Influence of Plant Growth Retardants on Quality of Codonopsis Radix
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. PGR Treatment of C. Radix Did Not Affect Lobetyolin and Atractylenolide III Contents
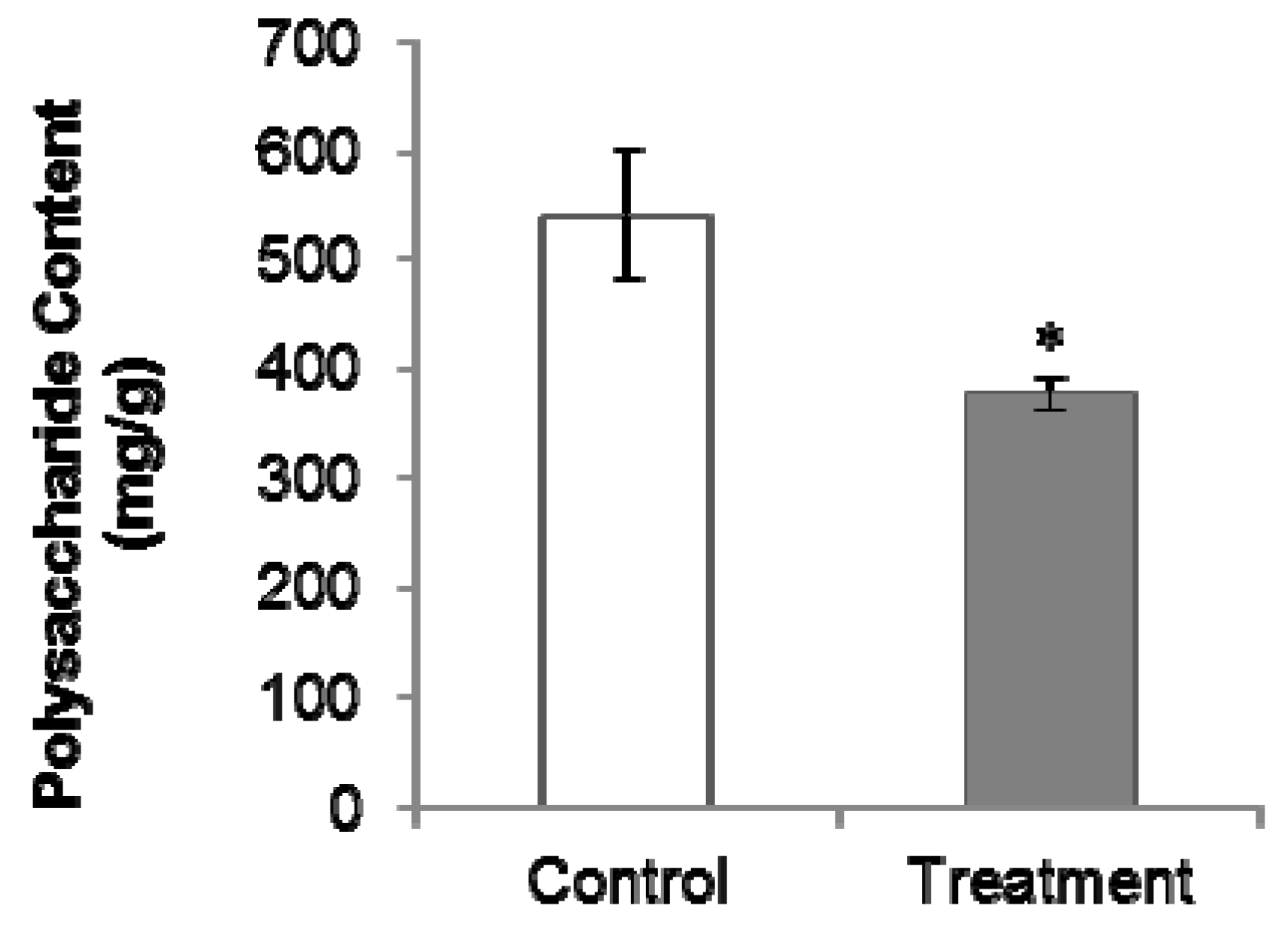
2.2. PGR Treatment Significantly Decreased Polysaccharides and Internal Volatiles Contents
2.3. General Increase in Free Amino Acids Content by PGR Treatment
2.4. Application of PGR Altered the Composition of Secondary Metabolites in C. Radix
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Materials and Treatments
3.2. Extraction and Analysis of Total Polysaccharides
3.3. Extraction and Analysis of Free Amino Acids
3.4. Extraction and Analysis of Internal Volatiles
3.5. Extraction and Analysis of Characteristic Compounds and Unknown Differential Metabolites
3.6. Data Analysis
4. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (in Chinese); China Medical Science Press: Peking, China, 2010; vol I, p. 264. ISBN 978-75-0674-437-9. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.X.; Liu, J.C. Structural characterization of a water-soluble polysaccharide from the roots of Codonopsis pilosula and its immunity activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2008, 43, 279–282. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.G.; Sun, W.J.; Xiao, X.; Tang, X.J.; Hu, Q.L.; Xu, S.F. Water extract from Codonopsis thalictrifolia wall affects the reproductive system of male infant rats. Nat. J. Androl. 2014, 20, 641–646. [Google Scholar]
- Weon, J.B.; Yun, B.R.; Lee, J.; Eom, M.R.; Ko, H.J.; Lee, H.Y.; Park, D.S.; Chung, H.C.; Chung, J.Y.; Ma, C.J. Neuroprotective effect of steamed and fermented Codonopsis Lanceolata. Biomol. Ther. 2014, 22, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.M.; Yan, Y.F.; Wang, Z.C. Experimental study on the cardiotonic action of extract from Codonopsis pilosula (Franch.) Nannf (in Chinese). China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 1994, 19, 238–240. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.Y.; Ma, N.; Zhu, S.; Komatsu, K.; Li, Z.Y.; Fu, W.M. The genus Codonopsis (Campanulaceae): A review of phytochemistry, bioactivity and quality control. J. Nat. Med. 2015, 69, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.Y.; Kim, J.A.; Jeon, H.J.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Whang, W.K. Chemical fingerprinting of Codonopsis pilosula and simultaneous analysis of its major components by HPLC-UV. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2014, 37, 1148–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rademacher, W. Growth retardants: Effects on gibberellin biosynthesis and other metabolic pathways. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 2000, 51, 501–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.W.; Ding, Y.H.; Li, C.Y.; Chen, F.Q.; Yang, S.T.; Chen, J.; Li, S.; Gao, X.Y. Study on effects of Dangshen Zhuanggenling on quality of Codondpisis Pilosula (Franch.) Nannf (in Chinese). Chin J. Pharm. Anal. 2011, 31, 254–257. [Google Scholar]
- Dumlu, M.U.; Gurkan, E.; Tuzlaci, E. Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of Campanula alliariifolia. Nat. Prod. Res. 2008, 22, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.Q.; He, L.C.; Jin, J.Q. Atractylenolide I and atractylenolide III inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-α and NO production in macrophages. Phytother. Res. 2007, 21, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.T.; Chen, L.G.; Wu, C.H.; Chang, C.C.; Wang, C.C. Gastroprotective activity of atractylenolide III from Atractylodes Ovata on ethanol-induced gastric ulcer in vitro and in vivo. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 62, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, T.H.; Bang, J.Y.; Kim, M.H.; Kang, I.C.; Kim, H.M.; Jeong, H.J. Atractylenolide III, a sesquiterpenoid, induces apoptosis in human lung carcinoma A549 cells via mitochondria-mediated death pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, R.; Ma, P.; Sun, N.N.; Li, L.Y. Effect of fertilization on the yield and quality of Codonopsis Tangshen Oliv (in Chinese). World Sci. Technol. 2010, 12, 254–259. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.R.; Li, Z.M.; Gao, J.P. Separation and structural characterization and anti-tumor effect in vitro of polysaccharides from Radix Codonopsis (in Chinese). Lishizhen Med. Mater. Medica Res. 2011, 12, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, X.F.; Wu, G.; Yin, Y.L. Roles of phytochemicals in amino acid nutrition. Front. Biosci. 2011, 3, 372–384. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.E.; Zhang, X.Y. Influence of plant growth regulater on yield and quality of Salvia Miltiorrhiza (in Chinese). China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2014, 39, 1992–1994. [Google Scholar]
- Tengstrand, E.; Rosén, J.; Hellenäs, K.E.; Åberg, K.M. A concept study on non-targeted screening for chemical contaminants in food using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry in combination with a metabolomics approach. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herreroyr, M.; Simó, C.; García-Cañas, V.; Ibáñez, E.; Cifuentes, A. Foodomics: MS-based strategies in modern food science and nutrition. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2012, 31, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jansen, W.T.; Hogenboom, S.; Thijssen, M.J.; Kamerling, J.P.; Vliegenthart, J.F.; Verhoef, J. Synthetic 6B di-, tri-, and tetrasaccharide-protein conjugates contain pneumococcal type 6A and 6B common and 6B-specific epitopes that elicit protective antibodies in mice. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorpe, S.J.; Feizi, T. Species differences in the expression of carbohydrate differentiation antigens on mammalian blood cells revealed by immunofluorescence with monoclonal antibodies. Biosci. Rep. 1984, 4, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von, G.S.; Smith, D.F.; Cummings, R.D.; Riedel, S.; Miescher, S.; Schaub, A. Intravenous immunoglobulin contains a broad repertoire of anticarbohydrate antibodies that is not restricted to the IgG 2 subclass. J. Allergy Clin. Immun. 2009, 123, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar]
- Truong, N.M.; Dang, Q.T. Application of hydrolytic enzymes for improvement of red dragon fruit juice processing. Asian Pac. J. Sustain. Agr. Food Energ. 2016, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Foresti, R.; Hoque, M.; Monti, D.; Green, C.J.; Motterlini, R. Differential activation of heme oxygenase-1 by chalcones and rosolic acid in endothelial cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 312, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikkelsen, M.D.; Halkier, B.A. Metabolic engineering of valine and isoleucine-derived glucosinolates in Arabidopsis expressing CYP79D2 from cassava. Plant Physiol. 2003, 131, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, T.; Liu, C.C.; Yang, J.Y.; Liu, Q.G.; Li, J.L. Hijiki Seaweed (Hizikia fusiformis): Nutritional value, safety concern and arsenic removal method. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 634, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Fu, X.M.; Mei, X.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, S.H.; Zeng, L.T.; Dong, F.; Yang, Z.Y. Proteolysis of chloroplast proteins is responsible for accumulation of free amino acids in dark-treated tea (Camellia sinensis) leaves. J. Proteom. 2017, 157, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.M.; Cheng, S.H.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Du, B.; Feng, C.; Zhou, Y.; Mei, X.; Jiang, Y.M.; Duan, X.W.; Yang, Z.Y. Differential responses of four biosynthetic pathways of aroma compounds in postharvest strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) under interaction of light and temperature. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds including lobetyolin, atractylenolide III, and ethyl decanoate are available from the authors. |



| Internal Volatile Metabolite | Treatment | Control | T/CK |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dodecane | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.56 * |
| Hexadecane | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 0.23 ± 0.02 | 0.57 * |
| 2-Furanmethanol | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 0.46 * |
| Phytane | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.17 ± 0.03 | 0.59 * |
| Octacosane | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.50 * |
| Dihydroanethole | 0.27 ± 0.10 | 1.42 ± 0.28 | 0.19 * |
| Oxalic acid, dodecyl 2-methylphenyl ester | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.46 * |
| Ethylhexyl benzoate | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.57 * |
| Methyl hexadecanoate | 0.16 ± 0.01 | 0.24 ± 0.03 | 0.67 * |
| Diethyl Phthalate | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 0.71 * |
| n-Heptadecylcyclohexane | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.50 * |
| Methyl octadeca-9,12-dienoate | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.21 ± 0.04 | 0.52 * |
| Diisobutyl phthalate | 0.72 ± 0.08 | 1.10 ± 0.10 | 0.66 * |
| Phthalic acid, decyl 2,7-dimethyloct-7-en-5-yn-4-yl ester | 0.54 ± 0.07 | 0.79 ± 0.03 | 0.69 * |
| Free Amino Acid | Treatment (μg/g) | Control (μg/g) | T/CK |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glutamic acid | 3234.18 ± 811.83 | 465.59 ± 174.63 | 6.95 * |
| Asparagine | 172.88 ± 44.88 | 34.36 ± 15.40 | 5.03 * |
| α-Aminoadipic Acid | 3270.40 ± 898.05 | 659.44 ± 244.17 | 4.96 * |
| Ornithine | 13.08 ± 1.59 | 6.41 ± 2.04 | 2.04 * |
| Taurine | 121.03 ± 85.58 | 7.56 ± 5.38 | 16.01 |
| Phosphatidylserine | 32.91 ± 16.27 | 10.05 ± 1.71 | 3.27 |
| Carbamide | 17619.48 ± 7948.53 | 9652.14 ± 3208.69 | 1.83 |
| Leucine | 22.65 ± 7.09 | 12.91 ± 4.08 | 1.75 |
| Arginine | 5431.27 ± 1205.33 | 3164.94 ± 1227.21 | 1.72 |
| Serine | 47.96 ± 11.59 | 32.21 ± 12.45 | 1.49 |
| Citrulline | 214.58 ± 74.13 | 149.97 ± 60.34 | 1.43 |
| β-Aminoisobutyric acid | 1.72 ± 0.42 | 1.28 ± 0.58 | 1.34 |
| Valine | 12.34 ± 2.41 | 9.42 ± 3.65 | 1.31 |
| Isoleucine | 61.95 ± 20.73 | 51.04 ± 16.87 | 1.21 |
| Lysine | 50.74 ± 9.78 | 44.94 ± 18.04 | 1.13 |
| β-Alanine | 4.93 ± 2.66 | 4.47 ± 2.49 | 1.10 |
| Phenylalanine | 18.95 ± 4.69 | 17.45 ± 5.79 | 1.09 |
| Alanine | 270.21 ± 102.56 | 291.28 ± 111.14 | 0.93 |
| Glycine | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 3.20 ± 1.10 | 0.00 * |
| Tyrosine | 8.98 ± 2.76 | 11.19 ± 4.72 | 0.80 |
| Histidine | 2448.93 ± 786.52 | 2454.37 ± 360.11 | 1.00 |
| γ-Aminobutyric acid | 27.76 ± 8.04 | 44.82 ± 10.31 | 0.62 |
| Tryptophan | 21.32 ± 8.14 | 37.35 ± 17.81 | 0.57 |
| Threonine | 9.96 ± 5.08 | 45.86 ± 53.54 | 0.22 |
| No. | Identification and Tentative Identification | Molecular Formula | RT (min) | m/z | T/CK | Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Arginine | C6H14N4O2 | 0.70 | 173.1045[M − H]− | 1.57 * | C18, ES− |
| 2 | Verbascose | C30H52O26 | 0.75 | 827.2670[M − H]− | 1.71 ** | C18, ES− |
| 3 | (4-Aminomethyl-1,2,3-triazol-1-acetylamino)-5-hydroxybenzoic acid | C12H13N5O4 | 0.82 | 290.0883 [M − H]− | 2.23 ** | C18, ES− |
| 4 | 4-Mannopyranosyl-5-O-phosphono-ribitol | C11H23O12P | 0.82 | 377.0859 [M − H]− | 1.62 * | C18, ES− |
| 5 | Acetylneuraminyl-galactose | C17H29NO14 | 0.82 | 470.1523 [M − H]− | 2.67 ** | C18, ES− |
| 6 | Deamino neuraminyl-galactosyl-acetyl glucosamine | C23H39NO19 | 0.82 | 632.2041 [M − H]− | 3.19 ** | C18, ES− |
| 7 | Glycoloyloxy-acetic acid | C4H6O5 | 0.87 | 133.0144 [M − H]− | 1.51 ** | C18, ES− |
| 8 | Bougainvillein-γ-I | C30H36N2O18 | 11.68 | 729.2257[M − NH4]− | 1.25 | Amide, ES− |
| 9 | Aurin | C19H14O3 | 20.27 | 307.1207[M+NH4]− | 1.72 ** | Amide, ES− |
| 10 | 9-Methylthio-2-nonanoic acid | C10H18O3S | 20.32 | 217.0906 [M − H]− | 1.38 ** | Amide, ES− |
| 11 | 5,6,7,8-Tetrahydromethanopterin | C30H45N6O16P | 7.20 | 794.3002[M+NH4] | 6.29 ** | Amide, ES+ |
| No. | Identification and Tentative Identification | Molecular Formula | RT (min) | m/z | T/CK | Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3-Hexadecanoylamino-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentyl-phosphonic acid | C22H46NO5P | 1.05 | 453.3469[M + NH4] | 0.02 ** | Amide, ES+ |
| 2 | 4,4′-Dioxo-carotene-3,3′-diyl didecanoate | C60H88O6 | 1.05 | 905.6666[M + H]+ | 0.01 ** | Amide, ES+ |
| 3 | 1-Dimethylylidene-4-dihydrazinecarboximidamide-2,3-dimethoxybenzene | C12H18N8O2 | 4.18 | 324.1880[M + NH4] | 0.08 ** | Amide, ES+ |
| 4 | Phenylalanyl-glycyl-histidine | C17H21N5O4 | 1.74 | 358.1504 [M − H]− | 0.27 ** | C18, ES− |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, Y.; Zeng, L.; Li, P.; Sun, T.; Wang, C.; Li, F.; Chen, Y.; Du, B.; Yang, Z. Influence of Plant Growth Retardants on Quality of Codonopsis Radix. Molecules 2017, 22, 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101655
Liao Y, Zeng L, Li P, Sun T, Wang C, Li F, Chen Y, Du B, Yang Z. Influence of Plant Growth Retardants on Quality of Codonopsis Radix. Molecules. 2017; 22(10):1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101655
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Yinyin, Lanting Zeng, Pan Li, Tian Sun, Chao Wang, Fangwen Li, Yiyong Chen, Bing Du, and Ziyin Yang. 2017. "Influence of Plant Growth Retardants on Quality of Codonopsis Radix" Molecules 22, no. 10: 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101655




