Protective Effect of Tempol against Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
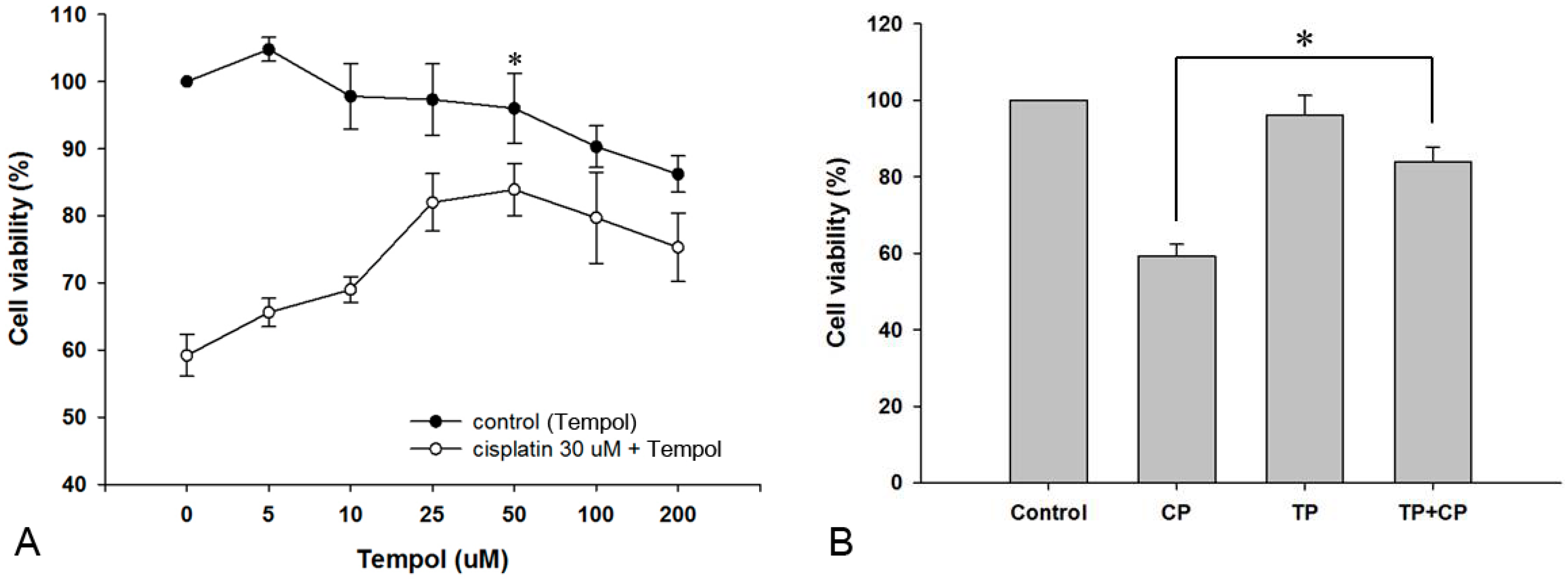
2.1. Effect of Tempol on the Viability of House Ear Institute-Organ of Corti 1 (HEI-OC1) Cells
2.2. Protective Effect of Tempol against Cisplatin Cytotoxicity
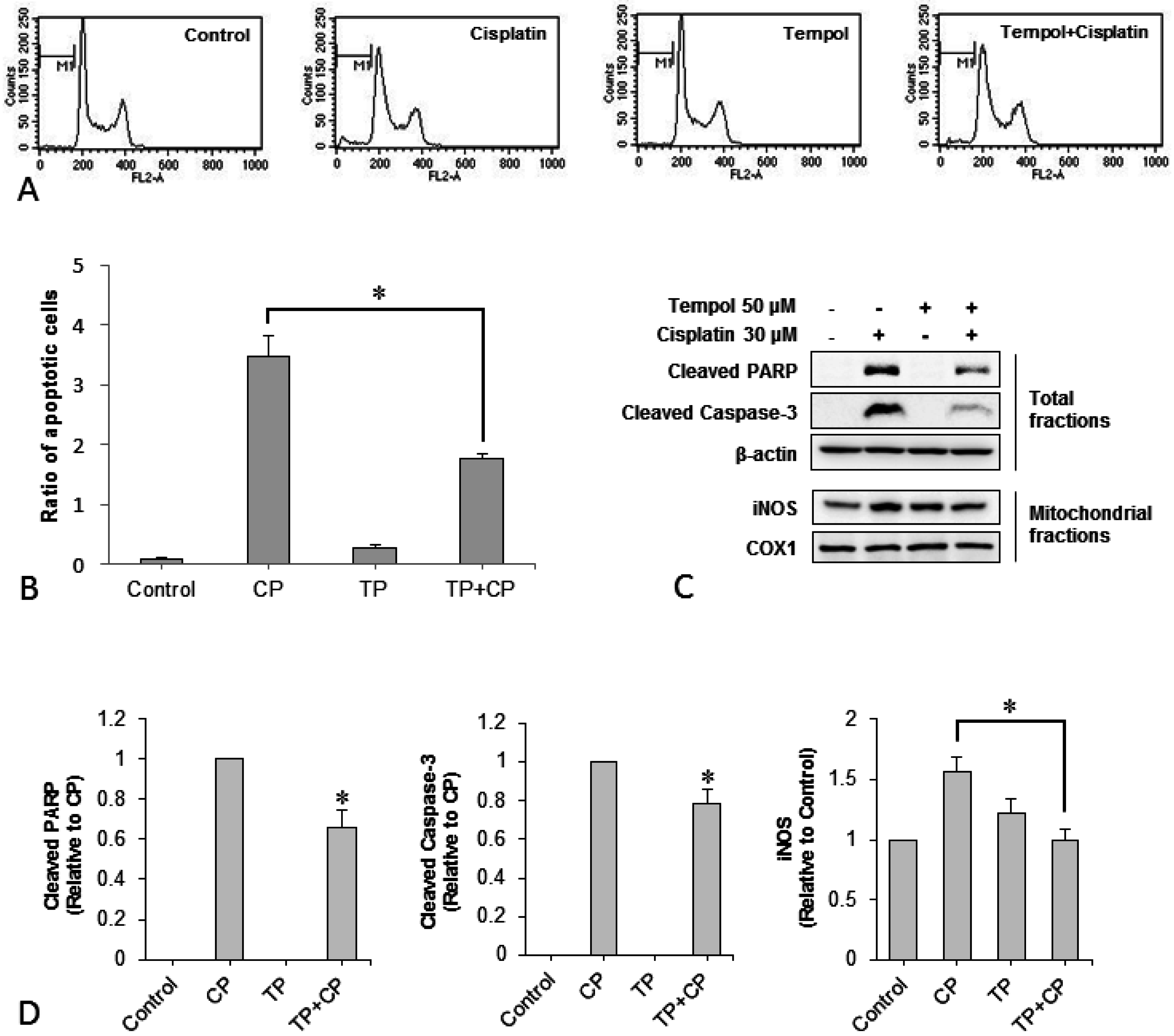
2.3. Changes in Apoptotic Characteristics of Cells
2.4. Changes in the Number of Apoptotic Cells
2.5. Changes in Expression of the Apoptotic Proteins Cleaved Poly ADP-Ribose Polymerase (PARP), Cleaved-Caspase 3, and Mitochondrial Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (iNOS)
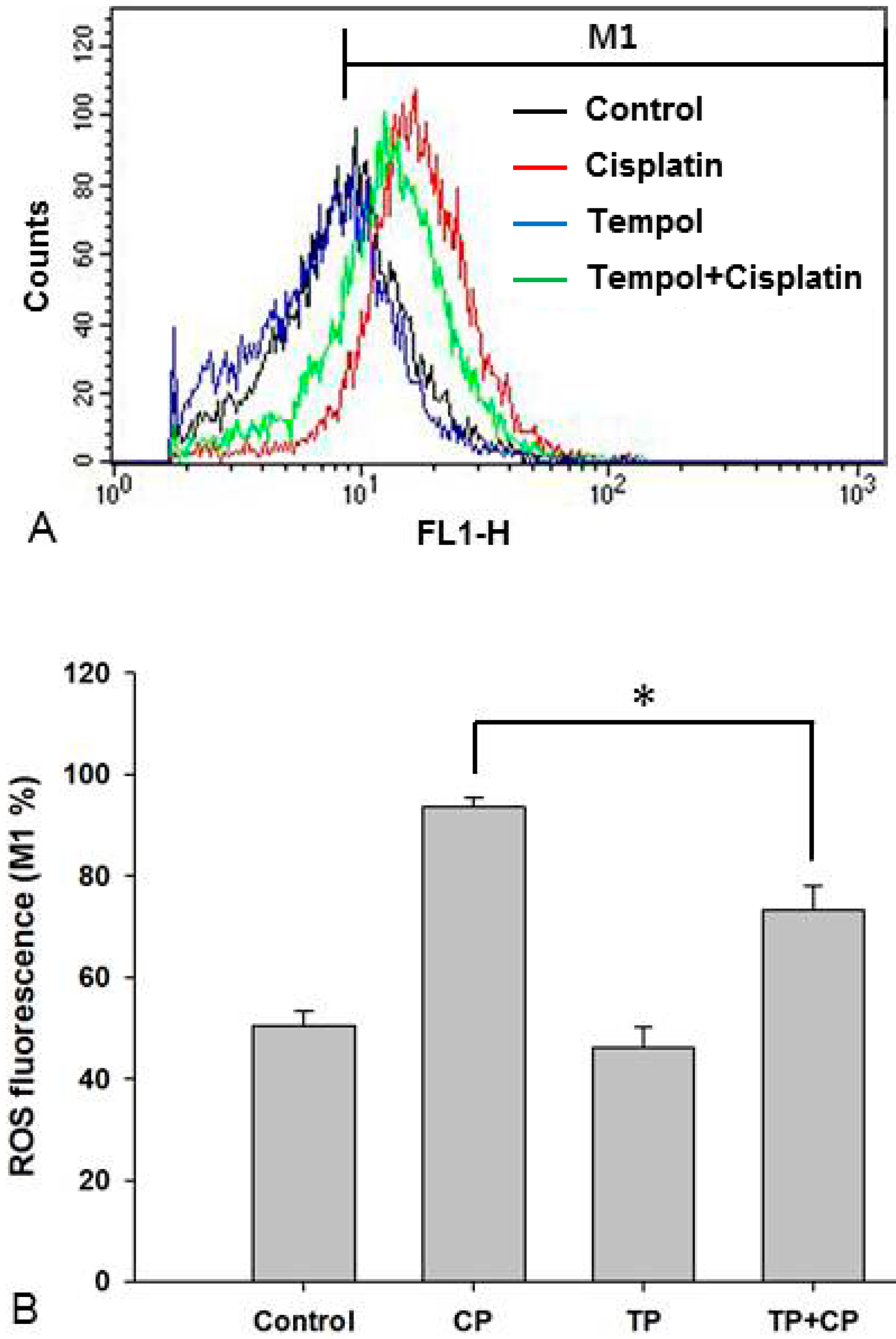
2.6. Changes in Intracellular ROS Levels
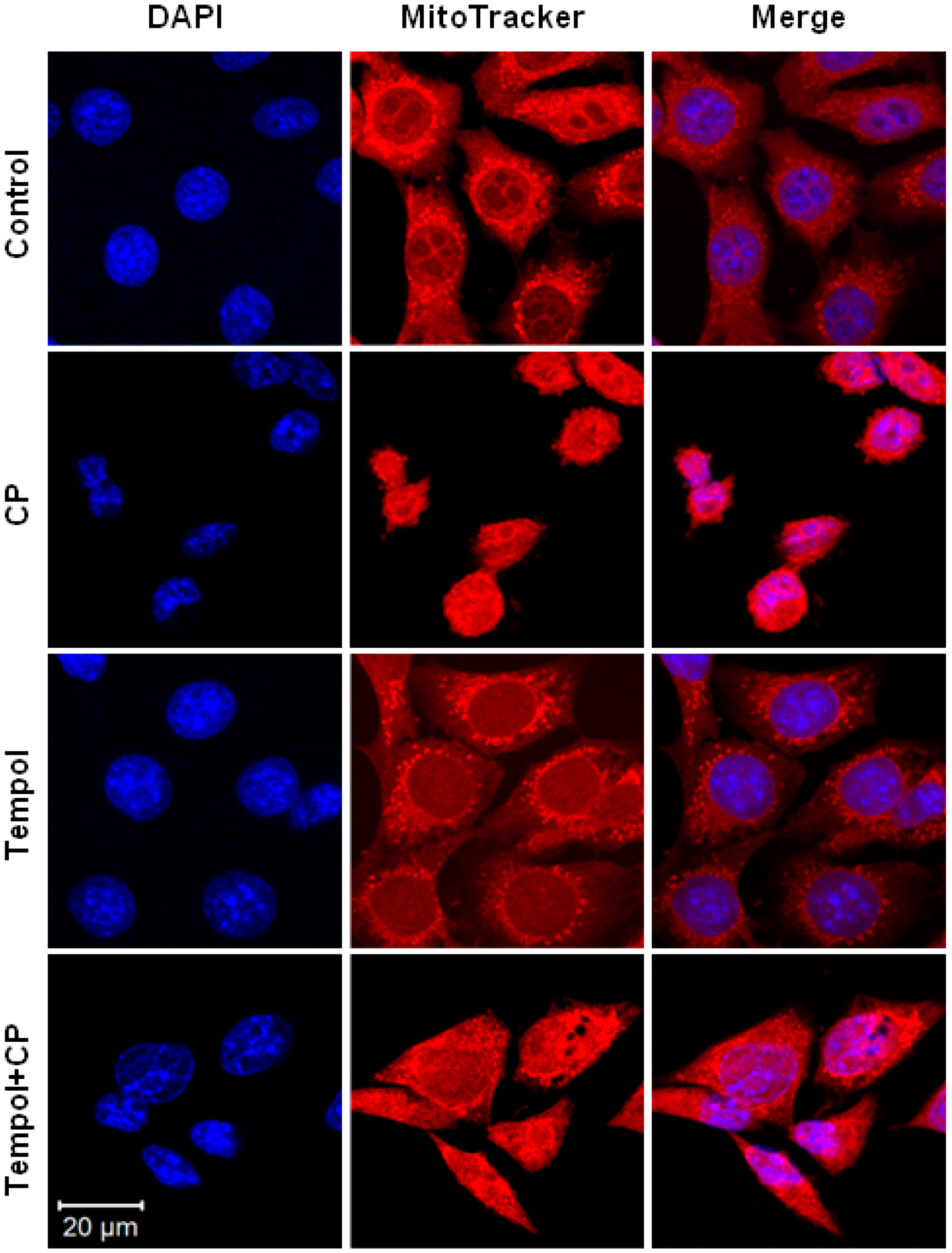
2.7. Mitochondrial and Nuclear Changes
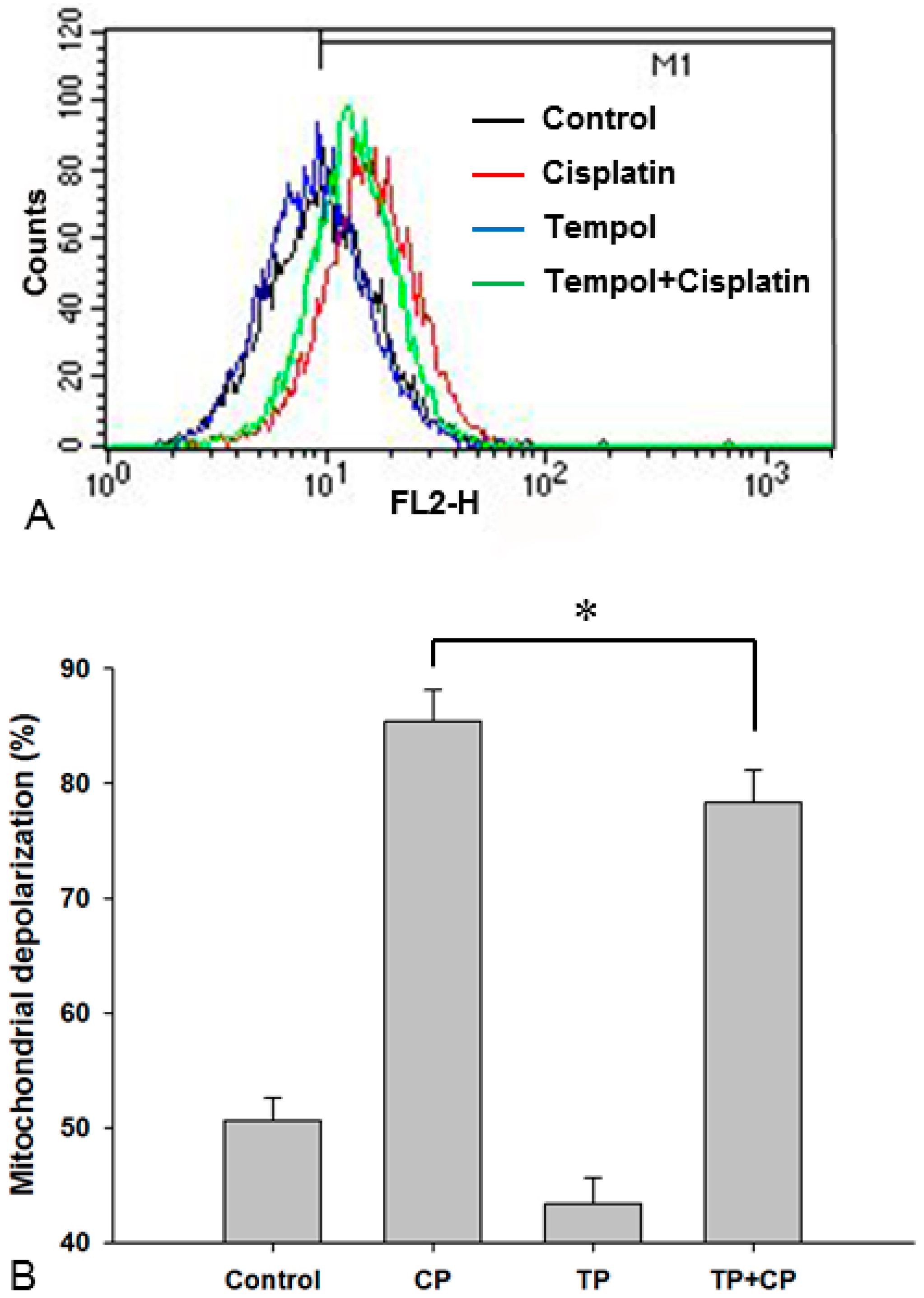
2.8. Changes in the Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. MTT Assay
4.3. TUNEL Assay
4.4. Apoptosis Analysis Using Flow Cytometry
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. Intracellular ROS Measurement
4.7. Confocal Microscopic Evaluation of Mitochondria
4.8. Analysis of the Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
4.9. Isolation of the Mitochondria
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HEI-OC1 | House Ear Institute-Organ of Corti 1 |
| MTT | 3-[4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| PARP | Poly ADP-ribose polymerase |
| NOS | Nitric oxide synthase |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| CP | Cisplatin |
| TP | Tempol |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| PBS | Phosphate buffered saline |
| PI | Propidium iodide |
References
- Rybak, L.P.; Whitworth, C.A.; Mukherjea, D.; Ramkumar, V. Mechanisms of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity and prevention. Hear. Res. 2007, 226, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehne, N.; Lautermann, J.; Petrat, F.; Rauen, U.; de Groot, H. Cisplatin ototoxicity: Involvement of iron and enhanced formation of superoxide anion radicals. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2001, 174, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves, M.S.; Silveira, A.F.; Teixeira, A.R.; Hyppolito, M.A. Mechanisms of cisplatin ototoxicity: Theoretical review. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2013, 127, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, L.A.; Shehata, N.I.; Abdelkader, N.F.; Khattab, M.M. Tempol, a superoxide dismutase mimetic agent, ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity through alleviation of mitochondrial dysfunction in mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, M.C.; Zacharowski, K.; Bowes, J.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Thiemermann, C. Tempol reduces infarct size in rodent models of regional myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 27, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khabour, O.F.; Alzoubi, K.H.; Mfady, D.S.; Alasseiri, M.; Hasheesh, T.F. Tempol protects human lymphocytes from genotoxicity induced by cisplatin. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liang, Q.; Smith, A.D.; Pan, S.; Tyurin, V.A.; Kagan, V.E.; Hastings, T.G.; Schor, N.F. Neuroprotective effects of Tempol in central and peripheral nervous system models of Parkinson’s disease. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 70, 1371–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, K.C.M.; Kalkanis, J.; Glatz, F.R. Ototoxicity: Mechanisms, protective agents, and monitoring. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2000, 8, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, L.P.; Mukherjea, D.; Jajoo, S.; Ramkumar, V. Cisplatin ototoxicity and protection: Clinical and experimental studies. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2009, 219, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, C.S. Effects of tempol and redox-cycling nitroxides in models of oxidative stress. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 126, 119–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuni, A.; Krishna, C.M.; Riesz, P.; Finkelstein, E.; Russo, A. A novel metal-free low molecular weight superoxide dismutase mimic. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 17921–17924. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thiemermann, C. Membrane-permeable radical scavengers (Tempol) for shock, ischemia-reperfusion injury, and inflammation. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 31, S76–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, E.J.; Peterson, A.; Malley, S.; Daniel, M.; Lambert, D.; Kosofsky, M.; Vizzard, M.A. The effects of tempol on cyclophosphamide-induced oxidative stress in rat micturition reflexes. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 545048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Januschowski, K.; Mueller, S.; Dollinger, R.; Schnichels, S.; Hofmann, J.; Spitzer, M.S.; Bartz-Schmidt, K.U.; Szurman, P.; Thaler, S. Investigating retinal toxicity of tempol in a model of isolated and perfused bovine retina. Graefes. Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2014, 252, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanyong, Y.; Zefeng, T.; Xiufeng, X.; Dawei, D.; Xiaoyan, L.; Ying, Z.; Yaogao, F. Tempol alleviates intracerebral hemorrhage-induced brain injury possibly by attenuating nitrative stress. Neuroreport 2015, 26, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng-Bryant, Y.; Singh, I.N.; Carrico, K.M.; Hall, E.D. Neuroprotective effects of tempol, a catalytic scavenger of peroxynitrite-derived free radicals, in a mouse traumatic brain injury model. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2008, 28, 1114–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.; Chen, Y.; Dennehy, K.; Blau, J.; Connors, S.; Mendonca, M.; Tarpey, M.; Krishna, M.; Mitchell, J.B.; Welch, W.J.; et al. Acute antihypertensive action of nitroxides in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2006, 290, R37–R43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, C.S.; Pearlman, A. Chemistry and antihypertensive effects of tempol and other nitroxides. Pharmacol. Rev. 2008, 60, 418–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, R.T.; Galatsis, P.; Borosky, S.; Kopec, K.K.; Kumar, V.; Althaus, J.S.; Hall, E.D. 4-Hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl (Tempol) inhibits peroxynitrite-mediated phenol nitration. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2000, 13, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjea, D.; Jajoo, S.; Whitworth, C.; Bunch, J.R.; Turner, J.G.; Rybak, L.P.; Ramkumar, V. Short interfering RNA against transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 attenuates cisplatin-induced hearing loss in the rat. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 13056–13065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borner, C. The Bcl-2 protein family: Sensors and checkpoints for life-or-death decisions. Mol. Immunol. 2003, 39, 615–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margiotta, N.; Denora, N.; Ostuni, R.; Laquintana, V.; Anderson, A.; Johnson, S.W.; Trapani, G.; Natile, G. Platinum(II) complexes with bioactive carrier ligands having high affinity for the translocator protein. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 5144–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawrocki, S.T.; Kelly, K.R.; Smith, P.G.; Espitia, C.M.; Possemato, A.; Beausoleil, S.A.; Milhollen, M.; Blakemore, S.; Thomas, M.; Berger, A.; et al. Disrupting protein NEDDylation with MLN4924 is a novel strategy to target cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 3577–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casares, C.; Ramirez-Camacho, R.; Trinidad, A.; Roldan, A.; Jorge, E.; Garcia-Berrocal, J.R. Reactive oxygen species in apoptosis induced by cisplatin: Review of physiopathological mechanisms in animal models. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2012, 269, 2455–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minami, S.B.; Yamashita, D.; Ogawa, K.; Schacht, J.; Miller, J.M. Creatine and Tempol attenuate noise-induced hearing loss. Brain Res. 2007, 1148, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murashita, H.; Tabuchi, K.; Hoshino, T.; Tsuji, S.; Hara, A. The effects of Tempol, 3-aminobenzamide and nitric oxide synthase inhibitors on acoustic injury of the mouse cochlea. Hear. Res. 2006, 214, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagashima, R.; Yamaguchi, T.; Tanaka, H.; Ogita, K. Mechanism underlying the protective effect of Tempol and Nomega-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester on acoustic injury: Possible involvement of c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway and connexin26 in the cochlear spiral ligament. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 114, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, T.; am Zehnhoff-Dinnesen, A.; Radtke, S.; Meitert, J.; Zolk, O. Understanding platinum-induced ototoxicity. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 34, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinec, G.M.; Webster, P.; Lim, D.J.; Kalinec, F. A cochlear cell line as an in vitro system for drug ototoxicity screening. Audiol. Neurootol. 2003, 8, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Youn, C.K.; Kim, J.; Jo, E.-R.; Oh, J.; Do, N.Y.; Cho, S.I. Protective Effect of Tempol against Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111931
Youn CK, Kim J, Jo E-R, Oh J, Do NY, Cho SI. Protective Effect of Tempol against Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(11):1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111931
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoun, Cha Kyung, Jun Kim, Eu-Ri Jo, Jeonghyun Oh, Nam Yong Do, and Sung Il Cho. 2016. "Protective Effect of Tempol against Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 11: 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111931





