Adaptive Response, Evidence of Cross-Resistance and Its Potential Clinical Use
Abstract
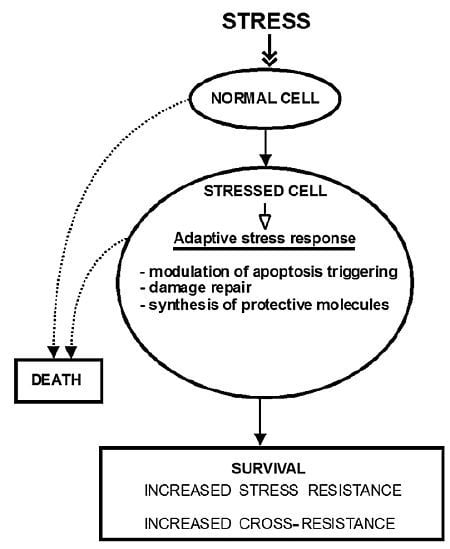
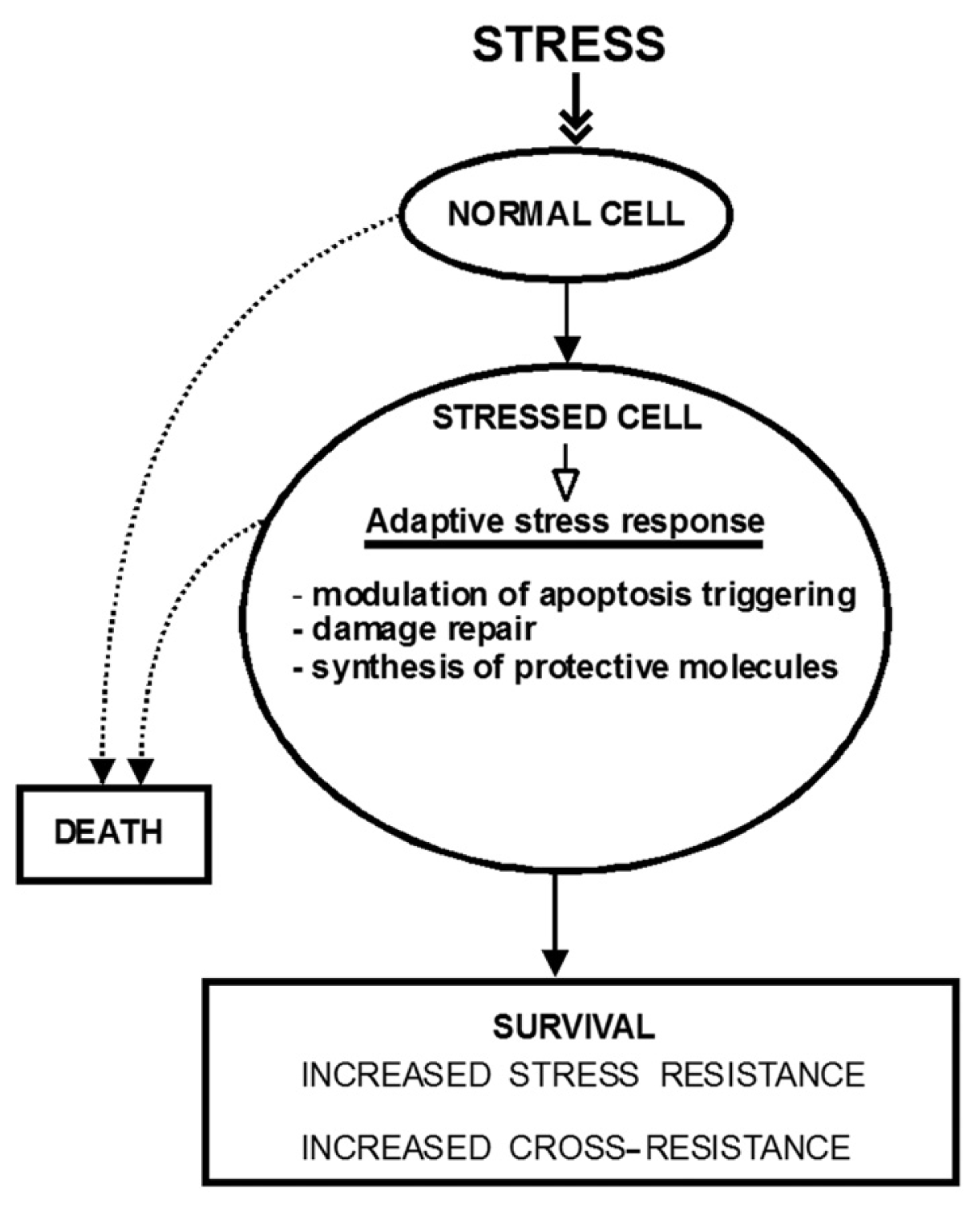
:1. Introduction
2. The Molecular Mechanisms of Stress-Induced Adaptive Responses
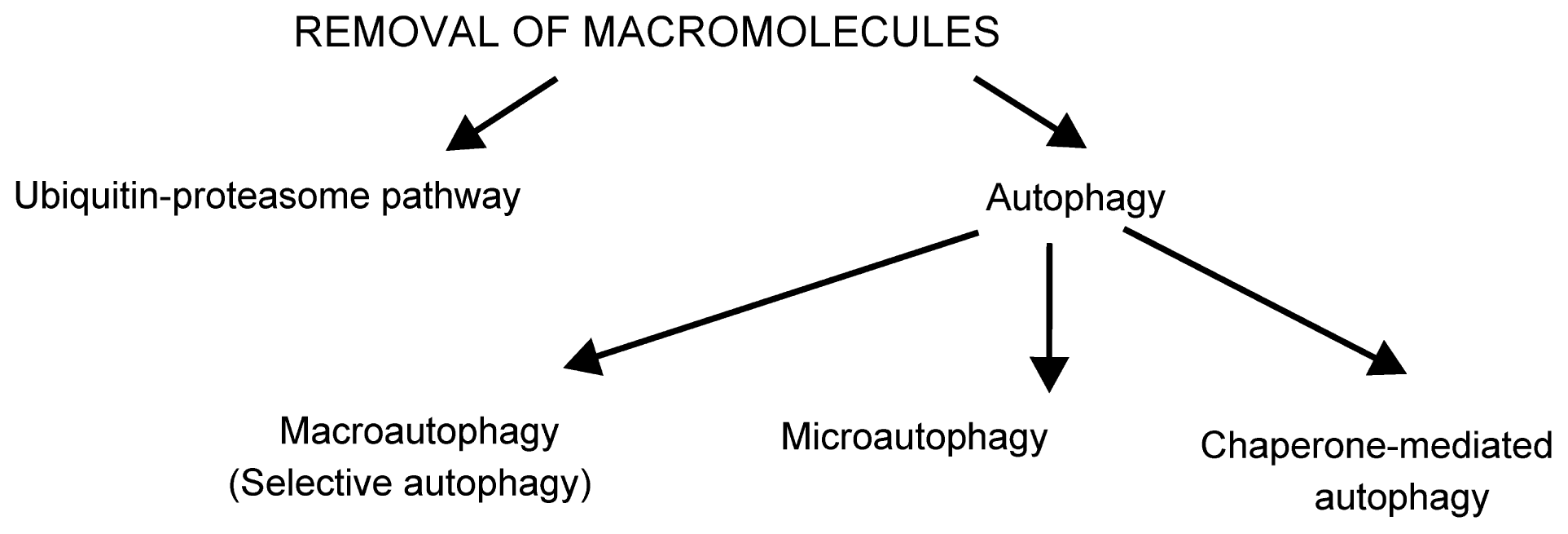
2.1. Removal of Damaged Macromolecules
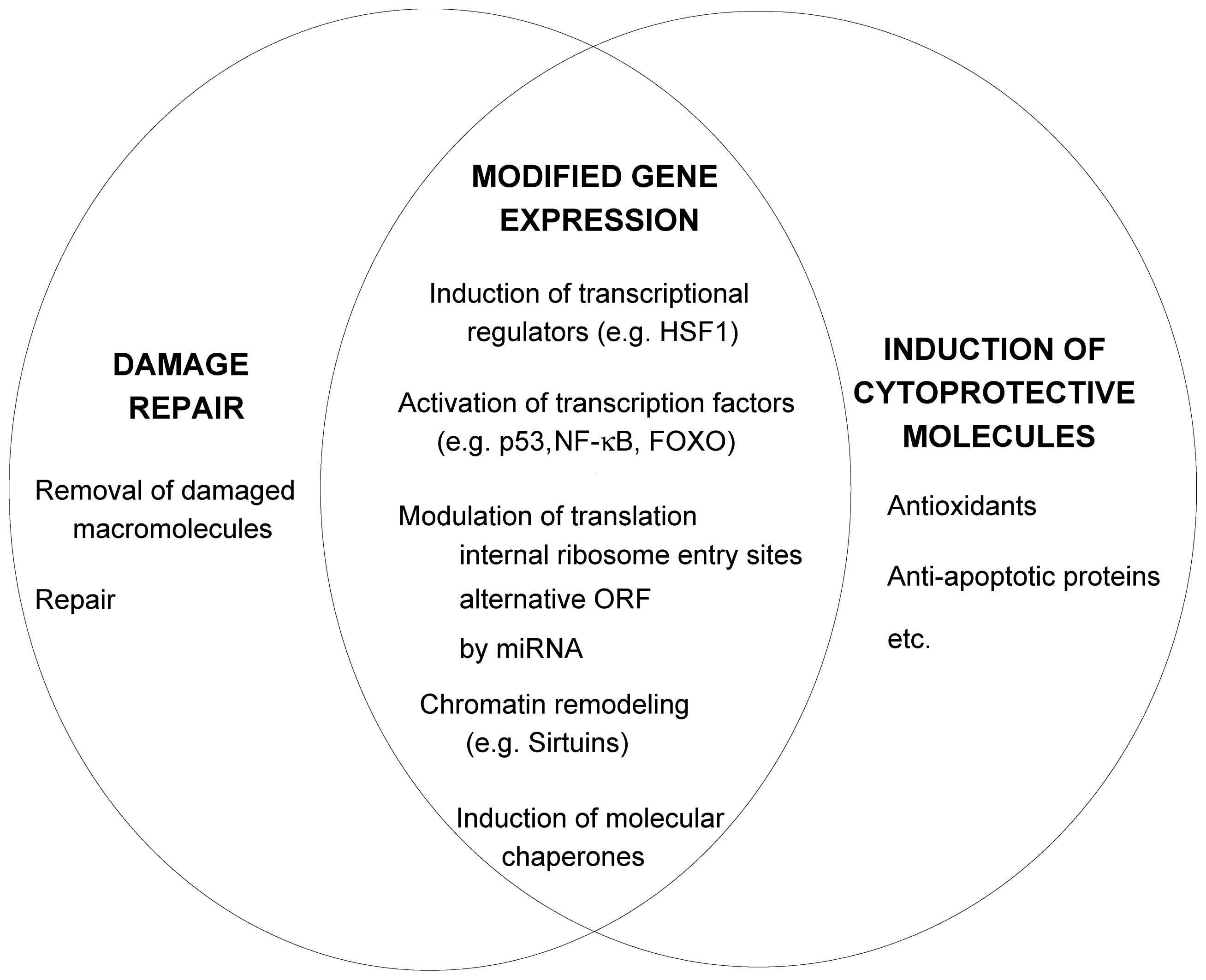
2.2. Damage Repair
2.3. Increased Synthesis of Protective Molecules
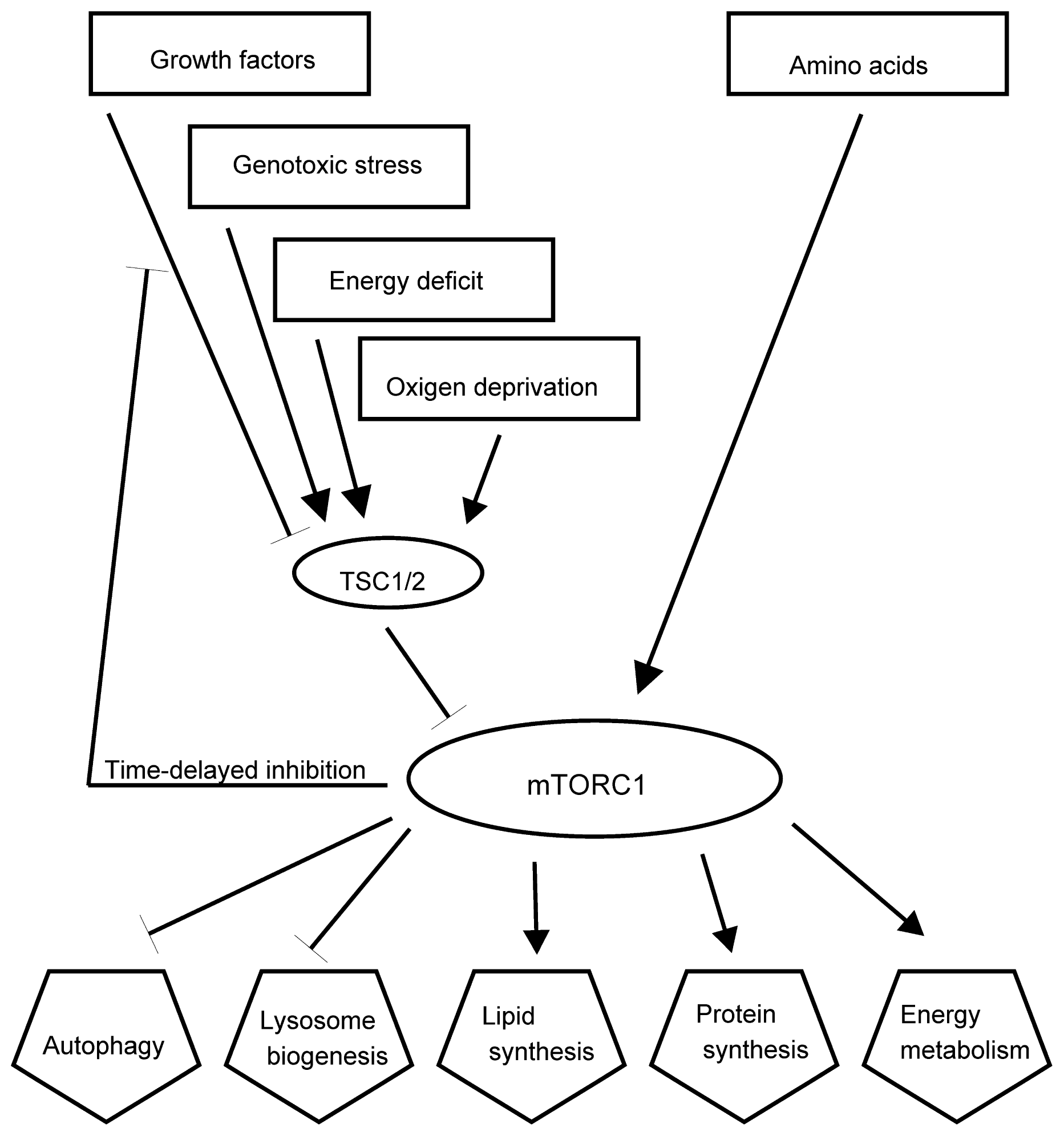
2.4. Stress Signaling Pathways
3. Adaptive Response and Cross-Resistance
3.1. Oxidative Stress Inducers (Oxidants)
3.2. Temperature Shock
3.3. Exposure to Chemicals and Toxins
3.4. Ischemia
3.5. Physical Activity
3.6. Caloric Restriction
3.7. Hypergravity
4. Clinical Applications of Adaptive Stress Response
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
- Conflict of InterestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Halliwell, B.; Gutteridge, J.M.C. Cellular Responses to Oxidative Stress: Adaptation, Damage, Repair, Senescence and Death. In Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine, 4th ed; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 187–267. [Google Scholar]
- Portt, L.; Norman, G.; Clapp, C.; Greenwood, M.; Greenwood, M.T. Anti-Apoptosis and cell survival: A review. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 238–259. [Google Scholar]
- Fulda, S.; Gorman, A.M.; Hori, O.; Samali, A. Cellular stress responses: Cell survival and cell death. Int. J. Cell Biol 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B. The antioxidant paradox. Lancet 2000, 355, 1179–1180. [Google Scholar]
- Nipic, D.; Pirc, A.; Banic, B.; Suput, D.; Milisav, I. Preapoptotic cell stress response of primary hepatocytes. Hepatology 2010, 51, 2140–2151. [Google Scholar]
- Banič, B.; Nipič, D.; Suput, D.; Milisav, I. DMSO modulates the pathway of apoptosis triggering. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett 2011, 16, 328–341. [Google Scholar]
- Fulda, S. Evasion of apoptosis as a cellular stress response in cancer. Int. J. Cell Biol 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourtis, N.; Tavernarakis, N. Cellular stress response pathways and ageing: Intricate molecular relationships. EMBO J 2011, 30, 2520–2531. [Google Scholar]
- Stancevic, B.; Kolesnick, R. Ceramide-Rich platforms in transmembrane signaling. FEBS Lett 2010, 584, 1728–1740. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolova-Karakashian, M.N.; Rozenova, K.A. Ceramide in stress response. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol 2010, 688, 86–108. [Google Scholar]
- Van Brocklyn, J.R.; Williams, J.B. The control of the balance between ceramide and sphingosine-1-phosphate by sphingosine kinase: Oxidative stress and the seesaw of cell survival and death. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Biochem. Mol. Biol 2012, 163, 26–36. [Google Scholar]
- Gerczuk, P.Z.; Kloner, R.A. An update on cardioprotection: A review of the latest adjunctive therapies to limit myocardial infarction size in clinical trials. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol 2012, 59, 969–978. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, P.D.; Huang, B.W.; Tsuji, Y. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis and redox regulation in cellular signaling. Cell Signal 2012, 24, 981–990. [Google Scholar]
- Milisav, I. Cellular Stress Responses. In Advances in Regenerative Medicine; Wislet-Gendebien, Sabine, Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 215–232. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, F.; Taylor, A. Ubiquitin-Proteasome pathway and cellular responses to oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med 2011, 51, 5–16. [Google Scholar]
- Baumeister, W.; Walz, J.; Zühl, F.; Seemüller, E. The proteasome: Paradigm of a self-compartmentalizing protease. Cell 1998, 92, 367–380. [Google Scholar]
- Strickland, E.; Hakala, K.; Thomas, P.J.; DeMartino, G.N. Recognition of misfolding proteins by PA700, the regulatory subcomplex of the 26S proteasome. J. Biol. Chem 2000, 275, 5565–5572. [Google Scholar]
- Pacifici, R.E.; Salo, D.C.; Davies, K.J. Macroxyproteinase (M.O.P.): A 670 kDa proteinase complex that degrades oxidatively denatured proteins in red blood cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med 1989, 7, 521–536. [Google Scholar]
- Salo, D.C.; Pacifici, R.E.; Lin, S.W.; Giulivi, C.; Davies, K.J. Superoxide dismutase undergoes proteolysis and fragmentation following oxidative modification and inactivation. J. Biol. Chem 1990, 265, 11919–11927. [Google Scholar]
- Shringarpure, R.; Grune, T.; Mehlhase, J.; Davies, K.J. Ubiquitin conjugation is not required for the degradation of oxidized proteins by proteasome. J. Biol. Chem 2003, 278, 311–318. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrington, D.A.; Sun, H.; Murray, K.K.; Costa, J.; Williams, T.D.; Bigelow, D.J.; Squier, T.C. Selective degradation of oxidized calmodulin by the 20S proteasome. J. Biol. Chem 2001, 276, 937–943. [Google Scholar]
- Balog, E.M.; Lockamy, E.L.; Thomas, D.D.; Ferrington, D.A. Site-Specific methionine oxidation initiates calmodulin degradation by the 20S proteasome. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 3005–3016. [Google Scholar]
- Grune, T.; Reinheckel, T.; Davies, K.J. Degradation of oxidized proteins in K562 human hematopoietic cells by proteasome. J. Biol. Chem 1996, 271, 15504–15509. [Google Scholar]
- Grune, T.; Merker, K.; Jung, T.; Sitte, N.; Davies, K.J. Protein oxidation and degradation during postmitotic senescence. Free Radic. Biol. Med 2005, 39, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar]
- Grune, T.; Reinheckel, T.; Joshi, M.; Davies, K.J. Proteolysis in cultured liver epithelial cells during oxidative stress. Role of the multicatalytic proteinase complex, proteasome. J. Biol. Chem 1995, 270, 2344–2351. [Google Scholar]
- Grune, T.; Blasig, I.E.; Sitte, N.; Roloff, B.; Haseloff, R.; Davies, K.J. Peroxynitrite increases the degradation of aconitase and other cellular proteins by proteasome. J. Biol. Chem 1998, 273, 10857–10862. [Google Scholar]
- Sitte, N.; Merker, K.; von Zglinicki, T.; Grune, T.; Davies, K.J. Protein oxidation and degradation during cellular senescence of human BJ fibroblasts: Part I—Effects of proliferative senescence. FASEB J 2000, 14, 2495–2502. [Google Scholar]
- Giulivi, C.; Pacifici, R.E.; Davies, K.J. Exposure of hydrophobic moieties promotes the selective degradation of hydrogen peroxide-modified hemoglobin by the multicatalytic proteinase complex, proteasome. Arch. Biochem. Biophys 1994, 311, 329–341. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, K.J.; Shringarpure, R. Preferential degradation of oxidized proteins by the 20S proteasome may be inhibited in aging and in inflammatory neuromuscular diseases. Neurology 2006, 66, S93–S96. [Google Scholar]
- Hershko, A.; Heller, H.; Eytan, E.; Reiss, Y. The protein substrate binding site of the ubiquitin-protein ligase system. J. Biol. Chem 1986, 261, 11992–11999. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, F.; Nowell, T.R., Jr; Taylor, A. Removal of oxidatively damaged proteins from lens cells by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Exp. Eye Res. 2001, 73, 229–238. [Google Scholar]
- Dudek, E.J.; Shang, F.; Valverde, P.; Liu, Q.; Hobbs, M.; Taylor, A. Selectivity of the ubiquitin pathway for oxidatively modified proteins: Relevance to protein precipitation diseases. FASEB J 2005, 19, 1707–1709. [Google Scholar]
- Iwai, K.; Drake, S.K.; Wehr, N.B.; Weissman, A.M.; LaVaute, T.; Minato, N.; Klausner, R.D.; Levine, R.L.; Rouault, T.A. Iron-Dependent oxidation, ubiquitination, and degradation of iron regulatory protein 2: Implications for degradation of oxidized proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 4924–4928. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.L.; Shang, F.; Nowell, T.R., Jr; Taylor, A. Degradation of differentially oxidized alpha-crystallins in bovine lens epithelial cells. Exp. Eye Res. 1995, 61, 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Yamanaka, K.; Ishikawa, H.; Megumi, Y.; Tokunaga, F.; Kanie, M.; Rouault, T.A.; Morishima, I.; Minato, N.; Ishimori, K.; Iwai, K. Identification of the ubiquitin-protein ligase that recognizes oxidized IRP2. Nat. Cell Biol 2003, 5, 336–340. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.H.; Lee, M.J.; Park, S.; Oh, D.C.; Elsasser, S.; Chen, P.C.; Gartner, C.; Dimova, N.; Hanna, J.; Gygi, S.P.; et al. Enhancement of proteasome activity by a small-molecule inhibitor of USP14. Nature 2010, 467, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Dunten, R.L.; Cohen, R.E. Recognition of modified forms of ribonuclease a by the ubiquitin system. J. Biol. Chem 1989, 264, 16739–16747. [Google Scholar]
- Pacifici, R.E.; Kono, Y.; Davies, K.J. Hydrophobicity as the signal for selective degradation of hydroxyl radical-modified hemoglobin by the multicatalytic proteinase complex, proteasome. J. Biol. Chem 1993, 268, 15405–15411. [Google Scholar]
- Zetterberg, M.; Zhang, X.; Taylor, A.; Liu, B.; Liang, J.J.; Shang, F. Glutathiolation enhances the degradation of gammaC-crystallin in lens and reticulocyte lysates, partially via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci 2006, 47, 3467–3473. [Google Scholar]
- Lasch, P.; Petras, T.; Ullrich, O.; Backmann, J.; Naumann, D.; Grune, T. Hydrogen peroxide-induced structural alterations of RNAse A. J. Biol. Chem 2001, 276, 9492–9502. [Google Scholar]
- Villeneuve, N.F.; Lau, A.; Zhang, D.D. Regulation of the Nrf2-Keap1 antioxidant response by the ubiquitin proteasome system: An insight into cullin-ring ubiquitin ligases. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2010, 13, 1699–1712. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.; Sherratt, P.J.; Huang, H.C.; Yang, C.S.; Pickett, C.B. Increased protein stability as a mechanism that enhances Nrf2-mediated transcriptional activation of the antioxidant response element. Degradation of Nrf2 by the 26 S proteasome. J. Biol. Chem 2003, 278, 4536–4541. [Google Scholar]
- Fengsrud, M.; Roos, N.; Berg, T.; Liou, W.; Slot, J.W.; Seglen, P.O. Ultrastructural and immunocytochemical characterization of autophagic vacuoles in isolated hepatocytes: Effects of vinblastine and asparagine on vacuole distributions. Exp. Cell Res 1995, 221, 504–519. [Google Scholar]
- Orsi, A.; Polson, H.E.; Tooze, S.A. Membrane trafficking events that partake in autophagy. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol 2010, 22, 150–156. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkin, V.; Dikic, I. Ubiquitin networks in cancer. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev 2011, 21, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Mijaljica, D.; Prescott, M.; Devenish, R.J. Microautophagy in mammalian cells: Revisiting a 40-year-old conundrum. Autophagy 2011, 7, 673–682. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.W.; Li, J.; Bao, J.K. Microautophagy: Lesser-Known self-eating. Cell Mol. Life Sci 2012, 69, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Yang, Q.; Mao, Z. Chaperone-Mediated autophagy: Machinery, regulation and biological consequences. Cell Mol. Life Sci 2011, 68, 749–763. [Google Scholar]
- Kaspar, J.W.; Niture, S.K.; Jaiswal, A.K. Nrf2:INrf2 (Keap1) signaling in oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med 2009, 47, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar]
- Venugopal, R.; Jaiswal, A.K. Nrf1 and Nrf2 positively and c-Fos and fra1 negatively regulate the human antioxidant response element-mediated expression of NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase1 gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 14960–14965. [Google Scholar]
- Wild, A.C.; Moinova, H.R.; Mulcahy, R.T. Regulation of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase subunit gene expression by the transcription factor Nrf2. J. Biol. Chem 1999, 274, 33627–33636. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.; Huang, H.C.; Pickett, C.B. Transcriptional regulation of the antioxidant response element. Activation by Nrf2 and repression by MafK. J. Biol. Chem 2000, 275, 15466–15473. [Google Scholar]
- Dikic, I.; Wakatsuki, S.; Walters, K.J. Ubiquitin-binding domains—From structures to functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2009, 10, 659–671. [Google Scholar]
- Moscat, J.; Diaz-Meco, M.T.; Wooten, M.W. Signal integration and diversification through the p62 scaffold protein. Trends Biochem. Sci 2007, 32, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Korolchuk, V.I.; Saiki, S.; Lichtenberg, M.; Siddiqi, F.H.; Roberts, E.A.; Imarisio, S.; Jahreiss, L.; Sarkar, S.; Futter, M.; Menzies, F.M.; et al. Lysosomal positioning coordinates cellular nutrient responses. Nat. Cell Biol 2011, 13, 453–460. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, M.P. How mitochondria produce reactive oxygen species. Biochem. J 2009, 417, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Shacka, J.J.; Roth, K.A.; Zhang, J. The autophagy-lysosomal degradation pathway: Role in neurodegenerative disease and therapy. Front. Biosci 2008, 13, 718–736. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Giordano, S.; Zhang, J. Autophagy, mitochondria and oxidative stress: Cross-Talk and redox signalling. Biochem. J 2012, 441, 523–540. [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta, S.; Peterson, T.R.; Sabatini, D.M. Regulation of the mTOR complex 1 pathway by nutrients, growth factors, and stress. Mol. Cell 2010, 40, 310–322. [Google Scholar]
- De Duve, C.; Wattiaux, R. Functions of lysosomes. Annu. Rev. Physiol 1966, 28, 435–492. [Google Scholar]
- Nowikovsky, K.; Reipert, S.; Devenish, R.J.; Schweyen, R.J. Mdm38 protein depletion causes loss of mitochondrial K+/H+ exchange activity, osmotic swelling and mitophagy. Cell Death Differ 2007, 14, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, P.; Moshitch-Moshkovitz, S.; Kvam, E.; O’Toole, E.; Winey, M.; Goldfarb, D.S. Piecemeal microautophagy of nucleus in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 129–141. [Google Scholar]
- Krick, R.; Muehe, Y.; Prick, T.; Bremer, S.; Schlotterhose, P.; Eskelinen, E.L.; Millen, J.; Goldfarb, D.S.; Thumm, M. Piecemeal microautophagy of the nucleus requires the core macroautophagy genes. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 4492–4505. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, Y.; Koller, A.; Rangell, L.K.; Keller, G.A.; Subramani, S. Peroxisome degradation by microautophagy in Pichia pastoris: Identification of specific steps and morphological intermediates. J. Cell Biol 1998, 141, 625–636. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, W.A., Jr; Cregg, J.M.; Kiel, J.A.; van der Klei, I.J.; Oku, M.; Sakai, Y.; Sibirny, A.A.; Stasyk, O.V.; Veenhuis, M. Pexophagy: The selective autophagy of peroxisomes. Autophagy 2005, 1, 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Dubouloz, F.; Deloche, O.; Wanke, V.; Cameroni, E.; de Virgilio, C. The TOR and EGO protein complexes orchestrate microautophagy in yeast. Mol. Cell 2005, 19, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Agarraberes, F.A.; Dice, J.F. A molecular chaperone complex at the lysosomal membrane is required for protein translocation. J. Cell Sci 2001, 114, 2491–2499. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, H.L.; Terlecky, S.R.; Plant, C.P.; Dice, J.F. A role for a 70-kilodalton heat shock protein in lysosomal degradation of intracellular proteins. Science 1989, 246, 382–385. [Google Scholar]
- Cuervo, A.M.; Dice, J.F. A receptor for the selective uptake and degradation of proteins by lysosomes. Science 1996, 273, 501–503. [Google Scholar]
- Dice, J.F.; Chiang, H.L.; Spencer, E.P.; Backer, J.M. Regulation of catabolism of microinjected ribonuclease A. Identification of residues 7–11 as the essential pentapeptide. J. Biol. Chem 1986, 261, 6853–6859. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, H.L.; Dice, J.F. Peptide sequences that target proteins for enhanced degradation during serum withdrawal. J. Biol. Chem 1988, 263, 6797–6805. [Google Scholar]
- Finn, P.F.; Mesires, N.T.; Vine, M.; Dice, J.F. Effects of small molecules on chaperone-mediated autophagy. Autophagy 2005, 1, 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Kaushik, S.; Massey, A.C.; Mizushima, N.; Cuervo, A.M. Constitutive activation of chaperone-mediated autophagy in cells with impaired macroautophagy. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 2179–2192. [Google Scholar]
- Wing, S.S.; Chiang, H.L.; Goldberg, A.L.; Dice, J.F. Proteins containing peptide sequences related to Lys-Phe-Glu-Arg-Gln are selectively depleted in liver and heart, but not skeletal muscle, of fasted rats. Biochem. J 1991, 275, 165–169. [Google Scholar]
- Kiffin, R.; Christian, C.; Knecht, E.; Cuervo, A.M. Activation of chaperone-mediated autophagy during oxidative stress. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 4829–4840. [Google Scholar]
- Cuervo, A.M.; Dice, J.F. Age-Related decline in chaperone-mediated autophagy. J. Biol. Chem 2000, 275, 31505–31513. [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs, K.A.; Bushell, M.; Willis, A.E. Translational regulation of gene expression during conditions of cell stress. Mol. Cell 2010, 40, 228–237. [Google Scholar]
- Buchberger, A.; Bukau, B.; Sommer, T. Protein quality control in the cytosol and the endoplasmic reticulum: Brothers in arms. Mol. Cell 2010, 40, 238–252. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, A.K.; Sharp, P.A. MicroRNA functions in stress responses. Mol. Cell 2010, 40, 205–215. [Google Scholar]
- Akerfelt, M.; Morimoto, R.I.; Sistonen, L. Heat shock factors: Integrators of cell stress, development and lifespan. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2010, 11, 545–555. [Google Scholar]
- Biamonti, G.; Vourc’h, C. Nuclear stress bodies. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol 2010, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Tollefsbol, T.O. Glucose restriction can extend normal cell lifespan and impair precancerous cell growth through epigenetic control of hTERT and p16 expression. FASEB J 2010, 24, 1442–1453. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, H.Y.; Miller, C.; Bitterman, K.J.; Wall, N.R.; Hekking, B.; Kessler, B.; Howitz, K.T.; Gorospe, M.; de Cabo, R.; Sinclair, D.A. Calorie restriction promotes mammalian cell survival by inducing the SIRT1 deacetylase. Science 2004, 305, 390–392. [Google Scholar]
- Speidel, D. Transcription-Independent p53 apoptosis: An alternative route to death. Trends Cell Biol 2010, 20, 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ak, P.; Levine, A.J. p53 and NF-κB: Different strategies for responding to stress lead to a functional antagonism. FASEB J 2010, 24, 3643–3652. [Google Scholar]
- Brunet, A.; Bonni, A.; Zigmond, M.J.; Lin, M.Z.; Juo, P.; Hu, L.S.; Anderson, M.J.; Arden, K.C.; Blenis, J.; Greenberg, M.E. Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 1999, 96, 857–868. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Nikolaev, A.Y.; Imai, S.; Chen, D.; Su, F.; Shiloh, A.; Guarente, L.; Gu, W. Negative control of p53 by Sir2alpha promotes cell survival under stress. Cell 2001, 107, 137–148. [Google Scholar]
- Langley, E.; Pearson, M.; Faretta, M.; Bauer, U.M.; Frye, R.A.; Minucci, S.; Pelicci, P.G.; Kouzarides, T. Human SIR2 deacetylates p53 and antagonizes PML/p53-induced cellular senescence. EMBO J 2002, 21, 2383–2396. [Google Scholar]
- Vaziri, H.; Dessain, S.K.; Ng Eaton, E.; Imai, S.I.; Frye, R.A.; Pandita, T.K.; Guarente, L.; Weinberg, R.A. hSIR2(SIRT1) functions as an NAD-dependent p53 deacetylase. Cell 2001, 107, 149–159. [Google Scholar]
- Motta, M.C.; Divecha, N.; Lemieux, M.; Kamel, C.; Chen, D.; Gu, W.; Bultsma, Y.; McBurney, M.; Guarente, L. Mammalian SIRT1 represses forkhead transcription factors. Cell 2004, 116, 551–563. [Google Scholar]
- Frescas, D.; Valenti, L.; Accili, D. Nuclear trapping of the forkhead transcription factor FoxO1 via Sirt-dependent deacetylation promotes expression of glucogenetic genes. J. Biol. Chem 2005, 280, 20589–20595. [Google Scholar]
- Tabas, I.; Ron, D. Integrating the mechanisms of apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Nat. Cell Biol 2011, 13, 184–190. [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell, B.; Gutteridge, J.M.C. Antioxidant Defenses: Endogenous and Diet Derived. In Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine, 4th ed; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 79–186. [Google Scholar]
- Poljsak, B. Strategies for reducing or preventing the generation of oxidative stress. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev 2011, 2011, 194586:1–194586:15. [Google Scholar]
- Cheeseman, K.H.; Slater, T.F. An introduction to free radical biochemistry. Br. Med. Bull 1993, 49, 481–493. [Google Scholar]
- Chipuk, J.E.; Moldoveanu, T.; Llambi, F.; Parsons, M.J.; Green, D.R. The BCL-2 family reunion. Mol. Cell 2010, 37, 299–310. [Google Scholar]
- Llambi, F.; Green, D.R. Apoptosis and oncogenesis: Give and take in the BCL-2 family. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev 2011, 21, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Martinou, J.C.; Youle, R.J. Mitochondria in apoptosis: Bcl-2 family members and mitochondrial dynamics. Dev. Cell 2011, 21, 92–101. [Google Scholar]
- Bajwa, N.; Liao, C.; Nikolovska-Coleska, Z. Inhibitors of the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins: A patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat 2012, 22, 37–55. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.X.; Pervaiz, S. BCL-2: Pro-Or anti-oxidant? Front. Biosci. (Elite Ed) 2009, 1, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Laplante, M.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR Signaling. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol 2012, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.M.; Blenis, J. Molecular mechanisms of mTOR-mediated translational control. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2009, 10, 307–318. [Google Scholar]
- Laplante, M.; Sabatini, D.M. An emerging role of mTOR in lipid biosynthesis. Curr. Biol 2009, 19, R1046–R1052. [Google Scholar]
- Laplante, M.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell 2012, 149, 274–293. [Google Scholar]
- McCormick, M.A.; Tsai, S.Y.; Kennedy, B.K. TOR and ageing: A complex pathway for a complex process. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond Biol. Sci 2011, 366, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; McPhee, C.K.; Zheng, L.; Mardones, G.A.; Rong, Y.; Peng, J.; Mi, N.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wan, F.; et al. Termination of autophagy and reformation of lysosomes regulated by mTOR. Nature 2010, 465, 942–946. [Google Scholar]
- Sancak, Y.; Bar-Peled, L.; Zoncu, R.; Markhard, A.L.; Nada, S.; Sabatini, D.M. Ragulator-rag complex targets mTORC1 to the lysosomal surface and is necessary for its activation by amino acids. Cell 2010, 141, 290–303. [Google Scholar]
- Dames, S.A.; Mulet, J.M.; Rathgeb-Szabo, K.; Hall, M.N.; Grzesiek, S. The solution structure of the FATC domain of the protein kinase target of rapamycin suggests a role for redox-dependent structural and cellular stability. J. Biol. Chem 2005, 280, 20558–20564. [Google Scholar]
- Scherz-Shouval, R.; Shvets, E.; Fass, E.; Shorer, H.; Gil, L.; Elazar, Z. Reactive oxygen species are essential for autophagy and specifically regulate the activity of Atg4. EMBO J 2007, 26, 1749–1760. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkland, R.A.; Saavedra, G.M.; Franklin, J.L. Rapid activation of antioxidant defenses by nerve growth factor suppresses reactive oxygen species during neuronal apoptosis: Evidence for a role in cytochrome c redistribution. J. Neurosci 2007, 27, 11315–11326. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkland, R.A.; Adibhatla, R.M.; Hatcher, J.F.; Franklin, J.L. Loss of cardiolipin and mitochondria during programmed neuronal death: Evidence of a role for lipid peroxidation and autophagy. Neuroscience 2002, 115, 587–602. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Azad, M.B.; Gibson, S.B. Superoxide is the major reactive oxygen species regulating autophagy. Cell Death Differ 2009, 16, 1040–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z. p53 regulation of the IGF-1/AKT/mTOR pathways and the endosomal compartment. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol 2010, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toker, A.; Newton, A.C. Cellular signaling: Pivoting around PDK-1. Cell 2000, 103, 185–188. [Google Scholar]
- Datta, S.R.; Dudek, H.; Tao, X.; Masters, S.; Fu, H.; Gotoh, Y.; Greenberg, M.E. Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell 1997, 91, 231–241. [Google Scholar]
- Verdin, E.; Hirschey, M.D.; Finley, L.W.; Haigis, M.C. Sirtuin regulation of mitochondria: Energy production, apoptosis, and signaling. Trends Biochem. Sci 2010, 35, 669–675. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.J.; Defossez, P.A.; Guarente, L. Requirement of NAD and SIR2 for life-span extension by calorie restriction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science 2000, 289, 2126–2128. [Google Scholar]
- Bordone, L.; Cohen, D.; Robinson, A.; Motta, M.C.; van Veen, E.; Czopik, A.; Steele, A.D.; Crowe, H.; Marmor, S.; Luo, J.; et al. SIRT1 transgenic mice show phenotypes resembling calorie restriction. Aging Cell 2007, 6, 759–767. [Google Scholar]
- Kanfi, Y.; Peshti, V.; Gozlan, Y.M.; Rathaus, M.; Gil, R.; Cohen, H.Y. Regulation of SIRT1 protein levels by nutrient availability. FEBS Lett 2008, 582, 2417–2423. [Google Scholar]
- Crujeiras, A.B.; Parra, D.; Goyenechea, E.; Martínez, J.A. Sirtuin gene expression in human mononuclear cells is modulated by caloric restriction. Eur. J. Clin. Invest 2008, 38, 672–678. [Google Scholar]
- Wakeling, L.A.; Ions, L.J.; Ford, D. Could Sirt1-mediated epigenetic effects contribute to the longevity response to dietary restriction and be mimicked by other dietary interventions? Age (Dordr) 2009, 31, 327–341. [Google Scholar]
- Schilling, M.M.; Oeser, J.K.; Boustead, J.N.; Flemming, B.P.; O’Brien, R.M. Gluconeogenesis: Re-evaluating the FOXO1-PGC-1alpha connection. Nature 2006, 443, E10–E11. [Google Scholar]
- Vega, R.B.; Huss, J.M.; Kelly, D.P. The coactivator PGC-1 cooperates with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha in transcriptional control of nuclear genes encoding mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation enzymes. Mol. Cell Biol 2000, 20, 1868–1876. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, D.P.; Scarpulla, R.C. Transcriptional regulatory circuits controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and function. Genes Dev 2004, 18, 357–368. [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein, B.; Lane, D.; Levine, A.J. Surfing the p53 network. Nature 2000, 408, 307–310. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, A.J.; Feng, Z.; Mak, T.W.; You, H.; Jin, S. Coordination and communication between the p53 and IGF-1-AKT-TOR signal transduction pathways. Genes Dev 2006, 20, 267–275. [Google Scholar]
- Buckbinder, L.; Talbott, R.; Velasco-Miguel, S.; Takenaka, I.; Faha, B.; Seizinger, B.R.; Kley, N. Induction of the growth inhibitor IGF-binding protein 3 by p53. Nature 1995, 377, 646–649. [Google Scholar]
- Stambolic, V.; MacPherson, D.; Sas, D.; Lin, Y.; Snow, B.; Jang, Y.; Benchimol, S.; Mak, T.W. Regulation of PTEN transcription by p53. Mol. Cell 2001, 8, 317–325. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Levine, A.J.; Jin, S. The coordinate regulation of the p53 and mTOR pathways in cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 8204–8209. [Google Scholar]
- Ditch, S.; Paull, T.T. The ATM protein kinase and cellular redox signaling: Beyond the DNA damage response. Trends Biochem. Sci 2012, 37, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Barzilai, A.; Rotman, G.; Shiloh, Y. ATM deficiency and oxidative stress: A new dimension of defective response to DNA damage. DNA Repair. (Amst) 2002, 1, 3–25. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, M.; Rosin, M.P.; Anderson, C.K. Response of fibroblast cultures from ataxia-telangiectasia patients to oxidative stress. Cancer Lett 1990, 54, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, A.J.; Olive, P.L.; Burr, A.H.; Rosin, M.P. Response of fibroblast cultures from ataxia-telangiectasia patients to reactive oxygen species generated during inflammatory reactions. Environ. Mol. Mutagen 1994, 24, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Shackelford, R.E.; Innes, C.L.; Sieber, S.O.; Heinloth, A.N.; Leadon, S.A.; Paules, R.S. The ataxia telangiectasia gene product is required for oxidative stress-induced G1 and G2 checkpoint function in human fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem 2001, 276, 21951–21959. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Kozlov, S.; Lavin, M.F.; Person, M.D.; Paull, T.T. ATM activation by oxidative stress. Science 2010, 330, 517–521. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, R.J. LKB1 and AMP-activated protein kinase control of mTOR signalling and growth. Acta Physiol. (Oxf) 2009, 196, 65–80. [Google Scholar]
- Peretz, S.; Jensen, R.; Baserga, R.; Glazer, P.M. ATM-Dependent expression of the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor in a pathway regulating radiation response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 1676–1681. [Google Scholar]
- Shahrabani-Gargir, L.; Pandita, T.K.; Werner, H. Ataxia-Telangiectasia mutated gene controls insulin-like growth factor I receptor gene expression in a deoxyribonucleic acid damage response pathway via mechanisms involving zinc-finger transcription factors Sp1 and WT1. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 5679–5687. [Google Scholar]
- Armata, H.L.; Golebiowski, D.; Jung, D.Y.; Ko, H.J.; Kim, J.K.; Sluss, H.K. Requirement of the ATM/p53 tumor suppressor pathway for glucose homeostasis. Mol. Cell Biol 2010, 30, 5787–5794. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, A.; Cai, S.L.; Kim, J.; Nanez, A.; Sahin, M.; MacLean, K.H.; Inoki, K.; Guan, K.L.; Shen, J.; Person, M.D.; et al. ATM signals to TSC2 in the cytoplasm to regulate mTORC1 in response to ROS. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4153–4158. [Google Scholar]
- Cam, H.; Easton, J.B.; High, A.; Houghton, P.J. mTORC1 signaling under hypoxic conditions is controlled by ATM-dependent phosphorylation of HIF-1α. Mol. Cell 2010, 40, 509–520. [Google Scholar]
- Mattson, M.P. Hormesis defined. Ageing Res. Rev 2008, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Spitz, D.R.; Dewey, W.C.; Li, G.C. Hydrogen peroxide or heat shock induces resistance to hydrogen peroxide in Chinese hamster fibroblasts. J. Cell Physiol 1987, 131, 364–373. [Google Scholar]
- Laval, F. Pretreatment with oxygen species increases the resistance of mammalian cells to hydrogen peroxide and gamma-rays. Mutat. Res 1988, 201, 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Cortés, F.; Dominguez, I.; Piñero, J.; Mateos, J.C. Adaptive response in human lymphocytes conditioned with hydrogen peroxide before irradiation with X-rays. Mutagenesis 1990, 5, 555–557. [Google Scholar]
- Rattan, S.I. Hormesis in aging. Aging Res. Rev 2008, 7, 63–78. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Mao, H.P.; Ruchalski, K.L.; Wang, Y.H.; Choy, W.; Schwartz, J.H.; Borkan, S.C. Heat stress prevents mitochondrial injury in ATP-depleted renal epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol 2002, 283, C917–C926. [Google Scholar]
- Lithgow, G.J.; White, T.M.; Melov, S.; Johnson, T.E. Thermotolerance and extended life-span conferred by single-gene mutations and induced by thermal stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 7540–7544. [Google Scholar]
- Le Bourg, E. A cold stress applied at various ages can increase resistance to heat and fungal infection in aged Drosophila melanogaster flies. Biogerontology 2011, 12, 185–193. [Google Scholar]
- Le Bourg, E. Hormetic effects of repeated exposures to cold at young age on longevity, aging and resistance to heat or cold shocks in Drosophila melanogaster. Biogerontology 2007, 8, 431–444. [Google Scholar]
- Korde, A.S.; Pettigrew, L.C.; Craddock, S.D.; Maragos, W.F. The mitochondrial uncoupler 2,4-dinitrophenol attenuates tissue damage and improves mitochondrial homeostasis following transient focal cerebral ischemia. J. Neurochem 2005, 94, 1676–1684. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.F.; Akaike, T. Dimethyl sulfoxide induces multilayer aggregates and prolongs survival of primary cultured hepatocytes. Biotechnol. Technol 1997, 11, 869–872. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, H.K.; Plyley, M.J.; Rodgers, C.D.; McKee, N.H. Skeletal muscle damage in the rat hindlimb following single or repeated daily bouts of downhill exercise. Int. J. Sports Med 1997, 18, 94–100. [Google Scholar]
- Bowles, D.K.; Farrar, R.P.; Starnes, J.W. Exercise training improves cardiac function after ischemia in the isolated, working rat heart. Am. J. Physiol 1992, 263, H804–H809. [Google Scholar]
- Holloszy, J.O. Exercise increases average longevity of female rats despite increased food intake and no growth retardation. J. Gerontol 1993, 48, B97–B100. [Google Scholar]
- Lennon, S.L.; Quindry, J.C.; French, J.P.; Kim, S.; Mehta, J.L.; Powers, S.K. Exercise and myocardial tolerance to ischaemia-reperfusion. Acta Physiol. Scand 2004, 182, 161–169. [Google Scholar]
- Ramires, P.R.; Ji, L.L. Glutathione supplementation and training increases myocardial resistance to ischemia-reperfusion in vivo. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol 2001, 281, H679–H688. [Google Scholar]
- Paffenbarger, R.S., Jr; Hyde, R.T.; Wing, A.L.; Lee, I.M.; Jung, D.L.; Kampert, J.B. The association of changes in physical-activity level and other lifestyle characteristics with mortality among men. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 538–545. [Google Scholar]
- Kavazis, A.N. Exercise preconditioning of the myocardium. Sports Med 2009, 39, 923–935. [Google Scholar]
- Mary, P.; Sautour, M.; Chihib, N.E.; Tierny, Y.; Hornez, J.P. Tolerance and starvation induced cross-protection against different stresses in Aeromonas hydrophila. Int. J. Food Microbiol 2003, 87, 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, D.E.; Schultz, J.E.; Matin, A. Starvation-Induced cross protection against heat or H2O2 challenge in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol 1988, 170, 3910–3914. [Google Scholar]
- Hartke, A.; Bouche, S.; Gansel, X.; Boutibonnes, P.; Auffray, Y. Starvation-Induced stress resistance in lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis IL1403. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 1994, 60, 3474–3478. [Google Scholar]
- Colman, R.J.; Anderson, R.M.; Johnson, S.C.; Kastman, E.K.; Kosmatka, K.J.; Beasley, T.M.; Allison, D.B.; Cruzen, C.; Simmons, H.A.; Kemnitz, J.W.; et al. Caloric restriction delays disease onset and mortality in rhesus monkeys. Science 2009, 325, 201–204. [Google Scholar]
- Willcox, D.C.; Willcox, B.J.; Todoriki, H.; Curb, J.D.; Suzuki, M. Caloric restriction and human longevity: What can we learn from the Okinawans? Biogerontology 2006, 7, 173–177. [Google Scholar]
- Minois, N. The hormetic effects of hypergravity on longevity and aging. Dose Response 2006, 4, 145–154. [Google Scholar]
- Pribenszky, C.; Molnár, M.; Cseh, S.; Solti, L. Improving post-thaw survival of cryopreserved mouse blastocysts by hydrostatic pressure challenge. Anim. Reprod. Sci 2005, 87, 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Lin, L.; Schmidt, M.; Bøgh, I.B.; Kragh, P.M.; Sørensen, C.B.; Li, J.; Purup, S.; Pribenszky, C.; Molnár, M.; et al. High hydrostatic pressure treatment of porcine oocytes before handmade cloning improves developmental competence and cryosurvival. Cloning Stem Cells 2008, 10, 325–330. [Google Scholar]
- Siqueira Filho, E.; Caixeta, E.S.; Pribenszky, C.; Molnar, M.; Horvath, A.; Harnos, A.; Franco, M.M.; Rumpf, R. Vitrification of bovine blastocysts pretreated with sublethal hydrostatic pressure stress: Evaluation of post-thaw in vitro development and gene expression. Reprod. Fertil. Dev 2011, 23, 585–590. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.Y.; Pribenszky, C.; Kuo, Y.H.; Teng, S.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Chung, M.T.; Chiu, Y.F. Hydrostatic pressure pre-treatment affects the protein profile of boar sperm before and after freezing-thawing. Anim. Reprod. Sci 2009, 112, 136–149. [Google Scholar]
- Pribenszky, C.; Horváth, A.; Végh, L.; Huang, S.Y.; Kuo, Y.H.; Szenci, O. Stress preconditioning of boar spermatozoa: A new approach to enhance semen quality. Reprod. Domest. Anim 2011, 46, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Torii, T.; Miyazawa, M.; Koyama, I. Effect of continuous application of shear stress on liver tissue: Continuous application of appropriate shear stress has advantage in protection of liver tissue. Transplant. Proc 2005, 37, 4575–4578. [Google Scholar]
- Rhee, S.G. Redox signaling: Hydrogen peroxide as intracellular messenger. Exp. Mol. Med 1999, 31, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.; Maulik, N.; Moraru, I.I.; Kreutzer, D.L.; Das, D.K. Molecular adaptation of vascular endothelial cells to oxidative stress. Am. J. Physiol 1993, 264, C715–7C22. [Google Scholar]
- Sen Gupta, S.; Bhattacharjee, S.B. Induction of repair functions by hydrogen peroxide in Chinese hamster cells. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. Relat. Stud. Phys. Chem. Med 1988, 53, 935–942. [Google Scholar]
- Sciandra, J.J.; Subjeck, J.R.; Hughes, C.S. Induction of glucose-regulated proteins during anaerobic exposure and of heat-shock proteins after reoxygenation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 4843–4847. [Google Scholar]
- Currie, R.W. Effects of ischemia and perfusion temperature on the synthesis of stress-induced (heat shock) proteins in isolated and perfused rat hearts. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol 1987, 19, 795–808. [Google Scholar]
- Turrens, J.F.; Crapo, J.D.; Freeman, B.A. Protection against oxygen toxicity by intravenous injection of liposome-entrapped catalase and superoxide dismutase. J. Clin. Invest 1984, 73, 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Gille, J.J.; Joenje, H. Chromosomal instability and progressive loss of chromosomes in HeLa cells during adaptation to hyperoxic growth conditions. Mutat. Res 1989, 219, 225–230. [Google Scholar]
- Kurapati, R.; Passananti, H.B.; Rose, M.R.; Tower, J. Increased hsp22 RNA levels in Drosophila lines genetically selected for increased longevity. J. Gerontol. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci 2000, 55, B552–B559. [Google Scholar]
- Morrow, G.; Battistini, S.; Zhang, P.; Tanguay, R.M. Decreased lifespan in the absence of expression of the mitochondrial small heat shock protein Hsp22 in Drosophila. J. Biol. Chem 2004, 279, 43382–43385. [Google Scholar]
- Préville, X.; Salvemini, F.; Giraud, S.; Chaufour, S.; Paul, C.; Stepien, G.; Ursini, M.V.; Arrigo, A.P. Mammalian small stress proteins protect against oxidative stress through their ability to increase glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity and by maintaining optimal cellular detoxifying machinery. Exp. Cell Res 1999, 247, 61–78. [Google Scholar]
- Lithgow, G.J.; Walker, G.A. Stress resistance as a determinate of C. elegans lifespan. Mech. Ageing Dev 2002, 123, 765–771. [Google Scholar]
- Mattson, M.P.; Cheng, A. Neurohormetic phytochemicals: Low-Dose toxins that induce adaptive neuronal stress responses. Trends Neurosci 2006, 29, 632–639. [Google Scholar]
- Raskin, I.; Ribnicky, D.M.; Komarnytsky, S.; Ilic, N.; Poulev, A.; Borisjuk, N.; Brinker, A.; Moreno, D.A.; Ripoll, C.; Yakoby, N.; et al. Plants and human health in the twenty-first century. Trends Biotechnol 2002, 20, 522–531. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, L.; Odhav, B.; Bhoola, K.D. Natural products for cancer prevention: A global perspective. Pharmacol. Ther 2003, 99, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Bravo, L. Polyphenols: Chemistry, dietary sources, metabolism, and nutritional significance. Nutr. Rev 1998, 56, 317–333. [Google Scholar]
- Sohal, R.S.; Weindruch, R. Oxidative stress, caloric restriction, and aging. Science 1996, 273, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Valko, M.; Izakovic, M.; Mazur, M.; Rhodes, C.J.; Telser, J. Role of oxygen radicals in DNA damage and cancer incidence. Mol. Cell Biochem 2004, 266, 37–56. [Google Scholar]
- Barbaste, M.; Berké, B.; Dumas, M.; Soulet, S.; Delaunay, J.C.; Castagnino, C.; Arnaudinaud, V.; Chèze, C.; Vercauteren, J. Dietary antioxidants, peroxidation and cardiovascular risks. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2002, 6, 209–223. [Google Scholar]
- Butterfield, D.A.; Castegna, A.; Drake, J.; Scapagnini, G.; Calabrese, V. Vitamin E and neurodegenerative disorders associated with oxidative stress. Nutr. Neurosci 2002, 5, 229–239. [Google Scholar]
- Kline, K.; Lawson, K.A.; Yu, W.; Sanders, B.G. Vitamin E and cancer. Vitam. Horm 2007, 76, 435–461. [Google Scholar]
- Riccioni, G.; Bucciarelli, T.; Mancini, B.; Di Ilio, C.; Capra, V.; D’Orazio, N. The role of the antioxidant vitamin supplementation in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2007, 16, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Poljsak, B.; Milisav, I. The neglected significance of “antioxidative stress”. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev 2012, 2012, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Soobrattee, M.A.; Bahorun, T.; Aruoma, O.I. Chemopreventive actions of polyphenolic compounds in cancer. Biofactors 2006, 27, 19–35. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Noyan Ashraf, M.H.; Facci, M.; Wang, R.; Paterson, P.G.; Ferrie, A.; Juurlink, B.H. Dietary approach to attenuate oxidative stress, hypertension, and inflammation in the cardiovascular system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 7094–7099. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.S.; Surh, Y.J. Nrf2 as a novel molecular target for chemoprevention. Cancer Lett 2005, 224, 171–184. [Google Scholar]
- Bautista, D.M.; Movahed, P.; Hinman, A.; Axelsson, H.E.; Sterner, O.; Högestätt, E.D.; Julius, D.; Jordt, S.E.; Zygmunt, P.M. Pungent products from garlic activate the sensory ion channel TRPA1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 12248–12252. [Google Scholar]
- Yellon, D.M.; Downey, J.M. Preconditioning the myocardium: From cellular physiology to clinical cardiology. Physiol. Rev 2003, 83, 1113–11151. [Google Scholar]
- Pong, K. Ischaemic preconditioning: Therapeutic implications for stroke? Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2004, 8, 125–139. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.Z.; Tang, X.L.; Park, S.W.; Qiu, Y.; Turrens, J.F.; Bolli, R. Evidence for an essential role of reactive oxygen species in the genesis of late preconditioning against myocardial stunning in conscious pigs. J. Clin. Invest 1996, 97, 562–576. [Google Scholar]
- Abete, P.; Rengo, F. Mild Stress in the Aging Heart. Role of Ischemic Preconditioning. In Mild Stress and Healthy Aging; Le Bourg, E., Rattan, S., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 139–156. [Google Scholar]
- Raeburn, C.D.; Zimmerman, M.A.; Banerjee, A.; Cleveland, C.J., Jr; Harken, A.H. Surgical applications of organ preconditioning. Min. Chir. 2004, 59, 209–218. [Google Scholar]
- Rietjens, S.J.; Beelen, M.; Koopman, R.; van Loon, L.J.; Bast, A.; Haenen, G.R. A single session of resistance exercise induces oxidative damage in untrained men. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc 2007, 39, 2145–2151. [Google Scholar]
- Hollander, J.; Fiebig, R.; Gore, M.; Bejma, J.; Ookawara, T.; Ohno, H.; Ji, L.L. Superoxide dismutase gene expression in skeletal muscle: Fiber-Specific adaptation to endurance training. Am. J. Physiol 1999, 277, R856–R862. [Google Scholar]
- Stupka, N.; Tarnopolsky, M.A.; Yardley, N.J.; Phillips, S.M. Cellular adaptation to repeated eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage. J. Appl. Physiol 2001, 91, 1669–1678. [Google Scholar]
- Powers, S.K.; Ji, L.L.; Leeuwenburgh, C. Exercise training-induced alterations in skeletal muscle antioxidant capacity: A brief review. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc 1999, 31, 987–997. [Google Scholar]
- Radák, Z.; Pucsuk, J.; Boros, S.; Josfai, L.; Taylor, A.W. Changes in urine 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine levels of super-marathon runners during a four-day race period. Life Sci 2000, 66, 1763–1767. [Google Scholar]
- Vasankari, T.J.; Kujala, U.M.; Vasankari, T.M.; Vuorimaa, T.; Ahotupa, M. Effects of acute prolonged exercise on-serum and LDL oxidation and antioxidant defences. Free Radic. Biol. Med 1997, 22, 509–513. [Google Scholar]
- Radak, Z.; Chung, H.Y.; Goto, S. Exercise and hormesis: Oxidative stress-related adaptation for successful aging. Biogerontology 2005, 6, 71–75. [Google Scholar]
- McCay, C.M.; Crowell, M.F.; Maynard, L.A. The effect of retarded growth upon the length of life span and upon the ultimate body size. 1935. Nutrition 1989, 5, 155–171. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, P.K.; Soare, A.; Meyer, T.E.; Cangemi, R.; Holloszy, J.O.; Fontana, L. Caloric restriction may reverse age-related autonomic decline in humans. Aging Cell 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bourg, E.; Fournier, D. Is lifespan extension accompanied by improved antioxidant defences? A study of superoxide dismutase and catalase in Drosophila melanogaster flies that lived in hypergravity at a young age. Biogerontology 2004, 5, 261–266. [Google Scholar]
- Le Bourg, E.; Valenti, P.; Payre, F. Lack of hypergravity-associated longevity extension in Drosophila melanogaster flies overexpressing hsp70. Biogerontology 2002, 3, 355–364. [Google Scholar]
- Poljšak, B.; Milisav, I. Clinical implications of cellular stress responses. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci 2012, 12, 122–126. [Google Scholar]
- Murry, C.E.; Richard, V.J.; Reimer, K.A.; Jennings, R.B. Ischemic preconditioning slows energy metabolism and delays ultrastructural damage during a sustained ischemic episode. Circ. Res 1990, 66, 913–931. [Google Scholar]
- Murry, C.E.; Jennings, R.B.; Reimer, K.A. Preconditioning with ischemia: A delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation 1986, 74, 1124–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Vander Heide, R. Clinically useful cardioprotection: Ischemic preconditioning then and now. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther 2011, 16, 251–254. [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks, S.L.; Brambrink, A.M. Preconditioning and postconditioning for neuroprotection: The most recent evidence. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol 2010, 24, 521–534. [Google Scholar]
- Shihab, F.S. Preconditioning: From experimental findings to novel therapies in acute kidney injury. Min. Urol. Nefrol 2009, 61, 143–157. [Google Scholar]
- Theodoraki, K.; Tympa, A.; Karmaniolou, I.; Tsaroucha, A.; Arkadopoulos, N.; Smyrniotis, V. Ischemia/reperfusion injury in liver resection: A review of preconditioning methods. Surg. Today 2011, 41, 620–629. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Z.M.; Wu, B.; Zhang, W.Q.; Lu, X.J.; Lin, Y.C.; Geng, Y.J.; Miao, Y.F. Neuroprotective effects of ischemic preconditioning and postconditioning on global brain ischemia in rats through the same effect on inhibition of apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2012, 13, 6089–6101. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, C.; Tillack, D.; Simonis, G.; Strasser, R.H.; Weinbrenner, C. Ischemic post-conditioning reduces infarct size of the in vivo rat heart: Role of PI3-K, mTOR, GSK-3beta, and apoptosis. Mol. Cell Biochem 2010, 339, 135–147. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.Q.; Corvera, J.S.; Halkos, M.E.; Kerendi, F.; Wang, N.P.; Guyton, R.A.; Vinten-Johansen, J. Inhibition of myocardial injury by ischemic postconditioning during reperfusion: Comparison with ischemic preconditioning. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol 2003, 285, H579–H588. [Google Scholar]
- Alreja, G.; Bugano, D.; Lotfi, A. Effect of remote ischemic preconditioning on myocardial and renal injury: Meta-Analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Invasive Cardiol 2012, 24, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Naesens, M. Replicative senescence in kidney aging, renal disease, and renal transplantation. Discov. Med 2011, 11, 65–75. [Google Scholar]
- Pribenszky, C.; Vajta, G. Cells under pressure: How sublethal hydrostatic pressure stress treatment increases gametes’ and embryos’ performance. Reprod. Fertil. Dev 2011, 23, 48–55. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.K.; Netland, P.A.; Kedrov, M.A.; Johnson, D.A. Preconditioning protects the retinal pigment epithelium cells from oxidative stress-induced cell death. Acta Ophthalmol 2009, 87, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- Uchida, Y.; Tamaki, T.; Tanaka, M.; Kaizu, T.; Tsuchihashi, S.; Takahashi, T.; Kawamura, A.; Kakita, A. Induction of specific stress response increases resistance of rat liver allografts to cold ischemia and reperfusion injury. Transplant. Int 2003, 16, 396–404. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, E.M.; Sharpe, E.; Bellamy, C.O.; McNally, S.J.; Devey, L.; Garden, O.J.; Ross, J.A.; Wigmore, S.J. Heat shock protein 90-binding agents protect renal cells from oxidative stress and reduce kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol 2008, 295, F397–F405. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, T.; Huang, W.; Wang, T.; Qian, J.; Xu, M.; Kranias, E.G.; Wang, Y.; Fan, G.C. Hsp20-engineered mesenchymal stem cells are resistant to oxidative stress via enhanced activation of Akt and increased secretion of growth factors. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 3021–3031. [Google Scholar]

| Stressor | Cell Type/Organism | Cross-Resistance | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| H2O2 | CHO cells | Heat shock | [143] |
| N-methyl-N′-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine (MNNG) | [144] | ||
| γ-ray irradiation | [144] | ||
| Human lymphocytes | X-ray irradiation | [145] | |
| Heat | CHO cells | H2O2 | [143] |
| Human skin fibroblasts | Delayed aging | [146] | |
| Renal epithelial cells | Cyanide | [147] | |
| C. elegans | Increased lifespan | [148] | |
| Cold | Drosophila melanogaster | Heat stress | [149,150] |
| Increased lifespan, delayed aging | [150] | ||
| Chemicals | |||
| Xanthine and xanthine oxidase | CHO cells | H2O2 and γ-irradiation | [144] |
| Rat hepatoma cells | H2O2 and γ-irradiation | [144] | |
| 2,4-dinitrophenol | Rat brain cells | Ischemia | [151] |
| Dimethyl sulfoxide | Hepatocytes | Improved survival | [152] |
| Exercise | Rat skeletal muscle | Oxidative stress | [153] |
| Rat heart | Ischemia | [154] | |
| Rats | Delayed aging | [155] | |
| Ischemia | [156,157] | ||
| Humans | Delayed aging | [158] | |
| Ischemia | [159] | ||
| Caloric restriction | Aeromonas hydrophila | Lowered temperature, sodium, and ethanol stresses | [160] |
| Escherichia coli | Heat stress and H2O2 | [161] | |
| Lactococcus lactis subsp. Lactis | Heat, ethanol, acid, osmotic, and oxidative stresses | [162] | |
| Rhesus monkeys | Delayed aging | [163] | |
| Humans | Delayed aging | [164] | |
| Hypergravity | Drosophyla sp. | Thermotolerance | [150] |
| Longevity, delayed aging | [150,165] | ||
| Hydrostatic pressure | Mouse blastocysts | Improved survival | [166] |
| Pig oocytes | Improved survival | [167,168] | |
| Bull, boar spermatozoa | Improved semen quality | [169,170] | |
| Shear forces | Liver tissue | Improved survival | [171] |
© 2012 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Milisav, I.; Poljsak, B.; Šuput, D. Adaptive Response, Evidence of Cross-Resistance and Its Potential Clinical Use. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 10771-10806. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms130910771
Milisav I, Poljsak B, Šuput D. Adaptive Response, Evidence of Cross-Resistance and Its Potential Clinical Use. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2012; 13(9):10771-10806. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms130910771
Chicago/Turabian StyleMilisav, Irina, Borut Poljsak, and Dušan Šuput. 2012. "Adaptive Response, Evidence of Cross-Resistance and Its Potential Clinical Use" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 13, no. 9: 10771-10806. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms130910771