Effects of Secondary Plant Metabolites on Microbial Populations: Changes in Community Structure and Metabolic Activity in Contaminated Environments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
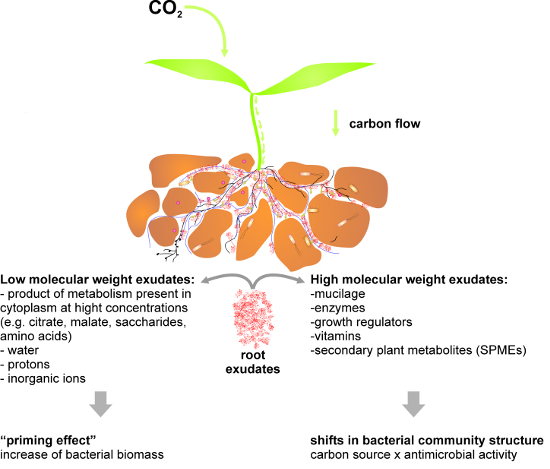
2. Root Exudates and Their Effects on Present Microflora
2.1. Root Exudates: Carbon Gateway to the Rhizosphere
2.2. Root Exudates: Effect on the Rhizosphere Microflora
2.3. Roots and Associated Microorganisms: How to Study Interactions?
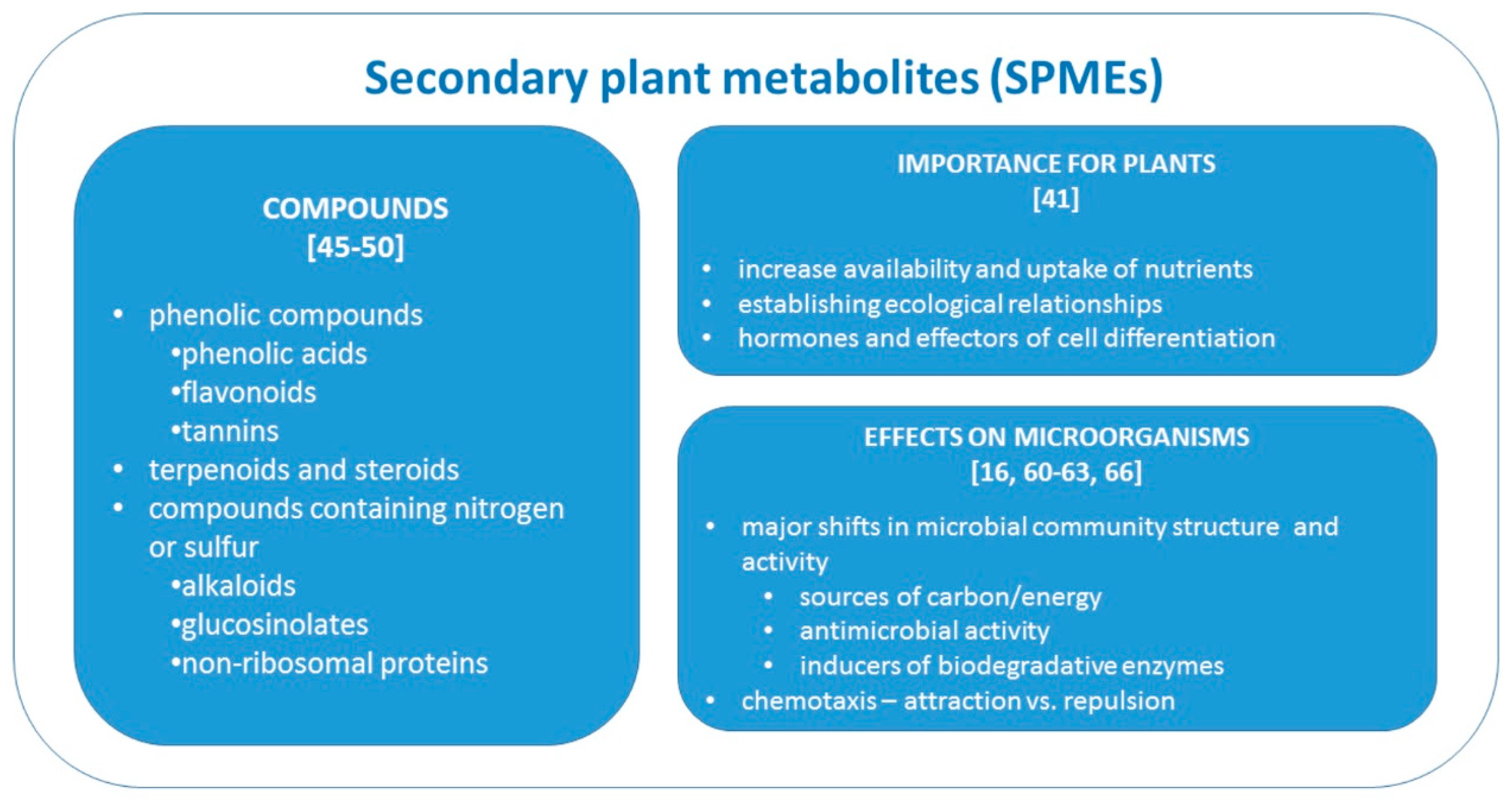
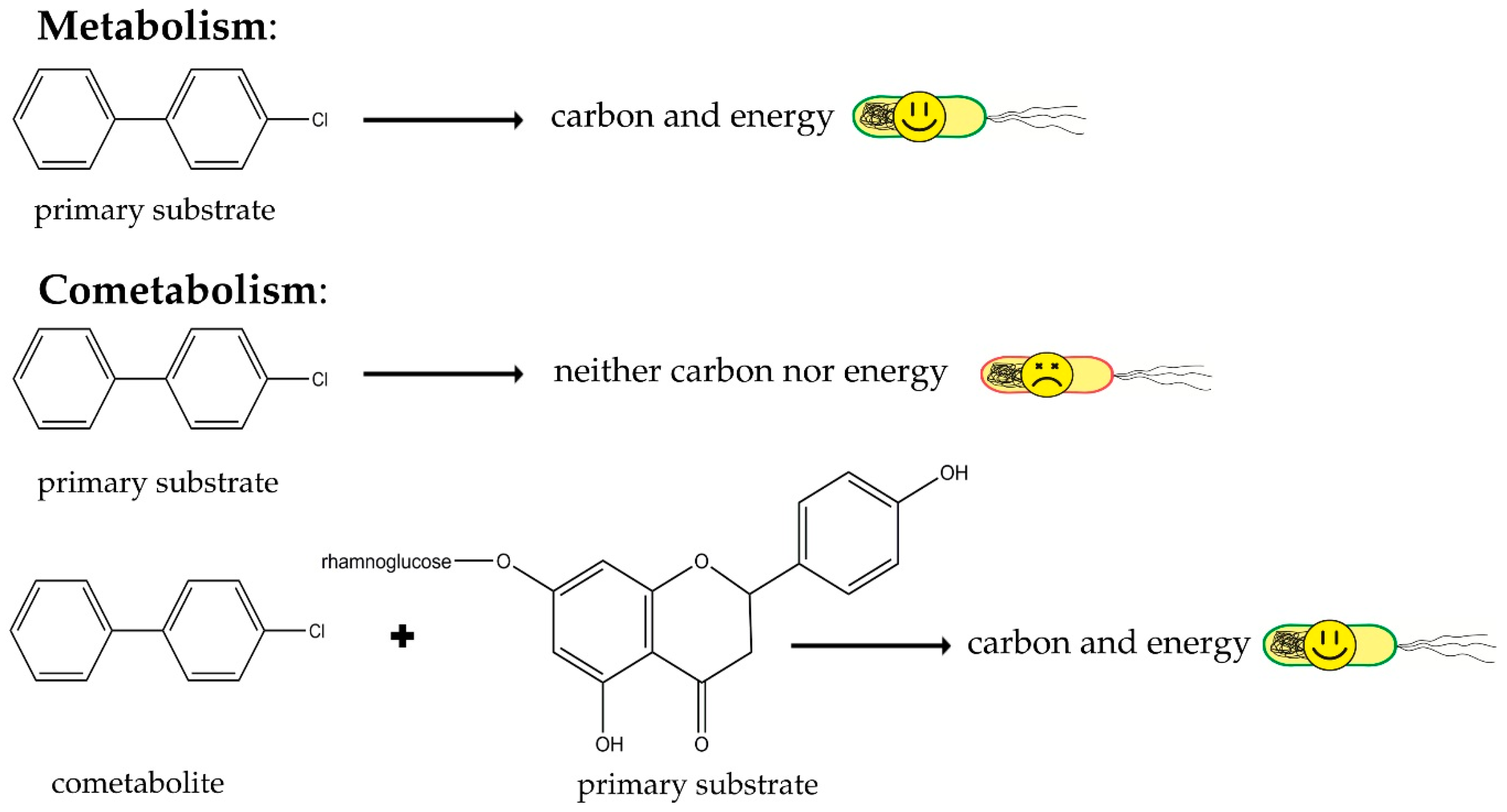
3. Role of Secondary Metabolites in Biodegradation of Organic Contaminants
3.1. Secondary Metabolites: Structural Similarities to Organic Pollutants
3.2. Phenolics: From Simple Phenolics to Flavonoids and Lignin, Their Biological Role and Effect on Biodegradation of Pollutants
3.3. Terpenes: Biological Role and Effect on Biodegradation of Pollutants
4. Complex Effect of Plant Metabolites on Bioremediation of Contaminated Soil
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SPMEs | secondary plant metabolites |
| PAHs | polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons |
| PCBs | polychlorinated biphenyls |
| LMW | low molecular weight |
| LMW-C | low molecular weight carbon containing |
| HMW | high molecular weight |
| LiP | lignin peroxidase |
| MnP | manganese peroxidase |
| CT | computed tomography |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| PET | positron emission tomography |
| FISH | fluorescence in situ hybridization |
| FISH-MAR | fluorescence in situ hybridization combined with microradiography |
| RIP | radioisotope probing |
| PLFA | phospholipid-derived fatty acids |
| SIP | stable isotope probing |
| VP | versatile peroxidase |
| DCP | dichlorophenol |
| CP | chlorophenol |
| TNT | trinitrotoluene |
Appendix A
A.1. Description of Our Experiment

References
- Hartmann, A.; Rothballer, M.; Schmid, M. Lorenz Hiltner, a pioneer in rhizosphere microbial ecology and soil bacteriology research. Plant Soil 2008, 312, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, P.A.H.M.; Berendsen, R.L.; Doornbos, R.F.; Wintermans, P.C.A.; Pieterse, C.M.J. The rhizosphere revisited: Root microbiomics. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smalla, K.; Wieland, G.; Buchner, A.; Zock, A.; Parzy, J.; Kaiser, S.; Roskot, N.; Heuer, H.; Berg, G. Bulk and rhizosphere soil bacterial communities studied by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis: Plant-dependent enrichment and seasonal shifts revealed. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 4742–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, G.; Smalla, K. Plant species and soil type cooperatively shape the structure and function of microbial communities in the rhizosphere. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 68, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiter, S.; Eltlbany, N.; Smalla, K. Microbial communities in the rhizosphere analyzed by cultivation-independent DNA-based methods. In Principles of Plant–Microbe Interactions: Microbes for Sustainable Agriculture; Lugtenberg, B., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 289–298. [Google Scholar]
- York, L.M.; Carminati, A.; Mooney, S.J.; Ritz, K.; Bennett, M.J. The holistic rhizosphere: Integrating zones, processes, and semantics in the soil influenced by roots. J. Exp. Bot. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.L.; Nguyen, C.; Finlay, R.D. Carbon flow in the rhizosphere: Carbon trading at the soil–root interface. Plant Soil 2009, 321, 5–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, V.; Selvaraj, G.; Bais, H.P. Functional soil microbiome: Belowground solutions to an aboveground problem. Plant Physiol. 2014, 166, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, C. Rhizodeposition of organic C by plant: Mechanisms and controls. In Sustainable Agriculture; Lichtfouse, E., Navarrete, M., Debaeke, P., Véronique, S., Alberola, C., Eds.; Springer: Houten, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 97–123. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Nakai, S.; Hosomi, M.; Zhang, H.; Kronzucker, H.J.; Shi, W. Stimulation of nitrogen removal in the rhizosphere of aquatic duckweed by root exudate components. Planta 2014, 239, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieterse, C.M.J.; de Jonge, R.; Berendsen, R.L. The soil-borne supremacy. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egamberdieva, D.; Abdiev, A.; Khaitov, B. Synergistic interactions among root-associated bacteria, rhizobia and chickpea under stress conditions. In Plant-Environment Interaction: Responses and Approaches to Mitigate Stress; Azooz, M.M., Ahmad, P., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2016; pp. 250–261. [Google Scholar]
- Barret, M.; Morrissey, J.P.; O’Gara, F. Functional genomics analysis of plant growth-promoting rhizobacterial traits involved in rhizosphere competence. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2011, 47, 729–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bais, H.P.; Weir, T.L.; Perry, L.G.; Gilroy, S.; Vivanco, J.M. The role of root exudates in rhizosphere interactions with plants and other organisms. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 233–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertin, C.; Yang, X.H.; Weston, L.A. The role of root exudates and allelochemicals in the rhizosphere. Plant Soil 2003, 256, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, P.K.; Hegde, R.S.; Fletcher, J.S. Growth of PCB-degrading bacteria on compounds from photosynthetic plants. Chemosphere 1994, 28, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, Q.; Blom-Zandstra, M.; Gupta, S.; Joner, E.J. Utilising the synergy between plants and rhizosphere microorganisms to enhance breakdown of organic pollutants in the environment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2005, 12, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, A.C.; Crowley, D.E.; Thompson, I.P. Secondary plant metabolites in phytoremediation and biotransformation. Trends Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbance, J.W.; Cole, J.; Saxman, P.; Tiedje, J.M. BSD: The biodegradative strain database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muangchinda, C.; Chavanich, S.; Viyakarn, V.; Watanabe, K.; Imura, S.; Vangnai, A.S.; Pinyakong, O. Abundance and diversity of functional genes involved in the degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons in Antarctic soils and sediments around Syowa Station. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 4725–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meckenstock, R.U.; Elsner, M.; Griebler, C.; Lueders, T.; Stumpp, C.; Aamand, J.; Agathos, S.N.; Albrechtsen, H.-J.; Bastiaens, L.; Bjerg, P.L.; et al. Biodegradation: Updating the concepts of control for microbial cleanup in contaminated aquifers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7073–7081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pausch, J.; Tian, J.; Riederer, M.; Kuzyakov, Y. Estimation of rhizodeposition at field scale: Upscaling of a 14C labeling study. Plant Soil 2013, 364, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marihal, A.K.; Jagadeesh, K.S. Plant–microbe interaction: A potential tool for enhanced bioremediation. In Plant Microbe Symbiosis: Fundamentals and Advances; Arora, K.N., Ed.; Springer India: New Delhi, India, 2013; pp. 395–410. [Google Scholar]
- Handelsman, J.; Rondon, M.R.; Brady, S.F.; Clardy, J.; Goodman, R.M. Molecular biological access to the chemistry of unknown soil microbes: A new frontier for natural products. Chem. Biol. 1998, 5, R245–R249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzker, M.L. Sequencing technologies—The next generation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Raskatov, A.; Kaupenjohann, M. Turnover and distribution of root exudates of Zea mays. Plant Soil 2003, 254, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.L.; Hodge, A.; Kuzyakov, Y. Plant and mycorrhizal regulation of rhizodeposition. New Phytol. 2004, 163, 459–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Watanabe, A.; Kimura, M. Input and distribution of photosynthesized carbon in a flooded rice soil. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2002, 16, 32-1–32-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, H.; Oades, J.M.; Martin, J.K. Input of carbon to soil from wheat plants. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1986, 18, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Kretzschmar, A.; Stahr, K. Contribution of Lolium perenne rhizodeposition to carbon turnover of pasture soil. Plant Soil 1999, 213, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, H.; Yang, X.; Feng, X.; Qian, X.; Hu, Y.; Ren, C.; Zeng, Z. Rhizodeposition of nitrogen and carbon by mungbean (Vigna radiata L.) and its contribution to intercropped oats (Avena nuda L.). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liljeroth, E.; Bååth, E.; Mathiasson, I.; Lundborg, T. Root exudation and rhizoplane bacterial abundance of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) in relation to nitrogen fertilization and root growth. Plant Soil 1990, 127, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, F.A.; Morgan, J.A.; Blumenthal, D.; Follett, R.F. Water limitation and plant inter-specific competition reduce rhizosphere-induced C decomposition and plant N uptake. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaullah, M.; Chabbi, A.; Rumpel, C.; Kuzyakov, Y. Carbon allocation in grassland communities under drought stress followed by 14C pulse labeling. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 55, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, G.; Römheld, V. The release of root exudates as affected by the plant physiological status. In The Rhizosphere: Biochemistry and Organic Substances at the Soil-Plant Interface, 2nd ed.; Pinton, R., Varanini, Z., Nannipieri, P., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 23–72. [Google Scholar]
- Salt, D.E.; Smith, R.D.; Raskin, I. Phytoremediation. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 1998, 49, 643–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hütsch, B.W.; Augustin, J.; Merbach, W. Plant rhizodeposition—An important source for carbon turnover in soils. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2002, 165, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, J.; Hawes, M.; Jones, D.; Lindow, S. How roots control the flux of carbon to the rhizosphere. Ecology 2003, 84, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, B.C.; George, S.J.; Price, C.A.; Ryan, M.H.; Tibbett, M. The role of root exuded low molecular weight organic anions in facilitating petroleum hydrocarbon degradation: Current knowledge and future directions. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 642–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.L. Organic acids in the rhizosphere—A critical review. Plant Soil 1998, 205, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demain, A.L.; Fang, A. The natural functions of secondary metabolites. In History of Modern Biotechnology I; Fiechter, A., Ed.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; Volumn 69, pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, R.A. Natural products and plant disease resistance. Nature 2001, 411, 843–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichersky, E.; Gang, D.R. Genetics and biochemistry of secondary metabolites in plants: An evolutionary perspective. Trends Plant Sci. 2000, 5, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, N.J.; Brown, D.E. Chemicals from Plants: Perspectives on Plant Secondary Products; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Crozier, A.; Jaganath, I.B.; Clifford, M.N. Phenols, polyphenols and tannins: An overview. In Plant Secondary Metabolites: Occurrence, Structure and Role in the Human Diet; Crozier, A., Clifford, M.N., Ashihara, H., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing, Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey, A.J.; Beale, M.H. Terpenes. In Plant Secondary Metabolites: Occurrence, Structure and Role in the Human Diet; Crozier, A., Clifford, M.N., Ashihara, H., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing, Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 47–101. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, L.P.; Brandt, K. Acetylenes and psoralens. In Plant Secondary Metabolites: Occurrence, Structure and Role in the Human Diet; Crozier, A., Clifford, M.N., Ashihara, H., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing, Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 137–173. [Google Scholar]
- Mithen, R. Sulphur-containing compounds. In Plant Secondary Metabolites: Occurrence, Structure and Role in the Human Diet; Crozier, A., Clifford, M.N., Ashihara, H., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing, Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 25–46. [Google Scholar]
- Zulak, K.G.; Liscombe, D.K.; Ashihara, H.; Facchini, P.J. Alkaloids. In Plant Secondary Metabolites: Occurrence, Structure and Role in the Human Diet; Crozier, A., Clifford, M.N., Ashihara, H., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing, Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 102–136. [Google Scholar]
- Iriti, M.; Faoro, F. Ozone-induced changes in plant secondary metabolism. In Climate Change and Crops; Singh, S.N., Ed.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 245–268. [Google Scholar]
- Noctor, G.; Mhamdi, A.; Chaouch, S.; Han, Y.I.; Neukermans, J.; Marquez-Garcia, B.; Queval, G.; Foyer, C.H. Glutathione in plants: An integrated overview. Plant Cell Environ. 2012, 35, 454–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlaeppi, K.; Bodenhausen, N.; Buchala, A.; Mauch, F.; Reymond, P. The glutathione-deficient mutant pad2–1 accumulates lower amounts of glucosinolates and is more susceptible to the insect herbivore Spodoptera littoralis. Plant J. 2008, 55, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandel, J.; Humbert, N.; Elhabiri, M.; Schalk, I.J.; Mislin, G.L.A.; Albrecht-Gary, A.-M. Pyochelin, a siderophore of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Physicochemical characterization of the iron(iii), copper(ii) and zinc(ii) complexes. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 2820–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.X.; Lin, Q.; Luo, Y.M.; He, Y.F.; Zhen, S.J.; Yu, Y.L.; Tian, G.M.; Wong, M.H. The role of citric acid on the phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.K. Heavy metals toxicity in plants: An overview on the role of glutathione and phytochelatins in heavy metal stress tolerance of plants. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2010, 76, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, S.; Hayat, Q.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Wani, A.S.; Pichtel, J.; Ahmad, A. Role of proline under changing environments: A review. Plant Signal. Behav. 2012, 7, 1456–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erb, M.; Lu, J. Soil abiotic factors influence interactions between belowground herbivores and plant roots. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontaine, S.; Mariotti, A.; Abbadie, L. The priming effect of organic matter: A question of microbial competition? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilers, K.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Shifts in bacterial community structure associated with inputs of low molecular weight carbon compounds to soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, H.; Gouin, T.; Leigh, M.B. Assessing the potential for rhizoremediation of PCB-contaminated soils in northern regions using native tree species. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, B.S.; Koh, S.C.; Chial, M.; Focht, D.D. Terpene-utilizing isolates and their relevance to enhanced biotransformation of polychlorinated biphenyls in soil. Biodegradation 1997, 8, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, A.C.; Smith, D.; Jury, W.A.; Hathuc, K.; Crowley, D.E. Impact of the plant rhizosphere and augmentation on remediation of polychlorinated biphenyl contaminated soil. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2003, 22, 1998–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlik, O.; Musilova, L.; Ridl, J.; Hroudova, M.; Vlcek, C.; Koubek, J.; Holeckova, M.; Mackova, M.; Macek, T. Plant secondary metabolite-induced shifts in bacterial community structure and degradative ability in contaminated soil. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 9245–9256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Teplitski, M.; Robinson, J.B.; Bauer, W.D. Production of substances by Medicago truncatula that affect bacterial quorum sensing. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2003, 16, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, C.-L.; Sam, C.-K.; Yin, W.-F.; Tan, L.Y.; Krishnan, T.; Chong, Y.M.; Chan, K.-G. Plant-derived natural products as sources of anti-quorum sensing compounds. Sensors 2013, 13, 6217–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernier, S.P.; Surette, M.G. Concentration-dependent activity of antibiotics in natural environments. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badri, D.V.; Vivanco, J.M. Regulation and function of root exudates. Plant Cell Environ. 2009, 32, 666–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.H.; Roberts, J.K.M. Improved cytoplasmic pH regulation, increased lactate efflux, and reduced cytoplasmic lactate levels are biochemical traits expressed in root tips of whole maize seedlings acclimated to a low-oxygen environment. Plant Physiol. 1994, 105, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Henry, A.; Doucette, W.; Norton, J.; Bugbee, B. Changes in crested wheatgrass root exudation caused by flood, drought, and nutrient stress. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juszczuk, I.; Wiktorowska, A.; Malusá, E.; Rychter, A. Changes in the concentration of phenolic compounds and exudation induced by phosphate deficiency in bean plants (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Plant Soil 2004, 267, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalhais, L.C.; Dennis, P.G.; Fedoseyenko, D.; Hajirezaei, M.-R.; Borriss, R.; von Wirén, N. Root exudation of sugars, amino acids, and organic acids by maize as affected by nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and iron deficiency. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2011, 174, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, M.B.; Fletcher, J.S.; Fu, X.; Schmitz, F.J. Root turnover: An important source of microbial substrates in rhizosphere remediation of recalcitrant contaminants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1579–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, E.; Kautz, T.; Perkons, U.; Uteau, D.; Peth, S.; Huang, N.; Horn, R.; Köpke, U. Root growth dynamics inside and outside of soil biopores as affected by crop sequence determined with the profile wall method. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2015, 51, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arcy-Lameta, A. Study of soybean and lentil root exudates. Plant Soil 1986, 92, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgarelli, D.; Schlaeppi, K.; Spaepen, S.; Themaat, E.V.L.V.; Schulze-Lefert, P. Structure and functions of the bacterial microbiota of plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2013, 64, 807–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlaeppi, K.; Dombrowski, N.; Oter, R.G.; van Themaat, E.V.L.; Schulze-Lefert, P. Quantitative divergence of the bacterial root microbiota in Arabidopsis thaliana relatives. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulgarelli, D.; Garrido-Oter, R.; Münch, P.C.; Weiman, A.; Dröge, J.; Pan, Y.; McHardy, A.C.; Schulze-Lefert, P. Structure and function of the bacterial root microbiota in wild and domesticated barley. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, A.; Schmid, M.; van Tuinen, D.; Berg, G. Plant-driven selection of microbes. Plant Soil 2009, 321, 235–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeAngelis, K.M.; Brodie, E.L.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Andersen, G.L.; Lindow, S.E.; Firestone, M.K. Selective progressive response of soil microbial community to wild oat roots. ISME J. 2008, 3, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzantor, E.K.; Woolston, J.E.; Momen, B. PCB dissipation and microbial community analysis in rhizosphere soil under substrate amendment conditions. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2002, 4, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İnceoğlu, Ö.; van Overbeek, L.S.; Salles, J.F.; van Elsas, J.D. Normal operating range of bacterial communities in soil used for potato cropping. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 1160–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, B.; Carvalhais, L.C.; Becker, A.; Fedoseyenko, D.; von Wirén, N.; Borriss, R. Transcriptomic profiling of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 in response to maize root exudates. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zyśko, A.; Sanguin, H.; Hayes, A.; Wardleworth, L.; Zeef, L.A.H.; Sim, A.; Paterson, E.; Singh, B.K.; Kertesz, M.A. Transcriptional response of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to a phosphate-deficient Lolium perenne rhizosphere. Plant Soil 2012, 359, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.L.; Subramanian, S.; Lamont, J.R.; Bywater-Ekegärd, M. Signaling in the phytomicrobiome: Breadth and potential. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toussaint, J.-P.; Pham, T.; Barriault, D.; Sylvestre, M. Plant exudates promote PCB degradation by a rhodococcal rhizobacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 95, 1589–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, U.; Staman, K.; Flint, L.; Shafer, S. Induction and/or selection of phenolic acid-utilizing bulk-soil and rhizosphere bacteria and their influence on phenolic acid phytotoxicity. J. Chem. Ecol. 2000, 26, 2059–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, A.; Yazaki, K. Root exudates of legume plants and their involvement in interactions with soil microbes. In Secretions and Exudates in Biological Systems; Vivanco, M.J., Baluška, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin & Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 27–48. [Google Scholar]
- De Weert, S.; Vermeiren, H.; Mulders, I.H.M.; Kuiper, I.; Hendrickx, N.; Bloemberg, G.V.; Vanderleyden, J.; de Mot, R.; Lugtenberg, B.J.J. Flagella-driven chemotaxis towards exudate components is an important trait for tomato root colonization by Pseudomonas fluorescens. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2002, 15, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Allen, C. Chemotaxis is required for virulence and competitive fitness of the bacterial wilt pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 3697–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Yao, J.; Allen, C. A MotN mutant of Ralstonia solanacearum is hypermotile and has reduced virulence. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 2477–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, G.; George, T.S.; Plassard, C. Strategies and methods for studying the rhizosphere—The plant science toolbox. Plant Soil 2009, 321, 431–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, C.; Miyahara, M.; Ohta, T.; Maximov, T.C. Response of larch root development to annual changes of water conditions in eastern Siberia. Polar Sci. 2016, 10, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.P.; Haines, B.; Coleman, D.; Hendrick, R. Fine root dynamics along an elevational gradient in the southern Appalachian mountains, USA. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 187, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oburger, E.; Schmidt, H. New methods to unravel rhizosphere processes. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downie, H.; Holden, N.; Otten, W.; Spiers, A.J.; Valentine, T.A.; Dupuy, L.X. Transparent soil for imaging the rhizosphere. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimungu, J.G.; Loades, K.W.; Lynch, J.P. Root anatomical phenes predict root penetration ability and biomechanical properties in maize (Zea mays). J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 3151–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooney, S.J.; Pridmore, T.P.; Helliwell, J.; Bennett, M.J. Developing X-ray computed tomography to non-invasively image 3-D root systems architecture in soil. Plant Soil 2012, 352, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mairhofer, S.; Zappala, S.; Tracy, S.; Sturrock, C.; Bennett, M.J.; Mooney, S.J. Recovering complete plant root system architectures from soil via X-ray µ-computed tomography. Plant Methods 2013, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stingaciu, L.; Schulz, H.; Pohlmeier, A.; Behnke, S.; Zilken, H.; Javaux, M.; Vereecken, H. In situ root system architecture extraction from magnetic resonance imaging for water uptake modeling. Vadose Zone J. 2013, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzner, R.; Eggert, A.; van Dusschoten, D.; Pflugfelder, D.; Gerth, S.; Schurr, U.; Uhlmann, N.; Jahnke, S. Direct comparison of MRI and X-ray CT technologies for 3D imaging of root systems in soil: Potential and challenges for root trait quantification. Plant Methods 2015, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oswald, S.E.; Menon, M.; Carminati, A.; Vontobel, P.; Lehmann, E.; Schulin, R. Quantitative imaging of infiltration, root growth, and root water uptake via neutron radiography. Vadose Zone J. 2008, 7, 1035–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downie, H.F.; Adu, M.O.; Schmidt, S.; Otten, W.; Dupuy, L.X.; White, P.J.; Valentine, T.A. Challenges and opportunities for quantifying roots and rhizosphere interactions through imaging and image analysis. Plant Cell Environ. 2015, 38, 1213–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dusschoten, D.; Metzner, R.; Kochs, J.; Postma, J.A.; Pflugfelder, D.; Buehler, J.; Schurr, U.; Jahnke, S. Quantitative 3D analysis of plant roots growing in soil using magnetic resonance imaging. Plant Physiol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Schepper, V.; Bühler, J.; Thorpe, M.; Roeb, G.; Huber, G.; van Dusschoten, D.; Jahnke, S.; Steppe, K. 11C-PET imaging reveals transport dynamics and sectorial plasticity of oak phloem after girdling. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larsen, M.; Santner, J.; Oburger, E.; Wenzel, W.W.; Glud, R.N. O2 dynamics in the rhizosphere of young rice plants (Oryza sativa L.) as studied by planar optodes. Plant Soil 2015, 390, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koop-Jakobsen, K.; Wenzhöfer, F. The dynamics of plant-mediated sediment oxygenation in Spartina anglica rhizospheres—A planar optode study. Estuaries Coasts 2015, 38, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blossfeld, S.; Schreiber, C.M.; Liebsch, G.; Kuhn, A.J.; Hinsinger, P. Quantitative imaging of rhizosphere pH and CO2 dynamics with planar optodes. Ann. Bot. 2013, 112, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faget, M.; Blossfeld, S.; von Gillhaussen, P.; Schurr, U.; Temperton, V.M. Disentangling who is who during rhizosphere acidification in root interactions: Combining fluorescence with optode techniques. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marschner, P.; Crowley, D.; Rengel, Z. Rhizosphere interactions between microorganisms and plants govern iron and phosphorus acquisition along the root axis—Model and research methods. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jusoh, W.; Wong, L.S. Exploring the potential of whole cell biosensor: A review in environmental applications. Int. J. Chem. Environ. Biol. Sci. 2014, 2, 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Porteous, F.; Killham, K.; Meharg, A. Use of a lux-marked rhizobacterium as a biosensor to assess changes in rhizosphere C flow due to pollutant stress. Chemosphere 2000, 41, 1549–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglisi, E.; Fragoulis, G.; Del Re, A.A.M.; Spaccini, R.; Piccolo, A.; Gigliotti, G.; Said-Pullicino, D.; Trevisan, M. Carbon deposition in soil rhizosphere following amendments with compost and its soluble fractions, as evaluated by combined soil–plant rhizobox and reporter gene systems. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobar, R.M.; Azcón-Aguilar, C.; Sanjuán, J.; Barea, J.M. Impact of a genetically modified Rhizobium strain with improved nodulation competitiveness on the early stages of arbuscular mycorrhiza formation. Appl. Soil Ecol. 1996, 4, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeAngelis, K.M.; Firestone, M.K.; Lindow, S.E. Sensitive whole-cell biosensor suitable for detecting a variety of N-acyl homoserine lactones in intact rhizosphere microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 3724–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Germaine, K.J.; Ryan, D.; Dowling, D.N. Whole-cell fluorescent biosensors for bioavailability and biodegradation of polychlorinated biphenyls. Sensors 2010, 10, 1377–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeAngelis, K.M.; Ji, P.; Firestone, M.K.; Lindow, S.E. Two novel bacterial biosensors for detection of nitrate availability in the rhizosphere. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8537–8547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, L.E.; Kragelund, L.; Nybroe, O. Expression of a nitrogen regulated lux gene fusion in Pseudomonas fluorescens DF57 studied in pure culture and in soil. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1998, 25, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragelund, L.; Christoffersen, B.; Nybroe, O.; de Bruijn, F.J. Isolation of lux reporter gene fusions in Pseudomonas fluorescens DF57 inducible by nitrogen or phosphorus starvation. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1995, 17, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppardt, A.; Vetterlein, D.; Harms, H.; Chatzinotas, A. Visualisation of gradients in arsenic concentrations around individual roots of Zea mays L. Using agar-immobilized bioreporter bacteria. Plant Soil 2010, 329, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger Iii, C.H.; Lindow, S.E.; Miller, W.; Clark, E.; Firestone, M.K. Mapping of sugar and amino acid availability in soil around roots with bacterial sensors of sucrose and tryptophan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 2685–2690. [Google Scholar]
- Loper, J.E.; Henkels, M.D. Availability of iron to Pseudomonas fluorescens in rhizosphere and bulk soil evaluated with an ice nucleation reporter gene. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amann, R.; Fuchs, B.M. Single-cell identification in microbial communities by improved fluorescence in situ hybridization techniques. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, M.; Haider, S. New trends in fluorescence in situ hybridization for identification and functional analyses of microbes. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2012, 23, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ling, N.; Yuan, Y.; Zheng, X.; Shen, B.; Shen, Q. Bacillus subtilis SQR 9 can control Fusarium wilt in cucumber by colonizing plant roots. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2011, 47, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khabbaz, S.E.; Zhang, L.; Cáceres, L.A.; Sumarah, M.; Wang, A.; Abbasi, P.A. Characterisation of antagonistic Bacillus and Pseudomonas strains for biocontrol potential and suppression of damping-off and root rot diseases. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2015, 166, 456–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buddrus-Schiemann, K.; Schmid, M.; Schreiner, K.; Welzl, G.; Hartmann, A. Root colonization by Pseudomonas sp. DSMZ 13134 and impact on the indigenous rhizosphere bacterial community of barley. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 60, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haichar, F.E.Z.; Heulin, T.; Guyonnet, J.P.; Achouak, W. Stable isotope probing of carbon flow in the plant holobiont. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 41, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlik, O.; Leewis, M.C.; Strejcek, M.; Musilova, L.; Mackova, M.; Leigh, M.B.; Macek, T. Stable isotope probing in the metagenomics era: A bridge towards improved bioremediation. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radajewski, S.; McDonald, I.R.; Murrell, J.C. Stable-isotope probing of nucleic acids: A window to the function of uncultured microorganisms. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2003, 14, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolausz, M.; Palatinszky, M.A.; Rusznyak, A.; Richnow, H.H.; Kappelmeyer, U.; Kastner, M. Novel approach using substrate-mediated radiolabelling of RNA to link metabolic function with the structure of microbial communities. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 274, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aelion, C.M.; Norman, R.S. Isotopic labeling in environmental and biodegradation studies. In Environmental Isotopes in Biodegradation and Bioremediation; Aelion, C.M., Höhener, P., Hunkeler, D., Aravena, R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 327–349. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J. Microbial ecology in the age of genomics and metagenomics: Concepts, tools, and recent advances. Mol. Ecol. 2006, 15, 1713–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, T.R.; Ramakrishnan, K.; Walshaw, J.; Heavens, D.; Alston, M.; Swarbreck, D.; Osbourn, A.; Grant, A.; Poole, P.S. Comparative metatranscriptomics reveals kingdom level changes in the rhizosphere microbiome of plants. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2248–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handelsman, J. Metagenomics: Application of genomics to uncultured microorganisms. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 669–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, J.A.; Hughes, M. Gene expression profiling: Metatranscriptomics. In High-Throughput Next Generation Sequencing: Methods and Applications; Kwon, M.Y., Ricke, C.S., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 195–205. [Google Scholar]
- Suenaga, H. Targeted metagenomics: A high-resolution metagenomics approach for specific gene clusters in complex microbial communities. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hettich, R.L.; Pan, C.; Chourey, K.; Giannone, R.J. Metaproteomics: Harnessing the power of high performance mass spectrometry to identify the suite of proteins that control metabolic activities in microbial communities. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 4203–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dam, N.M.; Bouwmeester, H.J. Metabolomics in the rhizosphere: Tapping into belowground chemical communication. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mairhofer, S.; Zappala, S.; Tracy, S.R.; Sturrock, C.; Bennett, M.; Mooney, S.J.; Pridmore, T. Rootrak: Automated recovery of three-dimensional plant root architecture in soil from X-ray micro-computed tomography images using visual tracking. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzner, R.; Dusschoten, D.; Bühler, J.; Schurr, U.; Jahnke, S. Belowground plant development measured with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): Exploiting the potential for non-invasive trait quantification using sugar beet as a proxy. Front. Plant. Sci. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beer, S.; Streun, M.; Hombach, T.; Buehler, J.; Jahnke, S.; Khodaverdi, M.; Larue, H.; Minwuyelet, S.; Parl, C.; Roeb, G.; et al. Design and initial performance of PlanTIS: A high-resolution positron emission tomograph for plants. Phys. Med. Biol. 2010, 55, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, S.; Ge, T.; Jing, H.; Li, B.; Liu, Q.; Lynn, T.M.; Wu, J.; Kuzyakov, Y. Microbial utilization of rice root exudates: 13C labeling and PLFA composition. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2016, 52, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chapman, S.J.; Yao, H. Incorporation of 13C-labelled rice rhizodeposition into soil microbial communities under different fertilizer applications. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 101, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschwendtner, S.; Engel, M.; Lueders, T.; Buegger, F.; Schloter, M. Nitrogen fertilization affects bacteria utilizing plant-derived carbon in the rhizosphere of beech seedlings. Plant Soil 2016, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santi, C.; Altermark, B.; Pierechod, M.M.; Ambrosino, L.; de Pascale, D.; Willassen, N.-P. Characterization of a cold-active and salt tolerant esterase identified by functional screening of arctic metagenomic libraries. BMC Biochem. 2016, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unno, Y.; Shinano, T. Metagenomic analysis of the rhizosphere soil microbiome with respect to phytic acid utilization. Microbes Environ. 2013, 28, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapelle, E.; Mendes, R.; Bakker, P.A.H.M.; Raaijmakers, J.M. Fungal invasion of the rhizosphere microbiome. ISME J. 2016, 10, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaparro, J.M.; Badri, D.V.; Vivanco, J.M. Rhizosphere microbiome assemblage is affected by plant development. ISME J. 2014, 8, 790–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yergeau, E.; Sanschagrin, S.; Maynard, C.; St-Arnaud, M.; Greer, C.W. Microbial expression profiles in the rhizosphere of willows depend on soil contamination. ISME J. 2014, 8, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, M.M.; Lorenz, N.; Hoilett, N.; Lee, N.R.; Dick, R.P.; Liles, M.R.; Ramsier, C.; Kloepper, J.W. Changes in rhizosphere bacterial gene expression following glyphosate treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 553, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hettich, R.L.; Sharma, R.; Chourey, K.; Giannone, R.J. Microbial metaproteomics: Identifying the repertoire of proteins that microorganisms use to compete and cooperate in complex environmental communities. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2012, 15, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becher, D.; Bernhardt, J.; Fuchs, S.; Riedel, K. Metaproteomics to unravel major microbial players in leaf litter and soil environments: Challenges and perspectives. Proteomics 2013, 13, 2895–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Wu, L.; Lin, S.; Zhang, A.; Zhou, M.; Lin, R.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, R. Metaproteomic analysis of ratoon sugarcane rhizospheric soil. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, J.M.; Benson, D.R. Comparative metabolomics of root nodules infected with Frankia sp. strains and uninfected roots from Alnus glutinosa and Casuarina cunninghamiana reflects physiological integration. Symbiosis 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaste, M.; Mistrik, R.; Shulaev, V. Applications of Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance (FT-ICR) and orbitrap based high resolution mass spectrometry in metabolomics and lipidomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, B.M.; Neale, H.C.; Geilfus, C.-M.; Jackson, R.W.; Arnold, D.L.; Preston, G.M. Early changes in apoplast composition associated with defence and disease in interactions between Phaseolus vulgaris and the halo blight pathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv. Phaseolicola. Plant Cell Environ. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oger, M.P.; Mansouri, H.; Nesme, X.; Dessaux, Y. Engineering root exudation of lotus toward the production of two novel carbon compounds leads to the selection of distinct microbial populations in the rhizosphere. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 47, 96–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costura, R.K.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Expression and longevity of toluene dioxygenase in Pseudomonas putida F1 induced at different dissolved oxygen concentrations. Water Res. 2000, 34, 3014–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szokol, J.; Rucka, L.; Simcikova, M.; Halada, P.; Nesvera, J.; Patek, M. Induction and carbon catabolite repression of phenol degradation genes in Rhodococcus erythropolis and Rhodococcus jostii. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 8267–8279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Inoue, R.; Kimura, N.; Furukawa, K. Versatile transcription of biphenyl catabolic bph operon in Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes KF707. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 31016–31023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Kim, S.W.; Choi, K.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, E. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of the genes encoding benzoate and p-hydroxybenzoate degradation by the halophilic Chromohalobacter sp. strain HS-2. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 280, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frascari, D.; Zanaroli, G.; Danko, A.S. In situ aerobic cometabolism of chlorinated solvents: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 382–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rentz, J.A.; Alvarez, P.J.J.; Schnoor, J.L. Benzo[a]pyrene co-metabolism in the presence of plant root extracts and exudates: Implications for phytoremediation. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 136, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorádová-Murínová, S.; Dudášová, H.; Lukáčová, L.; Čertík, M.; Šilharová, K.; Vrana, B.; Dercová, K. Adaptation mechanisms of bacteria during the degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls in the presence of natural and synthetic terpenes as potential degradation inducers. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 94, 1375–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leigh, M.B. Methods for rhizoremediation research: Approaches to experimental design and microbial analysis. In Phytoremediation and Rhizoremediation. Theoretical Background, 9th ed.; Macková, M., Dowling, D., Macek, T., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 33–55. [Google Scholar]
- Singer, A.C.; Thompson, I.P.; Bailey, M.J. The tritrophic trinity: A source of pollutant-degrading enzymes and its implications for phytoremediation. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2004, 7, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, A.C.; Gilbert, E.S.; Luepromchai, E.; Crowley, D.E. Bioremediation of polychlorinated biphenyl-contaminated soil using carvone and surfactant-grown bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 54, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandlich, R.; Brezna, B.; Dercova, K. The effect of terpenes on the biodegradation of polychlorinated biphenyls by Pseudomonas stutzeri. Chemosphere 2001, 44, 1547–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, M.; Beranova, K.; Dudkova, V.; Kochankova, L.; Demnerova, K.; Macek, T.; Mackova, M. Isolation and characterization of different plant associated bacteria and their potential to degrade polychlorinated biphenyls. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2009, 63, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, K.; Miyazaki, T. Cloning of a gene cluster encoding biphenyl and chlorobiphenyl degradation in Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes. J. Bacteriol. 1986, 166, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, K.; Suenaga, H.; Goto, M. Biphenyl dioxygenases: Functional versatilities and directed evolution. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 5189–5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macek, T.; Mackova, M.; Kas, J. Exploitation of plants for the removal of organics in environmental remediation. Biotechnol. Adv. 2000, 18, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Dudareva, N. The shikimate pathway and aromatic amino acid biosynthesis in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2012, 63, 73–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewick, P.M. The shikimate pathway: Aromatic amino acids and phenylpropanoids. In Medicinal Natural Products, 3rd ed.; Dewick, P.M., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2009; pp. 137–186. [Google Scholar]
- Duke, J.A. Handbook of Phytochemical Constituent Grass, Herbs and Other Economic Plants, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Winkel-Shirley, B. Flavonoid biosynthesis. A colorful model for genetics, biochemistry, cell biology, and biotechnology. Plant Physiol. 2001, 126, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dashtban, M.; Schraft, H.; Syed, T.A.; Qin, W. Fungal biodegradation and enzymatic modification of lignin. Int. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 1, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Dueñas, F.J.; Martínez, Á.T. Microbial degradation of lignin: How a bulky recalcitrant polymer is efficiently recycled in nature and how we can take advantage of this. Microb. Biotechnol. 2009, 2, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeffries, T. Biodegradation of lignin and hemicelluloses. In Biochemistry of Microbial Degradation; Ratledge, C., Ed.; Springer: Houten, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 233–277. [Google Scholar]
- Sainsbury, P.D.; Mineyeva, Y.; Mycroft, Z.; Bugg, T.D.H. Chemical intervention in bacterial lignin degradation pathways: Development of selective inhibitors for intradiol and extradiol catechol dioxygenases. Bioorg. Chem. 2015, 60, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.E.; Chang, M.C.Y. Exploring bacterial lignin degradation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2014, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kameshwar, A.k.S.; Qin, W. Recent developments in using advanced sequencing technologies for the genomic studies of lignin and cellulose degrading microorganisms. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 12, 156–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, P.; Kersten, P.; Vanden Wymelenberg, A.; Gaskell, J.; Cullen, D. Lignin peroxidase gene family of Phanerochaete chrysosporium: Complex regulation by carbon and nitrogen limitation and identification of a second dimorphic chromosome. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 5036–5042. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Alic, M.; Brown, J.A.; Gold, M.H. Regulation of manganese peroxidase gene transcription by hydrogen peroxide, chemical stress, and molecular oxygen. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Liers, C.; Ullrich, R.; Hofrichter, M.; Urynowicz, M.A. Depolymerization and solubilization of chemically pretreated powder river basin subbituminous coal by manganese peroxidase (MnP) from Bjerkandera adusta. Fuel 2013, 112, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirosue, S.; Tazaki, M.; Hiratsuka, N.; Yanai, S.; Kabumoto, H.; Shinkyo, R.; Arisawa, A.; Sakaki, T.; Tsunekawa, H.; Johdo, O.; et al. Insight into functional diversity of cytochrome P450 in the white-rot basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium: Involvement of versatile monooxygenase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 407, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullen, D. Recent advances on the molecular genetics of ligninolytic fungi. J. Biotechnol. 1997, 53, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, M.; Meux, E.; Mathieu, Y.; Thuillier, A.; Chibani, K.; Harvengt, L.; Jacquot, J.-P.; Gelhaye, E. Xenomic networks variability and adaptation traits in wood decaying fungi. Microb. Biotechnol. 2013, 6, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cvancarova, M.; Kresinova, Z.; Filipova, A.; Covino, S.; Cajthaml, T. Biodegradation of PCBs by ligninolytic fungi and characterization of the degradation products. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, J.S.; Quensen, J.F.; Tiedje, J.M.; Reddy, C.A. Degradation of polychlorinated biphenyl mixtures (Aroclors 1242, 1254, and 1260) by the white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium as evidenced by congener-specific analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 2560–2565. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krcmar, P.; Ulrich, R. Degradation of polychlorinated biphenyl mixtures by the lignin-degrading fungus Phanerochœte chrysosporium. Folia Microbiol. 1998, 43, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajthaml, T.; Erbanova, P.; Sasek, V.; Moeder, M. Breakdown products on metabolic pathway of degradation of benz[a]anthracene by a ligninolytic fungus. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cajthaml, T.; Erbanova, P.; Kollmann, A.; Novotný, C.; Sasek, V.; Mougin, C. Degradation of PAHs by ligninolytic enzymes of Irpex lacteus. Folia Microbiol. 2008, 53, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Sun, H.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q. Enzyme activities during degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium in soils. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byss, M.; Elhottova, D.; Triska, J.; Baldrian, P. Fungal bioremediation of the creosote-contaminated soil: Influence of Pleurotus ostreatus and Irpex lacteus on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons removal and soil microbial community composition in the laboratory-scale study. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 1518–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baborova, P.; Moder, M.; Baldrian, P.; Cajthamlova, K.; Cajthaml, T. Purification of a new manganese peroxidase of the white-rot fungus Irpex lacteus, and degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by the enzyme. Res. Microbiol. 2006, 157, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covino, S.; Svobodova, K.; Kresinova, Z.; Petruccioli, M.; Federici, F.; D’Annibale, A.; Cvancarova, M.; Cajthaml, T. In vivo and in vitro polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons degradation by Lentinus (Panus) tigrinus CBS 577.79. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 3004–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, A.; Watanabe, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Harazono, K.; Fukatsu, T. Screening for basidiomycetous fungi capable of degrading 2,7-dichlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2002, 213, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, K.C.; Chen, J.C.; Huebner, H.J.; Brown, K.W.; Autenrieth, R.L.; Bonner, J.S. Utility of four strains of white-rot fungi for the detoxification of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene in liquid culture. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1997, 16, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigas, F.; Dritsa, V.; Marchant, R.; Papadopoulou, K.; Avramides, E.J.; Hatzianestis, I. Biodegradation of lindane by Pleurotus ostreatus via central composite design. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rüttimann-Johnson, C.; Lamar, R.T. Binding of pentachlorophenol to humic substances in soil by the action of white rot fungi. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1997, 29, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlik, O.; Jecna, K.; Mackova, M.; Vlcek, C.; Hroudova, M.; Demnerova, K.; Paces, V.; Macek, T. Biphenyl-metabolizing bacteria in the rhizosphere of horseradish and bulk soil contaminated by polychlorinated biphenyls as revealed by stable isotope probing. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 6471–6477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leigh, M.B.; Prouzova, P.; Mackova, M.; Macek, T.; Nagle, D.P.; Fletcher, J.S. Polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB)-degrading bacteria associated with trees in a PCB-contaminated site. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2331–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridl, J.; Kolar, M.; Strejcek, M.; Strnad, H.; Stursa, P.; Paces, J.; Macek, T.; Uhlik, O. Plants rather than mineral fertilization shape microbial community structure and functional potential in legacy contaminated soil. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, C.; Koenen, B.; Carnahan, J.; Walworth, J.; Bhunia, P. Rhizosphere and nutrient effects on remediating subarctic soils. Situ On-Site Bioremediat. 1997, 4, 297–302. [Google Scholar]
- Leewis, M.-C.C.E.; Uhlik, O.; Fraraccio, S.; McFarlin, K.; Kottara, A.; Glover, C.; Macek, T.; Leigh, M.B. Differential impacts of willow and mineral fertilizer on bacterial communities and biodegradation in diesel fuel oil-contaminated soil. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, E.S.; Crowley, D.E. Plant compounds that induce polychlorinated biphenyl biodegradation by Arthrobacter sp. strain B1B. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 1933–1938. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, E.S.; Crowley, D.E. Repeated application of carvone-induced bacteria to enhance biodegradation of polychlorinated biphenyls in soil. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1998, 50, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, H.; Crowley, D.E. Biostimulation of PAH degradation with plants containing high concentrations of linoleic acid. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 4382–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLoughlin, E.; Rhodes, A.H.; Owen, S.M.; Semple, K.T. Biogenic volatile organic compounds as a potential stimulator for organic contaminant degradation by soil microorganisms. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scheublin, T.R.; Deusch, S.; Moreno-Forero, S.K.; Müller, J.A.; van der Meer, J.R.; Leveau, J.H.J. Transcriptional profiling of gram-positive Arthrobacter in the phyllosphere: Induction of pollutant degradation genes by natural plant phenolic compounds. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 2212–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suttinun, O.; Lederman, P.B.; Luepromchai, E. Application of terpene-induced cell for enhancing biodegradation of TCE contaminated soil. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2004, 26, 131–142. [Google Scholar]
- Dabrock, B.; Riedel, J.; Bertram, J.; Gottschalk, G. Isopropylbenzene (cumene)—A new substrate for the isolation of trichloroethene-degrading bacteria. Arch. Microbiol. 1992, 158, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirby, R. Actinomycetes and lignin degradation. In Advances in Applied Microbiology; Laskin, A.I., Bennett, J.W., Gadd, G.M., Sariaslani, S., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2005; Volumn 58, pp. 125–168. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, M.; Roberts, J.N.; Hardiman, E.M.; Singh, R.; Eltis, L.D.; Bugg, T.D.H. Identification of DypB from Rhodococcus jostii RHA1 as a lignin peroxidase. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 5096–5107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLeod, M.P.; Warren, R.L.; Hsiao, W.W.L.; Araki, N.; Myhre, M.; Fernandes, C.; Miyazawa, D.; Wong, W.; Lillquist, A.L.; Wang, D.; et al. The complete genome of Rhodococcus sp. RHA1 provides insights into a catabolic powerhouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15582–15587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tehrani, R.; Van Aken, B. Hydroxylated polychlorinated biphenyls in the environment: Sources, fate, and toxicities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 6334–6345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezek, J.; Macek, T.; Mackova, M.; Triska, J.; Ruzickova, K. Hydroxy-PCBs, methoxy-PCBs and hydroxy-methoxy-PCBs: Metabolites of polychlorinated biphenyls formed in vitro by tobacco cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5746–5751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francova, K.; Mackova, M.; Macek, T.; Sylvestre, M. Ability of bacterial biphenyl dioxygenases from Burkholderia sp. LB400 and Comamonas testosteroni B-356 to catalyse oxygenation of ortho-hydroxychlorobiphenyls formed from PCBs by plants. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 127, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.T.M.; Sondossi, M.; Sylvestre, M. Metabolism of doubly para-substituted hydroxychlorobiphenyls by bacterial biphenyl dioxygenases. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 4860–4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sondossi, M.; Barriault, D.; Sylvestre, M. Metabolism of 2,2′- and 3,3′-dihydroxybiphenyl by the biphenyl catabolic pathway of Comamonas testosteroni B-356. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tehrani, R.; Lyv, M.M.; Kaveh, R.; Schnoor, J.L.; van Aken, B. Biodegradation of mono-hydroxylated PCBs by Burkholderia xenovorans. Biotechnol. Lett. 2012, 34, 2247–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, T.T.M.; Tu, Y.; Sylvestre, M. Remarkable ability of Pandoraea pnomenusa B356 biphenyl dioxygenase to metabolize simple flavonoids. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 3560–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, T.T.; Pino Rodriguez, N.J.; Hijri, M.; Sylvestre, M. Optimizing polychlorinated biphenyl degradation by flavonoid-induced cells of the rhizobacterium Rhodococcus erythropolis U23A. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.H.; Aitken, M.D. Salicylate stimulates the degradation of high-molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by Pseudomonas saccharophila P15. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 33, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H.; Kondo, F. Bisphenol a degradation by bacteria isolated from river water. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2002, 43, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamath, R.; Schnoor, J.L.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Effect of root-derived substrates on the expression of nah-lux genes in Pseudomonas fluorescens HK44: Implications for PAH biodegradation in the rhizosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1740–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojcieszyńska, D.; Guzik, U.; Greń, I.; Perkosz, M.; Hupert-Kocurek, K. Induction of aromatic ring: Cleavage dioxygenases in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia strain KB2 in cometabolic systems. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 27, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greń, I.; Wojcieszyńska, D.; Guzik, U.; Perkosz, M.; Hupert-Kocurek, K. Enhanced biotransformation of mononitrophenols by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia KB2 in the presence of aromatic compounds of plant origin. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 26, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowell, P.L. Prevention and therapy of cancer by dietary monoterpenes. J. Nutr. 1999, 129, 775S–778S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ballal, N.R.; Bhattacharyya, P.K.; Rangachari, P.N. Perillyl alcohol dehydrogenase from a soil pseudomonad. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 1966, 23, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.K.; Day, D.F. Bacterial metabolism of α- and β-pinene and related monoterpenes by Pseudomonas sp. strain PIN. Process Biochem. 2002, 37, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, C.C.C.R.; Parreño-Marchante, B.; Neumann, G.; da Fonseca, M.M.R.; Heipieper, H.J. Adaptation of Rhodococcus erythropolis DCL14 to growth on n-alkanes, alcohols and terpenes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 67, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bicas, J.L.; Fontanille, P.; Pastore, G.M.; Larroche, C. A bioprocess for the production of high concentrations of R-(+)-α-terpineol from R-(+)-limonene. Process Biochem. 2010, 45, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, R.W.; Sandusky, P. Biotransformations of (+/−)-geosmin by terpene-degrading bacteria. Biodegradation 2010, 21, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Werf, M.J.; Swarts, H.J.; de Bont, J.A.M. Rhodococcus erythropolis DCL14 contains a novel degradation pathway for limonene. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 2092–2102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Dyk, M.S.; van Rensburg, E.; Moleleki, N. Hydroxylation of (+)limonene, (−)α-pinene and (−)β-pinene by a Hormonema sp. Biotechnol. Lett. 1998, 20, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, M.A.; Almeida, D.S.; Siani, A.C.; Lucchetti, L.; Lacerda, P.S.B.; Freitas, A.; Tappin, M.R.R.; Bon, E.P.S. Bioconversion of R-(+)-limonene to perillic acid by the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2013, 44, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.C.; Oriel, P. Bioproduction of perillyl alcohol and related monoterpenes by isolates of Bacillus stearothermophilus. J. Food Sci. 1994, 59, 660–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mars, A.; Gorissen, J.; van den Beld, I.; Eggink, G. Bioconversion of limonene to increased concentrations of perillic acid by Pseudomonas putida GS1 in a fed-batch reactor. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 56, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redondo-Nieto, M.; Barret, M.; Morrisey, J.P.; Germaine, K.; Martínez-Granero, F.; Barahona, E.; Navazo, A.; Sánchez-Contreras, M.; Moynihan, J.A.; Giddens, S.R.; et al. Genome sequence of the biocontrol strain Pseudomonas fluorescens F113. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 1273–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowley, D.E.; Focht, D.D.; Gilbert, E.S.; Hernandez, B.S. Composition and Method for Degradation of Polychlorinated Biphenyl Compounds. U.S. Patent US5968360 A, 19 October 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.R.M.; Thompson, I.P.; Paton, G.I.; Singer, A.C. Enhanced biotransformation of tce using plant terpenoids in contaminated groundwater. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 49, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radajewski, S.; Webster, G.; Reay, D.S.; Morris, S.A.; Ineson, P.; Nedwell, D.B.; Prosser, J.I.; Murrell, J.C. Identification of active methylotroph populations in an acidic forest soil by stable-isotope probing. Microbiology 2002, 148, 2331–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackova, M.; Uhlik, O.; Lovecka, P.; Viktorova, J.; Novakova, M.; Demnerova, K.; Sylvestre, M.; Macek, T. Bacterial degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls. In Geomicrobiology: Molecular and Environmental Perspective; Loy, A., Mandl, M., Barton, L.L., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 347–366. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Murrell, J.C. When metagenomics meets stable-isotope probing: Progress and perspectives. Trends Microbiol. 2010, 18, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musilová, L.; Uhlík, O.; Strejček, M.; Dudková, V.; Macková, M.; Macek, T. Enchancement of Polychlorinated Biphenyls Bioremediation by Soil Enrichment with Plant Secondary Metabolites. In Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Biosorption and Bioremediation, Prague, Czech Republic, 25–29 June 2012; Lovecká, P., Nováková, M., Prouzová, P., Uhlík, O., Eds.; ICT Prague Press: Prague, Czec, Republic, 2012; pp. 135–138. [Google Scholar]
- Duke, J., Dr. Duke’s Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Databases. Available online: https://phytochem.nal.usda.gov/phytochem/search (accessed on 10 June 2016).
- Bell, T.; Newman, J.A.; Silverman, B.W.; Turner, S.L.; Lilley, A.K. The contribution of species richness and composition to bacterial services. Nature 2005, 436, 1157–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardle, D.A.; Bonner, K.I.; Nicholson, K.S. Biodiversity and plant litter: Experimental evidence which does not support the view that enhanced species richness improves ecosystem function. Oikos 1997, 79, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, M.B.; Pellizari, V.H.; Uhlík, O.; Sutka, R.; Rodrigues, J.; Ostrom, N.E.; Zhou, J.; Tiedje, J.M. Biphenyl-utilizing bacteria and their functional genes in a pine root zone contaminated with polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). ISME J. 2007, 1, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Gentry, T.J.; Schadt, C.W.; Wu, L.; Liebich, J.; Chong, S.C.; Huang, Z.; Wu, W.; Gu, B.; Jardine, P.; et al. Geochip: A comprehensive microarray for investigating biogeochemical, ecological and environmental processes. ISME J. 2007, 1, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, S.; Julkunen-Tiitto, R.; Holappa, E.; Mikkola, K.; Nikula, A. Concentrations of foliar quercetin in natural populations of white birch (Betula pubescens) increase with latitude. J. Chem. Ecol. 2008, 34, 1382–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leewis, M.-C.; Reynolds, C.M.; Leigh, M.B. Long-term effects of nutrient addition and phytoremediation on diesel and crude oil contaminated soils in subarctic Alaska. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2013, 96, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrini, O. Fungal endophytes of tree leaves. In Microbial Ecology of Leaves; Andrews, J.H., Hirano, S.S., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 179–197. [Google Scholar]
- Compant, S.; Saikkonen, K.; Mitter, B.; Campisano, A.; Mercado-Blanco, J. Editorial special issue: Soil, plants and endophytes. Plant Soil 2016, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Aken, B.; Yoon, J.M.; Schnoor, J.L. Biodegradation of nitro-substituted explosives 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene, hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine, and octahydro-1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1,3,5-tetrazocine by a phytosymbiotic Methylobacterium sp. associated with poplar tissues (Populus deltoides × nigra DN34). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moore, F.P.; Barac, T.; Borrernans, B.; Oeyen, L.; Vangronsveld, J.; van der Lelie, D.; Campbell, C.D.; Moore, E.R.B. Endophytic bacterial diversity in poplar trees growing on a BTEX-contaminated site: The characterisation of isolates with potential to enhance phytoremediation. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 29, 539–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyens, N.; van der Lelie, D.; Taghavi, S.; Vangronsveld, J. Phytoremediation: Plant-endophyte partnerships take the challenge. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2009, 20, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siciliano, S.D.; Fortin, N.; Mihoc, A.; Wisse, G.; Labelle, S.; Beaumier, D.; Ouellette, D.; Roy, R.; Whyte, L.G.; Banks, M.K.; et al. Selection of specific endophytic bacterial genotypes by plants in response to soil contamination. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 2469–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlikova, D.; Macek, T.; Mackova, M.; Pavlik, M. Monitoring native vegetation on a dumpsite of PCB-contaminated soil. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2007, 9, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlik, O.; Wald, J.; Strejcek, M.; Musilova, L.; Ridl, J.; Hroudova, M.; Vlcek, C.; Cardenas, E.; Mackova, M.; Macek, T. Identification of bacteria utilizing biphenyl, benzoate, and naphthalene in long-term contaminated soil. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlík, O.; Strejček, M.; Junková, P.; Šanda, M.; Hroudová, M.; Vlček, C.; Macková, M.; Macek, T. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI)-time of flight mass spectrometry- and MALDI biotyper-based identification of cultured biphenyl-metabolizing bacteria from contaminated horseradish rhizosphere soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 6858–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Object of Study | Method | Reference | Example of Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| root growth and morphology | observation windows + imaging system | [92,93] | [92,93] |
| transparent culture media, e.g., PhytagelTM or NafionTM | [94,95] | [95] | |
| computed tomography (CT) | [97,139] | [97,139] | |
| magnetic resonance (MRI) | [99,140] | [99,140] | |
| neutron radiography | [101] | [101] | |
| nutrient transport | magnetic resonance (MRI) | [103] | [103] |
| neutron tomography | [102] | [102] | |
| 11C-positron emission tomography (11C-PET) | [104] | [141] | |
| optode | [106,107,108] | [105,106,107,108] | |
| radioisotope labelling (RIP) | [22] | [22] | |
| stable isotope labelling (SIP) | [127] | [142,143] | |
| interactions plant–microbes | biosensors | [110] | [111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121] |
| fluorescence in situ hybridization | [122] | [122,124,125,126] | |
| metagenomics | [134] | [63,144,145,146] | |
| metatranscriptomics | [135] | [147,148,149,150] | |
| metaproteomics | [151] | [152,153,154] | |
| metabolomics | [155] | [155,156] |
| Contaminant | Treatment | Observed Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCBs | limonene | reduction in diversity of bacterial community; | [63] |
| community dominated by Hydrogenophaga; | |||
| Azoarcus and Hydrogenophaga dominated utilization of 4-chloro-13C-biphenyl; | |||
| naringin | reduction of diversity of bacterial community; | ||
| Hydrogenophaga dominated utilization of 4-chloro-13C-biphenyl; | |||
| caffeic acid | largest reduction in diversity of bacterial community; | ||
| Burkholderia dominated utilization of 4-chloro-13C-biphenyl; | |||
| degradation of higher-chlorinated PCBs | |||
| PCBs | orange peel | complete mineralization of PCBs; | [61] |
| increased abundance of cultivable biphenyl-utilizing bacteria; | |||
| ivy leaves | complete mineralization of PCBs; | ||
| increased abundance of cultivable biphenyl-utilizing bacteria; | |||
| eucalyptus leaves | complete mineralization of PCBs; | ||
| increased abundance of cultivable biphenyl-utilizing bacteria | |||
| PCBs | grapefruit peel | reduction in diversity of bacterial community; | this paper |
| Hydrogenophaga, Caulobacter, and Skermanella dominated utilization of 4-chloro-13C-biphenyl; | |||
| Azotobacter dominated utilization of 4-chloro-13C-biphenyl; | |||
| increased abundance of cultivable biphenyl-utilizing bacteria; | |||
| lemon peel | largest reduction in diversity of bacterial community; | ||
| Nocardioides dominated utilization of 4-chloro-13C-biphenyl; | |||
| Skermanella dominated utilization of 4-chloro-13C-biphenyl; | |||
| increased abundance of cultivable biphenyl-utilizing bacteria; | |||
| pears | reduction in diversity of bacterial community; | ||
| Azotobacter dominated utilization of 4-chloro-13C-biphenyl; | |||
| increased abundance of cultivable biphenyl-utilizing bacteria | |||
| PCBs | horseradish | Hydrogenophaga dominated utilization of 13C-biphenyl | [202] |
| PCBs | Austrian pine | increased abundance of cultivable biphenyl-utilizing bacteria | [203] |
| ash | |||
| weeping birch | |||
| goat willow | |||
| black locust | |||
| PCBs | horseradish | microbial populations of the root zone of each plant significantly differed from one another and/or from the bulk soil | [204] |
| black nightshade | |||
| tobacco | |||
| diesel and crude oil | annual ryegrass | enhanced bioremediation | [205] |
| red fescue | |||
| diesel oil | Alaskan willow | willow had a significant role in structuring the total bacterial community and resulted in significant decreases in diesel range organics | [206] |
| PCBs | nitrogen-rich | fungus Pleurotus ostreatus disposes of PCB-degradation activity | [189] |
| nitrogen-limiting | |||
| PCBs | nitrogen-limiting | fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium disposes of PCB-degradation activity | [190] |
| PCBs | naringin | bacterium Cupriavidus necator H850 disposes of PCB-degrading activity while grown on the compounds as carbon sources | [16] |
| apigenin | |||
| catechin | |||
| morin | |||
| salicylic acid | [167] | ||
| PCBs | myricetin | bacterium Burkholderia xenovorans LB400 disposes of PCB-degrading activity | [16] |
| catechin | |||
| chrysin | |||
| PCBs | limonene | bacterium Pseudomonas stutzeri disposes of PCB-degrading activity while grown on the compounds as carbon sources | [168] |
| carvone | |||
| PCBs | Mentha spicata (carvone) | bacterium Arthrobacter sp. B1B disposes of PCB-degrading activity while grown on the compound as a carbon source | [207,208] |
| 4-chlorobiphenyl (PCB 3) | Arabidopsis thaliana exudates (flavanone) | bacterium Rhodococcus erythropolis U23A disposes of PCB-degrading activity while grown on the exudates as a carbon source | [85] |
| PAHs | radish (terpenes, salicylic acid) | enhanced bioremediation | [209] |
| potato | |||
| carrot | |||
| celery | |||
| PAHs | not specified | fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium disposes of PAH-degrading activity | [194] |
| PAHs | not specified | fungus Irpex lacteus disposes of PAH-degrading activity | [192,193] |
| PAHs | nitrogen-rich | fungus Lentinus tigrinus disposes of PAH-degradation activity | [197] |
| PCP | not specified | fungus Pleurotus ostreatus disposes of PCP-degradation activity | [201] |
| PCP | not specified | fungus Irpex lacteus disposes of PCP-degradation activity | [201] |
| PCP | not specified | fungus Trametes versicolor disposes of PCP-degradation activity | [201] |
| PCP | not specified | fungus Bjerkandera adusta disposes of PCP-degradation activity | [201] |
| PCP | carvone | bacterium Arthrobacter sp. B1B disposes of PCP-degradation activity | [210] |
| 4-chlorophenol (4-CP) | leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris | bacterium Arthrobacter chlorophenolicus A6 disposes of 4-CP-degradation activity | [211] |
| TCE | cumene | bacterium Rhodococcus gordoniae P3 disposes of TCE-degradation activity | [212] |
| TCE | cumene | bacterium Pseudomonas sp. JR1 disposes of TCE-degradation activity | [213] |
| TCE | cumene | bacterium Rhodococcus erythropolis BD1 disposes of TCE-degradation activity | [213] |
| TNT | not specified | fungus Pleurotus ostreatus disposes of TNT-degradation activity | [199] |
| TNT | not specified | fungus Phanerochaete sordida disposes of TNT-degradation activity | [199] |
| TNT | not specified | fungus Phlebia brevispora disposes of TNT-degradation activity | [199] |
| TNT | not specified | fungus Cyathus stercoreus disposes of TNT-degradation activity | [199] |
| lindane | intermediate nitrogen concentration | fungus Pleurotus ostreatus disposes of lindane-degradation activity | [200] |
| dioxins | not specified | fungus Panellus stipticus 99–334 disposes of dibenzo-p-dioxins-degradation activity | [198] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Musilova, L.; Ridl, J.; Polivkova, M.; Macek, T.; Uhlik, O. Effects of Secondary Plant Metabolites on Microbial Populations: Changes in Community Structure and Metabolic Activity in Contaminated Environments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081205
Musilova L, Ridl J, Polivkova M, Macek T, Uhlik O. Effects of Secondary Plant Metabolites on Microbial Populations: Changes in Community Structure and Metabolic Activity in Contaminated Environments. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(8):1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081205
Chicago/Turabian StyleMusilova, Lucie, Jakub Ridl, Marketa Polivkova, Tomas Macek, and Ondrej Uhlik. 2016. "Effects of Secondary Plant Metabolites on Microbial Populations: Changes in Community Structure and Metabolic Activity in Contaminated Environments" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 8: 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081205
APA StyleMusilova, L., Ridl, J., Polivkova, M., Macek, T., & Uhlik, O. (2016). Effects of Secondary Plant Metabolites on Microbial Populations: Changes in Community Structure and Metabolic Activity in Contaminated Environments. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(8), 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081205