 2005, 68, 804–806. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz, FJ; Agarwal, SK; Gunasekera, SP; Schmidt, PG; Shoolery, JN. Amphimedine, new aromatic alkaloid from a pacific sponge, Amphimedon sp. Carbon connectivity determination from natural abundance 13C-13C coupling constants. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1983, 105, 4835–4836. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, KM; Barrows, LR. Biological activities of pyridoacridines. Nat. Prod. Rep 2004, 21, 731–751. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, KM; Matsumoto, SS; Holden, JA; Concepcion, GP; Tasdemir, D; Ireland, CM; Barrows, LR. The anti-neoplastic and novel topoisomerase II-mediated cytotoxicity of neoamphimedine, a marine pyridoacridine. Biochem. Pharmacol 2003, 66, 447–458. [Google Scholar]
- Tasdemir, D; Marshall, KM; Mangalindan, GC; Concepcion, GP; Barrows, LR; Harper, MK; Ireland, CM. Deoxyamphimedine, a new pyridoacridine alkaloid from two tropical Xestospongia sponges. J. Org. Chem 2001, 66, 3246–3248. [Google Scholar]
- de Guzman, FS; Carte, B; Troupe, N; Faulkner, DJ; Harper, MK; Concepcion, GP; Mangalindan, GC; Matsumoto, SS; Barrows, LR; Ireland, CM. Neoamphimedine: a new pyridoacridine topoisomerase II inhibitor which catenates DNA. J. Org. Chem 1999, 64, 1400–1402. [Google Scholar]
- Thale, Z; Johnson, T; Tenney, K; Wenzel, PJ; Lobkovsky, E; Clardy, J; Media, J; Pietraszkiewicz, H; Valeriote, FA; Crews, P. Structures and cytotoxic properties of sponge-derived bisannulated acridines. J. Org. Chem 2002, 67, 9384–9391. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay, BS; Barrows, LR; Copp, BR. Structural requirements for biological activity of the marine alkaloid ascididemin. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 1995, 5, 739–742. [Google Scholar]
- Clement, JA; Kitagaki, J; Yang, Y; Sauceds, CJ; McMahon, JB. Discovery of new pyridoacridine alkloids from Lissoclinum cf. badium that inhibit the ubiquitin ligase activity of Hdm2 and stabilize p53. Bioorg. Med. Chem 2008, 16, 10022–10028. [Google Scholar]
- Charylulu, GA; McKee, TC; Ireland, CM. Diplamine, a cytotoxic polyaromatic alkaloid from the tunicate Diplosoma sp. Tetrahedron Lett 1989, 30, 4201–4202. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, PJ; Pitts, TP; Gunawardana, GP; Kelly-Borges, M; Pomponi, SA. Antifungal activity of meridine, a natural product from the marine sponge Corticium sp. J. Nat. Prod 1992, 55, 1664–1668. [Google Scholar]
- Luedtke, NW; Hwang, JS; Glazer, EC; Gut, D; Kol, M; Tor, Y. Eilatin Ru(II) complexes display anti-HIV activity and enantiomeric diversity in the binding of RNA. ChemBioChem 2002, 3, 766–771. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, KM; Holden, JA; Koller, A; Kashman, Y; Copp, BR; Barrows, LR. AK37: the first pyridoacridine described capable of stabilizing the topoisomerase I cleavable complex. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2004, 15, 907–913. [Google Scholar]
- Westerfield, M. A Guide for the Laboratory use of Zebrafish (Danio rerio), 3rd ed; University of Oregon Press: Eugene, OR, USA, 1995; p. 385. [Google Scholar]
- Nauduld, LD; Sandoval, IT; Chidester, S; Yost, HJ; Jones, DA. Adenomatous polyposis coli control of retinoic acid biosynthesis is critical for zebrafish intestinal development and differentiation. J. Biol. Chem 2004, 279, 51581–51589. [Google Scholar]
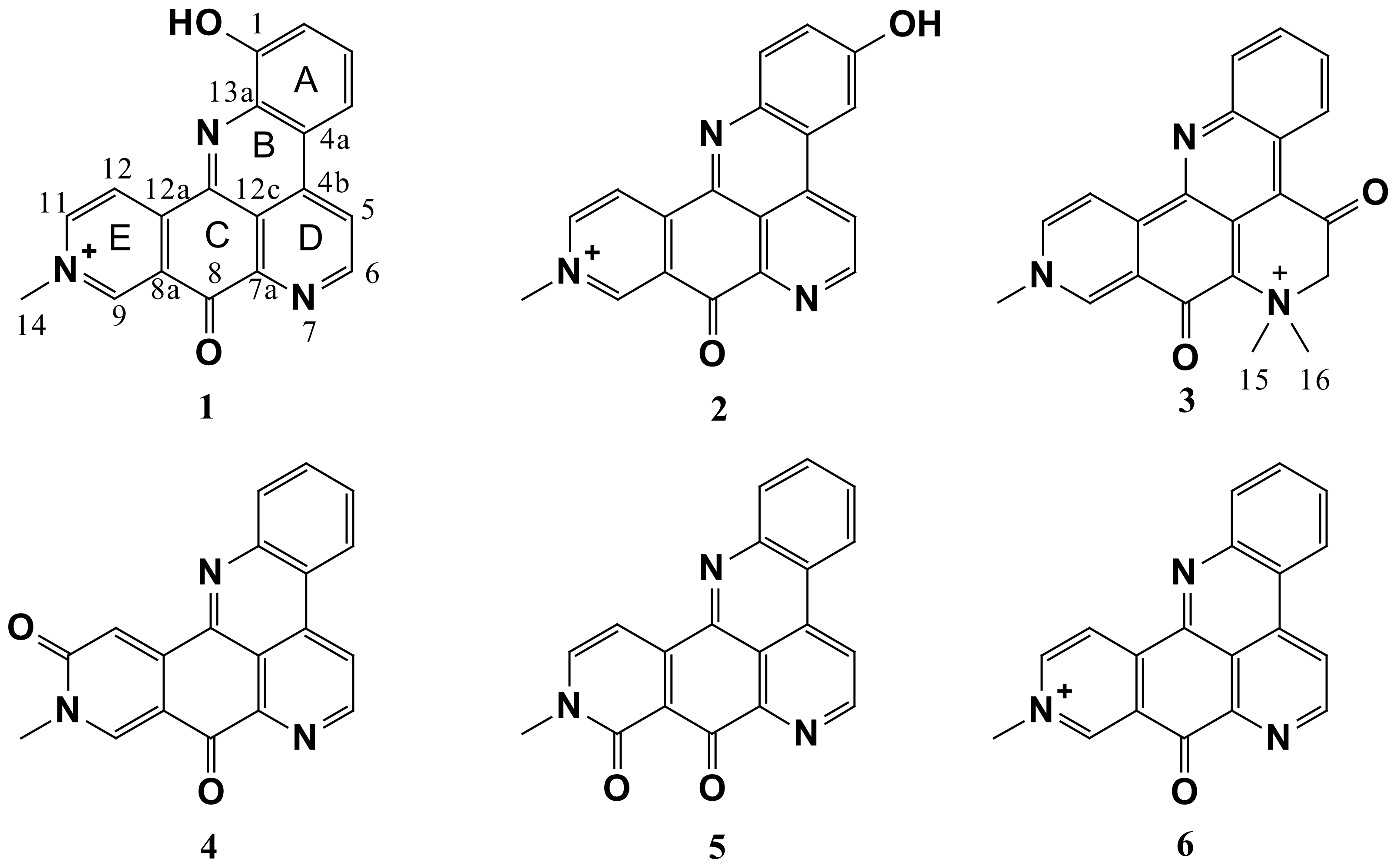
| Posn. | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH, mult (JH-H) | δC, mult a | δH, mult (JH-H) | δC, mult b | δH, mult (JH-H) | δC, mult c | ||||
| 1 | 156.1 | C | 8.39, d (9.0) | 135.8 | CH | 8.19, d (9.0) | 143.0 | CH | |
| 2 | 7.48, d (8.0) | 116.5 | CH | 7.63, dd (9.0, 2.5) | 124.3 | CH | 7.73, dd (9.0, 7.5) | 128.4 | CH |
| 3 | 7.91, dd (8.0, 8.0) | 133.3 | CH | 162.7 | C | 7.84, dd (8.0, 7.5) | 133.5 | CH | |
| 4 | 8.45, d (8.0) | 114.5 | CH | 8.20, d (2.5) | 108.0 | CH | 9.27, d (8.0) | 125.1 | CH |
| 4a | 123.8 | C | 126.6 | C | 125.2 | C | |||
| 4b | 137.9 | C | 140.9 | C | 115.8 | C | |||
| 5 | 9.13, d (6.0) | 121.8 | CH | 9.00, d (6.0) | 122.9 | CH | 187.2 | C | |
| 6 | 9.37, d (6.0) | 150.2 | CH | 9.30, d (6.0) | 151.4 | CH | 4.41, s | 71.4 | CH2 |
| 7a | 147.0 | C | 149.5 | C | 115.1 | C | |||
| 8 | 180.0 | C | 180.6 | C | 161.0 | C | |||
| 8a | 130.3 | C | 130.8 | C | 132.7 | C | |||
| 9 | 9.87, s | 146.0 | CH | 9.82, s | 147.9 | CH | 9.72, s | 145.9 | CH |
| 11 | 9.40, d (6.5) | 147.8 | CH | 9.17, d (6.5) | 148.7 | CH | 8.75, d (6.5) | 142.0 | CH |
| 12 | 9.90, d (6.5) | 123.5 | CH | 9.38, d (6.5) | 124.1 | CH | 9.39, d (6.5) | 122.9 | CH |
| 12a | 147.9 | C | 149.2 | C | 143.5 | C | |||
| 12b | 143.1 | C | 145.5 | C | 139.5 | C | |||
| 12c | 120.1 | C | 120.8 | C | 129.9 | C | |||
| 13a | 134.4 | C | 141.5 | C | 143.1 | C | |||
| 14 | 4.57, s | 48.3 | CH3 | 4.58, s | 49.3 | CH3 | 4.53 | 49.0 | CH3 |
| 15 | 3.84, s (3H) | 54.1 | CH3 | ||||||
| 16 | 3.84, s (3H) | 54.1 | CH3 | ||||||
© 2008 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, X.; Bugni, T.S.; Harper, M.K.; Sandoval, I.T.; Manos, E.J.; Swift, J.; Van Wagoner, R.M.; Jones, D.A.; Ireland, C.M. Evaluation of Pyridoacridine Alkaloids in a Zebrafish Phenotypic Assay. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1769-1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8061769
Wei X, Bugni TS, Harper MK, Sandoval IT, Manos EJ, Swift J, Van Wagoner RM, Jones DA, Ireland CM. Evaluation of Pyridoacridine Alkaloids in a Zebrafish Phenotypic Assay. Marine Drugs. 2010; 8(6):1769-1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8061769
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Xiaomei, Tim S. Bugni, Mary Kay Harper, Imelda T. Sandoval, Elizabeth J. Manos, Jennifer Swift, Ryan M. Van Wagoner, David A. Jones, and Chris M. Ireland. 2010. "Evaluation of Pyridoacridine Alkaloids in a Zebrafish Phenotypic Assay" Marine Drugs 8, no. 6: 1769-1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8061769




