Combination of Low-Temperature Electrosurgical Unit and Extractive Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry for Molecular Profiling and Classification of Tissues
Abstract
1. Introduction
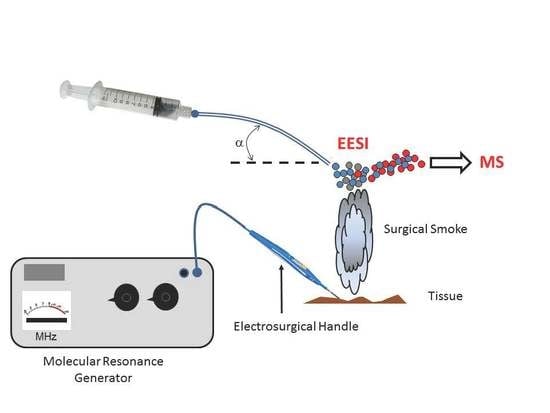
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mirnezami:, R.; Spagou, K.; Vorkas, P.A.; Lewis, M.R.; Kinross, J.; Want, E.; Shion, H.; Goldin, R.D.; Darzi, A.; Takats, Z.; et al. Chemical mapping of the colorectal cancer microenvironment via MALDI imaging mass spectrometry (MALDI-MSI) reveals novel cancer-associated field effects. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Mandal, R.; Catherman, A.; Thomas, P.M.; Kelleher, N.L.; Ikonomidou, C.; Li, L. Top-down proteomics with mass spectrometry imaging: A pilot study towards discovery of biomarkers for neurodevelopmental disorders. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, K.C.; Szaniszló, T.; Günther, S.; Balog, J.; Dénes, J.; Keserü, M.; Dezsö, B.; Tóth, M.; Spengler, B.; Takáts, Z. In situ, real-time identification of biological tissues by ultraviolet and infrared laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 1632–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolman, M.; Ferry, I.; Kuzan-Fischer, C.M.; Wu, M.; Zou, J.; Kiyota, T.; Isik, S.; Dara, D.; Aman, A.; Das, S.; et al. Rapid determination of medulloblastoma subgroup affiliation with mass spectrometry using a handheld picosecond infrared laser desorption probe. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 6508–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolman, M.; Gribble, A.; Bluemke, E.; Zou, J.; Ventura, M.; Bernards, N.; Wu, M.; Ginsberg, H.J.; Das, S.; Vitkin, A.; et al. Optimized Mass Spectrometry Analysis Workflow with Polarimetric Guidance for ex vivo and in situ Sampling of Biological Tissues. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takats, Z.; Wiseman, J.M.; Gologan, B. Mass Spectrometry Sampling Under Ambient Conditions with Desorption Electrospray Ionization. Science 2004, 306, 471–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarmusch, A.K.; Alfaro, C.M.; Pirro, V.; Hattab, E.M.; Cohen-Gadol, A.A.; Cooks, R.G. Differential Lipid profiles of normal human brain matter and gliomas by positive and negative mode desorption electrospray ionization—Mass spectrometry imaging. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sans, M.; Gharpure, K.; Tibshirani, R.; Zhang, J.; Liang, L.; Liu, J.; Young, J.H.; Dood, R.L.; Sood, A.K.; Eberlin, L.S. Metabolic markers and statistical prediction of serous ovarian cancer aggressiveness by ambient ionization mass spectrometry imaging. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2903–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Lai, Y.-H.; So, P.-K.; Chen, H.; Yao, Z.-P. Direct ionization of biological tissue for mass spectrometric analysis. Analyst 2012, 137, 3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerian, K.S.; Jarmusch, A.K.; Pirro, V.; Koch, M.O.; Masterson, T.A.; Cheng, L.; Cooks, R.G. Differentiation of prostate cancer from normal tissue in radical prostatectomy specimens by desorption electrospray ionization and touch spray ionization mass spectrometry. Analyst 2015, 140, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhou, W.; Chingin, K.; Ouyang, Y.; Zhu, T.; Wen, H.; Ding, J.; Xu, J.; Chen, H. Tissue spray ionization mass spectrometry for rapid recognition of human lung squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirro, V.; Seró, R.; Jarmusch, A.K.; Alfaro, C.M.; Cohen-Gadol, A.A.; Hattab, E.M.; Cooks, R.G. Analysis of human gliomas by swab touch spray—Mass spectrometry: Applications to intraoperative assessment of surgical margins and presence of oncometabolites. Analyst 2017, 142, 4058–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kertesz, V.; Van Berkel, G.J. Fully automated liquid extraction-based surface sampling and ionization using a chip-based robotic nanoelectrospray platform. J. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 45, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Rector, J.; Lin, J.Q.; Young, J.H.; Sans, M.; Katta, N.; Giese, N.; Yu, W.; Nagi, C.; Suliburk, J.; et al. Nondestructive tissue analysis for ex vivo and in vivo cancer diagnosis using a handheld mass spectrometry system. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sans, M.; Zhang, J.; Lin, J.Q.; Feider, C.L.; Giese, N.; Breen, M.T.; Sebastian, K.; Liu, J.; Sood, A.K.; Eberlin, L.S. Performance of the MasSpec Pen for Rapid Diagnosis of Ovarian Cancer. Clin. Chem. 2019, 65, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balog, J.; Szaniszló, T.; Schaefer, K.-C.; Denes, J.; Lopata, A.; Godorhazy, L.; Szalay, D.; Balogh, L.; Sasi-Szabó, L.; Toth, M.; et al. Identification of biological tissues by rapid evaporative ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 7343–7350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St John, E.R.; Balog, J.; McKenzie, J.S.; Rossi, M.; Covington, A.; Muirhead, L.; Bodai, Z.; Rosini, F.; Speller, A.V.M.; Shousha, S.; et al. Rapid evaporative ionisation mass spectrometry of electrosurgical vapours for the identification of breast pathology: Towards an intelligent knife for breast cancer surgery. Breast Cancer Res. 2017, 19, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.; Gildea, L.; Balog, J.; Speller, A.; McKenzie, J.; Muirhead, L.; Scott, A.; Kontovounisios, C.; Rasheed, S.; Teare, J.; et al. A novel methodology for in vivo endoscopic phenotyping of colorectal cancer based on real-time analysis of the mucosal lipidome: A prospective observational study of the iKnife. Surg. Endosc. Other Interv. Tech. 2017, 31, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, A.; Mansoori, P.; Sandoval, L.F.; Feldman, S.R.; Pearce, D.; Williford, P.M. Electrosurgery: Part I. Basics and principles. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 70, 591.e1–591.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr-Locke, D.L.; Day, J. Principles of electrosurgery. In Successful Training in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 125–134. [Google Scholar]
- Helmut, W.; Jurgen, L.; Hans-Jurgen, W.; Rainer, M.; Hans-Dieter, L. Characterization of tissue interaction by analyzation of electrosurgial smoke. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–23 September 1995; pp. 643–644. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, W.L.; Garber, S.M. Surgical smoke—A review of the literature. Is this just a lot of hot air? Surg. Endosc. Other Interv. Tech. 2003, 17, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensman, C.; Baty, D.; Willis, R.G.; Cuschieri, A. Chemical composition of smoke produced by high-frequency electrosurgery in a closed gaseous environment An in vitro study. Surg. Endosc. Other Interv. Tech. 1998, 12, 1017–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanker, D.; Vankov, A.; Jayaraman, P. On mechanisms of interaction in electrosurgery. New J. Phys. 2008, 10, 123022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balog, J.; Sasi-Szabo, L.; Kinross, J.; Lewis, M.R.; Muirhead, L.J.; Veselkov, K.; Mirnezami, R.; Dezso, B.; Damjanovich, L.; Darzi, A.; et al. Intraoperative Tissue Identification Using Rapid Evaporative Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 194ra93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guenther, S.; Schäfer, K.C.; Balog, J.; Dénes, J.; Majoros, T.; Albrecht, K.; Tóth, M.; Spengler, B.; Takáts, Z. Electrospray post-ionization mass spectrometry of electrosurgical aerosols. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 22, 2082–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Schiavon, M.; Calabrese, F.; Nicotra, S.; Marulli, G.; Pozzato, G.; Giacometti, C.; Valente, M.; Rea, F. Favorable tissue effects of quantum molecular resonance device (Vesalius) compared with standard electrocautery: A novel paradigm in lung surgery. Eur. Surg. Res. 2007, 39, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirhan, E.; Çukurova, İ.; Arslan, İ.B.; Ozkan, E.T.; Mengi, E.; Yigitbasi, O.G. Quantum Molecular Resonance–Assisted Phonomicrosurgery: Preliminary Experience. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2015, 152, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, K.C.; Dénes, J.; Albrecht, K.; Szaniszló, T.; Balogh, J.; Skoumal, R.; Katona, M.; Tóth, M.; Balogh, L.; Takáts, Z. In vivo, in situ tissue analysis using rapid evaporative ionization mass spectrometry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 8240–8242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Venter, A.; Cooks, R.G. Extractive electrospray ionization for direct analysis of undiluted urine, milk and other complex mixtures without sample preparation. Chem. Commun. 2006, 2042–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, W.S.; Wang, R.; Hu, B.; Berchtold, C.; Meier, L.; Chen, H.; Zenobi, R. On the Mechanism of Extractive Electrospray Ionization. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 82, 4494–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahy, E.; Sud, M.; Cotter, D.; Subramaniam, S. LIPID MAPS online tools for lipid research. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebisch, G.; Vizcaíno, J.A.; Köfeler, H.; Trötzmüller, M.; Griffiths, W.J.; Schmitz, G.; Spener, F.; Wakelam, M.J.O. Shorthand notation for lipid structures derived from mass spectrometry. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.; Xu, N.; Chen, H. Direct analysis of biological samples using extractive electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (EESI-MS). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 2145–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, B.O.; Sui, J.; Young, A.B.; Whittal, R.M. Interferences and contaminants encountered in modern mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 627, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Not available. |







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sukhikh, G.; Chagovets, V.; Wang, X.; Rodionov, V.; Kometova, V.; Tokareva, A.; Kononikhin, A.; Starodubtseva, N.; Chingin, K.; Chen, H.; et al. Combination of Low-Temperature Electrosurgical Unit and Extractive Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry for Molecular Profiling and Classification of Tissues. Molecules 2019, 24, 2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162957
Sukhikh G, Chagovets V, Wang X, Rodionov V, Kometova V, Tokareva A, Kononikhin A, Starodubtseva N, Chingin K, Chen H, et al. Combination of Low-Temperature Electrosurgical Unit and Extractive Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry for Molecular Profiling and Classification of Tissues. Molecules. 2019; 24(16):2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162957
Chicago/Turabian StyleSukhikh, Gennady, Vitaliy Chagovets, Xinchen Wang, Valeriy Rodionov, Vlada Kometova, Alisa Tokareva, Alexey Kononikhin, Natalia Starodubtseva, Konstantin Chingin, Huanwen Chen, and et al. 2019. "Combination of Low-Temperature Electrosurgical Unit and Extractive Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry for Molecular Profiling and Classification of Tissues" Molecules 24, no. 16: 2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162957
APA StyleSukhikh, G., Chagovets, V., Wang, X., Rodionov, V., Kometova, V., Tokareva, A., Kononikhin, A., Starodubtseva, N., Chingin, K., Chen, H., & Frankevich, V. (2019). Combination of Low-Temperature Electrosurgical Unit and Extractive Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry for Molecular Profiling and Classification of Tissues. Molecules, 24(16), 2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162957