Cinnamomum cassia Essential Oil Inhibits α-MSH-Induced Melanin Production and Oxidative Stress in Murine B16 Melanoma Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. The Chemical Composition of CC-EO
2.2. The Inhibitory Effects of CC-EO and Its Major Constituents on Mushroom Tyrosinase Activity
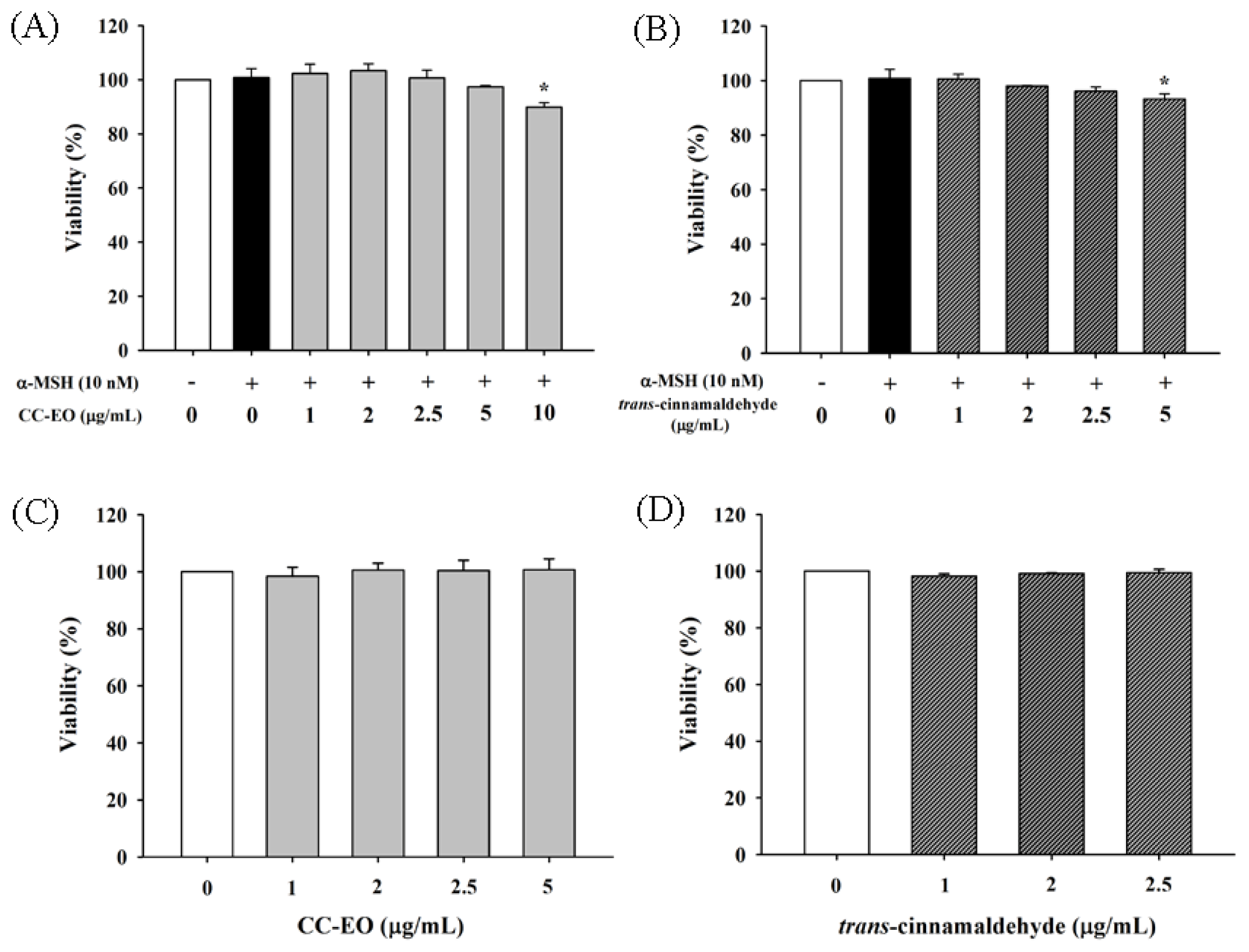
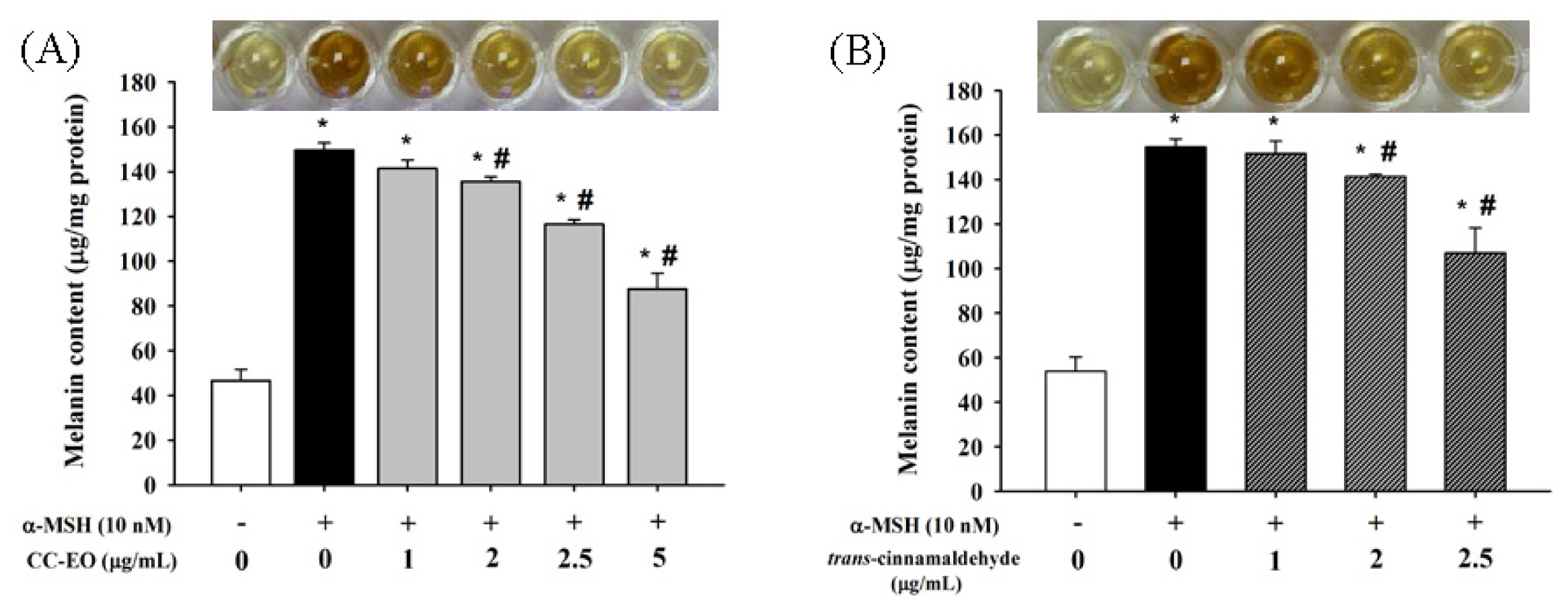
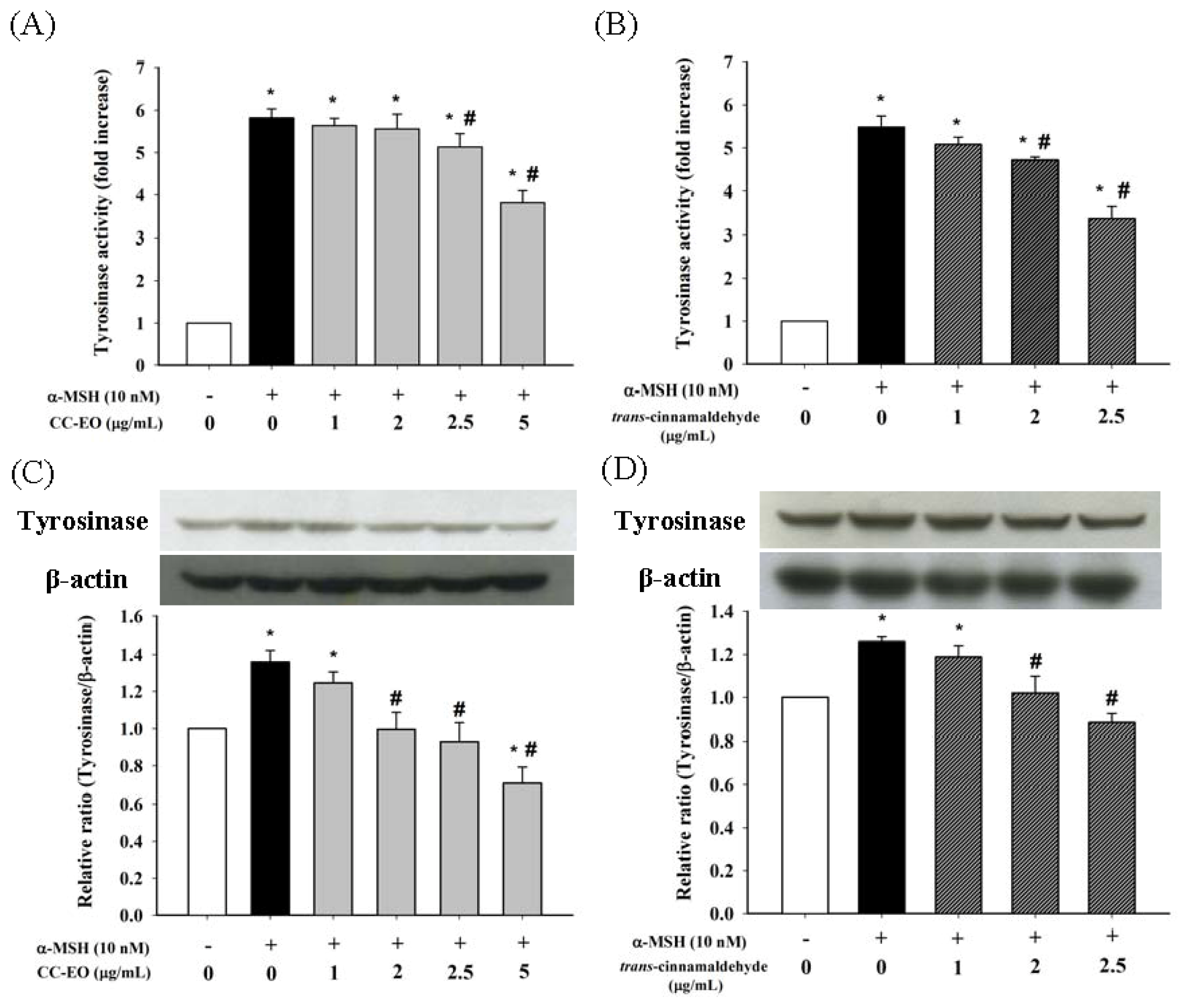
2.3. The Effects of CC-EO and Trans-Cinnamaldehyde on the Cell Viability, Melanin Content and Tyrosinase in α-MSH-Stimulated B16 Cells
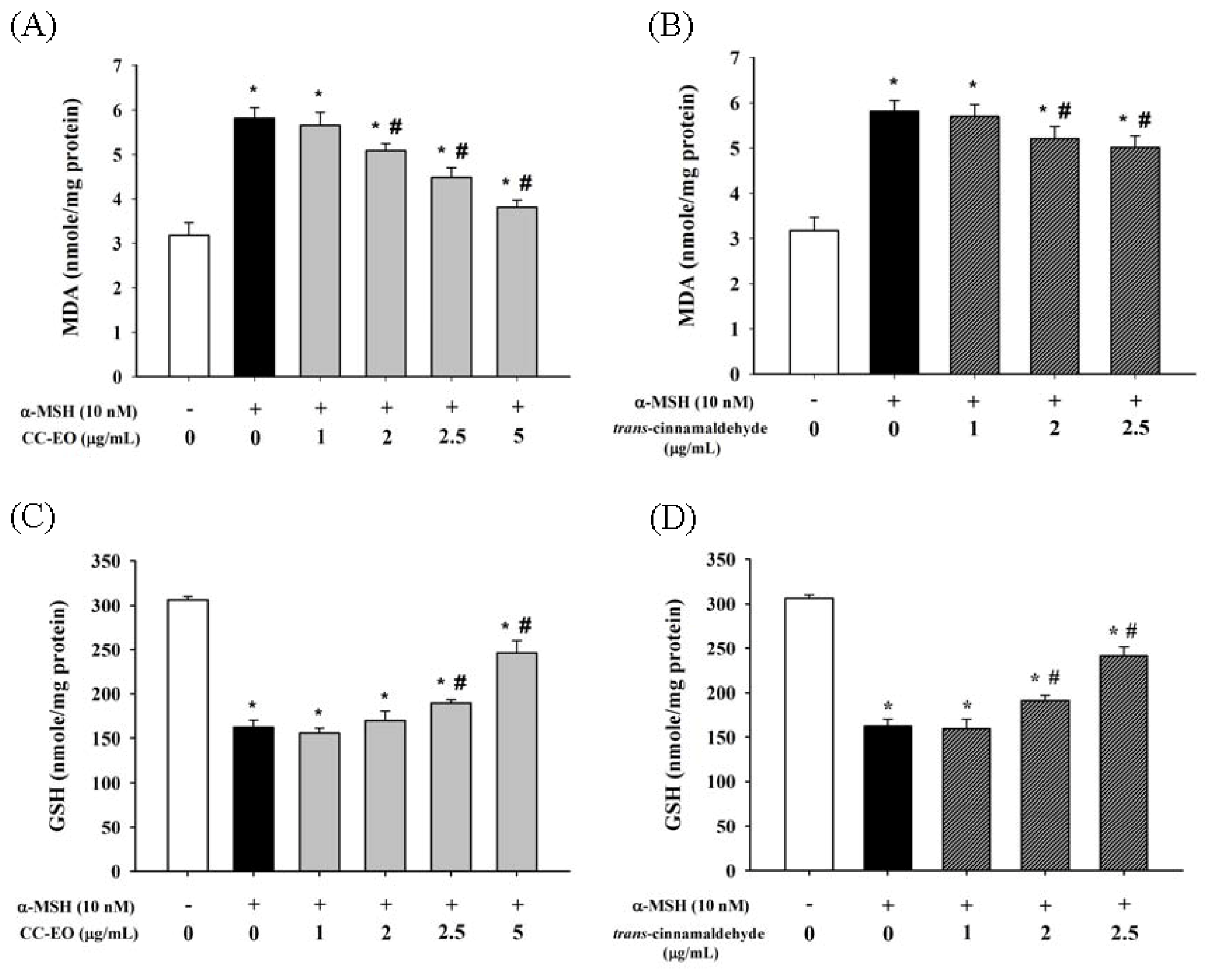
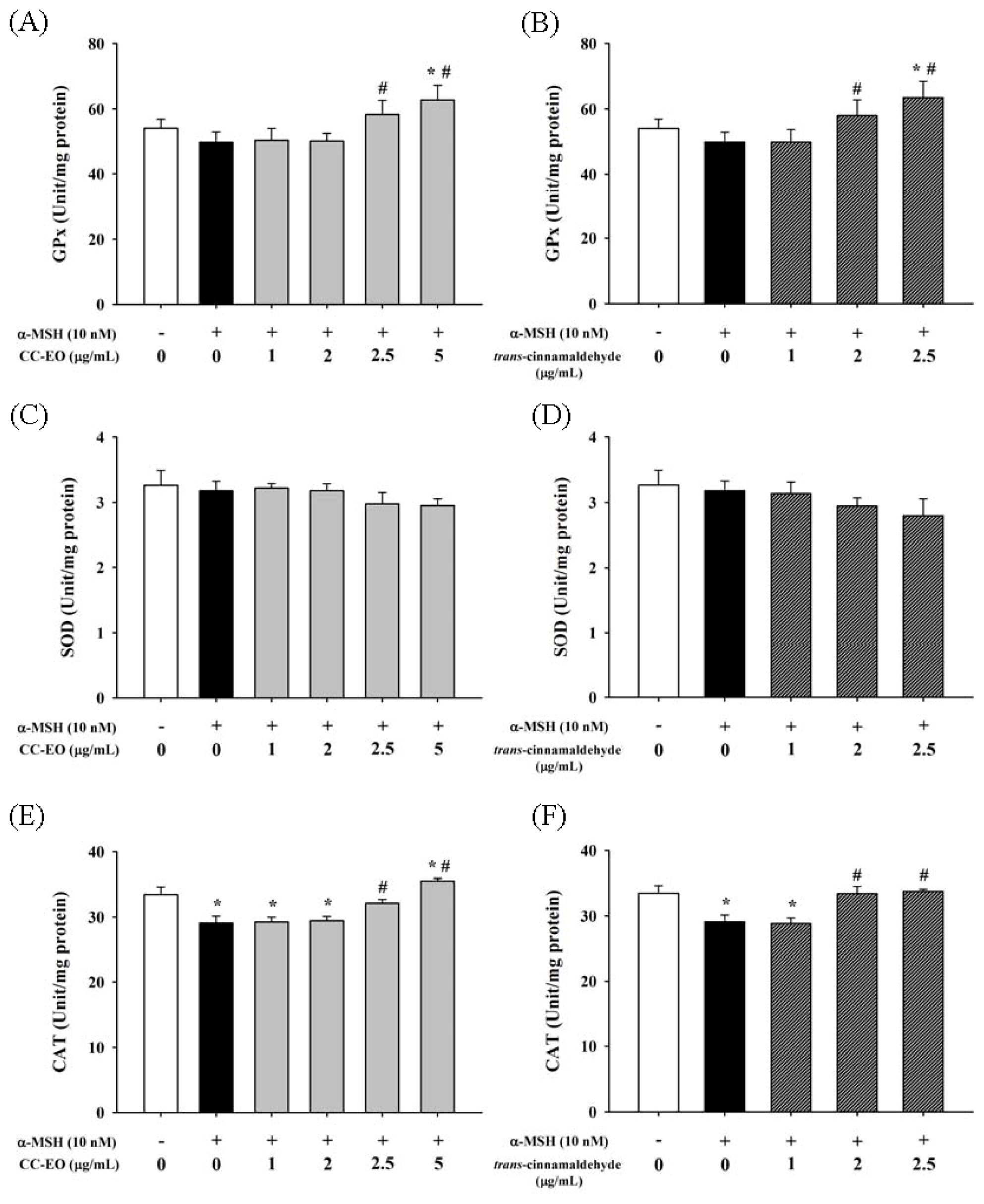
2.4. The Effects of CC-EO and Trans-Cinnamaldehyde on MDA Production, GSH Levels and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in α-MSH-Stimulated B16 Cells
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Essential Oils
3.2. Chemicals
3.3. GC-MS Analysis
3.4. Enzymatic Assay of Mushroom Tyrosinase
3.5. Cell Cultures
3.6. Cell Viability
3.7. The Assay of Melanin Content
3.8. The Assay of Cellular Tyrosinase Activity
3.9. Western Blot Analysis
3.10. The Measurement of the Lipid Peroxide and Glutathione (GSH) Levels and the Glutathione Peroxidase (GPx), Superoxide Dismutase (SOD), and Catalase (CAT) Activities
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seo, S.Y.; Sharma, V.K.; Sharma, N. Mushroom tyrosinase: Recent prospects. J. Agric. Food Chem 2003, 51, 2837–2853. [Google Scholar]
- Price, E.R.; Horstmann, M.A.; Wells, A.G.; Weilbaecher, K.N.; Takemoto, C.M.; Landis, M.W.; Fisher, D.E. α-Melanocyte-stimulating hormone signaling regulates expression of microphthalmia, a gene deficient in Waardenburg syndrome. J. Biol. Chem 1998, 273, 33042–33047. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick, T.B.; Eisen, A.Z.; Wolff, K.; Freedberg, I.M.; Austen, K.F. Updates: Dermatology in General Medicine. In Vitiligo: Ethology, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Treatment; Mosher, D.B., Pathak, M.A., Fitzpatrick, T.B., Eds.; Mcgraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, S.J.; Ha, Y.M.; Kim, J.A.; Park, J.Y.; Ha, T.K.; Park, D.; Chun, P.; Park, N.H.; Moon, H.R.; Chung, H.Y. A novel synthesized tyrosinase inhibitor: (E)-2-((2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)diazenyl)phenyl 4-Methylbenzenesulfonate as an azo-resveratrol Analog. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem 2013, 77, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.C.; Yang, C.H.; Chang, N.F.; Wu, P.S.; Chen, Y.S.; Lee, S.M.; Chen, C.W. Study on the stability of deoxyarbutin in an anhydrous emulsion systemy. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2011, 12, 5946–5954. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.W.; Chiang, H.M.; Lin, Y.C.; Wen, K.C. Natural products with skin-whitening effects. J. Food Drug Anal 2008, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Smit, N.; Vicanova, J.; Pavel, S. The hunt for natural skin whitening agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2009, 10, 5326–5349. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.J. Antimelanogenic and antioxidant properties of gallic acid. Biol. Pharm. Bull 2007, 30, 1052–1055. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, T.H.; Ding, H.Y.; Hung, W.J.; Liang, C.H. Antioxidative characteristics and inhibition of α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone-stimulated melanogenesis of vanillin and vanillic acid from Origanum vulgare. Exp. Dermatol 2010, 19, 742–750. [Google Scholar]
- Arung, E.T.; Matsubara, E.; Kusuma, I.W.; Sukaton, E.; Shimizu, K.; Kondo, R. Inhibitory components from the buds of clove (Syzygium aromaticum) on melanin formation in B16 melanoma cells. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 198–202. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, C.X.; Lin, M.; Lu, S.S.; Qi, X.Y.; Zhang, R.X.; Zhang, Y.Y. Curcumin inhibits melanogenesis in human melanocytes. Phytother. Res 2012, 26, 174–179. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.S.; Ahn, Y.J. Growth-inhibiting effects of Cinnamomum cassia bark-derived materials on human intestinal bacteria. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ka, H.; Park, H.J.; Jung, H.J.; Choi, J.W.; Cho, K.S.; Ha, J.; Lee, K.T. Cinnamaldehyde induces apoptosis by ROS-mediated mitochondrial permeability transition in human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells. Cancer Lett 2003, 196, 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.S.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, M.K. Suppression effect of Cinnamomum cassia bark-derived component on nitric oxide synthase. J. Agric. Food Chem 2002, 50, 7700–7703. [Google Scholar]
- Verspohl, E.J.; Bauer, K.; Neddermann, E. Antidiabetic effect of Cinnamomum cassia and Cinnamomum zeylanicum In Vivo and In Vitro. Phytother. Res 2005, 19, 203–206. [Google Scholar]
- Ngoc, T.M.; Lee, I.; Ha, D.T.; Kim, H.; Min, B.; Bae, K. Tyrosinase-inhibitory constituents from the twigs of Cinnamomum cassia. J. Nat. Prod 2009, 72, 1205–1208. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura, R.; Ukeda, H.; Sawamura, M. Tyrosinase inhibitory activity of citrus essential oils. J. Agric. Food Chem 2006, 54, 2309–2313. [Google Scholar]
- Kubo, I.; Kinst-Hori, I. Tyrosinase inhibitors from anise oil. J. Agric. Food Chem 1998, 46, 1268–1271. [Google Scholar]
- Marongiu, B.; Piras, A.; Porcedda, S.; Tuveri, E.; Sanjust, E.; Meli, M.; Sollai, F.; Zucca, P.; Rescigno, A. Supercritical CO2 extract of Cinnamomum zeylanicum: Chemical characterization and antityrosinase activity. J. Agric. Food Chem 2007, 55, 10022–10027. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.C.; Chang, T.Y.; Chang, L.Z.; Wang, H.F.; Yih, K.H.; Hsieh, W.Y.; Chang, T.M. Inhibition of melanogenesis versus antioxidant properties of essential oil extracted from leaves of Vitex negundo Linn and chemical composition analysis by GC-MS. Molecules 2012, 17, 3902–3916. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, S.; Kim, N.H.; Koo, B.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, A.Y. Lotus (Nelumbo nuficera) flower essential oil increased melanogenesis in normal human melanocytes. Exp. Mol. Med. 2009, 41, 517–525. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Zhu, J.X.; Mo, S.F.; Pan, Y.; Kong, L.D. Effects of cassia oil on serum and hepatic uric acid levels in oxonate-induced mice and xanthine dehydrogenase and xanthine oxidase activities in mouse liver. J. Ethnopharmacol 2006, 103, 357–365. [Google Scholar]
- Giordani, R.; Regli, P.; Kaloustian, J.; Portugal, H. Potentiation of antifungal activity of amphotericin B by essential oil from Cinnamomum cassia. Phytother. Res 2006, 20, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, S.; Cui, Z.; Huang, X.; Chen, Y.; Xu, D.; Xiong, P. Variations in essential oil yield and composition during Cinnamomum cassia bark growth. Ind. Crops Prod 2011, 33, 248–252. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.S. Tyrosinase inhibitors of Pulsatilla cernua root-derived materials. J. Agric. Food Chem 2002, 50, 1400–1403. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.E.; Kim, M.K.; Lee, S.G.; Ahn, Y.J.; Lee, H.S. Inhibitory effects of Cinnamomum cassia bark-derived materials on mushroom tyrosinase. Food Sci. Biotechnol 2000, 9, 330–333. [Google Scholar]
- Fiocco, D.; Fiorentino, D.; Frabboni, L.; Benvenuti, S.; Orlandini, G.; Pellati, F.; Gallone, A. Lavender and peppermint essential oils as effective mushroom tyrosinase inhibitors: A basic study. Flavour Fragr. J 2011, 26, 441–446. [Google Scholar]
- Munoz-Munoz, J.L.; Garcia-Molina, F.; Varon, R.; Tudela, J.; Garcia-Canovas, F.; Rodriguez-Lopez, J.N. Generation of hydrogen peroxide in the melanin biosynthesis pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1794, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar]
- Perluigi, M.; de Marco, F.; Foppoli, C.; Coccia, R.; Blarzino, C.; Luisa Marcante, M.; Cini, C. Tyrosinase protects human melanocytes from ROS-generating compounds. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2003, 305, 250–256. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.S.; Peshavariya, H.; Higuchi, M.; Brewer, A.C.; Chang, C.W.T.; Chan, E.C.; Dusting, G.J. Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor modulates expression of NADPH oxidase type 4: A negative regulator of melanogenesis. Free Radic. Biol. Med 2012, 52, 1835–1843. [Google Scholar]
- Panich, U.; Tangsupa-a-nan, V.; Onkoksoong, T.; Kongtaphan, K.; Kasetsinsombat, K.; Akarasereenont, P.; Wongkajornsilp, A. Inhibition of UVA-mediated melanogenesis by ascorbic acid through modulation of antioxidant defense and nitric oxide system. Arch. Pharm. Res 2011, 34, 811–820. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.; Li, H. Antioxidant effect of Cassia essential oil on deep-fried beef during the frying process. Meat Sci 2008, 78, 461–468. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.C.; Wu, S.J.; Chang, C.H.; Ng, L.T. Antioxidant activity of Cinnamomum cassia. Phytother. Res 2003, 17, 726–730. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, F.L.; Li, W.H.; Yu, C.W.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Yang, Y.F.; Liu, J.T.; Shih, J.; Chu, Y.J.; Yen, P.L.; Chang, S.T.; et al. In vivo antioxidant activities of essential oils and their constituents from leaves of the taiwanese Cinnamomum osmophloeum. J. Agric. Food Chem 2012, 60, 3092–3097. [Google Scholar]
- Villarama, C.D.; Maibach, H.I. Glutathione as a depigmenting agent: An overview. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci 2005, 27, 147–153. [Google Scholar]
- Busca, R.; Ballotti, R. Cyclic AMP a key messenger in the regulation of skin pigmentation. Pigment Cell Res 2000, 13, 60–69. [Google Scholar]
- Slominski, A.; Tobin, D.J.; Shibahara, S.; Wortsman, J. Melanin pigmentation in mammalian skin and its hormonal regulation. Physiol. Rev 2004, 84, 1155–1228. [Google Scholar]
- Busca, R.; Abbe, P.; Mantoux, F.; Aberdam, E.; Peyssonnaux, C.; Eychene, A.; Ortonne, J.P.; Ballotti, R. Ras mediates the cAMP-dependent activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) in melanocytes. EMBO J 2000, 19, 2900–2910. [Google Scholar]
- Englaro, W.; Rezzonico, R.; Durand-Clement, M.; Lallemand, D.; Ortonne, J.P.; Ballotti, R. Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway and AP-1 are activated during cAMP-induced melanogenesis in B-16 melanoma cells. J. Biol. Chem 1995, 270, 24315–24320. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.S.; Hwang, E.S.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, S.Y.; Kwon, S.B.; Park, K.C. Sphingosine-1-phosphate decreases melanin synthesis via sustained ERK activation and subsequent MITF degradation. J. Cell Sci 2003, 116, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Gong, L.; Haddad, M.M.; Bischof, O.; Campisi, J.; Yeh, E.T.H.; Medrano, E.E. Regulation of microphthalmia-associated transcription factor MITF protein levels by association with the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme hUBC9. Exp. Cell Res 2000, 255, 135–143. [Google Scholar]
- Smalley, K.; Eisen, T. The involvement of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in the α-melanocyte stimulating hormone (α-MSH)-induced melanogenic and anti-proliferative effects in B16 murine melanoma cells. FEBS Lett 2000, 476, 198–202. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, H.; Kaur, S.; Mittal, S.; Batish, D.; Kohli, R. Essential oil of Artemisia scoparia inhibits plant growth by generating reactive oxygen species and causing oxidative damage. J. Chem. Ecol 2009, 35, 154–162. [Google Scholar]
- Martindale, J.L.; Holbrook, N.J. Cellular response to oxidative stress: Signaling for suicide and survival. J. Cell. Physiol 2002, 192, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Corre, S.; Primot, A.; Sviderskaya, E.; Bennett, D.C.; Vaulont, S.; Goding, C.R.; Galibert, M.D. UV-induced expression of key component of the tanning process, the POMC and MC1R genes, is dependent on the p-38-activated upstream stimulating factor-1 (USF-1). J. Biol. Chem 2004, 279, 51226–51233. [Google Scholar]
- Yanase, H.; Ando, H.; Horikawa, M.; Watanabe, M.; Mori, T.; Matsuda, N. Possible involvement of ERK 1/2 in UVA-induced melanogenesis in cultured normal human epidermal melanocytes. Pigment Cell Res 2001, 14, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.; Lee, K.T.; Ka, H.; Jung, W.T.; Jung, H.J.; Park, H.J. Constituents of the essential oil of the Cinnamomum cassia stem bark and the biological properties. Arch. Pharm. Res 2001, 24, 418–423. [Google Scholar]
- Sladowski, D.; Steer, S.J.; Clothier, R.H.; Balls, M. An improved MIT assay. J. Immunol. Methods 1993, 157, 203–207. [Google Scholar]
- Thanigaimalai, P.; Lee, K.C.; Bang, S.C.; Lee, J.H.; Yun, C.Y.; Roh, E.; Hwang, B.Y.; Kim, Y.; Jung, S.H. Evaluation of 3,4-dihydroquinazoline-2(1H)-thiones as inhibitors of α-MSH-induced melanin production in melanoma B16 cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem 2010, 18, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, W.D.; Ryu, Y.B.; Curtis-Long, M.J.; Lee, C.W.; Ryu, H.W.; Jang, K.C.; Park, K.H. Evaluation of anti-pigmentary effect of synthetic sulfonylamino chalcone. Eur. J. Med. Chem 2010, 45, 2010–2017. [Google Scholar]
- Botsoglou, N.A.; Fletouris, D.J.; Papageorgiou, G.E.; Vassilopoulos, V.N.; Mantis, A.J.; Trakatellis, A.G. Rapid, sensitive, and specific thiobarbituric acid method for measuring lipid peroxidation in animal tissue, food, and feedstuff samples. J. Agric. Food Chem 1994, 42, 1931–1937. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.S.; Chou, S.T.; Liu, L.; Tsai, P.J.; Kuo, J.S. Effect of ageing on human plasma glutathione concentrations as determined by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorimetric detection. J. Chromatogr. B 1995, 674, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Paglia, D.E.; Valentine, W.N. Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. Lab. Clin. Med 1967, 70, 158–169. [Google Scholar]
- Marklund, S.; Marklund, G. Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur. J. Biochem 1974, 47, 469–474. [Google Scholar]
- Aebi, H. Catalase in Vitro. In Methods in Enzymology; Lester, P., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1984; pp. 121–126. [Google Scholar]
| Compounds | MFa | Rtb | KIc | Area % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benzaldehyde | C7H6O | 7.58 | 982 | 0.42 |
| 2,2,4,6,6-Pentamethylheptane | C12H26 | 7.84 | 983 | 0.21 |
| 2,5,9-Trimethyldecane | C13H28 | 9.10 | 1121 | 0.49 |
| 2,5-Dimethylundecane | C13H28 | 9.49 | 1136 | 0.33 |
| Phenylethyl alcohol | C8H10O | 11.79 | 1175 | 0.29 |
| Cinnamaldehyde | C9H8O | 16.57 | 1189 | 42.37 |
| 3,4-Dimethoxyphenethyl alcohol | C10H14O3 | 17.78 | 1514 | 0.79 |
| Germacrene D | C15H24 | 18.97 | 1515 | 0.32 |
| cis-2-Methoxycinnamic acid | C10H10O3 | 19.69 | 1546 | 43.06 |
| Cinnamyl acetate | C11H12O2 | 20.88 | 1589 | 1.83 |
| Coumarin | C9H6O2 | 20.99 | 1623 | 1.25 |
| o-Methoxycinnamaldehyde | C10H10O2 | 22.70 | 1745 | 5.11 |
| trans-Caryophyllene | C15H24 | 22.95 | 1832 | 0.43 |
| 1,2-Dimethoxy-4-(3-methoxy-1-propenyl) benzene | C12H16O3 | 24.11 | 1946 | 2.05 |
| 2-Ethyl-5-propylphenol | C11H16O | 24.78 | 1993 | 0.21 |
| β-Phenethyl cinnamate | C17H16O2 | 32.01 | 2041 | 0.16 |
| Concentration (mg/mL) | Inhibition of tyrosinase activity (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| CC-EO | trans-cinnamaldehyde | |
| 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| 0.78 | 16.70 ± 0.41 | 16.20 ± 0.58 |
| 1.56 | 27.26 ± 0.58 | 29.17 ± 0.84 |
| 3.13 | 38.28 ± 0.07 | 45.90 ± 0.89 |
| 6.25 | 50.83 ± 0.35 | 63.11 ± 0.54 |
| 12.50 | 62.41 ± 0.34 | 77.03 ± 0.46 |
| 25.00 | 72.12 ± 0.34 | 85.62 ± 0.20 |
| 50.00 | 79.83 ± 0.07 | 91.18 ± 0.18 |
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chou, S.-T.; Chang, W.-L.; Chang, C.-T.; Hsu, S.-L.; Lin, Y.-C.; Shih, Y. Cinnamomum cassia Essential Oil Inhibits α-MSH-Induced Melanin Production and Oxidative Stress in Murine B16 Melanoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 19186-19201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140919186
Chou S-T, Chang W-L, Chang C-T, Hsu S-L, Lin Y-C, Shih Y. Cinnamomum cassia Essential Oil Inhibits α-MSH-Induced Melanin Production and Oxidative Stress in Murine B16 Melanoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(9):19186-19201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140919186
Chicago/Turabian StyleChou, Su-Tze, Wen-Lun Chang, Chen-Tien Chang, Shih-Lan Hsu, Yu-Che Lin, and Ying Shih. 2013. "Cinnamomum cassia Essential Oil Inhibits α-MSH-Induced Melanin Production and Oxidative Stress in Murine B16 Melanoma Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 9: 19186-19201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140919186




