Convolutional Neural Network-Based Robot Navigation Using Uncalibrated Spherical Images †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A native “navigation via classification” framework based purely on fisheye panoramas is proposed in this paper, without the need of any additional calibration or unwarping preprocessing steps. Uncalibrated spherical images could be directly fed into the proposed framework for training and navigation, eliminating strenuous efforts such as pixel-level labeling of training images, or high resolution 3D point cloud generation for training.
- An end-to-end convolutional neural network (CNN) based framework is proposed, achieving extraordinary classification accuracy on our realistic dataset. The proposed CNN framework is significantly more computational efficient (in the testing phase) than SLAM-type algorithms and readily deployable on more mobile platforms, especially battery powered ones with limited computational capabilities.
- A novel fisheye panoramas dataset, i.e., the Spherical-Navi image dataset is collected, with a unique labeling strategy enabling automatic generation of an arbitrary number of negative samples (wrong heading direction).
2. Background and Related Work
2.1. Deep Learning in Navigation
2.2. Spherical Cameras in Navigation
3. CNN Based Robot Navigation Framework Using Spherical Images
3.1. Formulation: Navigation via Classification
3.2. Network Configuration and Training
4. Spherical-Navi Dataset
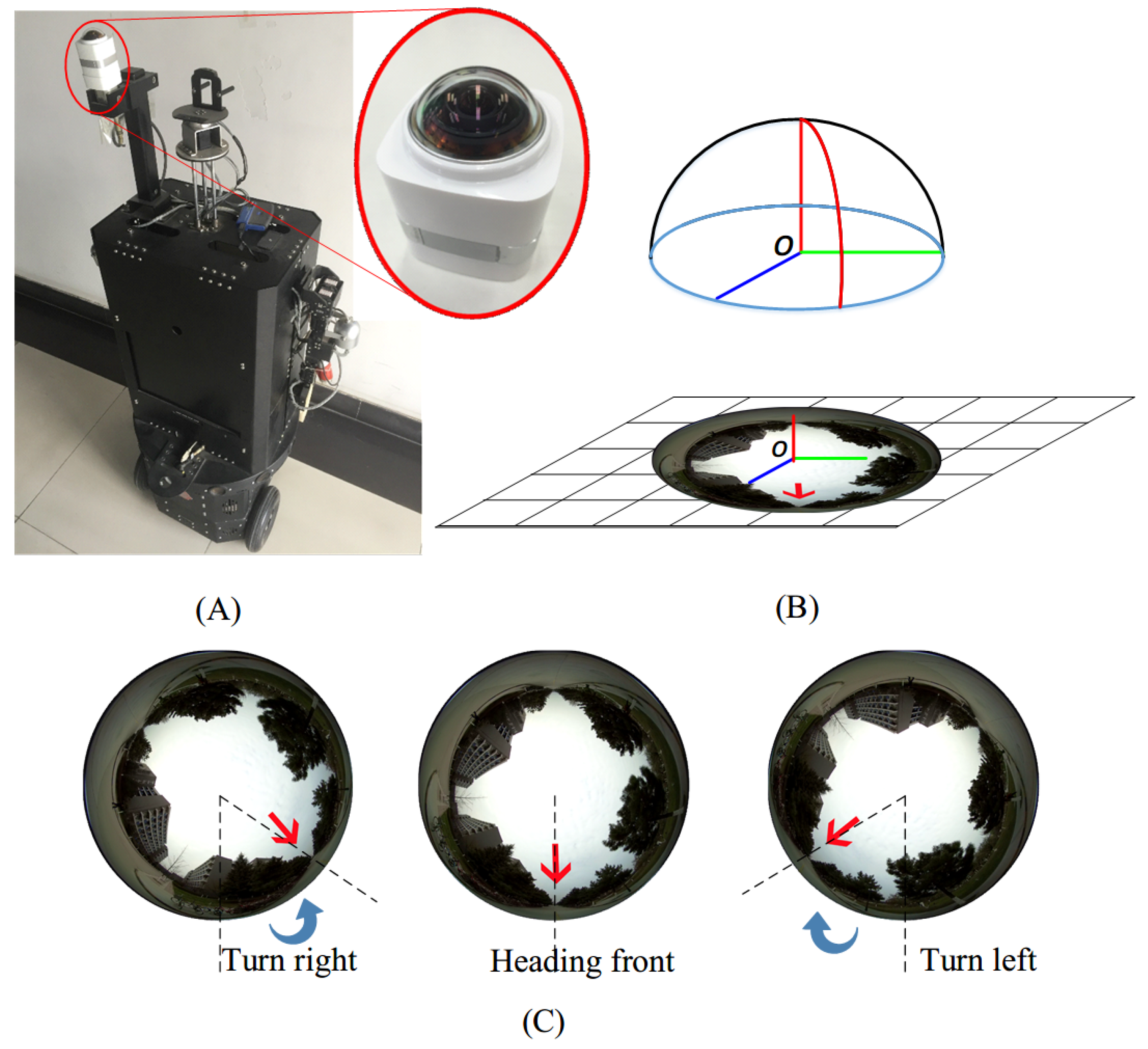
4.1. Data Formulation
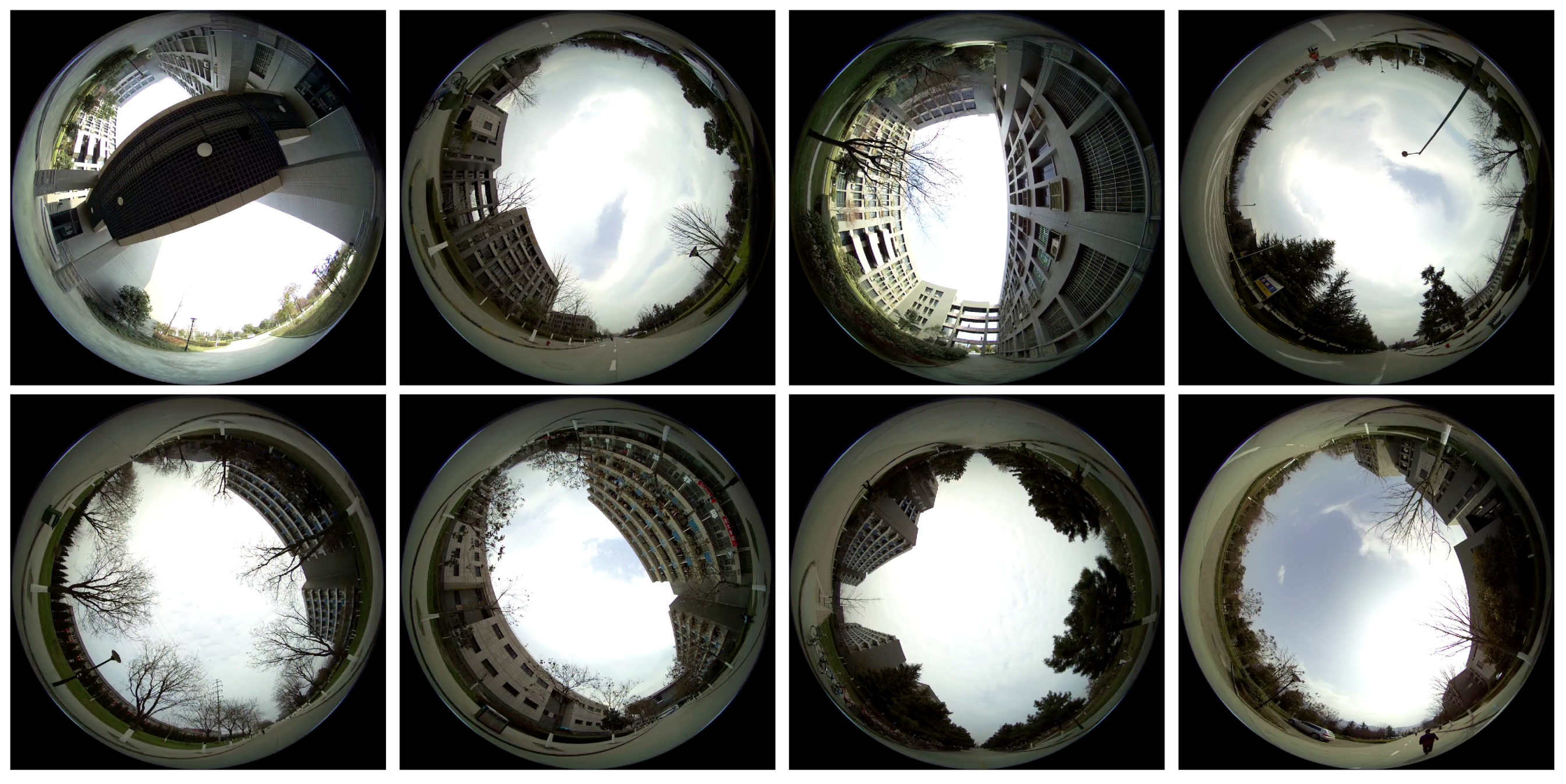
4.2. Data Capturing
4.3. Data Preparation
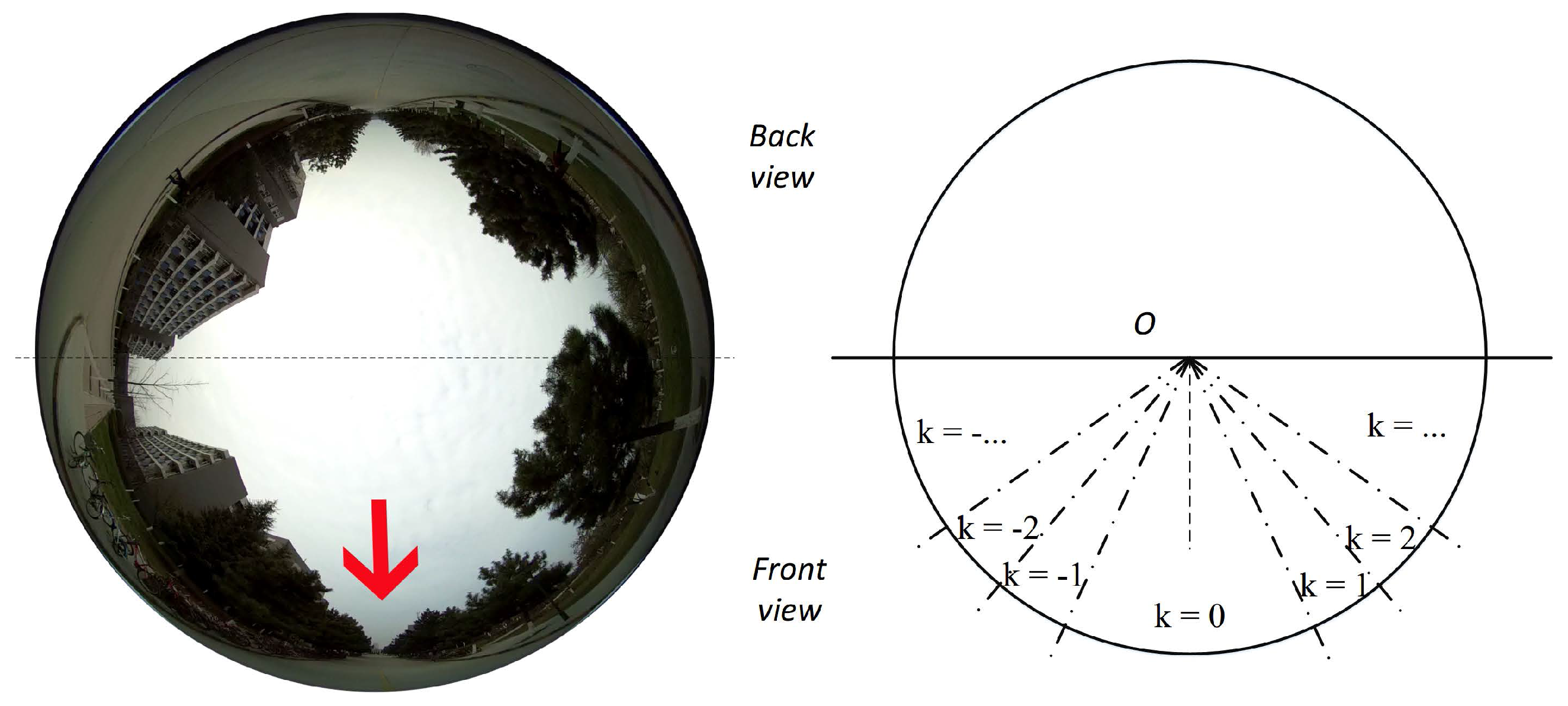
4.4. Label Synthesis
5. Experimental Results
5.1. Sky Pixels Elimination
5.2. Network Setup and Training
5.3. Quantitative Results and Discussion
5.4. Robot Navigation Evaluation
- Training data collection (Training data collection is illustrated in Figure 11a,d,g and Figure 12a,d,g): the robot platform is manually controlled to drive along 3 pre-defined paths multiple times, and the collected spherical images with synthesized optimal heading directions (detailed in Section 4.4) are used for “Model 2” network training.
- Navigation with smoothed network predictions (Navigation with smoothed network predictions is illustrated in Figure 11c,f,i) and Figure 12c,f,i): the robot platform is deployed at the starting point of each trail and it autonomously navigate along the path with smoothed network predictions as inputs. The smoothing is carried out with a temporal median filter of size 3.
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Networks |
| SLAM | Simultaneous Localization And Mapping |
References
- Davison, A.J.; Reid, I.D.; Molton, N.D.; Stasse, O. MonoSLAM: Real-time single camera SLAM. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2007, 29, 1052–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, G.; Murray, D. Parallel tracking and mapping for small AR workspaces. In Proceedings of the 2007 6th IEEE and ACM International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality, Nara, Japan, 13–16 November 2007; pp. 225–234. [Google Scholar]
- Cummins, M.; Newman, P. FAB-MAP: Probabilistic localization and mapping in the space of appearance. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2008, 27, 647–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newcombe, R.A.; Lovegrove, S.J.; Davison, A.J. DTAM: Dense tracking and mapping in real-time. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 2320–2327. [Google Scholar]
- Newcombe, R.A.; Izadi, S.; Hilliges, O.; Molyneaux, D.; Kim, D.; Davison, A.J.; Kohi, P.; Shotton, J.; Hodges, S.; Fitzgibbon, A. KinectFusion: Real-time dense surface mapping and tracking. In Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR), Basel, Switzerland, 26–29 October 2011; pp. 127–136. [Google Scholar]
- Caruso, D.; Engel, J.; Cremers, D. Large-Scale Direct SLAM for Omnidirectional Cameras. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hillel, A.B.; Lerner, R.; Levi, D.; Raz, G. Recent progress in road and lane detection: A survey. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2014, 25, 727–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, W.; Guo, D.; Liu, T. Adaptive Image-Based Trajectory Tracking Control of Wheeled Mobile Robots With an Uncalibrated Fixed Camera. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2015, 23, 2266–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Li, J.; An, X.; He, H. Vision sensor-based road detection for field robot navigation. Sensors 2015, 15, 29594–29617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.K.; Siagian, C.; Itti, L. Mobile robot vision navigation & localization using gist and saliency. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 October 2010; pp. 4147–4154. [Google Scholar]
- Pomerleau, D.A. Efficient training of artificial neural networks for autonomous navigation. Neural Comput. 1991, 3, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadsell, R.; Sermanet, P.; Ben, J.; Erkan, A.; Scoffier, M.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Muller, U.; LeCun, Y. Learning long-range vision for autonomous off-road driving. J. Field Robot. 2009, 26, 120–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, A.; Guzzi, J.; Ciresan, D.; He, F.L.; Rodriguez, J.P.; Fontana, F.; Faessler, M.; Forster, C.; Schmidhuber, J.; Di Caro, G.; et al. A Machine Learning Approach to Visual Perception of Forest Trails for Mobile Robots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2016, 1, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, T.; Zhang, P. Autonomous Wheeled Robot Navigation with Uncalibrated Spherical Images. In Chinese Conference on Intelligent Visual Surveillance; Springer: Singapore, 2016; pp. 47–55. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Hua, G. Multi-View Visual Recognition of Imperfect Testing Data. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual ACM Conference on Multimedia Conference, Brisbane, Australia, 26–30 October 2015; pp. 561–570. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Hua, G.; Liu, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z. Auxiliary Training Information Assisted Visual Recognition. IPSJ Trans. Comput. Vis. Appl. 2015, 7, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Hua, G.; Liu, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z. Can Visual Recognition Benefit from Auxiliary Information in Training? In Computer Vision—ACCV 2014; Springer: Singapore, 1–5 November 2014; Volume 9003, pp. 65–80. [Google Scholar]
- Abeida, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Merabtine, N. Iterative sparse asymptotic minimum variance based approaches for array processing. Signal Proc. IEEE Trans. 2013, 61, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Abeida, H.; Xue, M.; Rowe, W.; Li, J. Fast implementation of sparse iterative covariance-based estimation for source localization. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 131, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Abeida, H.; Xue, M.; Rowe, W.; Li, J. Fast implementation of sparse iterative covariance-based estimation for array processing. In Proceedings of the 2011 Conference Record of the Forty Fifth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers (ASILOMAR), Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 6–9 November 2011; pp. 2031–2035. [Google Scholar]
- Sermanet, P.; Eigen, D.; Zhang, X.; Mathieu, M.; Fergus, R.; LeCun, Y. Overfeat: Integrated recognition, localization and detection using convolutional networks. arXiv 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Region-based convolutional networks for accurate object detection and segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ouyang, W.; Wang, X.; Lu, H. STCT: Sequentially Training Convolutional Networks for Visual Tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, H.; Han, B. Learning Multi-Domain Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hua, G. CANNET: Context aware nonlocal convolutional networks for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Quebec City, QC, Canada, 27–30 September 2015; pp. 4669–4673. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Barron, J.T.; Papandreou, G.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Semantic Image Segmentation with Task-Specific Edge Detection Using CNNs and a Discriminatively Trained Domain Transform. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Huang, Y.Y.; Wei, L.; Zhang, F.; Li, H.C. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Hyperspectral Image Classification. J. Sens. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, W.; Yang, T. Bands Sensitive Convolutional Network for Hyperspectral Image Classification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Internet Multimedia Computing and Service, Xi’an, China, 19–21 August 2016; pp. 268–272. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–8 December 2012; pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.; Chen, Q.; Yan, S. Network In Network. In Proceedings of the International conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Banff, AB, Canada, 14–16 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S. Full-view spherical image camera. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR’06), Hong Kong, China, 20–24 August 2006; Volume 4, pp. 386–390. [Google Scholar]
- Makadia, A.; Sorgi, L.; Daniilidis, K. Rotation estimation from spherical images. In Proceedings of the 2004 17th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Cambridge, UK, 26 August 2004; Volume 3, pp. 590–593. [Google Scholar]
- Makadia, A.; Daniilidis, K. Rotation recovery from spherical images without correspondences. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2006, 28, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazin, J.C.; Demonceaux, C.; Vasseur, P.; Kweon, I. Rotation estimation and vanishing point extraction by omnidirectional vision in urban environment. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2012, 31, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zintgraf, L.M.; Cohen, T.S.; Adel, T.; Welling, M. Visualizing Deep Neural Network Decisions: Prediction Difference Analysis. arXiv 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, V.; Hinton, G.E. Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Haifa, Israel, 21–24 June 2010; pp. 807–814. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1026–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing Internal Covariate Shift. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Duchi, J.; Hazan, E.; Singer, Y. Adaptive subgradient methods for online learning and stochastic optimization. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2121–2159. [Google Scholar]
- Bottou, L. Large-scale machine learning with stochastic gradient descent. In Proceedings of COMPSTAT’2010; Springer: Paris, France, 2010; pp. 177–186. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Liao, R.; Tao, X.; Xu, L.; Jia, J.; Wu, E. Handling motion blur in multi-frame super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 5224–5232. [Google Scholar]
- Torralba, A.; Efros, A.A. Unbiased look at dataset bias. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 1521–1528. [Google Scholar]
- Collobert, R.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Farabet, C. Torch7: A matlab-like environment for machine learning. In Proceedings of the BigLearn, NIPS Workshop, Granada, Spain, 12–17 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.C.; Lin, C.J. LIBSVM: A library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2011, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehman, S.V. Selecting and interpreting measures of thematic classification accuracy. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 62, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawcett, T. An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
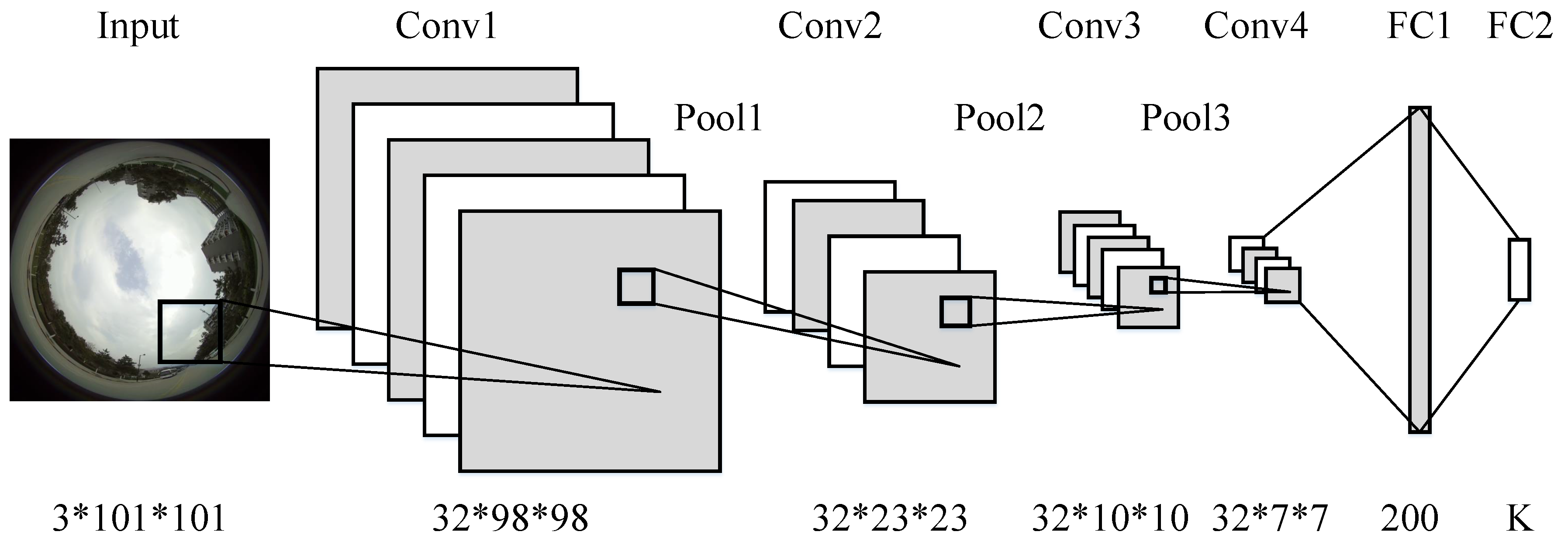

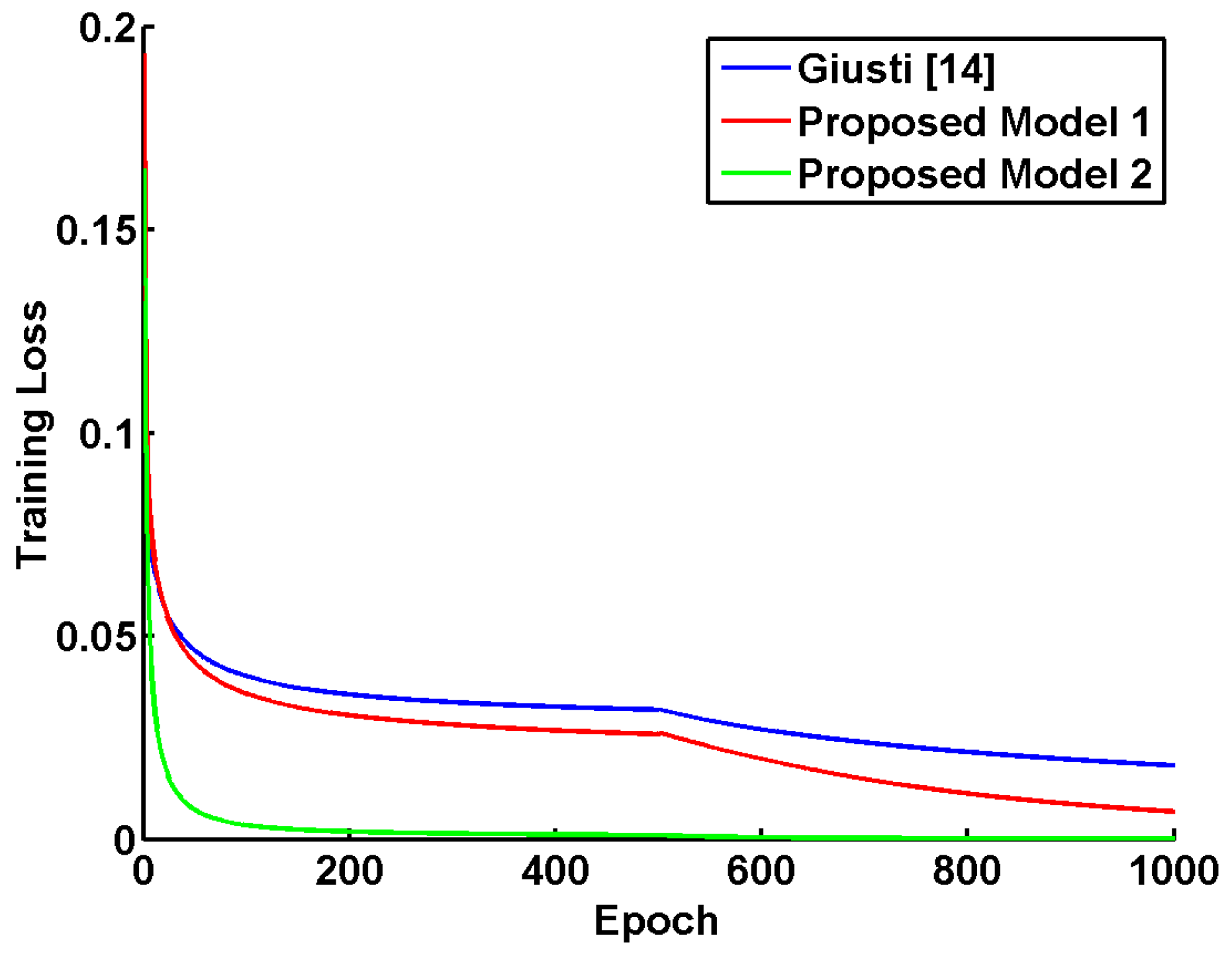

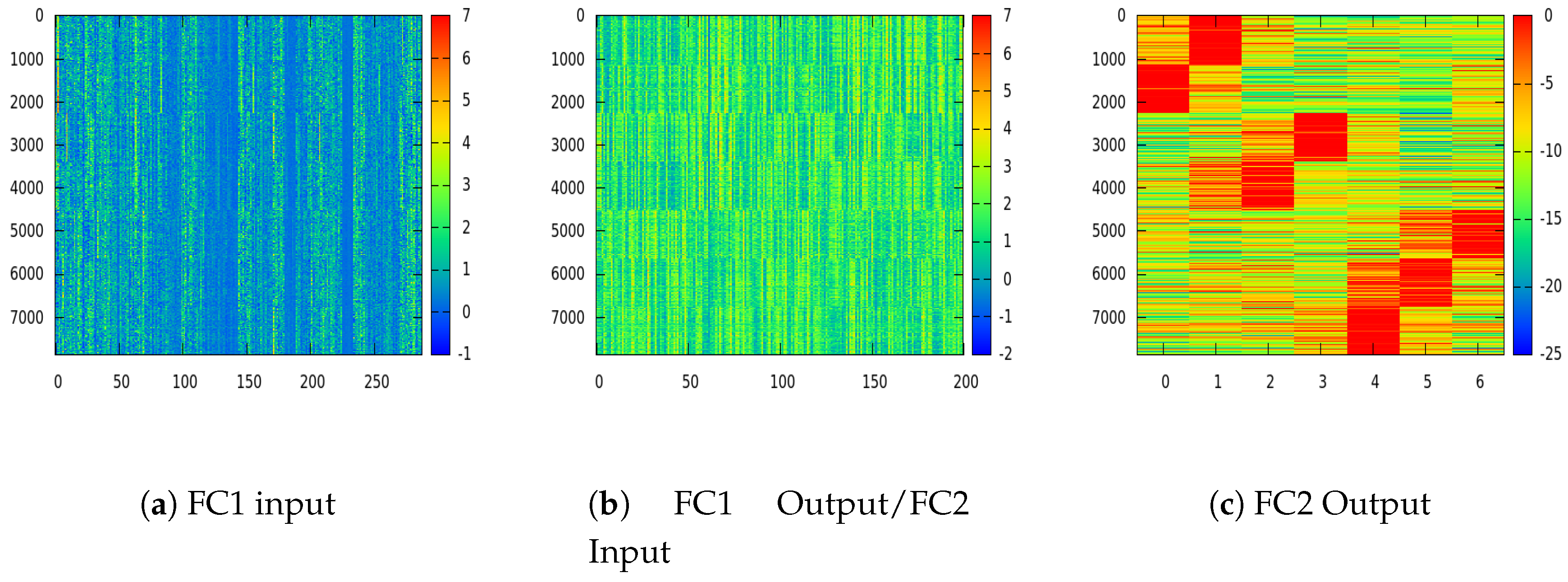




| Features | Giusti [13] | Proposed Model 1 | Proposed Model 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3 × 101 × 101 | Inputs | Inputs | Inputs |
| 1 | 32 × 98 × 98 | Conv | Conv | Conv |
| 2 | 32 × 49 × 49 | Pool | Pool | Pool |
| 3 | - | Tanh | ReLU | BN + PReLU |
| 4 | 32 × 46 × 46 | Conv | Conv | Conv |
| 5 | 32 × 23 × 23 | Pool | Pool | Pool |
| 6 | - | Tanh | ReLU | BN + PReLU |
| 7 | 32 × 20 × 20 | Conv | Conv | Conv |
| 8 | 32 × 10 × 10 | Pool | Pool | Pool |
| 9 | - | Tanh | ReLU | BN + PReLU |
| 10 | 32 × 7 × 7 | Conv | Conv | Conv |
| 11 | 32 × 3 × 3 | Pool | Pool | Pool |
| 12 | - | Tanh | ReLU | BN + PReLU |
| 13 | 288→200 | FC1 | FC1 | FC1 |
| 14 | - | Tanh | ReLU | PReLU |
| 15 | 200→K | FC2 | FC2 | FC2 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ran, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, T. Convolutional Neural Network-Based Robot Navigation Using Uncalibrated Spherical Images. Sensors 2017, 17, 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17061341
Ran L, Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Yang T. Convolutional Neural Network-Based Robot Navigation Using Uncalibrated Spherical Images. Sensors. 2017; 17(6):1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17061341
Chicago/Turabian StyleRan, Lingyan, Yanning Zhang, Qilin Zhang, and Tao Yang. 2017. "Convolutional Neural Network-Based Robot Navigation Using Uncalibrated Spherical Images" Sensors 17, no. 6: 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17061341






