High Genetic Diversity and Low Differentiation of Michelia coriacea (Magnoliaceae), a Critically Endangered Endemic in Southeast Yunnan, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
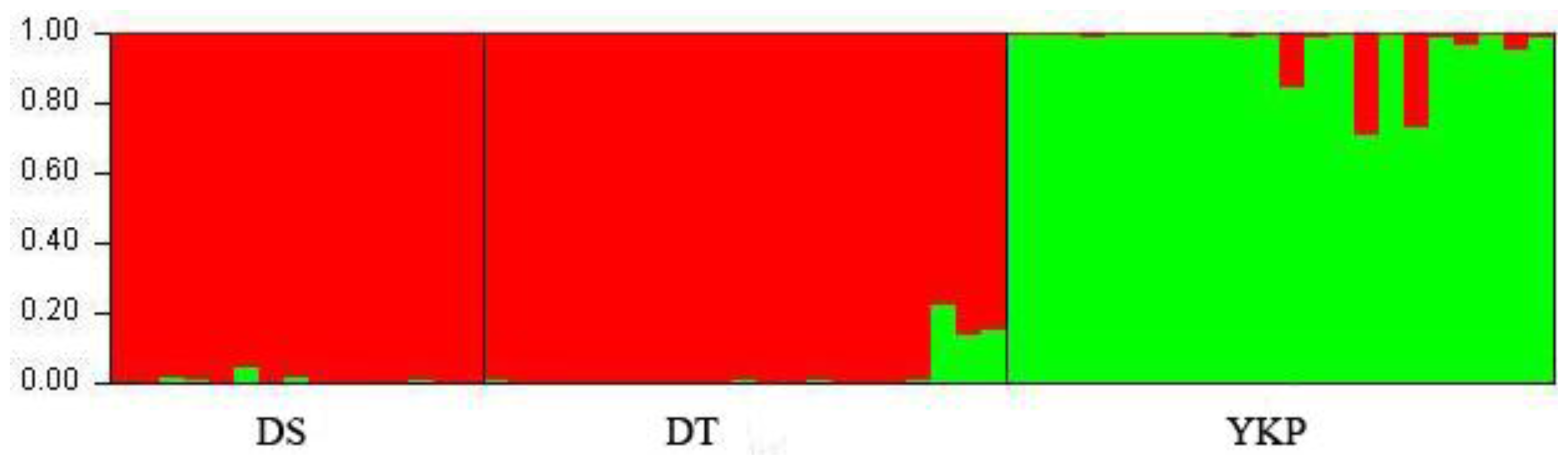
2.1. Genetic Diversity and Genetic Structure Investigated by ISSR Markers
2.2. Genetic Diversity and Genetic Divergence Based on SSR Markers
3. Discussion
3.1. Genetic Diversity in M. coriacea
3.2. Variation Between Populations
3.3. Conservation
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. The Study Species and Sampling Procedures
4.2. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
4.3. Data Analysis
4.3.1. ISSR Data
4.3.2. SSR Data
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Frankel, O.H.; Soulé, M.E. Conservation and Evolution; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Kingston, N.; Waldren, S.; Smyth, N. Conservation genetics and ecology of Angiopteris chauliodonta Copel. (Marattiaceae), a critically endangered fern from Pitcairn Island, South Central Pacific Ocean. Biol. Conserv 2004, 117, 309–319. [Google Scholar]
- Lande, R.; Barrowclough, G.F. Effective Population Size, Genetic Variation, and Their Use in Population Management. In Viable Populations for Conservation; Soulé, M.E., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1987; pp. 87–123. [Google Scholar]
- Rossetto, M.; Weaver, P.K.; Dixon, K.W. Use of RAPD analysis in devising conservation strategies for the rare and endangered Grevillea scapigera. Mol. Ecol 1995, 4, 321–329. [Google Scholar]
- Godt, M.J.W.; Caplow, F.; Hamrick, J.L. Allozyme diversity in the federally threatened olden paintbrush, Castilleya levisecta (Scrophulariaceae). Conserv. Genet 2005, 6, 87–99. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.H.; Chen, J.M.; Gituru, R.W.; Wang, Q.F. Gene flow in populations of the endangered aquatic fern Ceratopteris pteridoides in China as revealed by ISSR markers. Aquat. Bot 2007, 87, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Hamrick, J.L.; Godt, M.J. Effects of life history traits on genetic diversity in plant species. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B 1996, 351, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Loveless, M.D.; Hamrick, J.L. Ecological determinants of genetic structure of plant populations. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst 1984, 15, 65–95. [Google Scholar]
- Bauert, M.R.; Kalin, M.; Baltisberger, M.; Edwards, P.J. No genetic variation detected within isolated relic populations of Saxifraga cernua in the Alps using RAPD markers. Mol. Ecol 1998, 7, 1519–1527. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, X.H.; Ye, Q.G.; Kang, M.; Huang, H.W. Microsatellite analysis reveals interpopulation differention and gene flow in endangered tree Changiostyrax dolichocarpa (Styracaceae) with fragmented distribution in central China. New Phytol 2007, 176, 472–480. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, S.S.; Chiang, T.Y.; Gong, X. High genetic diversity vs. low genetic differentiation in Nouelia insignis (Asteraceae), a narrowly distributed and endemic species in China, revealed by ISSR fingerprinting. Ann. Bot 2006, 98, 583–589. [Google Scholar]
- Schaal, B.A.; Leverich, W.J.; Rogstad, S.H. Comparison of Methods for Assessing Genetic Variation in Plant Conservation Biology. In Genetics and Conservation of Rare Plants; Falk, D.A., Holsinger, K.E., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 123–134. [Google Scholar]
- Cicuzza, D.; Newton, A.; Oldfield, S. The Red List of Magnoliaceae; Fauna & Flora International: Cambridge, UK, 2007; p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.B.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, L.; Magin, G. Chinese magnolias—It’s mostly as bad as we thought. Oryx 2007, 41, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.L. Four new species of Michelia from Yunnan. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 1987, 3, 86–91. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.Y.; Zhu, Y.C.; Jiang, H.C. The Vegetation of Yunnan; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Shui, Y.M.; Cheng, Y.H. The Plants of Honghe Region, Yunnan; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.B.; Yan, Lu. Unpublished Report on Global Tree Compaign Fieldwork in China; FFI: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.F. Conservation Biology of the Critically Endangered Plant, Michelia coriacea. Master Thesis, The Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zawko, G.; Krauss, S.L.; Dixon, K.W.; Sivasithamparam, K. Conservation genetics of the rare and endangered Leucopogon obtectus (Ericaceae). Mol. Ecol 2001, 10, 2389–2396. [Google Scholar]
- Budak, H.; Pedraza, F.; Baenziger, P.S.; Cregan, P.B.; Dweikat, I. Development and utilization of SSR to estimate genetic diversity in a collection of pearl millet germplasm. Crop Sci 2003, 43, 2284–2290. [Google Scholar]
- Nybom, H. Comparison of different nuclear DNA markers for estimating intraspecific genetic diversity in plants. Mol. Ecol 2004, 13, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, W.F.; Xia, N.H.; Deng, Y.F.; Zheng, Q.Y. Study on genetic diversity of Manglietia deciduas (Magnoliaceae). Acta Bot. Yunnanica 2004, 26, 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi, S.; Ysagi, Y. SSR genetic variation in small and isolated populations of Magnolia sieboldii spp. japonica. Heredity 2002, 88, 313–321. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.F.; Hamrick, J.L.; Godt, M.J.W. High genetic diversity in Sarracenia leucophylla (Sarraceniaceae), a carnivorous wetland herb. J. Hered 2004, 95, 234–243. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Q.; Zhang, C.Q.; Milne, R.I. Population genetics and breeding system of Tupistra pingbianensis (Liliaceae), a naturally rare plant endemic to SW China. J. Syst. Evol 2010, 48, 47–57. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, Y.C.; Hung, K.H.; Schaal, B.A.; Ge, X.J.; Hsu, T.W.; Chaing, T.Y. Contrasting phylogeographical patterns between mainland and island taxa of the Pinus luchuensis complex. Mol. Ecol 2006, 15, 765–779. [Google Scholar]
- Maguire, T.L.; Sedgley, M. Genetic diversity in Banksia and Dryandra (Proteaceae) with emphasis on Banksia cuneata, a rare and endangered species. Heredity 1997, 79, 394–401. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.H.; Wu, R.F. Magnoliaceae. Flora Popularis Reipublicea Sinicae; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1996. [Google Scholar]Tomus 30(1), 175–335.
- Neigel, J.E. Is Fst obsolete? Conserv. Genet 2002, 3, 167–173. [Google Scholar]
- Nei, M. Analysis of gene diversity in subdivided populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1973, 70, 3321–3323. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.Y.; Hong, K.H.; Liu, S.L.; Cheng, Y.P.; Wu, W.L.; Chiang, T.Y. Genetic variation and population differentiation of Michelia formosana (Magnoliaceae) based on cpDNA variation and RAPD fingerprints: Relevance to post-Pleistocene recolonization. J. Plant Res 2002, 115, 203–216. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, W.; Morgante, M.; Andre, C.; Hanafey, M.; Vogel, J.; Tingey, S.; Rafalski, A. The comparison of RFLP, RAPD, AFLP and microsatellite (SSR) markers for germplasm analysis. Mol. Breed 1996, 2, 225–238. [Google Scholar]
- Archak, S.; Gaikwad, A.B.; Gautam, D.E.; Rao, V.V.B.; Swamy, K.R.M.; Karihaloo, J.L. Comparative assessment of DNA fingerprinting techniques (RAPD, ISSR and AFLP) for genetic analysis of cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.) accessions of India. Genome 2003, 46, 362–369. [Google Scholar]
- Belaj, A.; Satovic, Z.; Cipriani, G.; Baldoni, L.; Testolin, R.; Rallo, L.; Trujillo, I. Comparative study of the discriminating capacity of RAPD, AFLP and SSR markers and of their effectiveness in establishing genetic relationships in olive. Theor. Appl. Genet 2003, 107, 736–744. [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami, H.; Nogata, H.; Hirashima, K.; Awamura, M.; Nakahara, T. Analysis of genetic diversity among European and Asian fig varieties (Ficus carica L.) using ISSR, RAPD, and SSR markers. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol 2009, 56, 201–209. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.T.; Dong, S.S.; Li, S.; Zhao, G.F. Genetic structure within and among populations of Saruma henryi, an endangered plant endemic to China. Biochem. Genet 2012, 50, 146–158. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, X.J.; Zhou, X.L.; Li, Z.C.; Hsu, T.W.; Schaal, B.A.; Tzen-Yuh, C. Low genetic diversity and significant population structuring in the relict Amentotaxus argotaenia complex (Taxaceae) base on ISSR fingerprinting. J. Plant Res 2005, 118, 415–422. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.H.; Xia, N.H. Chromosome numbers of five species and one hybrid in Magnoliaceae. J. Trop. Subtrop. Bot 2005, 13, 516–518. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.F.; Sun, W.B.; Yang, J.B.; Meng, J. Isolation and characterization of 12 microsatellite loci for Michelia coriacea, (Magnoliaceae), a critically endangered endemic in China. Conserv. Genet 2009, 10, 1583–1585. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, T.M.; Wolfe, A.D. DNA Protocols for Plants-CTAB Total DNA Isolation. In Molecular Techniques in Taxonomy; Hewitt, G.M., Johnston, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1991; pp. 283–293. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, F.C.; Yang, R.C.; Boyle, T. POPGENE. Microsoft Windows-Based Freeware for Population Genetic Analysis, Release 1.31; Edmonton; University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock, M.C.; McCauley, D.E. Indirect measures of gene flow and migration: FST ≠ 1/(4Nm + 1). Heredity 1999, 82, 117–125. [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure from multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.P.; Milne, R.I.; Zhang, C.Q.; Yang, J.B. Unusual patterns of hybridization involving a narrow endemic Rhododendron species in Yunnan (Ericaceae), China. Am. J. Bot 2010, 97, 1749–1757. [Google Scholar]
- Dan, T.; Ikeda, H.; Mitsui, Y.; Isagi, Y.; Setoguchi, H. Genetic structure of refugial populations of the temperate plant Shortia rotundifolia (Diapensiaceae) on a subtropical island. Conserv. Genet 2009, 10, 859–867. [Google Scholar]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GENALEX 6: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 288–295. [Google Scholar]
- Excoffier, L.G.L.; Schneider, S. Arlequin ver. 3.0: An integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evol. Bioinform 2005, 1, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Benor, S.; Zhang, M.Y.; Wang, Z.F.; Zhang, H.S. Assessment of genetic variation in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) inbred lines using SSR molecular markers. J. Genet. Genomics 2008, 35, 373–379. [Google Scholar]
- Raymond, M.; Rousset, F. GENEPOP: Population genetics software for exact tests and ecumenicism.




| Primer code | Primer sequence (5′–3′) | Ta (°C) | No. of bands per primer | No. of polymorphic bands | Polymorphism (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 | (AG)8TC | 52 | 10 | 10 | 100.00 |
| 815 | (CT)8G | 52 | 13 | 12 | 92.31 |
| 824 | (TC)8G | 50 | 8 | 7 | 87.50 |
| 834 | (AG)8YT | 52 | 9 | 9 | 100.00 |
| 836 | (AT)8YA | 50 | 7 | 7 | 100.00 |
| 840 | (GA)8YT | 52 | 15 | 15 | 100.00 |
| 846 | (CA)8RT | 52 | 8 | 8 | 100.00 |
| 848 | (CA)8RG | 52 | 15 | 15 | 100.00 |
| 866 | (CTC)5 | 52 | 13 | 13 | 100.00 |
| 895 | AGA GTT GGT AGC TCT TGA TC | 52 | 12 | 10 | 83.33 |
| Total | 110 | 106 | 96.36 |
| Population | Polymorphic bands | Ao | Ae | H | Hpop | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | PrB | |||||
| DS | 66 | 60 | 0 | 1.600 (0.492) | 1.309 (0.349) | 0.188 (0.189) | 0.286 (0.271) |
| DT | 90 | 81.82 | 9 | 1.818 (0.388) | 1.386 (0.352) | 0.234 (0.179) | 0.363 (0.245) |
| YKP | 84 | 76.36 | 8 | 1.764 (0.427) | 1.430 (0.357) | 0.256 (0.184) | 0.387 (0.258) |
| Average | 80 | 72.73 | 5.67 | 1.727 (0.436) | 1.375 (0.353) | 0.226 (0.184) | 0.345 (0.258) |
| Species level | 106 | 96.36 | 1.964 (0.188) | 1.460 (0.315) | 0.283 (0.156) | 0.436 (0.204) | |
| Source of variation | d.f. | Sum of squares | Variance component | Percentage of variance | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISSRs | |||||
| Among population | 2 | 165.176 | 3.676 | 22.839 | <0.01 |
| Within population | 55 | 683.134 | 12.421 | 77.161 | <0.01 |
| SSRs | |||||
| Among population | 2 | 46.160 | 0.913 | 13.900 | <0.01 |
| Within population | 55 | 311.099 | 5.656 | 86.100 | <0.01 |
| Locus | Repeat motif | Size range (bp) | Ta (°C) | A | Ho | He | PIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC2 | (CA)8 | 192–206 | 60 | 3 | 0.535 | 0.582 | 0.517 |
| MC3 | (CT)16 | 292–306 | 68 | 3 | 0.500 | 0.624 | 0.553 |
| MC8 | (TC)15 | 189–211 | 58 | 6 | 0.759 | 0.782 | 0.750 |
| MC34 | (TC)4T3(TC)3-(TC)4 | 156–160 | 62 | 4 | 0.621 | 0.638 | 0.584 |
| MC35 | (CT)3-(CT)4-(CT)3 | 375–381 | 62 | 3 | 0.276 | 0.439 | 0.489 |
| MC41 | (TTTC)4-(CT)10 | 216–232 | 60 | 3 | 0.603 | 0.497 | 0.440 |
| MC45 | (CT)10T2(CT)2 | 116–124 | 62 | 3 | 0.172 | 0.247 | 0.433 |
| MC48 | (TC)8-(TC)5-(TC)6 | 137–157 | 58 | 5 | 0.328 | 0.496 | 0.417 |
| MC49 | (TC)8 | 140–158 | 64 | 7 | 0.224 | 0.531 | 0.480 |
| MC64 | (CT)4-(CT)4-(CT)2 | 248–252 | 60 | 2 | 0.259 | 0.274 | 0.436 |
| MC66 | (CT)8 | 295–305 | 54 | 6 | 0.257 | 0.449 | 0.421 |
| Mean | 4.091 | 0.412 | 0.505 | 0.502 | |||
| St. Dev | 1.640 | 0.197 | 0.157 |
| Population | PPL (%) | PrA | Ao | Ae | Ho | He |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS | 72.73 | 2 | 3.455 (1.214) | 2.170 (0.630) | 0.533 (0.257) | 0.498 (0.168) |
| DT | 91.90 | 3 | 3.455 (1.036) | 1.946 (0.604) | 0.335 (0.207) | 0.429 (0.210) |
| YKP | 81.82 | 2 | 3.455 (1.036) | 2.236 (0.962) | 0.407 (0.234) | 0.485 (0.190) |
| Average | 82.15 | 2.33 | 3.455 (1.095) | 2.117 (0.732) | 0.425 (0.232) | 0.470 (0.189) |
| Code | Locality | Altitude (m) | Latitude (N) | Longitude (E) | N (sample code) | Voucher number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS | Daping-Shipen, Malipo, Yunnan, China | 1504–1600 | 23°5′–23°7′ | 104°35′–104°40′ | 15 (DS1-DS15) | Z-005–007, Z-036–042, Z-051–053. |
| DT | Dongma-Tiechang, Xicou and Malipo, Yunnan, China | 1413–1496 | 23°2′–23°25′ | 104°54′–104°57′ | 21 (DT1-DT21) | Z-003–004, Z-009–25, Z-049. |
| YKP | Yang-Kai-Ping, Malipo, Yunnan, China | 1289–1305 | 23°7′–23°8′ | 104°51′ | 22 (YKP1-YKP22) | Z-YKP-01–22. |
© 2012 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Ma, Y.; Sun, W.; Wen, X.; Milne, R. High Genetic Diversity and Low Differentiation of Michelia coriacea (Magnoliaceae), a Critically Endangered Endemic in Southeast Yunnan, China. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 4396-4411. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13044396
Zhao X, Ma Y, Sun W, Wen X, Milne R. High Genetic Diversity and Low Differentiation of Michelia coriacea (Magnoliaceae), a Critically Endangered Endemic in Southeast Yunnan, China. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2012; 13(4):4396-4411. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13044396
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xingfeng, Yongpeng Ma, Weibang Sun, Xiangying Wen, and Richard Milne. 2012. "High Genetic Diversity and Low Differentiation of Michelia coriacea (Magnoliaceae), a Critically Endangered Endemic in Southeast Yunnan, China" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 13, no. 4: 4396-4411. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13044396
APA StyleZhao, X., Ma, Y., Sun, W., Wen, X., & Milne, R. (2012). High Genetic Diversity and Low Differentiation of Michelia coriacea (Magnoliaceae), a Critically Endangered Endemic in Southeast Yunnan, China. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(4), 4396-4411. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13044396




