Isolation, Characterization and Antiproliferative Activity of New Metabolites from the South African Endemic Red Algal Species Laurencia alfredensis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
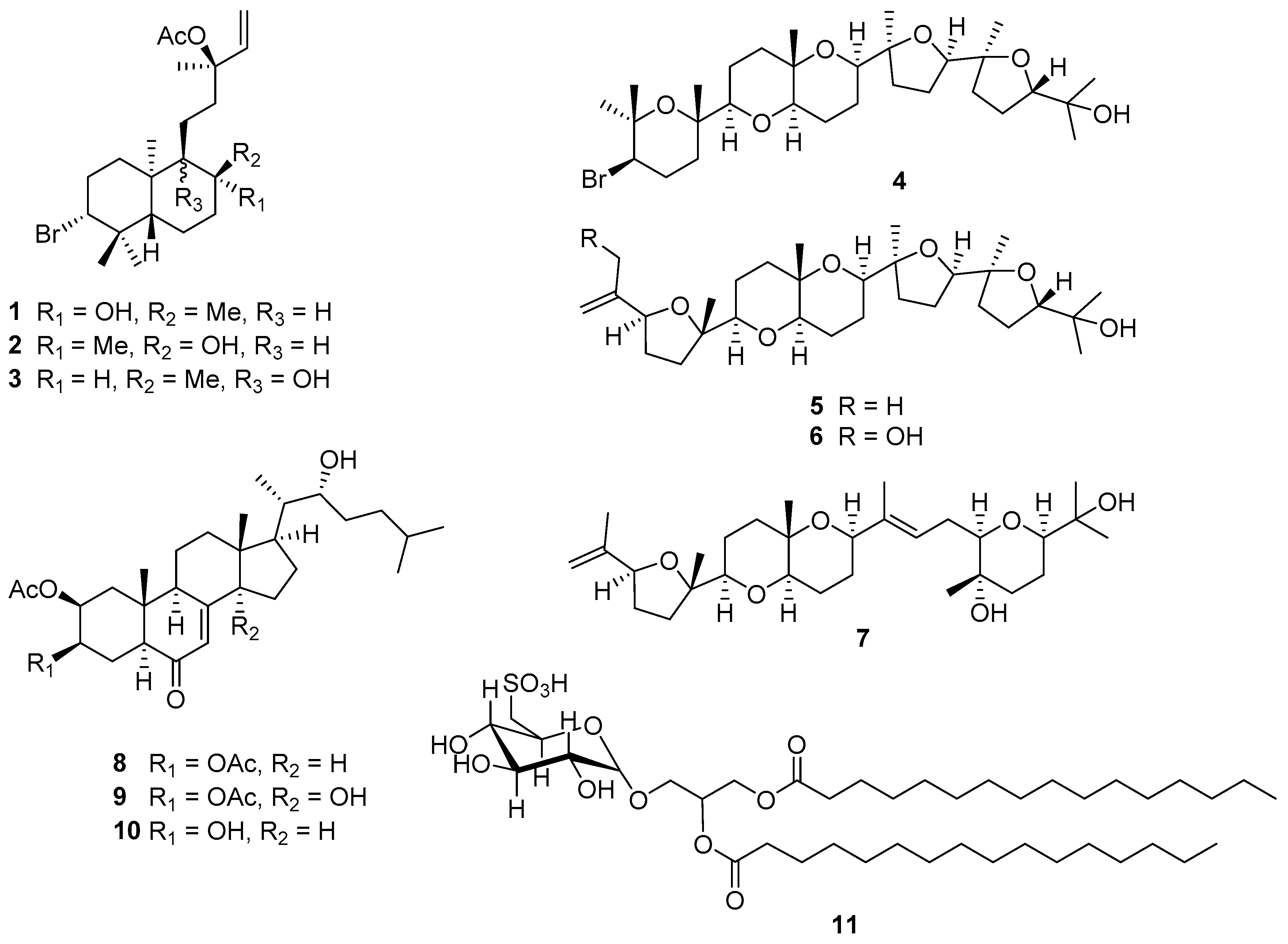
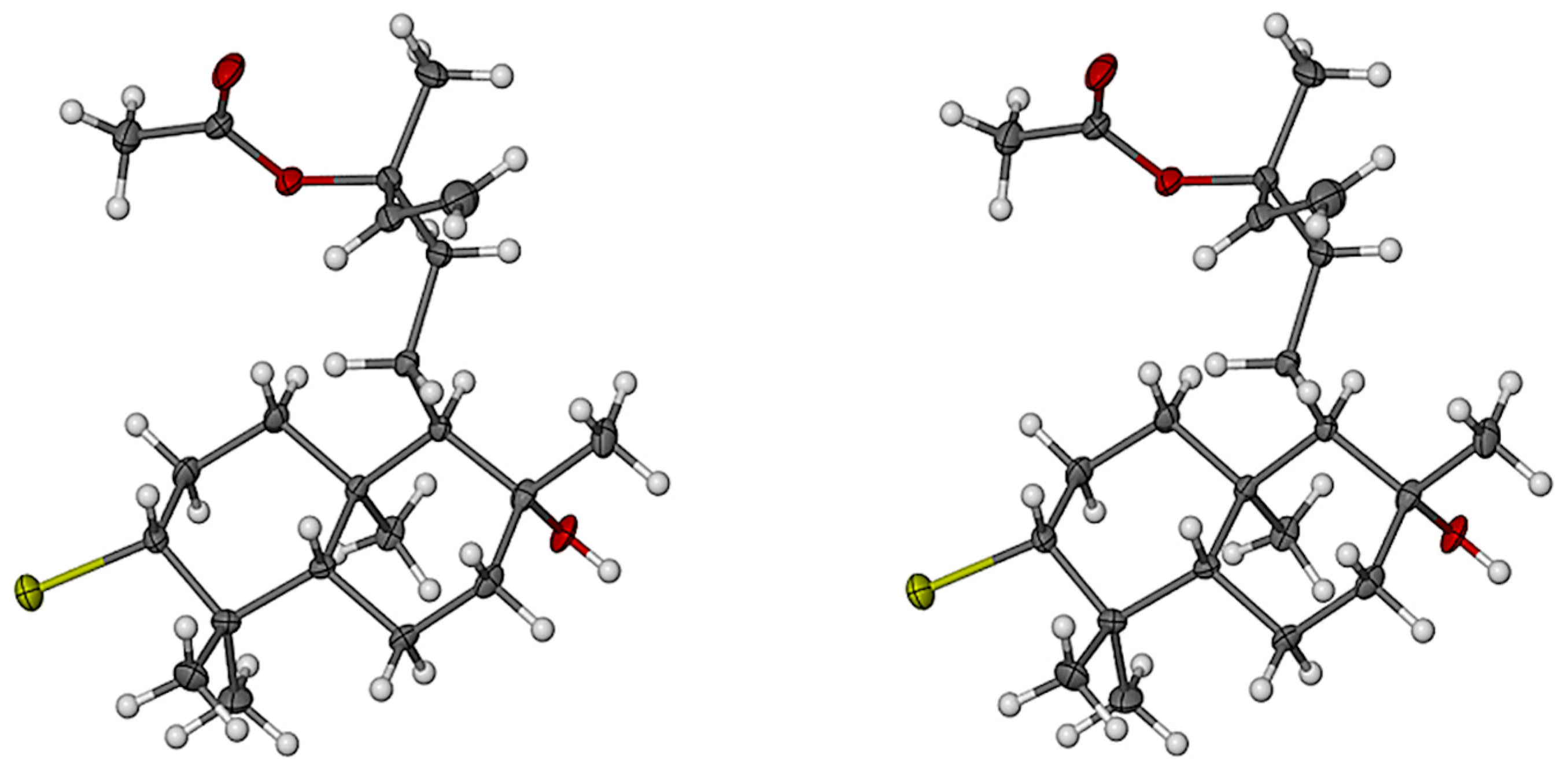
2.1. Structural Elucidation of Labdane-Type Diterpenes (1–3)
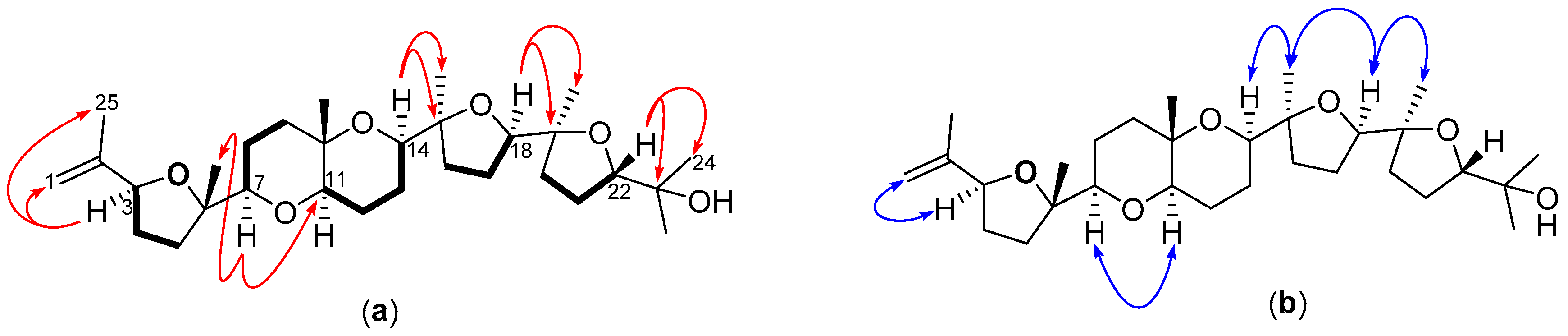
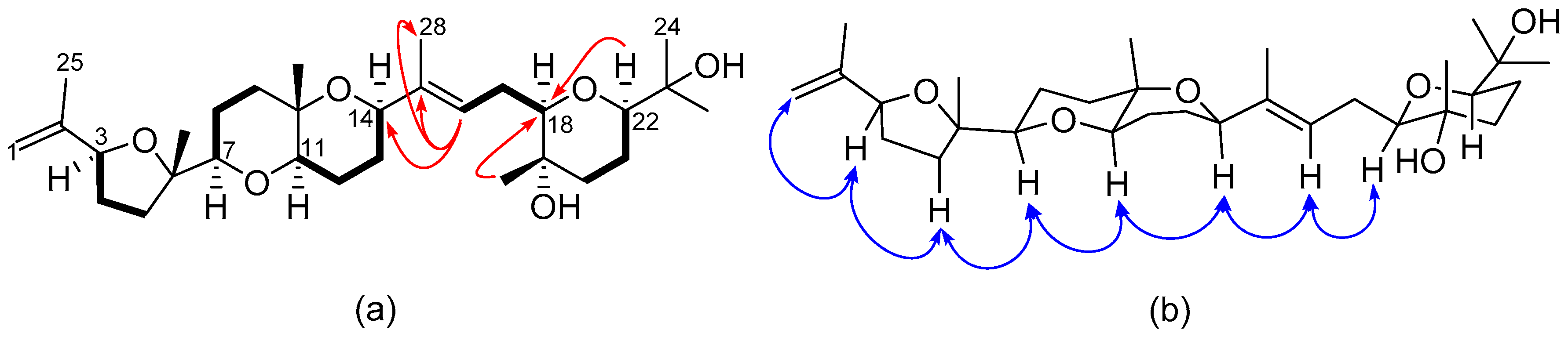
2.2. Structural Elucidation of Polyether Triterpenes (4–7)
2.3. Structural Elucidation of Cholestane-Type Ecdysteroids (8–10)
2.4. Characterization of Isolated Glycolipid (11)
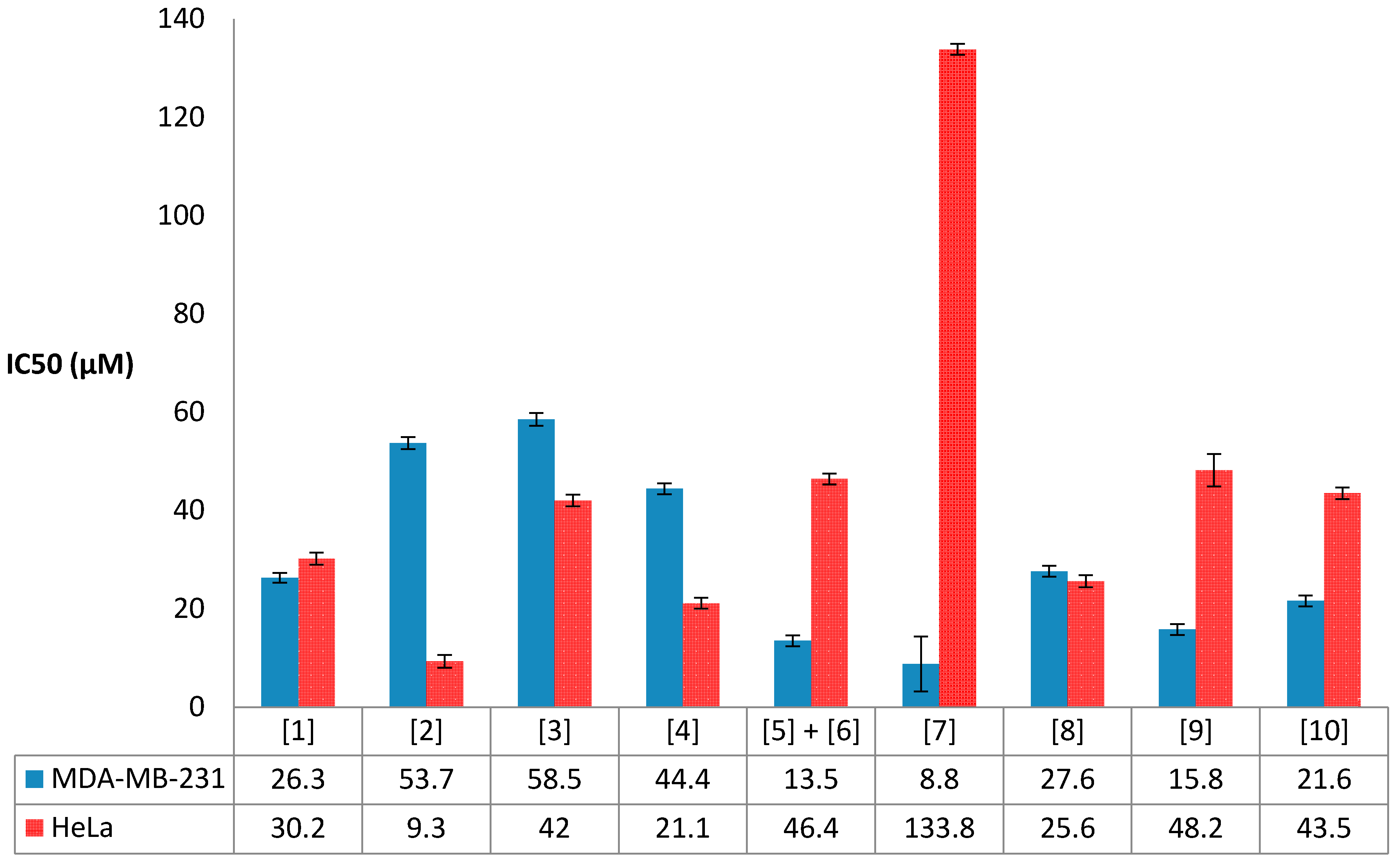
2.5. Antiproliferative Activity Results
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Plant Material
3.3. Extraction, Isolation, and Characterization
3.4. X-ray Crystallographic Data
3.5. Cell Culture and Antiproliferative Activity Assay
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M. AlgaeBase. World-Wide Electronic Publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. Available online: http://www.algaebase.org (accessed on 5 February 2017).
- Erickson, K.L. Marine Natural Products: Chemical and Biological Perspectives; Scheuer, P.J., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983; Volume V, pp. 131–257. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.G.; Gloer, J.B.; Ji, N.Y.; Zhao, J.C. Halogenated Organic Molecules of Rhodomelaceae Origin: Chemistry and Biology. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 3632–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, N.Y.; Wang, B.G. Nonhalogenated organic molecules from Laurencia algae. Phytochem. Rev. 2014, 13, 653–670. [Google Scholar]
- Reis, V.M.; Oliveira, L.S.; Passos, R.M.F.; Viana, N.B.; Mermelstein, C.; Sant’Anna, C.; Pereira, R.C.; Paradas, W.C.; Thompson, F.L.; Amado-Filho, G.M.; et al. Traffic of secondary metabolites to cell surface in the red alga Laurencia dendroidea depends on a two-step transport by the cytoskeleton. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.G.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 116–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, G.T.; Rinehart, K.L., Jr.; Li, L.H.; Kuentzel, S.L.; Connor, J.L. Brominated indoles from Laurencia brongniartii. Tetrahedron Lett. 1978, 19, 4479–4482. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, J.; Higa, T.; Bernardinelli, G.; Jefford, C.W. Itomanindoles A and B. Methylsulfinylindoles from Laurencia brongniartii. Tetrahedron Lett. 1988, 29, 6091–6094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, J.; Higa, T.; Bernardinelli, G.; Jefford, C.W. Sulfur-containing polybromoindoles from the red alga Laurencia brongniartii. Tetrahedron 1989, 45, 7301–7310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gamal, A.A.; Wang, W.L.; Duh, C.Y. Sulfur-Containing Polybromoindoles from the Formosan Red Alga Laurencia brongniartii. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 815–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, N.K.; Iwamoto, H.; Fukazawa, Y.; Uchio, Y. Five New Sulfur-containing Polybrominated Bisindoles from the Red Alga Laurencia brongniartii. Heterocycles 2005, 65, 2675–2682. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, N.Y.; Li, X.M.; Cui, C.M.; Wang, B.G. Terpenes and Polybromoindoles from the Marine Red Alga Laurencia decumbens (Rhodomelaceae). Helv. Chim. Acta 2007, 90, 1731–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, N.Y.; Li, X.M.; Ding, L.P.; Wang, B.G. Aristolane Sesquiterpenes and Highly Brominated Indoles from the Marine Red Alga Laurencia similis (Rhodomelaceae). Helv. Chim. Acta 2007, 90, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Yuan, Z.H.; Li, J.; Guo, S.J.; Deng, L.P.; Han, L.J.; Zhu, X.B.; Shi, D.Y. Two new bromoindoles from red alga Laurencia similis. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2009, 20, 456–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.S.; Li, X.M.; Cui, C.M.; Wang, B.G. Brominated Metabolites from the Marine Red Alga Laurencia similis. Z. Naturforsch. 2010, 65b, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakee, J. The Isolation, Characterization and Chemotaxonomic Significance of Secondary Metabolites from Selected South African Laurencia spp. (Rhodophyta). Ph.D. Thesis, Rhodes University, Grahamstown, South Africa, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cen-Pacheco, F.; Mollinedo, F.; Villa-Pulgarín, J.A.; Norte, M.; Fernández, J.J.; Daranas, A.H. Saiyacenols A and B: The key to solve the controversy about the configuration of aplysiols. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 7275–7279. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, D.H.R.; Feakins, P.G.; Poyser, J.P.; Sammes, P.G. A Synthesis of the Insect Moulting Hormone, Ecdysone, and Related Compounds. J. Chem. Soc. 1970, 1584–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantillo-Ciau, Z.; Moo-Puc, R.; Quijano, L.; Freile-Pelegrin, Y. The tropical brown alga Labophora variegata: A source of antiprotozoal compounds. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1292–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, B.M.; Fenical, W. Isococinndiol, a brominated diterpenoid from Laurencia snyderae var. guadalupensis. Phytochemistry 1980, 19, 2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.L.; Martín, J.D.; Estrada, D. The absolute configuration of (+)-isoconcinndiol. Acta Crystallogr. 1989, 45c, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuzawa, A.; Miyamoto, M.; Kumagai, Y.; Abiko, A.; Takaya, Y.; Masamune, T. Structure of new bromoditerpenes, pinnatols, from the marine red alga Laurencia pinnata Yamada. Chem. Lett. 1985, 14, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, J.J.; Lin, G.H.Y.; Wing, R.M.; Fenical, W. Marine natural products. Concinndiol, a bromo-diterpene alcohol from the red alga Laurencia concinna. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1973, 14, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, J.W.; Hartshorn, M.P.; McLennan, T.J.; Munro, M.H.G.; Robinson, W.T.; Yorke, S.C. Thyrsiferol, a squalene-derived metabolite of Laurencia thyrsifera. Tetrahedron Lett. 1978, 19, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.G.; Arteaga, J.M.; Fernandez, J.J.; Martin, J.D.; Norte, M.; Ruano, J.Z. Terpenoids of the red alga Laurencia pinnatifida. Tetrahedron 1984, 40, 2751–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen-Pacheco, F.; Villa-Pulgarín, J.A.; Mollinedo, F.; Martín, M.N.; Fernández, J.J.; Daranas, A.H. New polyether triterpenoids from Laurencia viridis and their biological evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2220–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayciriex, S.; Regazzetti, A.; Gaudin, M.; Prost, E.; Dargère, D.; Massicot, F.; Auzeil, N.; Laprévote, O. Development of a novel method for quantification of sterols and oxysterols by UPLC-ESI-HRMS: Application to a neuroinflammation rat model. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 404, 3049–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roengsumran, S.; Petsom, A.; Kuptiyanuwat, N.; Vilaivan, T.; Ngamrojnavanich, N.; Chaichantipyuth, C.; Phuthong, S. Cytotoxic labdane diterpenoids from Croton oblongifolius. Phytochemistry 2001, 56, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.O.; Choi, S.Z.; Choi, S.U.; Lee, K.C.; Chin, Y.W.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.C.; Lee, K.R. Labdane Diterpenes from Aster spathulifolius and Their Cytotoxic Effects on Human Cancer Cell Lines. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1471–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, R.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lou, H. Scapairrins A–Q, Labdane-Type Diterpenoids from the Chinese Liverwort Scapania irrigua and Their Cytotoxic Activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2087–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, J.J.; Souto, M.L.; Norte, M. Marine polyether triterpenes. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2000, 17, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, A.; Tóth, N.; Ványolós, A.; Béni, Z.; Zupkó, I.; Molnár, J.; Báthori, M.; Hunyadi, A. Significant Activity of Ecdysteroids on the Resistance to Doxorubicin in Mammalian Cancer Cells Expressing the Human ABCB1 Transporter. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 5034–5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, C.; Bolton, J.J.; Mattio, L.; Mandiwana-Neudani, T.G.; Anderson, R.J. Molecular systematics reveals increased diversity with the South African Laurencia complex (Rhodomelaceae, Rhodophyta). J. Phycol. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Metti, Y.; Millar, A.J.K.; Steinberg, P. A new molecular phylogeny of the Laurencia complex (Rhodophyta, Rhodomelaceae) and a review of key morphological characters result in a new genus, Coronaphycus, and a description of C. novus. J. Phycol. 2015, 51, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Mare, J.-A.; Lawson, J.C.; Chiwakata, M.T.; Beukes, D.R.; Edkins, A.L.; Blatch, G.L. Quinones and halogenated monoterpenes of algal origin show anti-proliferative effects against breast cancer cells in vitro. Investig. New Drugs 2012, 30, 2187–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Mare, J.-A.; Sterrenberg, J.N.; Sukhthankar, M.G.; Chiwakata, M.T.; Beukes, D.R.; Blatch, G.L.; Edkins, A.L. Assessment of potential anti-cancer stem cell activity of marine algal compounds using an in vitro mammosphere assay. Cancer Cell Int. 2013, 13, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 1, 4, 7, 8, and 11 are available from the authors. |




| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC | δH (J, Hz) | δC | δH (J, Hz) | δC | δH (J, Hz) | |
| 1a | 1.14, dt (3.5, 13.4) | 1.15, m | 1.42, m | |||
| 1b | 37.4, CH2 | 1.62, td (3.9, 12.9, 13.2) | 37.3, CH2 | 1.71, m | 33.5, CH2 | 1.71, m |
| 2a | 2.06, dq (3.9, 13.2) | 2.09, m | 2.12, m | |||
| 2b | 30.7, CH2 | 2.30, qd (3.9, 13.2) | 30.9, CH2 | 2.25, qd (3.8, 13.1) | 30.7, CH2 | 2.15, m |
| 3 | 69.7, CH | 3.92, dd (4.1, 12.8) | 69.2, CH | 3.93, dd (4.1, 12.7) | 69.6, CH | 4.00, dd (4.3, 12.4) |
| 4 | 39.5, C | 39.4, C | 39.6, C | |||
| 5 | 47.6, CH | 1.08, dd (2.5, 10.9) | 47.1, CH | 1.16, m | 47.0, CH | 1.64, dd (2.7, 12.3) |
| 6a | 1.50, m | 1.40, m | 1.39, m | |||
| 6b | 20.2, CH2 | 1.72, m | 22.0, CH2 | 1.64, m | 23.1, CH2 | 1.60, m |
| 7a | 1.46, m | 1.46, m | 1.29, m | |||
| 7b | 36.7, CH2 | 1.53, m | 37.2, CH2 | 1.58, m | 31.3, CH | 1.46, m |
| 8 | 74.7, C | 73.1, C | 35.9, CH | 1.73, m | ||
| 9 | 59.1, CH | 0.84, m | 60.9, CH | 0.95, m | 76.8, C | |
| 10 | 39.0, C | 38.7, C | 43.3, C | |||
| 11a | 1.00, m | 1.28, m | 1.40, m | |||
| 11b | 23.0, CH2 | 1.38, m | 20.8, CH2 | 1.71, m | 28.0, CH2 | 1.55, m |
| 12a | 1.74, m | 1.79, m | 1.74, m | |||
| 12b | 43.0, CH2 | 1.80, m | 42.9, CH2 | 1.82, m | 35.8, CH2 | 1.95, ddd, (5.1, 12.4, 13.7) |
| 13 | 82.9, C | 83.2, C | 83.3, C | |||
| 14 | 141.6, CH | 5.94, dd (11.0, 17.5) | 141.8, CH | 6.00, dd (11.0, 17.5) | 141.6, CH | 5.90, dd (11.0, 17.5) |
| 15a | 5.13, dd (0.9, 17.5) | 5.13, dd (0.9, 17.5) | 5.12, dd (0.7, 6.6) | |||
| 15b | 113.4, CH2 | 5.15, dd (0.9, 11.0) | 113.2, CH2 | 5.15, dd (0.9, 11.0) | 113.4, CH2 | 5.14, dd (0.7, 13.1) |
| 16 | 23.5, CH3 | 1.52, s | 23.7, CH3 | 1.52, s | 23.7, CH3 | 1.52, s |
| 17 | 30.9, CH3 | 1.20, s | 31.8, CH3 | 1.43, s | 16.0, CH3 | 0.82, d (6.6) |
| 18 | 17.7, CH3 | 0.95, s | 17.6, CH3 | 0.91, s | 18.4, CH3 | 0.96, s |
| 19 | 30.6, CH3 | 1.06, s | 30.5, CH3 | 1.07, s | 30.9, CH3 | 1.05, s |
| 20 | 24.7, CH3 | 1.28, s | 24.7, CH3 | 1.09, s | 16.2, CH3 | 0.95, s |
| 21 | 169.8, C | 169.9, C | 169.8, C | |||
| 22 | 22.1, CH3 | 2.00, s | 22.2, CH3 | 2.00, s | 22.1, CH3 | 2.00, s |
| No. | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC | δH (J, Hz) | δC | δH (J, Hz) | δC | δH (J, Hz) | δC | δH (J, Hz) | |
| 1a | 4.77, m | 5.23, m | 4.76, m | |||||
| 1b | 31.0 | 1.26, s | 110.2 | 4.98, m | 114.7 | 5.30, m | 110.2 | 4.97, m |
| 2 | 74.9 | 146.2 | 146.0 | 145.9 | ||||
| 3 | 59.0 | 3.88, dd (4.0, 12.3) | 83.4 | 4.35, dd (6.1, 8.9 | 80.7 | 4.53, dd (5.2, 9.5) | 83.3 | 4.34, dd (6.1, 8.7) |
| 4a | 2.09, dt (4.0, 13.5) | 1.71, m | 1.83, m | 1.71, m | ||||
| 4b | 28.2 | 2.23, qd (3.7, 13.1) | 31.4 | 2.02, m | 32.3 | 2.15, m | 31.3 | 2.01, m |
| 5a | 1.53, m | 1.64, m | 1.68, m | 1.62, m | ||||
| 5b | 37.4 | 1.80, m | 34.3 | 2.12, m | 34.1 | 1.81, m | 34.2 | 2.10, m |
| 6 | 74.4 | 84.5 | 84.5 | 84.4 | ||||
| 7 | 86.5 | 3.03, dd (2.3, 11.4) | 83.6 | 3.32, dd (2.6, 11.6) | 83.6 | 3.31, dd (2.6, 11.6) | 83.6 | 3.34, dd (2.7, 11.6) |
| 8a | 1.40, m | 1.44, m | 1.44, m | 1.45, m | ||||
| 8b | 23.0 | 1.70, m | 25.0 | 1.64, m | 25.0 | 1.64, m | 24.8 | 1.65, m |
| 9a | 1.52, m | 1.57, m | 1.57, m | 1.56, m | ||||
| 9b | 38.7 | 1.73, m | 38.8 | 1.76, m | 38.7 | 1.76, m | 38.8 | 1.78, m |
| 10 | 71.4 | 71.3 | 71.2 | 72.1 | ||||
| 11 | 76.7 | 3.53, dd (7.3, 11.0) | 76.6 | 3.58, dd (7.3, 11.0) | 76.6 | 3.58, dd (7.3, 11.0) | 77.8 | 3.51, dd (6.5, 11.2) |
| 12a | 1.48, m | 1.52, m | 1.52, m | 1.57, m | ||||
| 12b | 21.3 | 1.86, m | 21.4 | 1.93, m | 21.4 | 1.93, m | 21.7 | 1.88, m |
| 13a | 1.70, m | |||||||
| 13b | 21.4 | 1.77 | 21.5 | 1.78, m | 21.5 | 1.78, m | 25.8 | 2.02, m |
| 14 | 75.3 | 3.71, dd (4.3, 11.0) | 75.4 | 3.71, dd (4.8, 11.2) | 75.5 | 3.72, dd (4.8, 11.2) | 75.1 | 4.19, dd (4.0, 9.5) |
| 15 | 84.5 | 84.4 | 84.4 | 138.5 | ||||
| 16a | 1.61, m | 1.64, m | 1.64, m | |||||
| 16b | 35.5 | 1.95, m | 35.4 | 1.96, m | 35.4 | 1.96, m | 122.3 | 5.52, dd (2.7, 13.8) |
| 17a | 1.63, m | 1.66, m | 1.66, m | 2.06, m | ||||
| 17b | 27.6 | 1.84, m | 27.7 | 1.86, m | 27.7 | 1.86, m | 27.6 | 2.40, ddd (3.1, 7.6, 15.1) |
| 18 | 85.8 | 3.85, dd (6.1, 8.4) | 85.8 | 3.86, dd (5.8, 8.2) | 85.8 | 3.86, dd (5.8, 8.2) | 84.0 | 3.16, dd (3.2, 6.7) |
| 19 | 84.5 | 84.6 | 84.6 | 69.9 | ||||
| 20a | 1.59, m | 1.56, m | ||||||
| 20b | 33.9 | 1.96, m | 34.0 | 1.96, m | 34.0 | 1.96, m | 39.7 | 1.84, m |
| 21a | 1.49, m | |||||||
| 21b | 26.5 | 1.79, m | 26.6 | 1.80, m | 26.6 | 1.80, m | 24.5 | 1.60, m |
| 22 | 86.8 | 3.76, dd (6.8, 8.6) | 86.8 | 3.77, dd (6.7, 8.7) | 86.8 | 3.77, dd (6.7, 8.7) | 84.1 | 3.14, m |
| 23 | 70.6 | 70.6 | 70.6 | 71.6 | ||||
| 24 | 24.0 | 1.10, s | 24.0 | 1.10, s | 24.0 | 1.10, s | 23.9 | 1.12, s |
| 25 | 23.7 | 1.38, s | 17.7 | 1.68, s | 44.7 | 4.09, d (0.9) | 17.7 | 1.68, s |
| 26 | 20.0 | 1.19, s | 23.2 | 1.15, s | 23.3 | 1.17, s | 23.1 | 1.16, s |
| 27 | 21.2 | 1.16, s | 21.3 | 1.20, s | 21.3 | 1.20, s | 20.1 | 1.21, s |
| 28 | 21.5 | 1.07, s | 21.6 | 1.08, s | 21.6 | 1.08, s | 13.0 | 1.65, s |
| 29 | 23.6 | 1.13, s | 23.6 | 1.13, s | 23.6 | 1.13, s | 20.2 | 1.18, s |
| 30 | 27.5 | 1.18, s | 27.6 | 1.19, s | 27.6 | 1.19, s | 26.1 | 1.16, s |
| No. | 8 | 9 | 10 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC | δH (J, Hz) | δC | δH (J, Hz) | δC | δH (J, Hz) | |
| 1a | 1.72, m | 1.80, dd (3.4, 15.0) | ||||
| 1b | 36.7, CH2 | 2.00, m | 36.6, CH2 | 2.01, m | 36.1, CH2 | 1.88, m |
| 2 | 68.5, CH | 4.93, m | 68.5, CH | 4.93, m | 71.3, CH | 4.88, m |
| 3 | 68.5, CH | 5.04, m | 68.3, CH | 5.05, m | 66.4, CH | 4.01, m |
| 4a | 1.93, ddd (2.8, 12.6, 15.4) | 1.94, m | 1.87, m | |||
| 4b | 21.2, CH2 | 2.10, m | 21.1, CH2 | 2.10, m | 23.6, CH2 | 2.03, m |
| 5 | 48.7, CH | 2.58, dd (3.5, 12.5) | 49.0, CH | 2.63, dd (3.23, 12.2) | 47.8, CH | 2.74, dd (3.5, 12.4) |
| 6 | 199.6, C | 199.4, C | 200.6, C | |||
| 7 | 123.3, CH | 5.75, m | 127.0, CH | 5.93, d, (2.2) | 123.3, CH | 5.73, m |
| 8 | 162.5, C | 157.6, C | 162.6, C | |||
| 9 | 50.6, CH | 2.25, ddd (2.5, 6.9, 9.9) | 46.8, CH | 2.68, m | 50.7, CH | 2.25, ddd (2.5, 6.7, 11.7) |
| 10 | 37.7, C | 38.0, C | 37.9, C | |||
| 11a | 1.62, m | 1.58, m | 1.61, m | |||
| 11b | 21.5, CH2 | 1.78, m | 20.3, CH2 | 1.76, m | 21.5, CH2 | 1.79, m |
| 12a | 1.40, m | 1.69, m | 1.41, m | |||
| 12b | 38.7, CH2 | 2.14, m | 29.9, CH2 | 1.94, m | 38.7, CH2 | 2.12, dd (1.9, 13.0) |
| 13 | 44.8, C | 48.2, C | 44.8, C | |||
| 14 | 55.1, CH | 2.05, m | 96.1, C | 55.1, CH | 2.05, m | |
| 15a | 1.53, m | 1.72, m | 1.53, m | |||
| 15b | 22.6, CH2 | 1.64, m | 24.7, CH2 | 2.15, m | 22.6, CH2 | 1.65, m |
| 16a | 1.44, m | 1.52, m | 1.44, m | |||
| 16b | 26.9, CH2 | 1.80, m | 25.7, CH2 | 1.89, m | 26.9, CH2 | 1.82, m |
| 17 | 53.3, CH | 1.33, m | 47.9, CH | 1.89, m | 53.2, CH | 1.34, m |
| 18 | 12.3, CH3 | 0.61, s | 16.4, CH3 | 0.76, s | 12.3, CH3 | 0.60, s |
| 19 | 14.9, CH3 | 0.96, s | 14.7, CH3 | 0.97, s | 14.8, CH3 | 0.96, s |
| 20 | 42.4, CH | 1.68, m | 41.8, CH | 1.74, m | 42.4, CH | 1.69, m |
| 21 | 12.6, CH3 | 0.94, d (6.8) | 12.8, CH3 | 0.89, d (5.1) | 12.6, CH3 | 0.94, d (6.4) |
| 22 | 73.7, CH | 3.62, dd (1.6, 10.1) | 74.1, CH | 3.63, m | 73.8, CH | 3.61, m |
| 23a | 1.24, m | 1.23, m | 1.25, m | |||
| 23b | 27.8, CH2 | 1.36, m | 27.2, CH2 | 1.39, m | 27.7, CH2 | 1.36, m |
| 24a | 1.17, m | 1.17, m | 1.16, m | |||
| 24b | 36.0, CH2 | 1.39, m | 36.0, CH2 | 1.39, m | 36.0, CH2 | 1.42, m |
| 25 | 28.1, CH | 1.55, m | 28.2, CH | 1.56, m | 28.1, CH | 1.55, m |
| 26 | 22.4, CH3 | 0.89, d (6.8) | 22.4, CH3 | 0.90, d (6.4) | 22.4, CH3 | 0.89, d (6.9) |
| 27 | 22.9, CH3 | 0.90, d (6.8) | 23.0, CH3 | 0.92, d (6.4) | 22.9, CH3 | 0.90, d (6.9) |
| 28 | 169.3, C | 169.4, C | 170.0, C | |||
| 29 | 169.5, C | 169.6, C | 21.2, CH3 | 2.02, s | ||
| 30 | 21.1, CH3 | 2.03, s | 21.2, CH3 | 2.04, s | ||
| 31 | 21.2, CH3 | 2.04, s | 21.2, CH3 | 2.05, s | ||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dziwornu, G.A.; Caira, M.R.; Mare, J.-A.d.l.; Edkins, A.L.; Bolton, J.J.; Beukes, D.R.; Sunassee, S.N. Isolation, Characterization and Antiproliferative Activity of New Metabolites from the South African Endemic Red Algal Species Laurencia alfredensis. Molecules 2017, 22, 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22040513
Dziwornu GA, Caira MR, Mare J-Adl, Edkins AL, Bolton JJ, Beukes DR, Sunassee SN. Isolation, Characterization and Antiproliferative Activity of New Metabolites from the South African Endemic Red Algal Species Laurencia alfredensis. Molecules. 2017; 22(4):513. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22040513
Chicago/Turabian StyleDziwornu, Godwin A., Mino R. Caira, Jo-Anne de la Mare, Adrienne L. Edkins, John J. Bolton, Denzil R. Beukes, and Suthananda N. Sunassee. 2017. "Isolation, Characterization and Antiproliferative Activity of New Metabolites from the South African Endemic Red Algal Species Laurencia alfredensis" Molecules 22, no. 4: 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22040513







