Investigation of the Pyridinium Ylide—Alkyne Cycloaddition as a Fluorogenic Coupling Reaction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
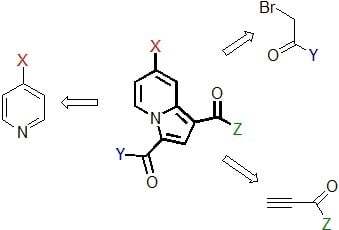
2. Results
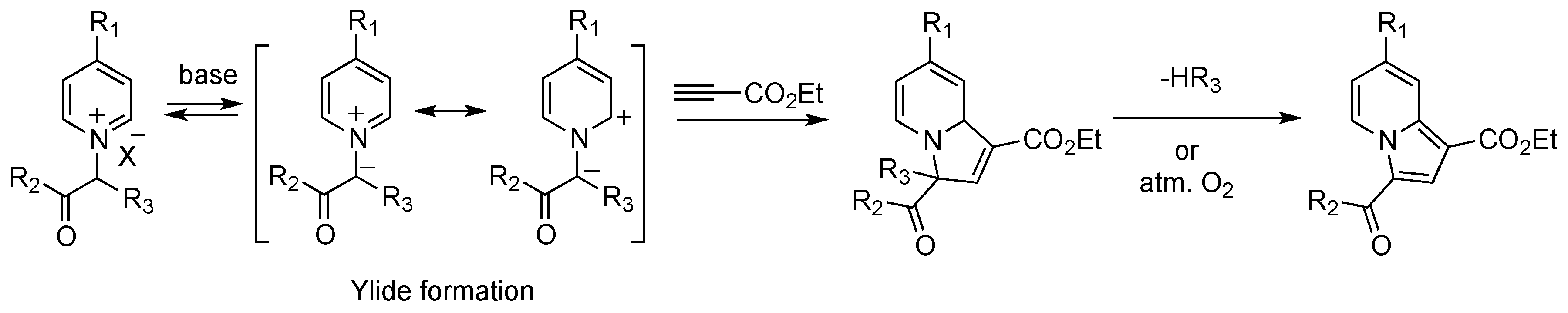
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of the Pyridinium Salt
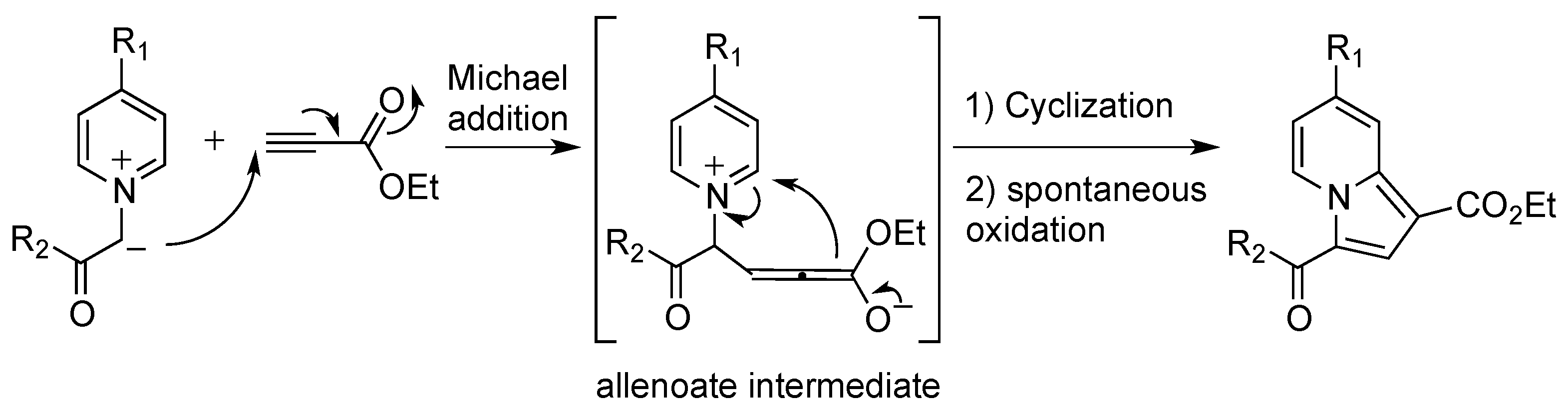
2.2. Reactivity Studies
2.2.1. Influence of the R1 Substituent
2.2.2. Influence of the Solvent and of the Nature of the Added Base
2.2.3. Effect of the R2 Group
2.2.4. Influence of the Dipolarophile
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Material and Methods
4.2. General Methods for the Synthesis of N-Heterocyclic Salts
4.3. General Methods for the Ylide-Alkyne Cycloaddition
4.4. pKa Determination
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DMF | N,N-dimethylformamide |
| DMSO-D6 | deuterated dimethylsulfoxide |
| TLC | thin-layer chromatography |
| TRIS | Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane |
References
- Huang, W.; Zuo, T.; Luo, X.; Jin, H.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Yu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L. Indolizine derivatives as HIV-1 VIF-elongin C interaction inhibitors. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2013, 81, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, G.S.; Mmatli, E.E. Recent progress in synthesis and bioactivity studies of indolizines. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 5237–5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vemula, V.R.; Vurukonda, S.; Bairi, C.K. Indolizine derivatives: Recent advances and potential pharmacological activities. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2011, 11, 159–163. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Xia, Z.; Nagai, M.; Lu, R.; Kostik, E.; Przewloka, T.; Song, M.; Chimmanamada, D.; James, D.; Zhang, S.; et al. Novel indolizine compounds as potent inhibitors of phosphodiesterase IV (PDE4): Structure–activity relationship. MedChemComm 2011, 2, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.M.; Lv, P.C.; Chen, W.; Liu, P.G.; Zhang, M.Z.; Zhu, H.L. Synthesis and antiproliferative activity of indolizine derivatives incorporating a cyclopropylcarbonyl group against Hep-G2 cancer cell line. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 3184–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Ma, B.; Wudl, F. Synthesis and optical properties of a series of pyrrolopyridazine derivatives: Deep blue organic luminophors for electroluminescent devices. J. Mater. Chem. 1999, 9, 2183–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Koh, M.; Lim, B.J.; Park, S.B. Emission wavelength prediction of a full-color-tunable fluorescent core skeleton, 9-aryl-1,2-dihydropyrrolo[3,4-b]indolizin-3-one. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 6642–6649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Koh, M.; Ryu, J.; Park, S.B. Combinatorial discovery of full-color-tunable emissive fluorescent probes using a single core skeleton, 1,2-dihydropyrrolo[3,4-b]indolizin-3-one. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 12206–12207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Lee, S.; Park, S.B. 9-Aryl-1,2-dihydropyrrolo[3,4-b]indolizin-3-one (Seoul-fluor) as a smart platform for colorful ratiometric fluorescent pH sensors. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 7734–7736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Lee, S.; Park, S.B. A Seoul-fluor-based bioprobe for lipid droplets and its application in image-based high throughput screening. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 2331–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerner, D.A.; Evleth, E.M. Photophysical properties of indolizine and some azaindolizines. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1972, 15, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, Z.-J.; Wu, N.; Li, M.; You, J.; Lan, J. Discovery of a full-color-tunable fluorescent core framework through direct C H (hetero)arylation of N-heterocycles. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 1599–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotaru, A.V.; Druta, I.; Oeser, T.; Müller, T.J.J. A novel coupling 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition sequence as a three-component approach to highly fluorescent indolizines. Helv. Chim. Acta 2005, 88, 1798–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becuwe, M.; Landy, D.; Delattre, F.; Cazier, F.; Fourmentin, S. Fluorescent indolizine-β-cyclodextrin derivatives for the detection of volatile organic compounds. Sensors 2008, 8, 3689–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lungu, N.C.; Dépret, A.; Delattre, F.; Surpateanu, G.G.; Cazier, F.; Woisel, P.; Shirali, P.; Surpateanu, G. Synthesis of a new fluorinated fluorescent β-cyclodextrin sensor. J. Fluor. Chem. 2005, 126, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgkiss, R.J.; Middleton, R.W.; Parrick, J.; Rami, H.K.; Wardman, P.; Wilson, G.D. Bioreductive fluorescent markers for hypoxic cells: A study of 2-nitroimidazoles with 1-substituents containing fluorescent, bridgehead-nitrogen, bicyclic systems. J. Med. Chem. 1992, 35, 1920–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayazit, M.K.; Coleman, K.S. Fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotubes following the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of pyridinium ylides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 10670–10676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Cao, H.; Li, B.; Yin, G. The synthesis and fluorescence quenching properties of well soluble hybrid graphene material covalently functionalized with indolizine. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 075202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kel'in, A.V.; Sromek, A.W.; Gevorgyan, V. A novel Cu-assisted cycloisomerization of alkynyl imines: Efficient synthesis of pyrroles and pyrrole-containing heterocycles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 2074–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardin, A.R.; Sarpong, R. Electronic effects in the Pt-catalyzed cycloisomerization of propargylic esters: Synthesis of 2,3-disubstituted indolizines as a mechanistic probe. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 4547–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernyak, D.; Gevorgyan, V. Organocopper-mediated two-component S(N)2′-substitution cascade towards N-fused heterocycles. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2012, 47, 1516–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.-R.; Ye, S.-C.; Lu, C.-J.; Xiang, B.; Gao, J.; Jia, Y.-X. Au-catalyzed ring-opening reactions of 2-(1-alkynyl-cyclopropyl) pyridines with nucleophiles. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 4855–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.-R.; Cai, Z.-Y.; Lu, C.-J.; Ye, S.-C.; Xiang, B.; Gao, J.; Jia, Y.-X. Indolizine synthesis via Cu-catalyzed cyclization of 2-(2-enynyl) pyridines with nucleophiles. Org. Chem. Front. 2015, 2, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.R.; Lu, C.J.; Zhang, M.D.; Gao, J.R.; Jia, Y.X. Palladium-catalyzed three-component cascade reaction: Facial access to densely functionalized indolizines. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 7057–7060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaloko, J.; Hayford, A. Direct synthesis of monofunctionalized indolizine derivatives bearing alkoxymethyl substituents at C-3 and their benzofused analogues. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 4305–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernyak, D.; Skontos, C.; Gevorgyan, V. Two-component approach toward a fully substituted N-fused pyrrole ring. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 3242–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Liao, P.; Liu, J.; Bi, X. Silver-catalyzed cyclization of 2-pyridyl alkynyl carbinols with isocyanides: Divergent synthesis of indolizines and pyrroles. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 11837–11839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, B.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y. Highly efficient synthesis of functionalized indolizines and indolizinones by copper-catalyzed cycloisomerizations of propargylic pyridines. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 7783–7786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, B.; Liu, Y. Gold-catalyzed multicomponent synthesis of aminoindolizines from aldehydes, amines, and alkynes under solvent-free conditions or in water. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 4323–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seregin, I.V.; Gevorgyan, V. Gold-catalyzed 1,2-migration of silicon, tin, and germanium en route to C-2 substituted fused pyrrole-containing heterocycles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 12050–12051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.R.; Bunnelle, E.M.; Rhodes, A.J.; Sarpong, R. Pt-catalyzed cyclization/1,2-migration for the synthesis of indolizines, pyrrolones, and indolizinones. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 1169–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katritzky, A.R.; Qiu, G.; Yang, B.; He, H.-Y. Novel syntheses of indolizines and pyrrolo[2,1-a]isoquinolines via benzotriazole methodology. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 7618–7621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elender, K.; Riebel, P.; Weber, A.; Sauer, J.R. 1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition reactions of stable bicyclic and monocyclic azomethine ylides: Kinetic aspects. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 4261–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, U.; Saikia, A.; Boruah, R.C. A novel microwave-mediated one-pot synthesis of indolizines via a three-component reaction. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinica, R.; Druta, I.; Pettinari, C. The synthesis of substituted 7,7′-bis-indolizines via 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition under microwave irradiation. Synlett 2000, 1013–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinica, R.M.; Furdui, B.; Ghinea, I.O.; Bahrim, G.; Bonte, S.; Demeunynck, M. Novel one-pot green synthesis of indolizines biocatalyzed by Candida antartica lipases. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglass, J.E.; Tabor, M.W.; Spradling, J.E., III. Effect of 4-substituents on the stability of pyridinium dicarbethoxymethylides. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 1972, 9, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgescu, E.; Caira, M.R.; Georgescu, F.; Draghici, B.; Popa, M.M.; Dumitrascu, F. One-pot, three-component synthesis of a library of new pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoline derivatives. Synlett 2009, 1795–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yu, S.; Ju, K.; He, X. New routes synthesis of indolizines via 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of pyridiniums and alkynes. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 6981–6984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisgen, R. On the mechanism of 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions. A reply. J. Org. Chem. 1968, 33, 2291–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Hayashi, N.; Ikemi, Y.; Toda, M.; Uchida, T.; Aoyama, Y.; Miyakoshi, Y. Inverse electron-demand 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reactions of cyclooctyne with pyridinium bis(methoxycarbonyl)methylides. J. Het. Chem. 2001, 38, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchenko, V.V.; Zhegalova, N.G.; Borsenko, A.O.; Nikolaev, A.E. On the most powerful chemical traps for bis(methoxycarbonyl)carbene (2-methoxy-1-(methoxycarbonyl)-2-oxoethylidene). Helv. Chim. Acta 2008, 91, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sustmann, R. A simple model for substituent effects in cycloaddition reactions. II. The diels-alder reaction. Tetrahedron Lett. 1971, 12, 2721–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sustmann, R. Orbital energy control of cycloaddition reactivity. Pure Appl. Chem. 1974, 40, 569–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandeep, C.; Padmashali, B.; Kulkarni, R.S. Efficient synthesis of indolizines and new imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines via the expected cyclization of aromatic cycloimmonium ylides with electron deficient alkynes and ethyl cyanoformate. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 6411–6414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandeep, C.; Padmashali, B.; Kulkarni, R.S.; Mallikarjuna, S.M.; Siddesh, M.B.; Nagesh, H.K.; Thriveni, K.S. Synthesis of substituted 5-acetyl-3-benzoylindolizine-1-carboxylate from substituted 2-acetyl pyridinium bromides. Het. Lett. 2014, 4, 371–376. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, W.G.; Ratts, K.W. Basicity of n-ylides. J. Org. Chem. 1970, 35, 3144–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dega-Szafran, Z.; Schroeder, G.; Szafran, M.; Szwajca, A.; Łeska, B.; Lewandowska, M. Experimental and quantum chemical evidences for C–H···N hydrogen bonds involving quaternary pyridinium salts and pyridinium ylides. J. Mol. Struct. 2000, 555, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Bordwell, F.G.; Van Der Puy, M.; Fried, H.E. Equilibrium acidities and homolytic bond dissociation energies of the acidic carbon-hydrogen bonds in N-substituted trimethylammonium and pyridinium cations. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 3060–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Droumaguet, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q. Fluorogenic click reaction. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotaru, A.; Druta, I.; Avram, E.; Danac, R. Synthesis and properties of fluorescent 1,3-substituted mono and biindolizines. ARKIVOC 2009, xiii, 287–289. [Google Scholar]
- Devaraj, N.K.; Weissleder, R. Biomedical applications of tetrazine cycloadditions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saracoglu, N. Recent advances and applications in 1,2,4,5-tetrazine chemistry. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 4199–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonte, S.; Ghinea, I.O.; Xuereb, J.-P.; Dinica, R.; Demeunynck, M. Playing with lipases to favor 1,2- versus 1,4-addition of nucleophiles to propiolic ester: Access to activated terminal alkines. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 5499–5500. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, W.B.; Bilow, N.; Kelleghan, W.J.; Lau, K.S.Y. Facile synthesis fo ethynylated benzoic acid derivatives and aromatic compounds via ethynyltrimethylsilane. J. Org. Chem. 1981, 46, 4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allgäuer, D.S.; Mayr, H. One-pot two-step synthesis of 1-(ethoxycarbonyl)indolizines via pyridinium ylides. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 2013, 6379–6388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seethalakshmi, T.; Venkatesan, P.; Fronczek, F.R.; Kaliannan, P.; Thamotharan, S. 4-amino-(1-carboxymethyl)pyridinium chloride. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. E Struct. Rep. Online 2006, 62, o3389–o3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundersen, L.-L.; Charnock, C.; Negussie, A.H.; Rise, F.; Teklu, S. Synthesis of indolizine derivatives with selective antibacterial activity against mycobacterium tuberculosis. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 30, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, K.; Fujita, H.; Deguchi, Y. Formation of a novel complex between pyridinium bis(alkoxycarbonyl)methylides and diphenylcyclopropenone; trapping of pyridinium bis(alkoxycarbonyl)methylide cation radicals. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1978, 817–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rečnik, S.; Svete, J.; Stanovnik, B. Ring contractions of 4-oxoquinolizine-3-diazonium tetrafluoroborates, by an aza-Wolff rearrangement, to alkyl indolizine-3-carboxylates. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 2001, 3705–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soare, M.-L.; Ungureanu, E.-M.; Georgescu, E.; Birzan, L. Synthesis and electrochemical characterization of substituted indolizine carboxylates. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2013, 78, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors.
| Salt | R1 | R2 | R3 | Yields % | R1 Hammett Cste | pKa a | 1H-NMR b δ H2/H6 | 1H-NMR b δ H3/H5 | 1H-NMR b δ CH2/CH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | OMe | H | 71 | 0 | 8.30 | 9.01 | 8.23 | 5.66 |
| 2 | NH2 | OMe | H | 83 | −0.66 | 8.84 | 8.09 | 6.92 | 5.12 |
| 3 | NHAc | OMe | H | 81 | 0.06 | 8.74 | 8.74 | 8.14 | 5.51 |
| 4 | CF3 | OMe | H | 54 | 0.54 | 8.25 | 9.39 | 8.66 | 5.83 |
| 5 | CONHPr | OMe | H | 80 | 0.36 | 8.24 | 9.19 | 8.52 | 5.75 |
| 6 | COCH3 | OMe | H | 64 | 0.50 | 8.04 | 9.35 | 8.63 | 5.88 |
| 7 | CN | OMe | H | 60 | 0.66 | 8.16 | 9.29 | 8.64 | 5.75 |
| 8 | CN | Ph | H | 70 | 8.11 | 9.30 | 8.85 | 6.61 | |
| 9 | CN | Ph-NO2 | H | 60 | 7.07 | 9.26 | 8.83 | 6.60 | |
| 10 | CN | NHC3H7 | H | 60 | nd | 9.24 | 8.59 | 5.60 | |
| 11 | H | OEt | CO2Et | 89 | 5.51 | 9.20 | 8.28 | Not obs. | |
| 12 | COCH3 | OEt | CO2Et | 99 | 5.04 | 9.36 | 8.61 | Not obs. | |
| 13 | CN | OEt | CO2Et | 40 | nd c | 9.44 | 8.66 | Not obs. |
| Entry | Pyridinium Salt | R1 | Hammett Constant | Indolizine | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | H | 0 | 14 | 59 |
| 2 | 2 | NH2 | −0.66 | 15 | 0 |
| 3 | 3 | NHAc | 0.06 | 16 | 0 |
| 4 | 5 | CONHPr | 0.36 | 17 | 66 |
| 5 | 6 | COCH3 | 0.50 | 18 | 77 |
| 6 | 4 | CF3 | 0.54 | 19 | 55 b |
| 7 | 7 | CN | 0.66 | 20 | 81 |

| Entry | R1 | Base (1 eq.) | Solvent | T °C | Time (h) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | COCH3 | K2CO3 | MeOH | 25 | 1 | 50 |
| 2 | COCH3 | K2CO3 | MeOH | 25 | 18 | 77 |
| 3 | COCH3 | NH4OH | MeOH | 25 | 1 | 45 |
| 4 | COCH3 | NEt3 | MeOH | 25 | 1 | 38 |
| 5 | COCH3 | K2CO3 | DMF | 25 | 1 | 88 |
| 6 | COCH3 | NH4OH | DMF | 25 | 1 | 44 |
| 7 | COCH3 | NEt3 | DMF | 25 | 1 | 45 |
| 8 | COCH3 | K2CO3 | DMF | 25 | 5 | >90 |
| 9 | COCH3 | NH4OH | DMF | 25 | 5 | 48 |
| 10 | COCH3 | NEt3 | DMF | 25 | 5 | 48 |
| 11 | CN | K2CO3 | MeOH | 25 | 5 | 45 |
| 12 | CN | K2CO3 | MeOH | 25 | 18 | 81 |
| 13 | CN | K2CO3 | DMF | 25 | 5 | 70 |
| 14 | CN | K2CO3 | MeOH | 40 | 18 | 38 |
| 15 | CN | pH 7.5 Phosphate buffer | H2O | 25 | 18 | 24 |

| Entry | R1 | Base | Solvent | T °C | Indolizine | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | pH 7.5 Tris buffer | H2O | 40 | 21 | 0 |
| 2 | COCH3 | pH 7.5 Tris buffer | H2O | 40 | 22 | 12 |
| 3 | CN | pH 7.5 Tris buffer | H2O | 40 | 23 | 40 |
| 4 | CN | pH 7.5 Tris buffer | H2O | 25 | 23 | 63 |
| 5 | CN | pH 7.5 phosphate buffer | H2O | 25 | 23 | 42 |
| 6 | CN | K2CO3 | MeOH | 25 | 23 | 0 |
| 7 | CN | K2CO3 | DMF | 25 | 23 | 93 |
| Entry | Pyridinium Salt | R2 | Indolizine | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7 | OMe | 20 | 81 |
| 2 | 8 | Ph | 24 | 50 |
| 3 | 9 | C6H4NO2 | 25 | 67 |
| 4 | 10 | NHC3H7 | 26 | 62 |
| Entry | Dipolarophile | Indolizine (Yield) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |  20 (81%) |
| 2 |  27 |  28 (40%) |
| 3 |  29 | Complex mixture |
| 4 |  30 | (0%) |
| 5 |  31 | (0%) |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonte, S.; Ghinea, I.O.; Dinica, R.; Baussanne, I.; Demeunynck, M. Investigation of the Pyridinium Ylide—Alkyne Cycloaddition as a Fluorogenic Coupling Reaction. Molecules 2016, 21, 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21030332
Bonte S, Ghinea IO, Dinica R, Baussanne I, Demeunynck M. Investigation of the Pyridinium Ylide—Alkyne Cycloaddition as a Fluorogenic Coupling Reaction. Molecules. 2016; 21(3):332. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21030332
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonte, Simon, Ioana Otilia Ghinea, Rodica Dinica, Isabelle Baussanne, and Martine Demeunynck. 2016. "Investigation of the Pyridinium Ylide—Alkyne Cycloaddition as a Fluorogenic Coupling Reaction" Molecules 21, no. 3: 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21030332