Erythropoietin Pathway: A Potential Target for the Treatment of Depression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Expression of EPO and EPOR in the Nervous System
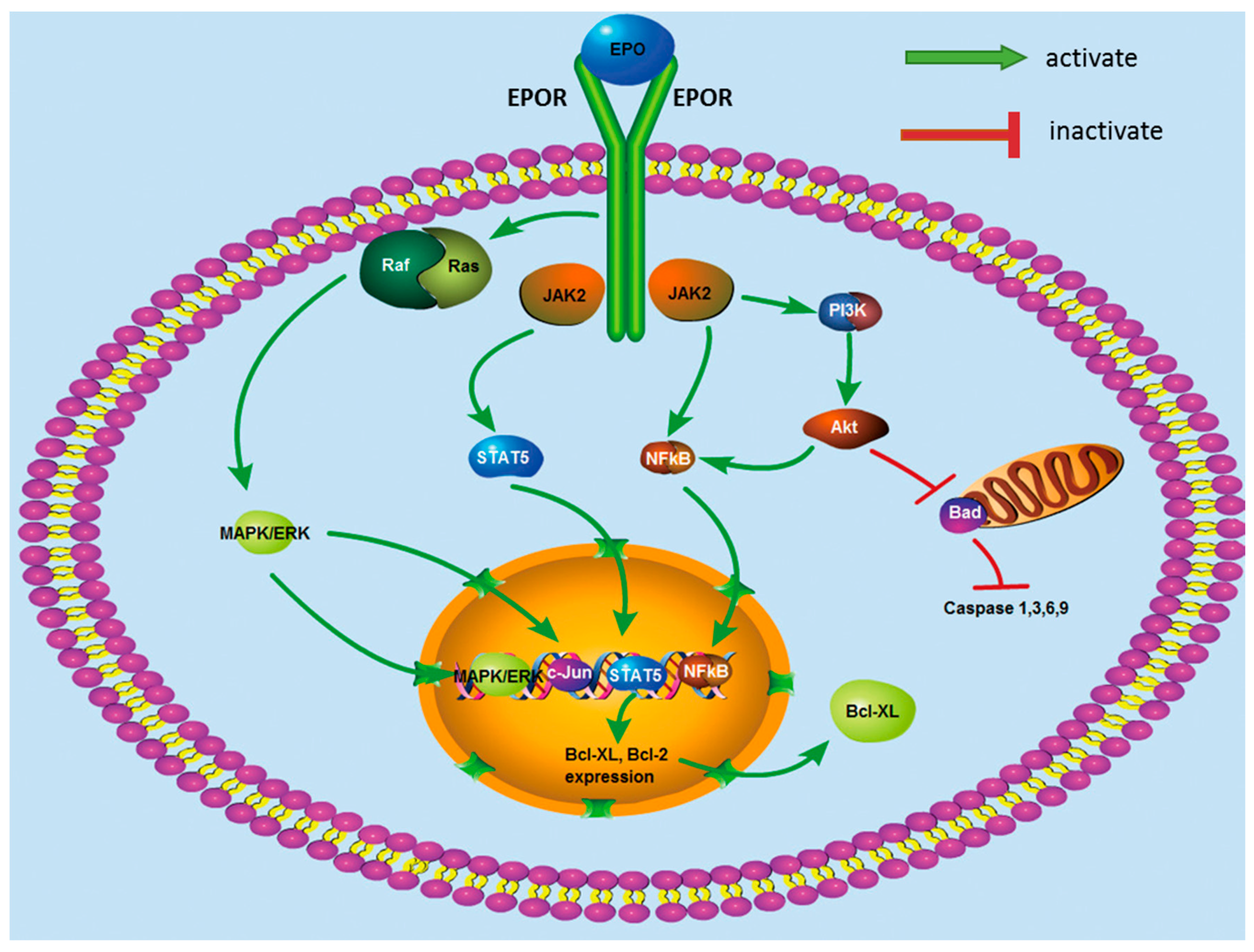
3. EPO-Induced Intracellular Signaling Pathways
3.1. JAK2
3.2. STAT5
3.3. NF-κB
3.4. PI3K/Akt
3.5. ERK/MAPK
4. EPO in the Treatment of Depression
4.1. Inflammation in EPO-Related Treatments
4.2. Neuroprogression in EPO-Related Treatment
5. Conclusions and Perspective
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EPO | Erythropoietin |
| EPOR | Erythropoietin receptor |
| βcR/CD131 | β-common receptor |
| 5-HT | 5-hydroxytryptamine |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neutrophic factor |
| ECs | Endothelial cells |
| BBB | Blood brain barrier |
| GM-CSF | granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor |
| IL-3 | Interleukin 3 |
| IL-5 | Interleukin 5 |
| EphB4 | Ephrin-type B receptor 4 |
| RhEPO | Recombinant human EPO |
| CEPO | Carbamylated erythropoietin |
| HIF | Hypoxia-inducible factor |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| JAK2 | Janus kinase 2 |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| STAT5 | Transducer and activator of transcription 5 |
| Akt | Protein Ser/Thr kinase |
| MAPK | P42/44 mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| SSRI | Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor |
| NSAIDs | Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| iNOS | Inducible NO synthase |
References
- Moussavi, S.; Chatterji, S.; Verdes, E.; Tandon, A.; Patel, V.; Ustun, B. Depression, chronic diseases, and decrements in health: Results from the World Health Surveys. Lancet 2007, 370, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M.; Meltzer, H. The serotonin hypothesis of major depression. Psychopharmacol. Fourth Gener. Prog. 1995, 10, 933–934. [Google Scholar]
- Rush, A.J.; Trivedi, M.H.; Stewart, J.W.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Fava, M.; Kurian, B.T.; Warden, D.; Morris, D.W.; Luther, J.F.; Husain, M.M. Combining medications to enhance depression outcomes (CO-MED): Acute and long-term outcomes of a single-blind randomized study. Am. J. Psychiatry 2011, 168, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John Rush, A.; Trivedi, M.H.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Stewart, J.W.; Warden, D.; Niederehe, G.; Thase, M.E.; Lavori, P.W.; Lebowitz, B.D. Acute and longer-term outcomes in depressed outpatients requiring one or several treatment steps: A STAR* D report. Am. J. Psychiatry 2006, 163, 1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behnken, A.; Schöning, S.; Gerß, J.; Konrad, C.; de Jong-Meyer, R.; Zwanzger, P.; Arolt, V. Persistent non-verbal memory impairment in remitted major depression—Caused by encoding deficits? J. Affect. Disord. 2010, 122, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preiss, M.; Kucerova, H.; Lukavsky, J.; Stepankova, H.; Sos, P.; Kawaciukova, R. Cognitive deficits in the euthymic phase of unipolar depression. Psychiatry Res. 2009, 169, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperner-Unterweger, B.; Kohl, C.; Fuchs, D. Immune changes and neurotransmitters: Possible interactions in depression? Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 48, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A. Systems genomics support for immune and inflammation hypothesis of depression. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, V.A.; Duman, R.S. Depression–emerging insights from neurobiology. Br. Med. Bull. 2001, 57, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, M.; Leonard, B.; Fernandez, A.; Kubera, M.; Nowak, G.; Veerhuis, R.; Gardner, A.; Ruckoanich, P.; Geffard, M.; Altamura, C. (Neuro) inflammation and neuroprogression as new pathways and drug targets in depression: From antioxidants to kinase inhibitors. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaváková, M.; Ďuračková, Z.; Trebatická, J. Markers of oxidative stress and neuroprogression in depression disorder. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gałecki, P.; Talarowska, M.; Anderson, G.; Berk, M.; Maes, M. Mechanisms underlying neurocognitive dysfunctions in recurrent major depression. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2015, 21, 1535. [Google Scholar]
- Leonard, B.; Maes, M. Mechanistic explanations how cell-mediated immune activation, inflammation and oxidative and nitrosative stress pathways and their sequels and concomitants play a role in the pathophysiology of unipolar depression. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012, 36, 764–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, G.; Berk, M.; Dean, O.; Moylan, S.; Maes, M. Role of immune-inflammatory and oxidative and nitrosative stress pathways in the etiology of depression: Therapeutic implications. CNS Drugs 2014, 28, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moylan, S.; Berk, M.; Dean, O.M.; Samuni, Y.; Williams, L.J.; O’Neil, A.; Hayley, A.C.; Pasco, J.A.; Anderson, G.; Jacka, F.N. Oxidative & nitrosative stress in depression: Why so much stress? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 45, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-K.; Na, K.-S.; Myint, A.-M.; Leonard, B.E. The role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in neuroinflammation, neurogenesis and the neuroendocrine system in major depression. Prog. Neuro Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 64, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, M.A.; Zunszain, P.A. Neuroimmune and neuroendocrine abnormalities in depression: Two sides of the same coin. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1351, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.T.; Lin, W.J.; Tang, M.M. Comparison of stress-induced and LPS-induced depressive-like behaviors and the alterations of central proinflammatory cytokines mRNA in rats. PsyCh J. 2015, 4, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reissmann, K.R. Studies on the mechanism of erythropoietic stimulation in parabiotic rats during hypoxia. Blood 1950, 5, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Plzak, L.; Fried, W.; Jacobson, L.; Bethard, W. Demonstration of stimulation of erythropoiesis by plasma from anemic rats using Fe59. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1955, 46, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nairz, M.; Sonnweber, T.; Schroll, A.; Theurl, I.; Weiss, G. The pleiotropic effects of erythropoietin in infection and inflammation. Microbes Infect. 2012, 14, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, M.; Broxmeyer, H. The humoral regulation of hematopoiesis. Hematol. Basic Princ. Pract. 2005, 5, 253–275. [Google Scholar]
- Buemi, M.; Cavallaro, E.; Floccari, F.; Sturiale, A.; Aloisi, C.; Trimarchi, M.; Grasso, G.; Corica, F.; Frisina, N. Erythropoietin and the brain: From neurodevelopment to neuroprotection. Clin. Sci. 2002, 103, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, R.; Wang, B.; Lu, W.; Maeda, Y. A distinct region in erythropoietin that induces immuno/inflammatory modulation and tissue protection. Neurotherapeutics 2015, 12, 850–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hand, C.C.; Brines, M. Promises and pitfalls in erythopoietin-mediated tissue protection: Are nonerythropoietic derivatives a way forward? J. Investig. Med. Off. Publ. Am. Fed. Clin. Res. 2011, 59, 1073. [Google Scholar]
- McGee, S.; Havens, A.; Shiozawa, Y.; Jung, Y.; Taichman, R. Effects of erythropoietin on the bone microenvironment. Growth Factors 2012, 30, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brines, M.; Cerami, A. Discovering erythropoietin’s extra-hematopoietic functions: Biology and clinical promise. Kidney Int. 2006, 70, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.; Schroer, S.A.; Lu, S.Y.; Wang, L.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gaisano, H.Y.; Wagner, K.-U.; Wu, H. Erythropoietin protects against diabetes through direct effects on pancreatic β cells. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 2831–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sytkowski, A.J. The neurobiology of erythropoietin. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2011, 31, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, S.; Chikuma, M.; Sasaki, R. Insulin-like growth factors and insulin stimulate erythropoietin production in primary cultured astrocytes. Brain Res. 1997, 746, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genc, S.; Kuralay, F.; Genc, K.; Akhisaroglu, M.; Fadiloglu, S.; Yorukoglu, K.; Fadiloğlu, M.; Gure, A. Erythropoietin exerts neuroprotection in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-treated C57/BL mice via increasing nitric oxide production. Neurosci. Lett. 2001, 298, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Ding, H.; Tang, Y.; Dong, Q. Erythropoietin protects against hemorrhagic blood–brain barrier disruption through the effects of aquaporin-4. Lab. Investig. 2014, 94, 1042–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brines, M.; Cerami, A. Erythropoietin and engineered innate repair activators. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 982, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Juul, S. Erythropoietin in the central nervous system, and its use to prevent hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Acta Paediatr. 2002, 91, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Z.; Kang, J.-Q.; Maiese, K. Erythropoietin: Cytoprotection in vascular and neuronal cells. Curr. Drug Targets-Cardiovasc. Hematol. Disord. 2003, 3, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genc, S.; Koroglu, T.F.; Genc, K. Erythropoietin as a novel neuroprotectant. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2003, 22, 105–119. [Google Scholar]
- Marti, H.H. Erythropoietin and the hypoxic brain. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 3233–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, S.; Okano, M.; Yamagishi, K.; Nagao, M.; Ueda, M.; Sasaki, R. A novel site of erythropoietin production. Oxygen-dependent production in cultured rat astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 19488–19493. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lappin, T.R.; Maxwell, A.P.; Johnston, P.G. EPO’s alter ego: Erythropoietin has multiple actions. Stem Cells 2002, 20, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brines, M.L.; Ghezzi, P.; Keenan, S.; Agnello, D.; De Lanerolle, N.C.; Cerami, C.; Itri, L.M.; Cerami, A. Erythropoietin crosses the blood–brain barrier to protect against experimental brain injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10526–10531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, R.K. Drug delivery systems, CNS protection, and the blood brain barrier. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssoufian, H.; Longmore, G.; Neumann, D.; Yoshimura, A.; Lodish, H. Structure, function, and activation of the erythropoietin receptor. Blood 1993, 81, 2223–2223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anagnostou, A.; Liu, Z.; Steiner, M.; Chin, K.; Lee, E.S.; Kessimian, N.; Noguchi, C.T. Erythropoietin receptor mRNA expression in human endothelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 3974–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogilvie, M.; Yu, X.; Nicolas-Metral, V.; Pulido, S.M.; Liu, C.; Ruegg, U.T.; Noguchi, C.T. Erythropoietin stimulates proliferation and interferes with differentiation of myoblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 39754–39761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhrt, D.; Wojchowski, D.M. Emerging EPO and EPO receptor regulators, and signal transducers. Blood 2015, 125, 3536–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juul, S.E.; Anderson, D.K.; Li, Y.; Christensen, R.D. Erythropoietin and erythropoietin receptor in the developing human central nervous system. Pediatr. Res. 1998, 43, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Gonias, S.L.; Campana, W.M. Schwann cells express erythropoietin receptor and represent a major target for Epo in peripheral nerve injury. Glia 2005, 51, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, C.; Martens, H.; Hassouna, I.; Oliveira, B.; Erck, C.; Zafeiriou, M.; Peteri, U.; Hesse, D.; Gerhart, S.; Altas, B. Widespread expression of erythropoietin receptor in brain and its induction by injury. Mol. Med. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, T.J.; Jenkins, B.J.; D’Andrea, R.J.; Gonda, T.J. Functional cross-talk between cytokine receptors revealed by activating mutations in the extracellular domain of the β-subunit of the GM-CSF receptor. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2002, 72, 1246–1255. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bond, W.S.; Rex, T.S. Evidence that erythropoietin modulates neuroinflammation through differential action on neurons, astrocytes, and microglia. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.-S.; Lu, K.-Y.; Yu, Y.-B.; Lee, H.-T.; Tsai, F.-C. β Common receptor mediates erythropoietin-conferred protection on OxLDL-induced lipid accumulation and inflammation in macrophages. Med. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, S.; Sinclair, A.M. The effect of erythropoietin on normal and neoplastic cells. Biol. Targets Ther. 2012, 6, 163. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Dey, S.; Alnaeeli, M.; Suresh, S.; Rogers, H.; Teng, R.; Noguchi, C.T. Erythropoietin action in stress response, tissue maintenance and metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 10296–10333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leist, M.; Ghezzi, P.; Grasso, G.; Bianchi, R.; Villa, P.; Fratelli, M.; Savino, C.; Bianchi, M.; Nielsen, J.; Gerwien, J. Derivatives of erythropoietin that are tissue protective but not erythropoietic. Science 2004, 305, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, F.; Bischoff, P. Non-erythropoietic tissue-protective peptides derived from erythropoietin: WO2009094172. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2010, 20, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brines, M.; Cerami, A. Emerging biological roles for erythropoietin in the nervous system. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brines, M.; Grasso, G.; Fiordaliso, F.; Sfacteria, A.; Ghezzi, P.; Fratelli, M.; Latini, R.; Xie, Q.-W.; Smart, J.; Su-Rick, C.-J. Erythropoietin mediates tissue protection through an erythropoietin and common β-subunit heteroreceptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14907–14912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, P.E.; Navarro, F.P.; Fares, R.P.; Nadam, J.; Georges, B.; Moulin, C.; Le Cavorsin, M.; Bonnet, C.; Ryvlin, P.; Belmeguenai, A. Erythropoietin receptor expression is concordant with erythropoietin but not with common β chain expression in the rat brain throughout the life span. J. Comp. Neurol. 2009, 514, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Um, M.; Lodish, H.F. Antiapoptotic effects of erythropoietin in differentiated neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells require activation of both the STAT5 and AKT signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 5648–5656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadam, J.; Navarro, F.; Sanchez, P.; Moulin, C.; Georges, B.; Laglaine, A.; Pequignot, J.-M.; Morales, A.; Ryvlin, P.; Bezin, L. Neuroprotective effects of erythropoietin in the rat hippocampus after pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Neurobiol. Dis. 2007, 25, 412–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradeep, S.; Huang, J.; Mora, E.M.; Nick, A.M.; Cho, M.S.; Wu, S.Y.; Noh, K.; Pecot, C.V.; Rupaimoole, R.; Stein, M.A. Erythropoietin stimulates tumor growth via EphB4. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 610–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Liu, X.; Yi, S.; Zhang, J.; Ge, J.; Liu, Z. EphB4 is overexpressed in gliomas and promotes the growth of glioma cells. Tumor Biol. 2013, 34, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Qian, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, T.; Jiang, L. Expression of ephrinB2 and EphB4 in a neonatal rat model of periventricular white matter damage. J. Perinat. Med. 2015, 43, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashton, R.S.; Conway, A.; Pangarkar, C.; Bergen, J.; Lim, K.-I.; Shah, P.; Bissell, M.; Schaffer, D.V. Astrocytes regulate adult hippocampal neurogenesis through ephrin-B signaling. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, C.T.; Wang, L.; Rogers, H.M.; Teng, R.; Jia, Y. Survival and proliferative roles of erythropoietin beyond the erythroid lineage. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2008, 10, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cataldi, A. Cell responses to oxidative stressors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, H.X.; Jones, N.M. Changes in Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 (HIF-1) and Regulatory Prolyl Hydroxylase (PHD) Enzymes Following Hypoxic–Ischemic Injury in the Neonatal Rat. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 41, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidbreder, M.; Fröhlich, F.; Jöhren, O.; Dendorfer, A.; Qadri, F.; Dominiak, P. Hypoxia rapidly activates HIF-3α mRNA expression. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 1541–1543. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaelin, W.G.; Ratcliffe, P.J. Oxygen sensing by metazoans: The central role of the HIF hydroxylase pathway. Mol. Cell 2008, 30, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzo, F.; Lavorgna, A.; Coluzzi, G.; Santucci, E.; Tarantino, F.; Rio, T.; Conti, E.; Autore, C.; Agati, L.; Andreotti, F. Erythropoietin in heart and vessels: Focus on transcription and signaling pathways. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2008, 26, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obara, N.; Imagawa, S.; Nakano, Y.; Suzuki, N.; Yamamoto, M.; Nagasawa, T. Suppression of erythropoietin gene expression by cadmium depends on inhibition of HIF-1, not stimulation of GATA-2. Arch. Toxicol. 2003, 77, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Obara, N.; Suzuki, N.; Kim, K.; Nagasawa, T.; Imagawa, S.; Yamamoto, M. Repression via the GATA box is essential for tissue-specific erythropoietin gene expression. Blood 2008, 111, 5223–5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Jiang, J.; Fan, Y.; Fu, G.; Wang, J.; Fan, W. Knockout of the tumor necrosis factor α receptor 1 gene can up-regulate erythropoietin receptor during myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Chin. Med. J. 2009, 122, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Erbaş, O.; Çınar, B.P.; Solmaz, V.; Çavuşoğlu, T.; Ateş, U. The neuroprotective effect of erythropoietin on experimental Parkinson model in rats. Neuropeptides 2015, 49, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, A.; Nakagawa, E.; Choi, H.B.; Hatori, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Kim, S.U. Erythropoietin and erythropoietin receptors in human CNS neurons, astrocytes, microglia, and oligodendrocytes grown in culture. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2001, 60, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.; Son, H. Effects of serotonin on erythropoietin expression in mouse hippocampus. Exp. Neurobiol. 2013, 22, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Gomez, A.; Belenguer-Benavides, A.; Martinez-Bronchal, B.; Fittipaldi-Marquez, M.; Forn, C. Structural and functional changes of the hippocampus in patients with multiple sclerosis and their relationship with memory processes. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 62, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, J.; Prust, M.; Kaiser, J. Chemotherapy, cognitive impairment and hippocampal toxicity. Neuroscience 2015, 309, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantinescu, S.N.; Ghaffari, S.; Lodish, H.F. The erythropoietin receptor: Structure, activation and intracellular signal transduction. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 10, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digicaylioglu, M.; Lipton, S.A. Erythropoietin-mediated neuroprotection involves cross-talk between Jak2 and NF-κB signaling cascades. Nature 2001, 412, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, C.T.; Asavaritikrai, P.; Teng, R.; Jia, Y. Role of erythropoietin in the brain. Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol. 2007, 64, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, P.; Melendez-Rodríguez, F.; Matchett, K.B.; Aragones, J.; Ben-Califa, N.; Jaekel, H.; Hengst, L.; Lindner, H.; Bernardini, A.; Brockmeier, U. Novel antibodies directed against the human erythropoietin receptor: Creating a basis for clinical implementation. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 168, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter-Su, C.; Schwartz, J.; Argetsinger, L.S. Growth Hormone Signaling Pathways. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2015, 28, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Zhang, G.; Li, R.; Duan, C. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt Pathway Mediates Fip1-like1-platelet-derived Growth Factor Receptor α-induced Cell Infiltration and Activation: Possible Molecular Mechanism for the Malignant Phenotype of Chronic Eosinophilic Leukemia. Cancer Transl. Med. 2015, 1, 31. [Google Scholar]
- van der Kooij, M.A.; Groenendaal, F.; Kavelaars, A.; Heijnen, C.J.; van Bel, F. Neuroprotective properties and mechanisms of erythropoietin in in vitro and in vivo experimental models for hypoxia/ischemia. Brain Res. Rev. 2008, 59, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, M.-S.; Kim, M.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Park, K.-D.; Yoo, S.-H.; Oh, I.-U.; Pak, S.; Seo, Y.-J. Erythropoietin exerts cell protective effect by activating PI3K/Akt and MAPK pathways in C6 Cells. Neurol. Res. 2014, 36, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serizawa, K.; Yogo, K.; Tashiro, Y.; Aizawa, K.; Kawasaki, R.; Hirata, M.; Endo, K. Epoetin beta pegol prevents endothelial dysfunction as evaluated by flow-mediated dilation in chronic kidney disease rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 767, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alliouachene, S.; Bilanges, B.; Chicanne, G.; Anderson, K.E.; Pearce, W.; Ali, K.; Valet, C.; Posor, Y.; Low, P.C.; Chaussade, C. Inactivation of the class II PI3K-C2β potentiates insulin signaling and sensitivity. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 1881–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouvard, C.; Galy-Fauroux, I.; Grelac, F.; Carpentier, W.; Lokajczyk, A.; Gandrille, S.; Colliec-Jouault, S.; Fischer, A.-M.; Helley, D. Low-Molecular-Weight Fucoidan Induces Endothelial Cell Migration via the PI3K/AKT Pathway and Modulates the Transcription of Genes Involved in Angiogenesis. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 7446–7462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellweg, C.E. The nuclear factor κB pathway: A link to the immune system in the radiation response. Cancer Lett. 2015, 368, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzillotta, A.; Porrini, V.; Bellucci, A.; Benarese, M.; Branca, C.; Parrella, E.; Spano, P.F.; Pizzi, M. NF-κB in innate neuroprotection and age-related neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Neurol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Correia, C.; Lee, S.-H.; Meng, X.W.; Vincelette, N.D.; Knorr, K.L.; Ding, H.; Nowakowski, G.S.; Dai, H.; Kaufmann, S.H. Emerging understanding of Bcl-2 biology: Implications for neoplastic progression and treatment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2015, 1853, 1658–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, C.; Willebrand, R.; Huber, S.; Rupec, R.A.; Wu, D.; Locksley, R.; Voehringer, D. Eosinophil-specific deletion of IκBα in mice reveals a critical role of NF-κ-induced Bcl-xL for inhibition of apoptosis. Blood 2015, 125, 3896–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, P.; Bigini, P.; Mennini, T.; Agnello, D.; Laragione, T.; Cagnotto, A.; Viviani, B.; Marinovich, M.; Cerami, A.; Coleman, T.R. Erythropoietin selectively attenuates cytokine production and inflammation in cerebral ischemia by targeting neuronal apoptosis. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 971–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcasoy, M.O.; Jiang, X.; Haroon, Z.A. Expression of erythropoietin receptor splice variants in human cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 307, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broxmeyer, H.E. Erythropoietin: Multiple targets, actions, and modifying influences for biological and clinical consideration. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haq, R.; Halupa, A.; Beattie, B.K.; Mason, J.M.; Zanke, B.W.; Barber, D.L. Regulation of erythropoietin-induced STAT serine phosphorylation by distinct mitogen-activated protein kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 17359–17366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Yan, D.; Mohi, G. Differential biological activity of disease-associated JAK2 mutants. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koulnis, M.; Porpiglia, E.; Hidalgo, D.; Socolovsky, M. Erythropoiesis: From Molecular Pathways to System Properties. In A Systems Biology Approach to Blood; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 37–58. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Cao, R.-J.; Zhu, X.-J.; Liu, X.-Y.; Li, L.-Y.; Cui, S.-S. Erythropoietin Attenuates the Apoptosis of Adult Neurons After Brachial Plexus Root Avulsion by Downregulating JNK Phosphorylation and c-Jun Expression and Inhibiting c-PARP Cleavage. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 56, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, W.; Zhang, J.; Lodish, H.F. Lnk inhibits erythropoiesis and Epo-dependent JAK2 activation and downstream signaling pathways. Blood 2005, 105, 4604–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.; Zhuo, L.; Gao, C.; Shi, S.; Wang, N.; Huang, Z.; Li, W.; Hao, L. Erythropoietin protects against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. J. Nephrol. 2013, 26, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imagawa, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Miura, Y. Negative regulation of the erythropoietin gene expression by the GATA transcription factors. Blood 1997, 89, 1430–1439. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wojchowski, D.M.; Gregory, R.C.; Miller, C.P.; Pandit, A.K.; Pircher, T.J. Signal transduction in the erythropoietin receptor system. Exp. Cell Res. 1999, 253, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, A.Q.; Cherry, B.H.; Scott, G.F.; Ryou, M.-G.; Mallet, R.T. Erythropoietin: Powerful protection of ischemic and post-ischemic brain. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014, 239, 1461–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, S.E.; Murray, P.J. Regulation of Macrophage Polarization by the STAT–SOCS Signaling Axis. In Macrophages: Biology and Role in the Pathology of Diseases; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 497–508. [Google Scholar]
- Rawlings, J.S.; Rosler, K.M.; Harrison, D.A. The JAK/STAT signaling pathway. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 1281–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihle, J.N. The Stat family in cytokine signaling. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2001, 13, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miljus, N.; Heibeck, S.; Jarrar, M.; Micke, M.; Ostrowski, D.; Ehrenreich, H.; Heinrich, R. Erythropoietin-mediated protection of insect brain neurons involves JAK and STAT but not PI3K transduction pathways. Neuroscience 2014, 258, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.; Grillot, D.; Benito, A.; Richard, C.; Nunez, G.; Fernandez-Luna, J.L. Erythropoietin can promote erythroid progenitor survival by repressing apoptosis through Bcl-XL and Bcl-2. Blood 1996, 88, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Han, B.H.; Li, Y.; Keogh, C.L.; Holtzman, D.M.; Yu, S.P. Cell death mechanism and protective effect of erythropoietin after focal ischemia in the whisker-barrel cortex of neonatal rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 317, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crampton, S.J.; O’keeffe, G.W. NF-κB: Emerging roles in hippocampal development and function. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 1821–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.M.; Nga, N.T.H.; Park, M.H.; Kim, K.S.; Cho, K.J.; Moon, D.C.; Kim, H.Y.; Hong, J.T. EPO receptor-mediated ERK kinase and NF-κB activation in erythropoietin-promoted differentiation of astrocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 320, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, H.; Davies, A.M. Regulation of neural process growth, elaboration and structural plasticity by NF-κB. Trends Neurosci. 2011, 34, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Wu, H.; Chi, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; Li, H. Electroacupuncture inhibits apoptosis of splenic lymphocytes in traumatized rats through modulation of the TNF-α/NF-κB signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coelho-Santos, V.; Leitão, R.A.; Cardoso, F.L.; Palmela, I.; Rito, M.; Barbosa, M.; Brito, M.A.; Fontes-Ribeiro, C.A.; Silva, A.P. The TNF-α/NF-κB signaling pathway has a key role in methamphetamine-induced blood-brain barrier dysfunction. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 35, 1260–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anisman, H.; Merali, Z.; Hayley, S. Neurotransmitter, peptide and cytokine processes in relation to depressive disorder: Comorbidity between depression and neurodegenerative disorders. Prog. Neurobiol. 2008, 85, 1–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padgett, D.A.; Glaser, R. How stress influences the immune response. Trends Immunol. 2003, 24, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.W.; Russo, S.J.; Ferguson, D.; Nestler, E.J.; Duman, R.S. Nuclear factor-κB is a critical mediator of stress-impaired neurogenesis and depressive behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2669–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Chopp, M. Treatment of stroke with erythropoietin enhances neurogenesis and angiogenesis and improves neurological function in rats. Stroke 2004, 35, 1732–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shingo, T.; Sorokan, S.T.; Shimazaki, T.; Weiss, S. Erythropoietin regulates the in vitro and in vivo production of neuronal progenitors by mammalian forebrain neural stem cells. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 9733–9743. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, H.; Johnston, M.V.; Lange, M.S.; Wilson, M.A. Protective effect of erythropoietin in neonatal hypoxic ischemia in mice. Neuroreport 2003, 14, 1757–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chateauvieux, S.; Grigorakaki, C.; Morceau, F.; Dicato, M.; Diederich, M. Erythropoietin, erythropoiesis and beyond. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 1291–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zou, Y.R.; Zhong, X.; Deng, H.D.F.; Pu, L.; Peng, K.; Wang, L. Erythropoietin pretreatment ameliorates renal ischaemia-reperfusion injury by activating PI3K/Akt signaling. Nephrology 2015, 20, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trincavelli, M.L.; da Pozzo, E.; Ciampi, O.; Cuboni, S.; Daniele, S.; Abbracchio, M.P.; Martini, C. Regulation of erythropoietin receptor activity in endothelial cells by different erythropoietin (EPO) derivatives: An in vitro study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 2258–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, T.; Miura, T.; Yano, T.; Takahashi, A.; Sakamoto, J.; Tanno, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Ikeda, Y.; Nishihara, M.; Naitoh, K. Alteration in erythropoietin-induced cardioprotective signaling by postinfarct ventricular remodeling. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 317, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Mo, S.-J.; Feng, Q.-Q.; Zhan, M.-L.; OuYang, L.-S.; Chen, J.-C.; Ma, Y.-X.; Wu, J.-J.; Lei, W.-L. EPO-dependent activation of PI3K/Akt/FoxO3a signaling mediates neuroprotection in in vitro and in vivo models of Parkinson’s disease. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2014, 53, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fingar, D.C.; Salama, S.; Tsou, C.; Harlow, E.; Blenis, J. Mammalian cell size is controlled by mTOR and its downstream targets S6K1 and 4EBP1/eIF4E. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 1472–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fingar, D.C.; Blenis, J. Target of rapamycin (TOR): An integrator of nutrient and growth factor signals and coordinator of cell growth and cell cycle progression. Oncogene 2004, 23, 3151–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Shankar, S.; Srivastava, R.K. Rottlerin induces autophagy and apoptosis in prostate cancer stem cells via PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 2014, 343, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ransome, M.I.; Turnley, A.M. Erythropoietin promotes axonal growth in a model of neuronal polarization. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2008, 38, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Yuan, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Ning, G.; Zhang, L.; Yao, L.; Feng, S. The role of the JAK-STAT pathway in neural stem cells, neural progenitor cells and reactive astrocytes after spinal cord injury (Review). Biomed. Rep. 2015, 3, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chong, Z.Z.; Kang, J.-Q.; Maiese, K. Apaf-1, Bcl-xL, cytochrome c, and caspase-9 form the critical elements for cerebral vascular protection by erythropoietin. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2003, 23, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, Z.Z.; Lin, S.H.; Kang, J.Q.; Maiese, K. Erythropoietin prevents early and late neuronal demise through modulation of Akt1 and induction of caspase 1, 3, and 8. J. Neurosci. Res. 2003, 71, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, Z.Z.; Kang, J.Q.; Maiese, K. Erythropoietin fosters both intrinsic and extrinsic neuronal protection through modulation of microglia, Akt1, Bad, and caspase-mediated pathways. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 138, 1107–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirén, A.-L.; Faßhauer, T.; Bartels, C.; Ehrenreich, H. Therapeutic potential of erythropoietin and its structural or functional variants in the nervous system. Neurotherapeutics 2009, 6, 108–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.S.; Yap, W.N.; Arfuso, F.; Kar, S.; Wang, C.; Cai, W.; Dharmarajan, A.M.; Sethi, G.; Kumar, A.P. Targeting the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in gastric carcinoma: A reality for personalized medicine? World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 12261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vairano, M.; Russo, C.D.; Pozzoli, G.; Battaglia, A.; Scambia, G.; Tringali, G.; Aloe-Spiriti, M.A.; Preziosi, P.; Navarra, P. Erythropoietin exerts anti-apoptotic effects on rat microglial cells in vitro. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 16, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urao, N.; Okigaki, M.; Yamada, H.; Aadachi, Y.; Matsuno, K.; Matsui, A.; Matsunaga, S.; Tateishi, K.; Nomura, T.; Takahashi, T. Erythropoietin-mobilized endothelial progenitors enhance reendothelialization via Akt-endothelial nitric oxide synthase activation and prevent neointimal hyperplasia. Circ. Res. 2006, 98, 1405–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, Y.G.; Chan, A.K.; Ibrahim, R.; Tang, Y.; Burow, M.E.; Alam, J.; Scandurro, A.B.; Beckman, B.S. NF-κB plays a key role in hypoxia-inducible factor-1-regulated erythropoietin gene expression. Exp. Hematol. 2002, 30, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, T.; Kataoka, T.R.; Ueshima, C.; Miyachi, Y.; Kabashima, K. A Case of Noonan Syndrome with Multiple Subcutaneous Tumours with MAPK-ERK/p38 Activation. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2016, 96, 130–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, C.; Xu, M.; Gan, J.; Yang, X.; Wu, N.; Song, L.; Yuan, W.; Liu, Z. Erythropoietin improves neurobehavior by reducing dopaminergic neuron loss in a 6-hydroxydopamine-induced rat model. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 34, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- New, L.; Li, Y.; Ge, B.; Zhong, H.; Mansbridge, J.; Liu, K.; Han, J. SB203580 promote EGF-stimulated early morphological differentiation in PC12 cell through activating ERK pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2001, 83, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strack, S. Overexpression of the protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunit Bγ promotes neuronal differentiation by activating the MAP kinase (MAPK) cascade. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 41525–41532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.J.; Stippec, S.A.; Goldsmith, E.; White, M.A.; Cobb, M.H. A constitutively active and nuclear form of the MAP kinase ERK2 is sufficient for neurite outgrowth and cell transformation. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, K.; Futter, M.; Voss, K.; Erent, M.; Skehel, P.A.; French, P.; Obosi, L.; Jones, M.W.; Bliss, T.V. The role of extracellular regulated kinases I/II in late-phase long-term potentiation. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 5432–5441. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, K.M.; Park, K.S.; Oh, J.H.; Jung, S.Y.; Yang, K.H.; Song, Y.S.; Son, D.J.; Park, Y.H.; Yun, Y.P.; Lee, M.K. Activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and activator protein-1 during the promotion of neurite extension of PC-12 cells by 15-deoxy-Δ12, 14-prostaglandin J2. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 63, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.S.; Da Lee, R.; Kang, S.-K.; Han, S.Y.; Park, K.L.; Yang, K.H.; Song, Y.S.; Park, H.J.; Lee, Y.M.; Yun, Y.P. Neuronal differentiation of embryonic midbrain cells by upregulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ via the JNK-dependent pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 297, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugawa, M.; Sakurai, Y.; Ishikawa-Ieda, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Asou, H. Effects of erythropoietin on glial cell development; oligodendrocyte maturation and astrocyte proliferation. Neurosci. Res. 2002, 44, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miskowiak, K.W.; Vinberg, M.; Harmer, C.J.; Ehrenreich, H.; Kessing, L.V. Erythropoietin: A candidate treatment for mood symptoms and memory dysfunction in depression. Psychopharmacology 2012, 219, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miu, A.C.; Olteanu, A.I.; Chiş, I.; Heilman, R.M. Have no fear, erythropoietin is here: Erythropoietin protects fear conditioning performances after functional inactivation of the amygdala. Behav. Brain Res. 2004, 155, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duman, C.H.; Newton, S.S. Evaluating effects of EPO in rodent behavioral assays related to depression. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leconte, C.; Bihel, E.; Lepelletier, F.-X.; Bouët, V.; Saulnier, R.; Petit, E.; Boulouard, M.; Bernaudin, M.; Schumann-Bard, P. Comparison of the effects of erythropoietin and its carbamylated derivative on behavior and hippocampal neurogenesis in mice. Neuropharmacology 2011, 60, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girgenti, M.J.; Hunsberger, J.; Duman, C.H.; Sathyanesan, M.; Terwilliger, R.; Newton, S.S. Erythropoietin induction by electroconvulsive seizure, gene regulation, and antidepressant-like behavioral effects. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 66, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viviani, B.; Bartesaghi, S.; Corsini, E.; Villa, P.; Ghezzi, P.; Garau, A.; Galli, C.L.; Marinovich, M. Erythropoietin protects primary hippocampal neurons increasing the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. J. Neurochem. 2005, 93, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelkmann, W. Erythropoietin: Structure, control of production, and function. Physiol Rev. 1992, 72, 449–489. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kramer, L.; Madl, C.; Stockenhuber, F.; Yeganehfar, W.; Eisenhuber, E.; Derfler, K.; Lenz, K.; Schneider, B.; Grimm, G. Beneficial effect of renal transplantation on cognitive brain function. Kidney Int. 1996, 49, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickett, J.L.; Theberge, D.C.; Brown, W.S.; Schweitzer, S.U.; Nissenson, A.R. Normalizing hematocrit in dialysis patients improves brain function. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1999, 33, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miskowiak, K.; O’sullivan, U.; Harmer, C.J. Erythropoietin reduces neural and cognitive processing of fear in human models of antidepressant drug action. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 62, 1244–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miskowiak, K.; Inkster, B.; Selvaraj, S.; Wise, R.; Goodwin, G.M.; Harmer, C.J. Erythropoietin improves mood and modulates the cognitive and neural processing of emotion 3 days post administration. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miskowiak, K.W.; Favaron, E.; Hafizi, S.; Inkster, B.; Goodwin, G.M.; Cowen, P.J.; Harmer, C.J. Effects of erythropoietin on emotional processing biases in patients with major depression: An exploratory fMRI study. Psychopharmacology 2009, 207, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerit, H.; Veer, I.M.; Dahan, A.; Niesters, M.; Harmer, C.J.; Miskowiak, K.W.; Rombouts, S.A.; van der Does, W. Testing the antidepressant properties of the peptide ARA290 in a human neuropsychological model of drug action. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 25, 2289–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miskowiak, K.W.; Favaron, E.; Hafizi, S.; Inkster, B.; Goodwin, G.M.; Cowen, P.J.; Harmer, C.J. Erythropoietin modulates neural and cognitive processing of emotional information in biomarker models of antidepressant drug action in depressed patients. Psychopharmacology 2010, 210, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falkai, P.; Schmitt, A. Erythropoietin as an innovative add-on therapy for depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 78, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miskowiak, K.W.; Vinberg, M.; Macoveanu, J.; Ehrenreich, H.; Køster, N.; Inkster, B.; Paulson, O.B.; Kessing, L.V.; Skimminge, A.; Siebner, H.R. Effects of erythropoietin on hippocampal volume and memory in mood disorders. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 78, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miskowiak, K.W.; Vinberg, M.; Harmer, C.J.; Ehrenreich, H.; Knudsen, G.M.; Macoveanu, J.; Hansen, A.R.; Paulson, O.B.; Siebner, H.R.; Kessing, L.V. Effects of erythropoietin on depressive symptoms and neurocognitive deficits in depression and bipolar disorder. Trials 2010, 11, 97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miskowiak, K.W.; Vinberg, M.; Christensen, E.M.; Bukh, J.D.; Harmer, C.J.; Ehrenreich, H.; Kessing, L.V. Recombinant human erythropoietin for treating treatment-resistant depression: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Neuropsychopharmacology 2014, 39, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinberg, M.; Miskowiak, K.; Hoejman, P.; Pedersen, M.; Kessing, L.V. The effect of recombinant erythropoietin on plasma brain derived neurotrophic factor levels in patients with affective disorders: A randomised controlled study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ongür, D.; Drevets, W.C.; Price, J.L. Glial reduction in the subgenual prefrontal cortex in mood disorders. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13290–13295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajkowska, G.; Miguel-Hidalgo, J.J.; Wei, J.; Dilley, G.; Pittman, S.D.; Meltzer, H.Y.; Overholser, J.C.; Roth, B.L.; Stockmeier, C.A. Morphometric evidence for neuronal and glial prefrontal cell pathology in major depression. Biol. Psychiatry 1999, 45, 1085–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M.; Meltzer, H.Y.; Bosmans, E.; Bergmans, R.; Vandoolaeghe, E.; Ranjan, R.; Desnyder, R. Increased plasma concentrations of interleukin-6, soluble interleukin-6, soluble interleukin-2 and transferrin receptor in major depression. J. Affect. Disord. 1995, 34, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M. Depression is an inflammatory disease, but cell-mediated immune activation is the key component of depression. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, M.; Galecki, P.; Chang, Y.S.; Berk, M. A review on the oxidative and nitrosative stress (O&NS) pathways in major depression and their possible contribution to the (neuro) degenerative processes in that illness. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 676–692. [Google Scholar]
- Duman, R.S.; Monteggia, L.M. A neurotrophic model for stress-related mood disorders. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 59, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.H.; Maletic, V.; Raison, C.L. Inflammation and its discontents: The role of cytokines in the pathophysiology of major depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berton, O.; Nestler, E.J. New approaches to antidepressant drug discovery: Beyond monoamines. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markoulaki, D.; Kostikas, K.; Papatheodorou, G.; Koutsokera, A.; Alchanatis, M.; Bakakos, P.; Gourgoulianis, K.I.; Roussos, C.; Koulouris, N.G.; Loukides, S. Hemoglobin, erythropoietin and systemic inflammation in exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2011, 22, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Mahmood, A.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, Z.G.; Qu, C.; Sager, T.N.; Chopp, M. Effects of posttraumatic carbamylated erythropoietin therapy on reducing lesion volume and hippocampal cell loss, enhancing angiogenesis and neurogenesis, and improving functional outcome in rats following traumatic brain injury. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 114, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowlati, Y.; Herrmann, N.; Swardfager, W.; Liu, H.; Sham, L.; Reim, E.K.; Lanctôt, K.L. A meta-analysis of cytokines in major depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furtado, M.; Katzman, M.A. Neuroinflammatory pathways in anxiety, posttraumatic stress, and obsessive compulsive disorders. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 229, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, F.; Liu, Y.-F.; Gao, F.; Jiang, W. Acetylsalicylic acid as an augmentation agent in fluoxetine treatment resistant depressive rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 499, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, R.; Zhu, D.; Bi, Y.; Yang, D.; Wang, Y. Erythropoietin inhibits gluconeogenesis and inflammation in the liver and improves glucose intolerance in high-fat diet-fed mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, R.; Maeda, Y.; Li, W.; Lu, W.; Cook, S.; Dowling, P. Erythropoietin: A potent inducer of peripheral immuno/inflammatory modulation in autoimmune EAE. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alnaeeli, M.; Noguchi, C.T. Erythropoietin and obesity-induced white adipose tissue inflammation: Redefining the boundaries of the immunometabolism territory. Adipocyte 2015, 4, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Calvert, J.W.; Zhang, J.H. Neonatal hypoxia/ischemia is associated with decreased inflammatory mediators after erythropoietin administration. Stroke 2005, 36, 1672–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Mahmood, A.; Qu, C.; Kazmi, H.; Zhang, Z.G.; Noguchi, C.T.; Schallert, T.; Chopp, M. Erythropoietin improves histological and functional outcomes after traumatic brain injury in mice in the absence of the neural erythropoietin receptor. J. Neurotrauma 2010, 27, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nairz, M.; Schroll, A.; Moschen, A.R.; Sonnweber, T.; Theurl, M.; Theurl, I.; Taub, N.; Jamnig, C.; Neurauter, D.; Huber, L.A. Erythropoietin contrastingly affects bacterial infection and experimental colitis by inhibiting nuclear factor-κB-inducible immune pathways. Immunity 2011, 34, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, T.; Bauer, I.E.; Meyer, T.D.; Kapczinski, F.; Soares, J.C. Neuroprogression and cognitive functioning in bipolar disorder: A systematic review. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2015, 17, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, S.; Marriott, M.; Nahmias, C.; MacQueen, G.M. Lower hippocampal volume in patients suffering from depression: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Psychiatry 2004, 161, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcewen, B.S. Allostasis and allostatic load: Implications for neuropsychopharmacology. Neuropsychopharmacology 2000, 22, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dranovsky, A.; Hen, R. Hippocampal neurogenesis: Regulation by stress and antidepressants. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 59, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborn, M.; Rustom, N.; Clarke, M.; Litteljohn, D.; Rudyk, C.; Anisman, H.; Hayley, S. Antidepressant-like effects of erythropoietin: A focus on behavioral and hippocampal processes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrenreich, H.; Aust, C.; Krampe, H.; Jahn, H.; Jacob, S.; Herrmann, M.; Sirén, A.-L. Erythropoietin: Novel approaches to neuroprotection in human brain disease. Metab. Brain Dis. 2004, 19, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuyama, T.; Tanaka, T.; Tatsumi, K.; Daijo, H.; Kai, S.; Harada, H.; Fukuda, K. Midazolam inhibits the hypoxia-induced up-regulation of erythropoietin in the central nervous system. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 761, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Chen, W.; Sinha, B.; Tu, Y.; Manning, S.; Thomas, N.; Zhou, S.; Jiang, H.; Ma, H.; Kroessler, D.A. Neuroprotective agents for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 1372–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.W.; Gonzalez, F.F. Erythropoietin: A novel therapy for hypoxic–ischaemic encephalopathy? Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2015, 57, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnello, D.; Bigini, P.; Villa, P.; Mennini, T.; Cerami, A.; Brines, M.L.; Ghezzi, P. Erythropoietin exerts an anti-inflammatory effect on the CNS in a model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Brain Res. 2002, 952, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sättler, M.; Merkler, D.; Maier, K.; Stadelmann, C.; Ehrenreich, H.; Bähr, M.; Diem, R. Neuroprotective effects and intracellular signaling pathways of erythropoietin in a rat model of multiple sclerosis. Cell Death Differ. 2004, 11, S181–S192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Maeda, Y.; Yuan, R.R.; Elkabes, S.; Cook, S.; Dowling, P. Beneficial effect of erythropoietin on experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 56, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berk, M.; Kapczinski, F.; Andreazza, A.; Dean, O.; Giorlando, F.; Maes, M.; Yücel, M.; Gama, C.; Dodd, S.; Dean, B. Pathways underlying neuroprogression in bipolar disorder: Focus on inflammation, oxidative stress and neurotrophic factors. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2011, 35, 804–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Liu, X.-L.; Li, J.; Mu, R.-H.; Liu, Q.; Yi, L.-T.; Geng, D. Macranthol promotes hippocampal neuronal proliferation in mice via BDNF–TrkB–PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 762, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.-Y.; Cao, Y.-G.; Ji, Z.; Zhou, H.-H.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Sun, H.-L. Topiramate protects against glutamate excitotoxicity via activating BDNF/TrkB-dependent ERK pathway in rodent hippocampal neurons. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 60, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criscuolo, C.; Fabiani, C.; Bonadonna, C.; Origlia, N.; Domenici, L. BDNF prevents amyloid-dependent impairment of LTP in the entorhinal cortex by attenuating p38 MAPK phosphorylation. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.M.; Zhang, G.; Bastian, B.C.; Arcasoy, M.O.; Karande, P.; Pushparajan, A.; Acs, G.; Xu, X. Erythropoietin receptor contributes to melanoma cell survival in vivo. Oncogene 2012, 31, 1649–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Li, H.-G.; Xia, Z.-S.; Wen, J.-M.; Lv, J. Prognostic significance of erythropoietin and erythropoietin receptor in gastric adenocarcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 3933–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rózsás, A.; Berta, J.; Rojkó, L.; Horváth, L.Z.; Keszthelyi, M.; Kenessey, I.; László, V.; Berger, W.; Grusch, M.; Hoda, M.A. Erythropoietin receptor expression is a potential prognostic factor in human lung adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77459. [Google Scholar]
- Fuge, F.; Doleschel, D.; Rix, A.; Gremse, F.; Wessner, A.; Winz, O.; Mottaghy, F.; Lederle, W.; Kiessling, F. In-vivo detection of the erythropoietin receptor in tumours using positron emission tomography. Eur. Radiol. 2015, 25, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author | EPO Form | Subject | Drug Administration | Randomized | Double-Blind | Main Finding | Limitations | Safety |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kamilla W. Miskowiak et al. (2008) [161] | Erythropoietin (40,000 International Unit, IU) | healthy volunteers (N = 24) | injection once | Y | Y | During faces processing EPO enhanced activation in the left amygdala and right precuneus to happy and fearful expressions. This was paired with improved recognition of all facial expressions, in particular of low intensity happiness and fear. This is similar to behavioral effects observed with acute administration of serotonergic antidepressants. | 1, pharmacological fMRI studies in general is the possibility that drug effects on neural response may be confounded by non-specific effects on neural coupling and cerebral hemodynamics. 2, more detailed examination of the mood and arousal changes seen following EPO and their relation to changes in emotional processing observed three days post-administration should be performed. 3, the clinical effect in patients suffering from depression is unknown. | Blood pressure and subjective state were monitored for 2 h following the injection. |
| Hilâl Cerit et al. (2008) [163] | ARA290 (2 mg) | healthy volunteers (N = 36) | injection, once | Y | Y | ARA290-treated individuals displayed lower neural responses to happy faces in the fusiform gyrus. ARA290 tended to lower the recognition of happy and disgust facial expressions. Although ARA290 was not associated with a better memory for positive words, it was associated with faster categorization of positive vs. negative words. Finally, ARA290 increased attention towards positive emotional pictures. No effects were observed on mood and affective symptoms. | 1, the limited clinical potential of EPO to treat depressive symptoms in non-anemic patients, due to the hematopoietic actions of EPO with repeated administration. 2, the human proof-of-concept studies were conducted in relatively small samples. | After administration, the participant was monitored for 10 min. Dose selection was based on previous studies in humans in which no safety concerns were reported. |
| Kamilla W. Miskowiak et al. (2009) [162] | Erythropoietin (40,000 IU) | depressed patients (N = 17) | injection once | Y | Y | EPO reduced neural response to negative vs. positive pictures three days post-administration in a network of areas including the hippocampus, ventromedial prefrontal and parietal cortex. After the scan, EPO-treated patients showed improved memory compared with those that were given placebo. The effects occurred in the absence of changes in mood or hematological parameters, suggesting that they originated from direct neurobiological actions of EPO. | 1, an exploratory study in a small patient sample. 2, The majority of patientswere also taking antidepressant medication | Blood pressure, well-being and subjective state was monitored for 2 h following the injection. |
| Kamilla W. Miskowiak et al. (2010) [164] | Erythropoietin(40,000 IU) | depressed patients (N = 19) | injection once | Y | Y | EPO reduced neural response to fearful vs. happy faces in the amygdala and hippocampus, and to fearful faces vs. baseline in superior temporal and occipitoparietal regions three days after administration in acutely depressed patients. This was accompanied by a specific reduction in the recognition of fear in EPO-treated patients after the scan similar to the effects on face recognition seen with antidepressant drug treatment. | 1, an exploratory study in a small patient sample. 2, the majority of patients were taking antidepressant medication. 3, the current study used a between-groups design, and it is unknown whether baseline differences existed between the two groups. 4, the application of EPO in the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorder may have some undesirable effects. | Following EPO/saline administration, blood pressure, well-being, and subjective state were monitored for 2 h. |
| Kamilla W. Miskowiak et al. (2014) [168] | Erythropoietin(40,000 IU) | depressed patients (N = 40) | injection weekly (8 weeks) | Y | Y | HDRS-17, GAF, and remission rates showed no effects of EPO over saline at week 9. However, EPO improved BDI and WHOQOL-BREF, and this was maintained at follow-up week 14. EPO enhanced verbal recall and recognition, which was sustained at follow-up. Exploratory analysis in patients fulfilling depression severity criteria at trial start revealed ameliorated HDRS-17 in EPO vs. saline groups, which was sustained at week 14. Exploratory analysis in the complete cohort showed that EPO reduced depression composite at weeks 9 and 14. | 1, the extensive exclusion criteria may limit the ability to generalize our findings to clinical practice. 2, the EPO-associated increase in red blood cell levels could confound the interpretation of the effects of EPO as neural in origin. 3, they did not screen for or exclude co-morbid axis II disorder as this would have resulted in a subsample of patients who were not representative for the target population of treatment-resistant patients. 4, their study may not have been adequately powered to detect a significant effect on primary outcome measure, although a positive signal was apparent on the additional depression-relevant outcomes and explorative score of depressive syndrome severity. 5, patients had been treated for years without any improvement, and that a treatment period of eight weeks is very short in such chronic, recurrent condition. | Weekly monitoring of blood tests and any side effects was performed by a physician not involved in outcome measure assessments. |
| Kamilla W. Miskowiak et al. (2015) [166] | Erythropoietin(40,000 IU) | BD/TRD patients (N = 69 ) | injection weekly (8 weeks) | Y | Y | Compared with saline, EPO was associated with mood-independent memory improvement and reversal of brain matter loss in the left hippocampalcornu ammonis 1 to cornu ammonis 3 and subiculum. Using the entire sample, memory improvement was associated with subfield hippocampal volume increase independent of mood change. | 1, their cohort included both patients with TRD and BD, since these mood disorders may involve differential, although partially overlapping, pathogenic processes. 2, three complementary methods to capture different aspects of hippocampal volume changes have their own limitations, and reflect different structural measures. | Blood tests were taken on a weekly basis from baseline to week 10 (two weeks after treatment completion) and again in week 14. |
| Maj Vinberg et al. (2015) [169] | Erythropoietin(40,000 IU) | BD/TRD patients (N = 83 ) | injection weekly (8 weeks) | Y | Y | EPO down-regulated plasma BDNF levels in patients with TRD (mean reduction at week 9 (95% CI): EPO 10.94 ng/L (4.51–21.41 ng/L); mean increase at week 9: Saline 0.52 ng/L, p = 0.04 (−5.88–4.48 ng/L) p = 0.04, partial η2 = 0.12). No significant effects were found on BDNF levels in partially remitted patients with BD (p = 0.35). | 1, they did not register daily physical exercise level, and since EPO is well known for its potential doping capacity, the change in BDNF levels could be due to increased exercise levels in the intervention group. 2, the relatively few participants is a limitation. 3, patients received weekly intravenous infusions of either EPO or saline for eight weeks (weeks 1–8) in addition to their current antidepressant medication. | Blood tests were taken on a weekly basis from baseline to week 10. |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, C.; Cheng, F.; Wang, X.; Zhai, C.; Yue, W.; Lian, Y.; Wang, Q. Erythropoietin Pathway: A Potential Target for the Treatment of Depression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050677
Ma C, Cheng F, Wang X, Zhai C, Yue W, Lian Y, Wang Q. Erythropoietin Pathway: A Potential Target for the Treatment of Depression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(5):677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050677
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Chongyang, Fafeng Cheng, Xueqian Wang, Changming Zhai, Wenchao Yue, Yajun Lian, and Qingguo Wang. 2016. "Erythropoietin Pathway: A Potential Target for the Treatment of Depression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 5: 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050677
APA StyleMa, C., Cheng, F., Wang, X., Zhai, C., Yue, W., Lian, Y., & Wang, Q. (2016). Erythropoietin Pathway: A Potential Target for the Treatment of Depression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(5), 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050677






