Identification and Characterization of an Anti-Fibrotic Benzopyran Compound Isolated from Mangrove-Derived Streptomyces xiamenensis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Isolation and Structural Elucidation of Compound 1

| Position | 1 | R/S-MPA-1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH (J in Hz) | δC, type | HMBC | δR | δS | ΔδRS | |
| 1 | -- | -- | ||||
| 2 | -- | 79.8, C | ||||
| 3 | 3.77, t b | 66.3, CH | 4a, 2, 9, 15 | |||
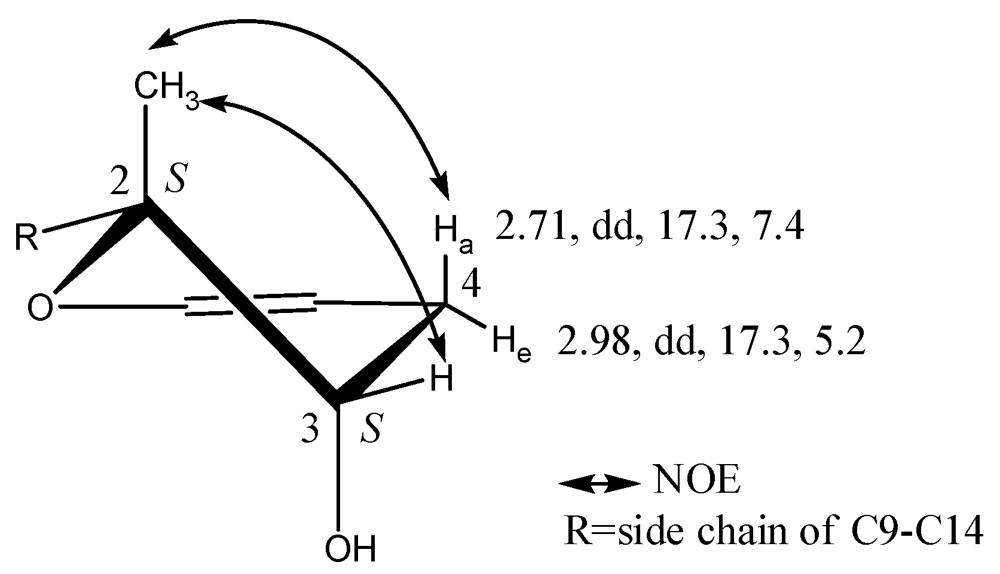
| 4 | 2.71, dd (17.3, 7.4) | 31.2, CH2 | 8a, 5, 4a, 2, 3 | 2.54 | 2.82 | −0.28 |
| 2.98, dd (17.3, 5.2) | 3.09 | 3.23 | −0.14 | |||
| 4a | -- | 120.6, C | ||||
| 5 | 7.67, s | 129.8, CH | 7, 8a, 4, 1′ | |||
| 6 | -- | 126.0, C | ||||
| 7 | 7.63, d (8.4) | 127.2, CH | 5, 8a, 1′ | |||
| 8 | 6.81, d (8.4) | 116.7, CH | 4a, 8a, 6 | |||
| 8a | -- | 156.1, C | ||||
| 9 | 1.60, m | 38.0, CH2 | 11, 12, 2,3 | 1.55 | 1.29 | +0.26 |
| 1.47 | 1.21 | +0.26 | ||||
| 10 | 2.10, m | 21.6, CH2 | 11, 12 | 2.05 | 1.95 | +0.10 |
| 11 | 5.12, dd (7.1, 1.3) | 124.8, CH | 13, 10, 14, 9 | 5.01 | 4.89 | +0.12 |
| 12 | -- | 131.3, C | ||||
| 13 | 1.57, s | 17.9, CH3 | 11 | 1.51 | 1.47 | +0.04 |
| 14 | 1.65, s | 25.9, CH3 | 11 | 1.60 | 1.58 | +0.02 |
| 15 | 1.18, s | 18.7, CH3 | 2, 3, 9 | 1.27 | 0.97 | +0.30 |
| 1′ | -- | 166.6, C | ||||
| 2′ | 7.78, d (7.8) | -- | 1′ | 8.29 | 8.40 | −0.11 |
| 3′ | 4.38, brd | 58.9, CH | 4′, 6′ | 4.81 | 4.84 | −0.03 |
| 4′ | 4.18, brs | 67.1, CH | ||||
| 5′ | 1.12, d (6.0) | 20.9, CH3 | 1.27 | 1.10 | +0.17 | |
| 6′ | -- | 172.8, C | ||||
2.2. Absolute Configurations of Compound 1
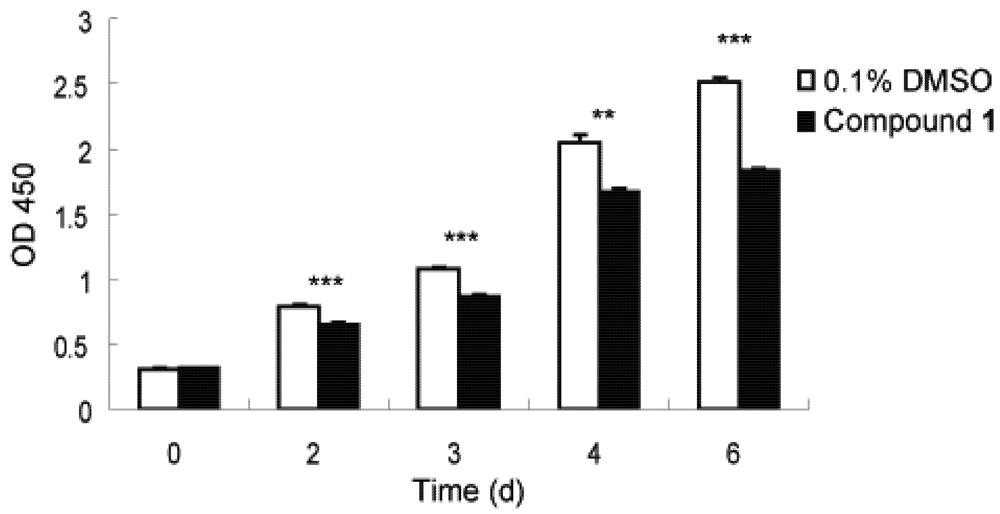
2.3. Inhibition of Proliferation on Human Diploid Lung Fibroblast (WI26) Cells by Compound 1.
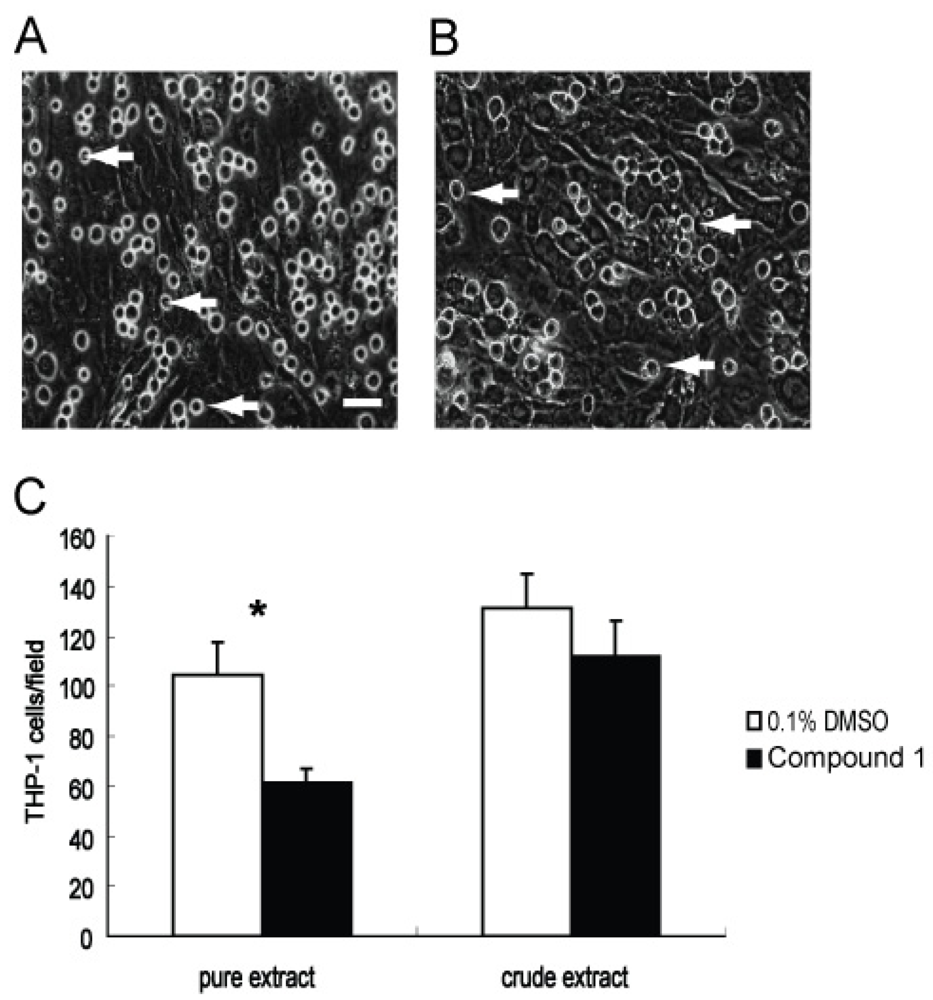
2.4. Effect of Compound 1 on the Adhesion of THP-1 Cells to a Monolayer of WI26 Cells
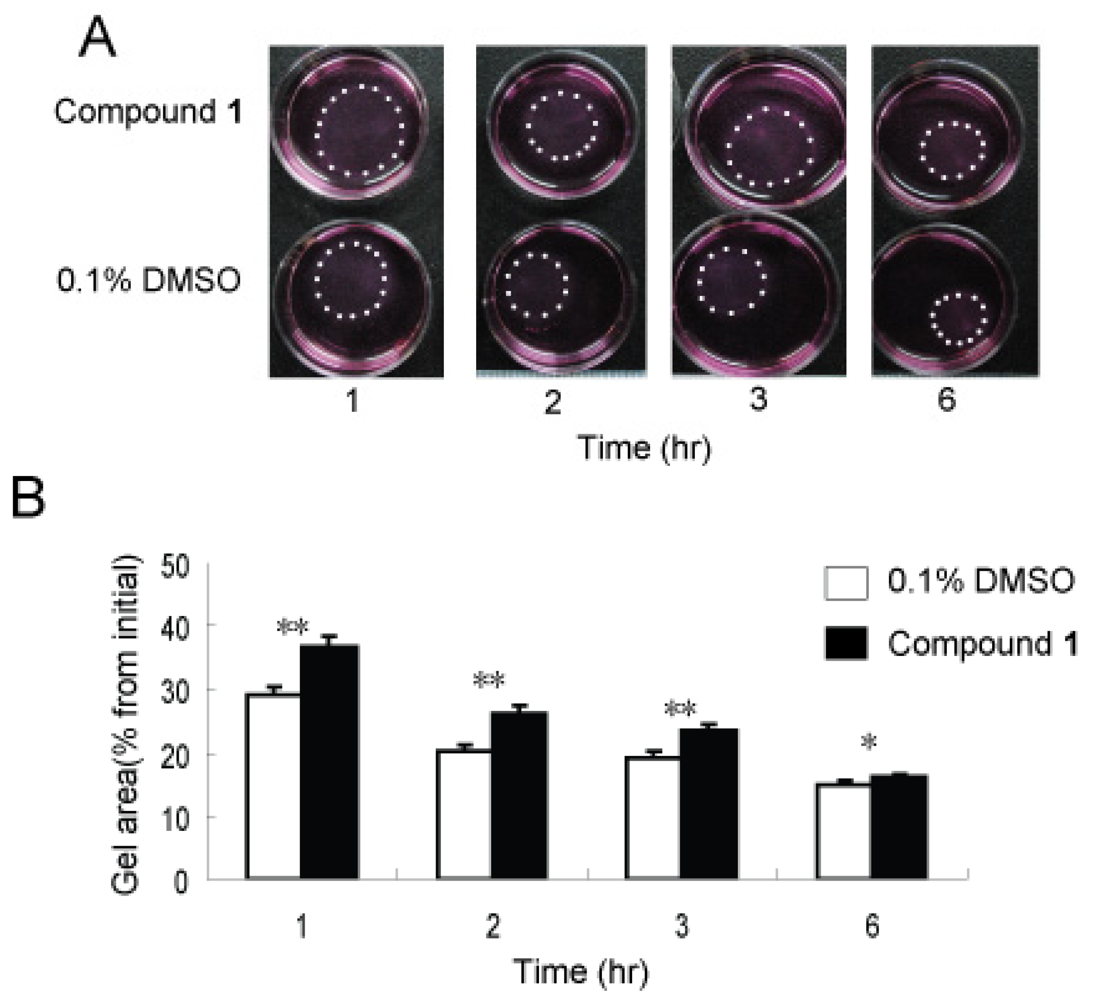
2.5. Effects of Compound 1 on Contraction of WI26 Cells in 3D Collagen Lattices
2.6. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General
3.2. Strain Cultivation
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. (R)- and (S)-MPA Esterification
3.5. Hydrolysis of Compound 1, Derivatization with Marfey’s Reagent
3.6. Cell Culture
3.7. Cell Proliferation Assay
3.8. Cell Adhesion Assay
3.9. Fibroblast Contraction Assay
3.10. Statistical Analysis
3.11. Computational Methods
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Wynn, T.A. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of fibrosis. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 199–210. [Google Scholar]
- Borm, P. Toxicity of Selected: Toxicology of Fibers and Particles; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gurtner, G.C.; Werner, S.; Barrandon, Y.; Longaker, M.T. Wound repair and regeneration. Nature 2008, 453, 314–321. [Google Scholar]
- Nathan, C.; Ding, A.H. Nonresolving Inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 871–882. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, S.; Grabley, S.; Groth, I.; Lin, W.; Christner, A.; Guo, D.; Sattler, I. Structure determination of germacrane-type sesquiterpene alcohols from an endophyte Streptomyces griseus subsp. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2005, 43, 1028–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.H.; Sattler, I.; Lin, W.H.; Guo, D.A.; Grabley, S. p-Aminoacetophenonic acids produced by a mangrove endophyte: Streptomyces griseus subsp. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1198–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Li, L.; Fu, H.; Sattler, I.; Huang, X.; Grabley, S. New cyclopentenone derivatives from an endophytic Streptomyces sp. isolated from the mangrove plant Aegiceras comiculatum. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 2005, 58, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xu, M.; Li, Q.; Sattler, I.; Lin, W. p-Aminoacetophenonic acids produced by a mangrove endophyte Streptomyces sp. (strain HK10552). Molecules 2010, 15, 2782–2790. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Gessner, G.; Groth, I.; Lange, C.; Christner, A.; Bruhn, T.; Deng, Z.; Li, X.; Heinemann, S.H.; Grabley, S.; et al. Shearinines D-K, new indole triterpenoids from an endophytic Penicillium sp. (strain HKI0459) with blocking activity on large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 435–444. [Google Scholar]
- Ravangpai, W.; Sommit, D.; Teerawatananond, T.; Sinpranee, N.; Palaga, T.; Pengpreecha, S.; Muangsin, N.; Pudhom, K. Limonoids from seeds of Thai Xylocarpus moluccensis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 4485–4489. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Yu, S.; Proksch, P.; Gu, J.; Lin, W. TNF-alpha inhibitory diterpenoids from the Chinese mangrove plant Excoecaria agallocha L. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 2124–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurtner, G.C.; Dauskardt, R.H.; Wong, V.W.; Bhatt, K.A.; Wu, K.; Vial, I.N.; Padois, K.; Korman, J.M.; Longaker, M.T. Improving cutaneous scar formation by controlling the mechanical environment: Large animal and phase I studies. Ann. Surg. 2011, 254, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Xie, S.J.; Xu, J.; Xiao, J.; Ruan, J.S. Streptomyces xiamenensis sp. nov., isolated from mangrove sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 472–476. [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura, N.; Tsuji, E.; Watanabe, Y.; Tsuchihashi, K.; Takako, T. Benzopyran derivatives, their manufacture with Streptomyces species, and their use for treatment of asthma and rheumatoid arthritis. Mercian Corp.: Kyoto, Japan, 2000 March 7; Daiichi Seiyaku Co., Ltd. [Google Scholar]
- Plavec, J.; Tong, W.; Chattopadhyaya, J. How do the gauche and anomeric effects drive the pseudorotational equilibrium of the pentofuranose moiety of nucleosides? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 9734–9746. [Google Scholar]
- Goodlett, D.R.; Abuaf, P.A.; Savage, P.A.; Kowalski, K.A.; Mukherjee, T.K.; Tolan, J.W.; Corkum, N.; Goldstein, G.; Crowther, J.B. Peptide chiral purity determination: Hydrolysis in deuterated acid, derivatization with Marfey’s reagent and analysis using high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 1995, 707, 233–244. [Google Scholar]
- Wynn, T.A.; Barron, L. Macrophages: Master regulators of inflammation and fibrosis. Semin. Liver Dis. 2010, 30, 245–257. [Google Scholar]
- Barron, L.; Wynn, T.A. Fibrosis is regulated by Th2 and Th17 responses and by dynamic interactions between fibroblasts and macrophages. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 300, G723–G728. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, V.W.; Rustad, K.C.; Akaishi, S.; Sorkin, M.; Glotzbach, J.P.; Januszyk, M.; Nelson, E.R.; Levi, K.; Paterno, J.; Vial, I.N.; et al. Focal adhesion kinase links mechanical force to skin fibrosis via inflammatory signaling. Nat. Med. 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Oakes, P.W.; Patel, D.C.; Morin, N.A.; Zitterbart, D.P.; Fabry, B.; Reichner, J.S.; Tang, J.X. Neutrophil morphology and migration are affected by substrate elasticity. Blood 2009, 114, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, V.W.; Akaishi, S.; Longaker, M.T.; Gurtner, G.C. Pushing back: Wound mechanotransduction in repair and regeneration. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 2186–2196. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, D.J.; Eckes, B.; Rajkumar, V.; Krieg, T. New developments in fibroblast and myofibroblast biology: Implications for fibrosis and scleroderma. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2007, 9, 136–143. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, V.W.; Paterno, J.; Sorkin, M.; Glotzbach, J.P.; Levi, K.; Januszyk, M.; Rustad, K.C.; Longaker, M.T.; Gurtner, G.C. Mechanical force prolongs acute inflammation via T-cell-dependent pathways during scar formation. FASEB J. 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell, F. Fibroblast biology in three-dimensional collagen matrices. Trends Cell Biol. 2003, 13, 264–269. [Google Scholar]
- Churg, A.; Brauer, M. Ambient atmospheric particles in the airways of human lungs. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2000, 24, 353–361. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, E.; Tanahashi, Y.; Yamasaki, Y.; Oda, N.; Nozawa, Y.; Terakawa, H.; Miyoshi, K.; Muranaka, Y.; Miyake, H.; Matsuura, N. Inhibitory effect of TAS-301, a new synthesized constrictive remodeling regulator, on renarrowing after balloon overstretch injury of porcine coronary artery. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 295, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Eckes, B.; Nischt, R.; Krieg, T. Cell-matrix interactions in dermal repair and scarring. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 2010, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Strieter, R.M.; Gomperts, B.N.; Keane, M.P. The role of CXC chemokines in pulmonary fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 549–556. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfram, D.; Tzankov, A.; Pulzl, P.; Piza-Katzer, H. Hypertrophic scars and keloids—A review of their pathophysiology, risk factors, and therapeutic management. Dermatol. Surg. 2009, 35, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, G.J.; Chambers, R.C.; Hill, M.R.; McAnulty, R.J. Regulation of matrix turnover: Fibroblasts, forces, factors and fibrosis. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delavary, B.M.; van der Veer, W.M.; van Egmond, M.; Niessen, F.B.; Beelen, R.H. Macrophages in skin injury and repair. Immunobiology 2011, 216, 753–762. [Google Scholar]
- Holt, D.J.; Chamberlain, L.M.; Grainger, D.W. Cell-cell signaling in co-cultures of macrophages and fibroblasts. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 9382–9394. [Google Scholar]
- Long, E.O. ICAM-1: Getting a grip on leukocyte adhesion. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 5021–5023. [Google Scholar]
- Kelemen, O.; Kollar, L. Current methods of treatment and prevention of pathologic scars. Magy. Seb. 2007, 60, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa, R. The most current algorithms for the treatment and prevention of hypertrophic scars and keloids. Plast. Reconstruct. Surg. 2010, 125, 557–568. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.; Ashby, D.; Smyth, R.L. Oral steroids for long-term use in cystic fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hunzelmann, N.; Moinzadeh, P.; Genth, E.; Krieg, T.; Lehmacher, W.; Melchers, I.; Meurer, M.; Müller-Ladner, U.; Olski, T.M.; Pfeiffer, C.; et al. High frequency of corticosteroid and immunosuppressive therapy in patients with systemic sclerosis despite limited evidence for efficacy. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Pfaff, A.W.; Georges, S.; Candolfi, E. Different effect of Toxoplasma gondii infection on adhesion capacity of fibroblasts and monocytes. Parasite Immunol. 2008, 30, 487–490. [Google Scholar]
- Taub, D.D.; Lloyd, A.R.; Conlon, K.; Wang, J.M.; Ortaldo, J.R.; Harada, A.; Matsushima, K.; Kelvin, D.J.; Oppenheim, J.J. Recombinant human interferon-inducible protein 10 is a chemoattractant for human monocytes and T lymphocytes and promotes T cell adhesion to endothelial cells. J. Exp. Med. 1993, 177, 1809–1814. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.G.; Bothe, I.; Hirche, F.; Zweers, M.; Gullberg, D.; Pfitzer, G.; Krieg, T.; Eckes, B.; Aumailley, M. Interactions of primary fibroblasts and keratinocytes with extracellular matrix proteins:Contribution of α2β1 integrin. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 1886–1895. [Google Scholar]
- Gaussian 9, Revision A.02; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009.
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D.G. Density functionals with broad applicability in chemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 157–167. [Google Scholar]
- Marenich, A.V.; Cramer, C.J.; Truhlar, D.G. Universal solvation model based on solute electron density and on a continuum model of the solvent defined by the bulk dielectric constant and atomic surface tensions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6378–6396. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Sample of compound 1 is available from authors.
Supplementary Files
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, M.-J.; Liu, X.-J.; Zhao, Y.-L.; Liu, D.; Xu, Z.-H.; Lang, X.-M.; Ao, P.; Lin, W.-H.; Yang, S.-L.; Zhang, Z.-G.; et al. Identification and Characterization of an Anti-Fibrotic Benzopyran Compound Isolated from Mangrove-Derived Streptomyces xiamenensis. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 639-654. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10030639
Xu M-J, Liu X-J, Zhao Y-L, Liu D, Xu Z-H, Lang X-M, Ao P, Lin W-H, Yang S-L, Zhang Z-G, et al. Identification and Characterization of an Anti-Fibrotic Benzopyran Compound Isolated from Mangrove-Derived Streptomyces xiamenensis. Marine Drugs. 2012; 10(3):639-654. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10030639
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Min-Juan, Xiao-Jin Liu, Yi-Lei Zhao, Dong Liu, Zhen-Hao Xu, Xiao-Meng Lang, Ping Ao, Wen-Han Lin, Song-Lin Yang, Zhi-Gang Zhang, and et al. 2012. "Identification and Characterization of an Anti-Fibrotic Benzopyran Compound Isolated from Mangrove-Derived Streptomyces xiamenensis" Marine Drugs 10, no. 3: 639-654. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10030639








