2. Results and Discussion
Sinularone A (
1) has a molecular formula of C
15H
24O
2 as established by the HRESIMS (
m/z 259.1674 [M + Na]
+, calcd. 259.1674) and NMR data, indicating 4° unsaturation. The IR absorptions at 1738 and 1717 cm
−1 suggested the presence of carbonyl groups. The
1H NMR spectrum exhibited the signals for a single olefinic proton at
δH 5.12 (1H, t,
J = 7.2 Hz, H-8), four methyl singlets at
δH 1.01 (3H, s, H
3-13), 1.13 (3H, s, H
3-14), 1.61 (3H, s, H
3-15) and 2.07 (3H, s, H
3-12), together with 11 aliphatic protons. APT spectra displayed 15 carbon resonances, involving two ketones at
δC 220.0 (C-1) and 208.5 (C-11), and two olefinic carbons at
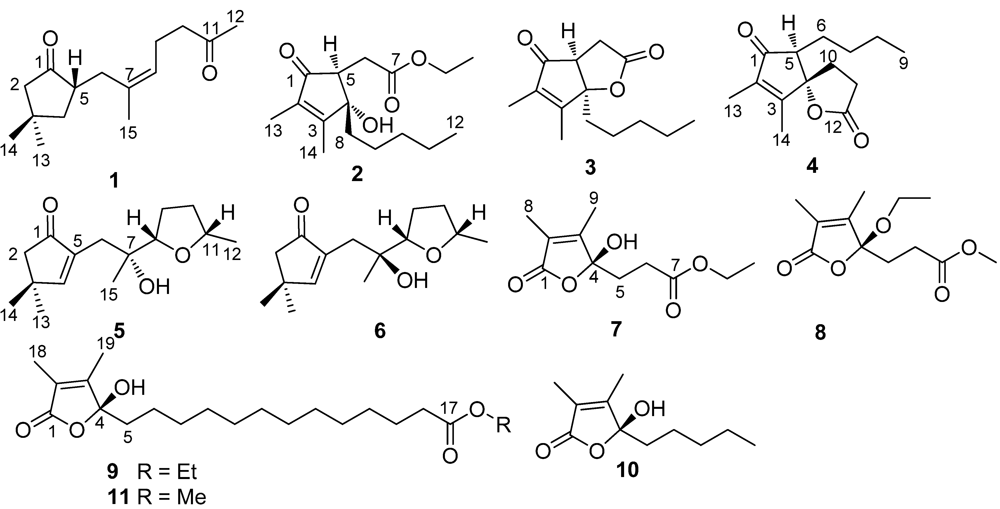
δC 125.7 (CH, C-8) and 133.9 (C, C-7). The proton signals and their associated carbons were assigned by HMQC. The COSY cross-peaks allowed to establish the proton-proton spin systems from C-4 to C-6 and from C-8 to C-10, while the HMBC interactions from the olefinic H
3-15 to C-6 (
δC 32.3), C-7, and C-8, and from H
3-12 to C-11 and C-10 (
δC 43.4) led to the connectivity of the subunits to form a linear chain defined as a 7-methylhept-7-en-11-one group (
Figure 2). Additional HMBC interactions from the geminal protons H
α,β-2 (
δH 2.08, 2.16) to C-3 (
δC 34.0), C-4 (
δC 43.5), C-5 (
δC 46.7) and C-1, along with the correlations from both H
3-13 and H
3-14 to C-2 (
δC 52.8), C-3, and C-4, and from H-5 (
δH 2.49, m) to C-1 and C-3 indicated the presence of a 3,3-dimethylcyclopentanone nucleus. Subsequently, the linear side chain was determined to be linked to the nucleus at C-5 on the basis of the COSY relationships in addition to the HMBC interactions from H
2-4 (
δH 1.41, 1.84) to C-6 and from H
2-6 to C-1, C-4, and C-5. The geometry of Δ
7 was assigned to 7
Z according to the NOE interaction between H
3-15 and H-8 in addition to the chemical shift of C-15 (
δC 23.5), higher than 20 ppm [
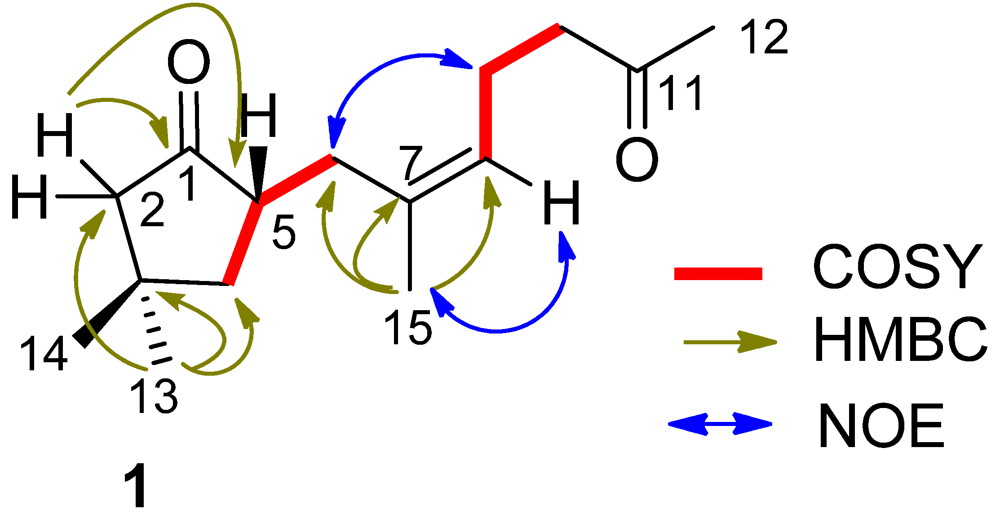
11]. In regard to the configuration of the stereogenic center C-5, the CD spectrum showed a negative Cotton effect at 212 nm for
n–π* transition in agreement with the electronic circular dichroism (ECD) data which was calculated for 5
S configuration by time dependent density functional theory (TD DFT) at 6-31+G(
d,
p)//DFT B3LYP/6-31+G(
d,
p) level [
12]. This assignment was also supported by the octant rule which allowed the side chain to be located at the negative CD region (
Figure 3) [
13].
Figure 2.
Key COSY, HMBC and NOE relationships of (1).
Figure 2.
Key COSY, HMBC and NOE relationships of (1).
Figure 3.
CD, electronic circular dichroism (ECD) and octant rule of (1).
Figure 3.
CD, electronic circular dichroism (ECD) and octant rule of (1).
Sinularone B (
2) has a molecular formula of C
16H
26O
4 as determined by the HRESIMS (
m/z 305.1732 [M + Na]
+, calcd. 305.1729) and NMR data, indicating 4° unsaturation. The IR absorptions at 3489, 1737, 1707 and 1653 cm
−1 suggested the presence of hydroxy, carbonyl, and olefinic groups. The
1H NMR spectrum exhibited two terminal methyls appearing as doublets at
δH 0.80 (3H, t,
J = 7.0 Hz, H
3-12) and 1.21 (3H, t,
J = 7.1 Hz, H
3-1′), and two olefinic methyl singlets at
δH 1.62 (3H, s, H
3-13) and 1.90 (3H, s, H
3-14), in addition to 13 aliphatic protons (
Table 1). APT spectrum displayed a total of 16 carbon resonances, of which two carbonyl carbons, two olefinic carbons, an oxygen-bearing sp
3 carbon, and an oxymethylene were observed (
Table 2). The presence of a
n-pentyl unit was recognized by the COSY and HMBC relationships to establish a side chain from C-8 to C-12, while an ethoxy group was ascribed to the COSY coupling between H
3-1′ and
δH 4.10 (2H, q,
J = 7.1 Hz, H
2-2′). In HMBC spectrum, the interactions from H
3-13 to the carbons at
δC 203.8 (C-1), 134.3 (C-2), and 170.0 (C-3), and from H
3-14 to C-2, C-3, and C-4 (
δC 80.1), in addition to the interaction from a methine proton
δH 2.89 (1H, dd,
J = 5.6, 8.4, H-5) to C-1, C-2, C-3, and C-4, conducted to establish a 2,3-dimethylcyclopent-2-enone nucleus. The COSY coupling between H-5 and the methylene protons H
2-6 at
δH 2.44 (1H, dd,
J = 5.6, 16.0 Hz) and 2.35 (1H, dd,
J = 8.4, 16.0 Hz) in association with the HMBC interaction from the carbonyl carbon (
δC 172.5, C-7) to H-5, H
2-6, and the oxymethylene H
2-2′, ascertained an ethylacetate unit linked to C-5 (
δC 55.3). The oxygenated quaternary carbon C-4 was determined to be co-positioned by a
n-pentyl unit and a hydroxy group on the basis of the HMBC interactions between H-5 and the methylene carbon C-8 (
δC 35.9), and in turn from H
2-8 (
δH 1.54, 1.58) to C-3, C-4, and C-5, in addition to a D
2O exchangeable proton (
δH 5.28, s) showing HMBC relationship with C-4. The NOE interaction between H
2-6 and H
2-8 (
δH 1.54, 1.58) was indicative of their
cis relationship. Thus, the relative configurations of the stereogenic centers were depicted to be 4
S* and 5
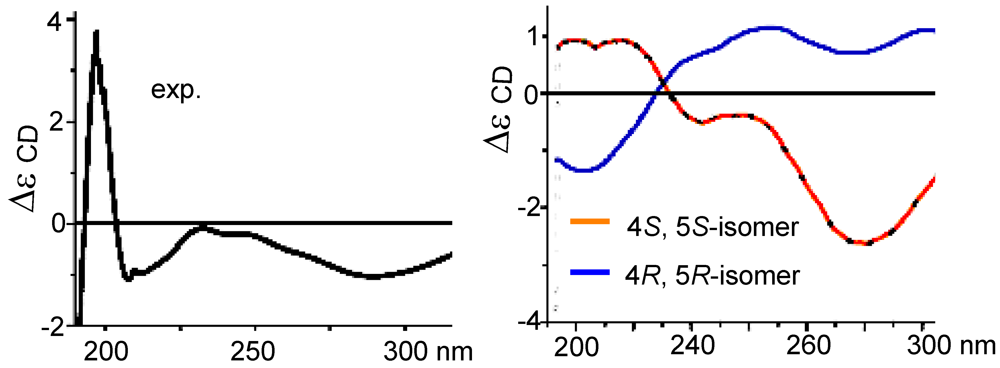
S*. The measured CD curve of
2 was closely similar to the calculated ECD for 4
S,5
S-isomer in opposite to the data for 4
R,5
R-isomer (
Figure 4), indicating
2 to be in agreement with 4
S and 5
S.
The NMR spectroscopic data of sinularone C (3) were closely related to those of 2, except for the absence of the signals for an ethoxy group. Analysis of 1D and 2D NMR (COSY, HMQC and HMBC) disclosed a 2,3-dimethylcyclopent-2-enone nucleus, and a n-pentyl group being linked to the nucleus at C-4, showing the partial structure to be the same as that of 2. The COSY cross-peaks between H-5 (δH 3.11) and H2-6 (δH 2.49, 3.08) and the HMBC interactions of these protons with a carbonyl carbon C-7 (δC 174.9) and the ketone C-1 (δC 204.9) allowed to link C-6 of an acetyl unit to cyclopent-2-enone nucleus at C-5. In addition, a quaternary carbon observed at δC 92.4 was assigned to C-4 on the basis of the HMBC interactions of C-4 to H-5 and H2-6. The molecular formula (C14H20O3) (HRESIMS m/z 259.1315 [M + Na]+) of 3 showing a C2H6O unit less than that of 2 and requiring 5° unsaturation, in association with the obvious downfield shifted C-4 in comparison with that of 2, allowed to connect C-4 and C-7 to form a γ-lactone, which was fused to the cyclopentenone ring across C-4 and C-5. The observed NOE interactions from H-5 to H2-8 (δH 1.79, 1.97) and H2-9 (δH 1.10, 1.16) indicated H-5 to be oriented in the same face as n-pentyl group. This assignment was supported by the irradiation of H2-8 causing the NOE enhancement of H-5 (1.7%, 1.2%). Compound 3 is likely a precursor to generate 2 by ethoxylation. Thus, the absolute configuration of C-5 in 3 is suggested to be the same as that of 2. Accordingly, the chiral centers of 3 were assumed to be 4R and 5S.
Table 1.
1H NMR data of sinulactones A–H (1–8) (500 MHz, δH, J in Hz).
Table 1.
1H NMR data of sinulactones A–H (1–8) (500 MHz, δH, J in Hz).
| No. | 1 a | 2 a | 3 a | 4 a | 5 a | 6 a | 7 a | 8 b |
|---|
| 2 | 2.08 d (16.4) | | | | 2.18 s | 2.18 d (18.0) | | |
| 2.16 d (16.4) | | | | 2.18 s | 2.22 d (18.0) | | |
| 4 | 1.41 dd (11.5, 12.4) | | | | 7.35 s | 7.35 s | | |
| 1.84 dd (8.4, 12.4) | | | | | | | |
| 5 | 2.49 m | 2.89 dd (5.6, 8.4) | 3.11 dd (5.5, 10.2) | 2.55 t (6.5) | | | 1.91 ddd (6.0, 6.0, 17.0) | 1.97 ddd (7.8, 7.8, 15.5) |
| | | | | | 2.32 ddd (6.0, 8.0, 17.0) | 2.22 m |
| 6 | 2.06 m | 2.35 dd (8.4, 16.0) | 2.49 dd (10.2, 15.5) | 1.45 m | 2.09 d (13.9) | 2.21 s | 2.49 ddd (6.0, 6.0, 18.0) | 2.24 m |
| 2.29 dd (4.2, 13.4) | 2.44 dd (5.6, 16.0) | 3.08 dd (5.5, 15.5) | 1.67 m | 2.27 d (13.9) | 2.21 s | 2.78 ddd (6.0, 8.0, 18.0) | 2.27 m |
| 7 | | | | 1.30 m | | | | |
| | | | 1.46 m | | | | |
| 8 | 5.12 t (7.2) | 1.54 ddd (4.0, 11.0, 12.0) | 1.79 ddd (4.7, 12.1, 13.5) | 1.30 m | 3.57 t (7.2) | 3.56 dd (7.4, 7.4) | 1.80 s | 1.77 s |
| 1.58 ddd (5.5, 11.0, 12.0) | 1.97 ddd (4.5, 12.1, 13.5) | 1.32 m | | | | |
| 9 | 2.16 ddt (7.2, 7.4, 12.0) | 0.53 m | 1.10 m | 0.88 t (7.2) | 1.75 m | 1.71 m | 1.96 s | 1.87 s |
| 2.19 ddt (7.2, 7.4, 12.0) | 0.66 m | 1.16 m | | 1.80 m | 1.78 m | | |
| 10 | 2.44 dd (7.4, 7.4) | 1.15 m | 1.29 m | 2.16 ddd (7.7, 10.6, 13.9) | 1.27 m | 1.30 m | | |
| | | 2.23 ddd (6.2, 10.3, 13.9) | 1.87 m | 1.87 m | | |
| 11 | | 1.18 m | 1.29 m | 2.72 ddd (7.7, 10.3, 18.4) | 3.83 m | 3.86 m | | |
| | | 2.78 ddd (6.2, 10.6, 18.4) | | | | |
| 12 | 2.07 s | 0.80 t (7.0) | 0.86 t (7.1) | | 1.13 d (6.0) | 1.14 d (6.0) | | |
| 13 | 1.01 s | 1.62 s | 1.67 s | 1.65 s | 1.15 s | 1.15 s | | |
| 14 | 1.13 s | 1.90 s | 2.02 s | 1.97 s | 1.15 s | 1.15 s | | |
| 15 | 1.61 s | | | | 0.87 s | 0.84 s | | |
| EtO | | 4.10 q (7.1) | | | | | 4.17 q (7.1) | 3.13 dq (7.0, 12.0) |
| 1.21 t (7.1) | | | | | 1.27 t (7.1) | 3.24 dq (7.0, 12.0) |
| | | | | | | 1.09 t (7.0) |
| | | | | | | 3.58 s |
| OH-4 | | 5.28 s | | | | | 5.26 s | |
| OH-7 | | | | | 4.16 s | 4.16 s | | |
Table 2.
13C NMR data of sinulactones A−H (1−8) (125 MHz, δC, mult.).
Table 2.
13C NMR data of sinulactones A−H (1−8) (125 MHz, δC, mult.).
| No. | 1 a | 2 a | 3 a | 4 a | 5 a | 6 a | 7 a | 8 b |
|---|
| 1 | 220.0 C | 203.8 C | 204.9 C | 203.4 C | 209.4 C | 209.4 C | 171.8 C | 171.1 C |
| 2 | 52.8 CH2 | 134.3 C | 138.7 C | 136.4 C | 49.8 CH2 | 49.8 CH2 | 124.7 C | 127.1 C |
| 3 | 34.0 C | 170.0 C | 166.7 C | 164.9 C | 38.9 C | 38.9 C | 158.2 C | 156.7 C |
| 4 | 43.5 CH2 | 80.1 C | 92.4 C | 91.5 C | 170.8 C | 170.7 C | 105.5 C | 109.1 C |
| 5 | 46.7 CH | 55.3 CH | 46.4 CH | 54.5 CH | 138.8 C | 138.9 C | 31.3 CH2 | 31.3 CH2 |
| 6 | 32.3 CH2 | 29.6 CH2 | 32.3 CH2 | 24.8 CH2 | 33.5 CH2 | 32.2 CH2 | 28.9 CH2 | 28.0 CH2 |
| 7 | 133.9 C | 172.5 C | 174.9 C | 29.3 CH2 | 72.5 C | 72.3 C | 174.8 C | 172.9 C |
| 8 | 125.7 CH | 35.9 CH2 | 34.0 CH2 | 22.2 CH2 | 85.2 CH | 85.2 CH | 8.4 CH3 | 8.6 CH3 |
| 9 | 22.3 CH2 | 24.6 CH2 | 23.0 CH2 | 13.7 CH3 | 26.2 CH2 | 26.1 CH2 | 10.6 CH3 | 11.0 CH3 |
| 10 | 43.4 CH2 | 31.9 CH2 | 31.7 CH2 | 25.3 CH2 | 33.3 CH2 | 33.2 CH2 | | |
| 11 | 208.5 C | 22.3 CH2 | 22.3 CH2 | 28.7 CH2 | 75.3 CH | 75.2 CH | | |
| 12 | 30.2 CH3 | 14.3 CH3 | 14.3 CH3 | 176.1 C | 21.3 CH3 | 21.4 CH3 | | |
| 13 | 28.1 CH3 | 8.0 CH3 | 8.3 CH3 | 7.8 CH3 | 28.6 CH3 | 28.5 CH3 | | |
| 14 | 29.9 CH3 | 11.6 CH3 | 12.3 CH3 | 10.6 CH3 | 28.4 CH3 | 28.5 CH3 | | |
| 15 | 23.5 CH3 | | | | 21.9 CH3 | 23.4 CH3 | | |
| 16 | | | | | | | | |
| 17 | | | | | | | | |
| 18 | | | | | | | | |
| EtO | | 14.5 CH3 | | | | | 14.1 CH3 | 15.4 CH3 |
| | 60.5 CH2 | | | | | 61.5 CH2 | 58.4 CH2 |
| MeO | | | | | | | | 51.9 CH3 |
Figure 4.
CD and ECD spectra of (2).
Figure 4.
CD and ECD spectra of (2).
The molecular formula (C
14H
20O
3) of sinularone D (
4) was determined to be the same as that of
3 on the basis of the HRESIMS data (
m/z 259.1313 [M + Na]
+, calcd. 259.1310) and NMR data. The IR absorptions at 1778, 1710 and 1657 cm
−1 were characteristic of lactone, ketone, and olefinic groups. Comparison of the NMR data revealed the resonances of
4 in respect to those of a 2,3-dimethylcyclopent-2-enone nucleus (
Table 1 and
Table 2) compatible to the data of
3. However, the COSY and HMBC relationships revealed a
n-butyl group to replace a
n-pentyl group of
3. This unit was determined to be linked to C-5 (
δC 54.5) as evident from the COSY correlation between H
2-6 (
δH 1.45, 1.67) and H-5 (
δH 2.55, t,
J = 6.5 Hz) in association with the HMBC interactions from H
2-6 to C-1 (
δC 203.4). The remaining resonances included two methylenes and a carbonyl carbon (
δC 176.1, C-12). The COSY correlation between H
2-10 (
δH 2.16, 2.23) and H
2-11 (
δH 2.72, 2.78) and the HMBC interactions from H
2-10 to C-12 and from H
2-11 to C-4 (
δC 91.5, C), in association with the molecular formula requiring 5° unsaturation, conducted the quaternary carbon C-4 to be located by a γ-lactone. The NOE interaction between H
2-6 and H
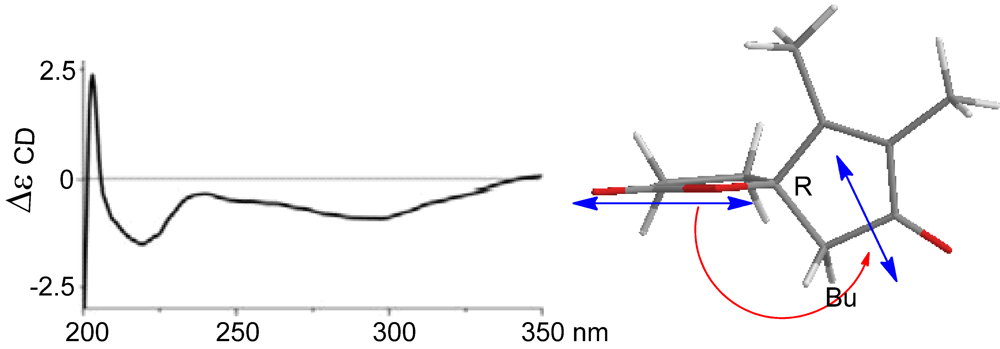
2-10 reflected the same orientation of H-5 and the heterocyclic atom of lactone. In regard to the absolute configuration of the
spiro carbon C-4, we extended the CD method originally used for the chiral center of allylic amines [
14]. The negative Cotton effect at 222 nm belonging to the π–π* charge-transfer transition polarized by the lactone carbonyl group and the enone unit, correlated with anti-clockwise screw (
Figure 5). Therefore, the sign of the Cotton effect reflected a 4
R configuration. In combination with NOE data, C-5 was thus assigned to
S configuration.
Figure 5.
Cotton effect of (4).
Figure 5.
Cotton effect of (4).
The NMR spectroscopic data of 5 and 6 are very similar, while HRESIMS data revealed both compounds shared the same molecular formula (C15H24O3), indicating 4° unsaturation. APT spectrum of 5 displayed 15 carbon resonances, involving one ketone (δC 209.4, C-1), two olefinic carbons (δC 138.8, C-5; 170.8, C-4), two oxymethines at δC 85.2 (C-8) and 75.3 (C-11) and four methyls (δC 21.3, 21.9, 28.4, 28.6). The observation of HMBC interactions from the isolated methylene protons at δH 2.18 (2H, s, H2-2) to C-1, C-3 (δC 38.9, C), C-4, and C-5 and from H-4 (δH 7.35, s) to C-1, C-2, and C-3, in addition to the methyl singlets at δH 1.15 (6H, s, H3-13 and H3-14) to C-2, C-3, and C-4, ascertained the presence of 5-substituted 3,3-dimethylcyclopent-4-enone. In regard to the remaining resonances, the COSY correlations extended a moiety from C-8 to C-12, in which C-8 and C-11 were oxygenated. Additionally, the HMBC interactions from H3-15 (δH 0.87, s) to the methylene carbon C-6 (δC 33.5), quaternary carbon C-7 (δC 72.5) and C-8 and from H-8 (δH 3.57, t, J = 7.2 Hz) to C-11 indicated the formation of an ether bridge across C-8 and C-11, while C-7 was co-positioned by a methyl and a hydroxy groups. The side chain was linked to C-5 as evident from the HMBC relationships of H2-6 (δH 2.09, 2.27) with C-1, C-5, and C-4. Based on the NOE interaction between H-8 and H-11, a cis-geometry of the 8,11-epoxy bonding was assigned. Thus, the relative configurations were suggested to be 8S* and 11S*.
Analysis of 2D NMR data revealed sinularone F (
6) to be a stereoisomer of
5. Both compounds showed the NOE interaction between H-8 and H-11, indicating them to be oriented in the same face toward tetrahydrofuran ring. The major difference was found by the chemical shifts at C-6 and C-15 (
Table 2), implying
6 to be a C-7 epimer of
5 rather than an enantiomer. Since the calculated ECD data could not provide confidential evidence to judge the configurations, the calculation for specific rotation and
13C NMR data was performed. The conformations with relative energies from 0 to 2.5 kcal/mol were used in optical rotation computations at B3LYP/6-311+G(2
d,
p) level, while Boltzmann statistics were used for rotation computations of all conformations. The computed specific rotation [
15] for 7
S,8
R,11
R-isomer is −16.9 and −27.5 for 7
R,8
R,11
R-isomer. These data are in opposite sign to the experimental data that of
5 ([α]
D23 +18.0) and
6 ([α]
D23 +22.6), indicating
5 and
6 to be the enantiomers of the calculated isomers. These assignments were also supported by the relative shift errors of the experimental
13C NMR data of
6 and
5 that were in accordance with the error distribution calculated at B3LYP/6-311+G(2
d,
p) level (
Table 3) [
16]. Thus, the absolute configurations of
5 were in agreement with 7
R,8
S,11
S, whereas those of
6 were assigned to 7
S,8
S,11
S.
Table 3.
The error patents of 13C NMR data of 6 and 5 in experiments and computations.
Table 3.
The error patents of 13C NMR data of 6 and 5 in experiments and computations.
| Position | 6 | 5 | Δδ6−5 | 6 * | 5 * | Δδ6−5 |
|---|
| 1 | 209.4 | 209.4 | 0.0 | 206.0 | 205.8 | 0.2 |
| 2 | 49.8 | 49.8 | 0.0 | 49.2 | 49.2 | 0.0 |
| 3 | 38.9 | 38.9 | 0.0 | 41.9 | 42.0 | −0.1 |
| 4 | 170.7 | 170.8 | −0.1 | 171.2 | 171.1 | 0.1 |
| 5 | 138.9 | 138.8 | 0.1 | 142.8 | 142.5 | 0.3 |
| 6 | 32.2 | 33.5 | −1.3 | 32.7 | 39.8 | −7.1 |
| 7 | 72.3 | 72.5 | −0.2 | 72.4 | 72.7 | −0.3 |
| 8 | 85.2 | 85.2 | 0.0 | 84.8 | 84.1 | 0.7 |
| 9 | 26.1 | 26.2 | −0.1 | 27.2 | 27.4 | −0.2 |
| 10 | 33.2 | 33.3 | −0.1 | 34.3 | 34.7 | −0.4 |
| 11 | 75.2 | 75.3 | −0.1 | 75.7 | 75.8 | −0.1 |
| 12 | 21.4 | 21.3 | 0.1 | 18.5 | 18.6 | −0.1 |
| 13 | 28.5 | 28.6 | −0.1 | 26.2 | 26.4 | −0.2 |
| 14 | 28.5 | 28.4 | 0.1 | 26.2 | 26.2 | 0.0 |
| 15 | 23.4 | 21.9 | 1.5 | 24.4 | 17.4 | 7.0 |
Sinularone G (
7) has a molecular formula of C
11H
16O
5 as determined by HRESIMS data (
m/z 251.0886 [M + Na]
+, calcd. 251.0895), requiring 4° unsaturation. The
1H NMR exhibited two olefinic methyl singlets at
δH 1.80 (3H, s, H
3-8) and 1.96 (3H, s, H
3-9) and a methyl triplet (
δH 1.27, H
3-1′), while
13C NMR involved two carbonyl carbons at
δC 171.8 (C-1) and 174.8 (C-7), two olefinic carbons at
δC 124.7 (C-2) and 158.2 (C-3), and an acetal carbon at
δC 105.5 (C-4). The HMBC interactions of H
3-8 to C-1, C-2, and C-3 and from H
3-9 to C-2, C-3, and C-4 disclosed a α,β-unsaturated 2,3-dimethyl-γ-lactone, the same as that of a known butenolide [
17]. In addition, an ethylpropanoate was recognized by the COSY relationships between two vicinal methylenes along with a methyl triplet H
3-1′ coupled to the oxymethylene at
δH 4.17 (H
2-2′), in combination with the HMBC interactions from C-7 to the protons of H
2-6 (
δH 2.49, 2.78), H
2-5 (
δH 1.91, 2.32), and the oxymethylene (
δC 61.5). The positive specific rotation ([α]
D +4.03°) and the similar Cotton effect in comparison with those of a known butenolide (
11) supposed C-4 to be 4
S configuration [
11,
17].
The NMR data of sinularone H (8) were similar to those of 7 with the exception of the presence of an additional methoxy group. Examination of the HMBC cross-peaks afforded the interactions between the carbonyl carbon (δC 172.9, C-7) and the methoxy protons (δH 3.58, s) and between the acetal carbon (δC 109.1, C-4) and the oxymethylene (δH 3.13, 3.24), requiring the formation of a methyl ester, while the ethoxy group was substituted to C-4. The absolute configuration of C-4 was supposed to be the same as that of 7 on the basis of similar specific rotation and CD data.
The NMR data of sinularone I (
9) were mostly identical to those of a known butenolide (
11) [
17]. The distinction was attributed to the presence of an ethyl ester to replace a methyl ester of the known analogue, as evident from the molecular weight of
9 (C
21H
36O
5) to be 14 amu more than that of the latter, and the presence of an ethoxy group in its NMR spectra. The absolute configuration was determined to be 4
S on the basis of the similar specific rotation and Cotton effect as those of
8 and the known analogues [
17].
In addition, the spectroscopic data and the specific rotation indicated the butenolide
10 to be identical to (
S)-4-hydroxy-2,3-dimethyl-4-pentyl-γ-lactone, isolated from the fruiting bodies of a fungus [
11].
All compounds were tested for their cytotoxicity against a panel of tumor cell lines including human ovarian carcinoma A2780, human lung adenocarcinoma A549, human gastric carcinoma BGC823, human hepatoma Bel7402, and human colonic carcinoma HCT-8. However, they showed weak inhibitory activity with IC
50 > 10 μg/mL. In order to detect whether these compounds play a role for ecological functions, the test for antifouling activity against the larvae of the barnacle
Balanus amphitrite was performed [
18,
19]. The bioassay results revealed compounds
1–
2,
7–
10 showed potent inhibition with the EC
50 values (
Table 4) lower than the standard requirement (EC
50 < 25 μg/mL) in regard to the efficacy level of natural antifouling agents as established by the US navy program [
20]. However, compounds
3–
6 showed weak inhibition with EC
50 > 50 μg/mL. In addition, the bioactive compounds (
1–
2,
7–
10)showed weak toxicity against the barnacle with LC
50 > 50 μg/mL. A primary discussion of structure-activity relationship implied that α,β-unsaturated 2,3-dimethyl-γ-lactone is a functional unit for anti-barnacle. Among the active compounds,
10 is the most active, suggesting it to be a promising candidate as a nontoxic natural antifouling agent.
Table 4.
Antifouling activity of compounds against the larvae of barnacle B. amphitrite *.
Table 4.
Antifouling activity of compounds against the larvae of barnacle B. amphitrite *.
| Compounds | Balanus amphitrite Larvae |
|---|
| EC50 (µg/mL) | LC50 (µg/mL) | LC50/EC50 |
|---|
| 1 | 13.86 | >50 | >3.61 |
| 2 | 23.50 | >50 | >2.13 |
| 7 | 18.65 | >50 | >2.69 |
| 8 | 21.39 | >50 | >2.34 |
| 9 | 12.58 | >50 | >3.97 |
| 10 | 3.84 | >50 | >13.02 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General
Optical rotations were measured on a Perkin-Elmer 243B polarimeter. IR spectra were determined on a Thermo Nicolet Nexus 470 FTIR spectrometer. CD spectra were measured using J-810-150s spectropolarimeter (Jasco, Darmstadt, Germany). 1H and 13C NMR and 2D NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker Avance 600 MHz and Bruker Avance 500 MHz using TMS as an internal standard. HRESIMS data were obtained on a LTQ Orbitrap XL instrument. HPLC was performed with a C18 packed column (250 × 10 nm) and using a DAD detector.
3.2. Animal Material
The soft coral Sinularia sp. was collected from the inner coral reef at a depth of around 8 m in Hainan Island of China, in May 2004, and the samples were frozen immediately after collection. The specimen was identified by Leen van Ofwegen (National Museum of National History Naturalis). The voucher specimens (HSF-15) are deposited at the State Key Laboratory of Natural and Biomimetic Drugs, Peking University, China.
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
The soft coral Sinularia sp. (3.7 kg) was homogenized, and then extracted with 95% EtOH (5 L × 3). The EtOH extract (102.5 g) was partitioned between H2O (400 mL) and EtOAc (200 mL). The EtOAc fraction (10.0 g) was subjected to column chromatography (3.5 × 25 cm) using 160–200 mesh Si gel (120 g) and was eluted with a gradient of petroleum ether (PE)/acetone (20:1, 10:1, 1:1) to obtain nine fractions (F1–F9). F3 (260 mg) was fractionated on an ODS column (C18, 2.0 × 25 cm) and eluted with a gradient of MeOH/H2O (75%–100%) to collect three portions PA–PC. Portion PB (85% MeOH, 180 mg) were then subjected to a Sephadex LH-20 column (1.5 × 35 cm) eluting with acetone to give 2 (7.0 mg), 3 (11.7 mg), and 4 (2.6 mg). Portion PA (75% MeOH, 70 mg) was subjected to semi-preparative HPLC (ODS, 5 μm, 2 × 25 cm) with 50% MeOH as a mobile phase to obtain 5 (1.5 mg), 6 (1.4 mg), 7 (2.4 mg), and 10 (3.2 mg). Compounds 1 (14.9 mg), 8(3.5 mg) and 9 (3.4 mg) were isolated from F4 (300 mg) using Sephadex LH-20 column (1.5 × 35 cm) and semi-preparative RP-18 HPLC (5 μm, 2 × 25 cm) with 45% MeOH as a mobile phase.
3.4. Computational Calculation
The computational ECD, specific rotation, and
13C NMR calculations were performed by the B3LYP functional and a generic basis set, employ the 6-311+G(
d,
p) basis set [
21,
22]. This generic basis set has been shown to be effective, both efficient and reliable, in predicting structural and reactivity properties for homogeneous systems. All calculations are performed with the Gaussian 03 package with tight self-consistent field convergence and ultrafine integration grids.
3.5. Larval Settlement Bioassays
Adults of the barnacle
Balanus amphitrite Darwin were exposed to air for more than 6 h, and then were placed in a container filled with fresh 0.22 µm filtered sea water (FSW) to release nauplii. The collected nauplii were reared to cyprid stage according to the method described by Thiyagarajan
et al. [
23]. When kept at 26–28 °C and fed with
Chaetoceros gracilis, larvae developed to cyprids within four days. Fresh cyprids were used in the tests.
3.6. Cytotoxic Assay
The cytotoxic properties of the isolated compounds were tested in vitro using human tumor cell lines including human ovarian carcinoma cell line A2780, human lung adenocarcinoma epithelial cell line A549, human gastric carcinoma cell line BGC823, human hepatoma cell line Bel7402, and human colonic carcinoma cell line HCT-8 by MTT method.
Sinularone A (
1): obtained as colorless oil; [α]
D23 +7.26 (
c = 0.27, MeOH); IR (KBr) ν
max cm
−1: 2956, 2868, 1738, 1717, 1457, 1407, 1368, 1262, 1158, 1079;
1H and
13C NMR data, see
Table 1 and
Table 2; HRESIMS (
m/z): 259.1674 [M + Na]
+ (calcd. for C
15H
24O
2Na, 259.1674); CD λ
max nm (Δε): 212 (−2.8).
Sinularone B (
2): obtained as colorless oil; [α]
D23 +0.60 (
c = 0.43, MeOH); IR (KBr) ν
max cm
−1: 3489, 2957, 2868, 1737, 1707, 1653, 1377, 1326, 1046;
1H and
13C NMR data, see
Table 1 and
Table 2; HRESIMS (
m/z): 305.1732 [M + Na]
+ (calcd. for C
16H
26O
4Na, 305.1729); CD λ
max nm (Δε): 210 (+3.6).
Sinularone C (
3): obtained as colorless oil; [α]
D23 +2.20 (
c = 0.14, MeOH); IR (KBr) ν
max cm
−1: 2954, 2920, 2863, 1730, 1710, 1654, 1458, 1377, 1164, 1062;
1H and
13C NMR data, see
Table 1 and
Table 2; HRESIMS (
m/z): 259.1315 [M + Na]
+ (calcd. for C
16H
26O
4Na, 259.1310); CD λ
max nm (Δε): 203 (+5.0).
Sinularone D (
4): obtained as colorless oil; [α]
D23 −3.22 (
c = 0.09, MeOH); IR (KBr) ν
max cm
−1: 2958, 2926, 2872, 1778, 1710, 1657, 1458, 1378, 1165;
1H and
13C NMR data, see
Table 1 and
Table 2; HRESIMS (
m/z): 259.1313 [M + Na]
+ (calcd. for C
16H
26O
4Na, 259.1310); CD λ
max nm (Δε): 222 (−1.3).
Sinularone E (
5): obtained as colorless oil; [α]
D23 +18.0 (
c = 0.04, MeOH); IR (KBr) ν
max cm
−1: 3422, 2959, 2854, 1735, 1629, 1458, 1377, 1165;
1H and
13C NMR data, see
Table 1 and
Table 2; HRESIMS (
m/z): 275.1612 [M + Na]
+ (calcd. for C
15H
24O
3Na, 275.1623); CD λ
max nm (Δε): 221 (+5.59).
Sinularone F (
6): obtained as colorless oil; [α]
D23 +22.6 (
c = 0.03, MeOH); IR (KBr) ν
max cm
−1: 3420, 2958, 2856, 1730, 1612, 1459, 1377, 1120;
1H and
13C NMR data, see
Table 1 and
Table 2; HRESIMS (
m/z): 275.1610 [M + Na]
+ (calcd. for C
15H
24O
3Na, 275.1623); CD λ
max nm (Δε): 219 (−2.56).
Sinularone G (
7): obtained as colorless oil; [α]
D23 +4.03 (
c = 0.10, MeOH); IR (KBr) ν
max cm
−1: 3446, 2958, 2921, 1730, 1633, 1457, 1376, 1163;
1H and
13C NMR data, see
Table 1 and
Table 2; HRESIMS (
m/z): 251.0886 [M + Na]
+ (calcd. for C
11H
16O
5Na, 251.0895); CD λ
max nm (Δε): 213(+1.21), 245 (+0.31).
Sinularone H (
8): obtained as colorless oil; [α]
D23 +3.70 (
c = 0.12, MeOH); IR (KBr) ν
max cm
−1: 3445, 2958, 2924, 1725, 1630, 1456, 1376, 1165;
1H and
13C NMR data, see
Table 1 and
Table 2; HRESIMS (
m/z): 265.1041 [M + Na]
+ (calcd. for C
12H
18O
5Na, 265.1052); CD λ
max nm (Δε): 213 (+0.25), 230 (−0.01).
Sinularone I (9): obtained as colorless oil; [α]D23 +5.44 (c 0.18, MeOH); IR (KBr) νmax 3432, 2959, 2923, 1734, 1633, 1458, 1376, 1162 cm−1 : 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 1.67 (1H, m, H-5a), 1.86 (1H, m, H-5b), 1.03 (1H, m, H-6a), 1.12 (1H, m, H-6b), 1.22 (14H, H2-7-H2-14), 1.50 (2H, m, H2-15), 2.25 (2H, t, J = 7.4 Hz, H2-16), 1.70 (3H, s, H3-18), 1.85 (3H, s, H3-19), 4.04 (2H, q, J = 7.1 Hz, Me-CH2), 1.17 (3H, t, J = 7.1 Hz); 13C NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 172.1 (C, C-1), 123.9 (C, C-2), 158.9 (C, C-3), 107.7 (C, C-4), 36.1 (CH2, C-5), 23.0 (CH2, C-6), 29.3 (CH2, C-7), 29.2 (CH2, C-8), 29.1 (CH2, C-9), 28.8 (CH2, C-10), 29.1 (CH2, C-11), 29.2 (CH2, C-12), 29.2 (CH2, C-13), 29.1 (CH2, C-14), 24.9 (CH2, C-15), 33.9 (CH2, C-16), 173.2 (C, C-17), 8.5 (CH3, C-18), 11.0 (CH3, C-19), 14.1 (CH3), 60.0 (CH2); HRESIMS (m/z): 391.2456 [M + Na]+ (calcd. for C21H36O5Na, 391.2460); CD λmax nm (Δε):213 (+1.25), 221 (−0.02), 244 (−1.10).