Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Biological Evaluation of a Series of Phloretin Derivatives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
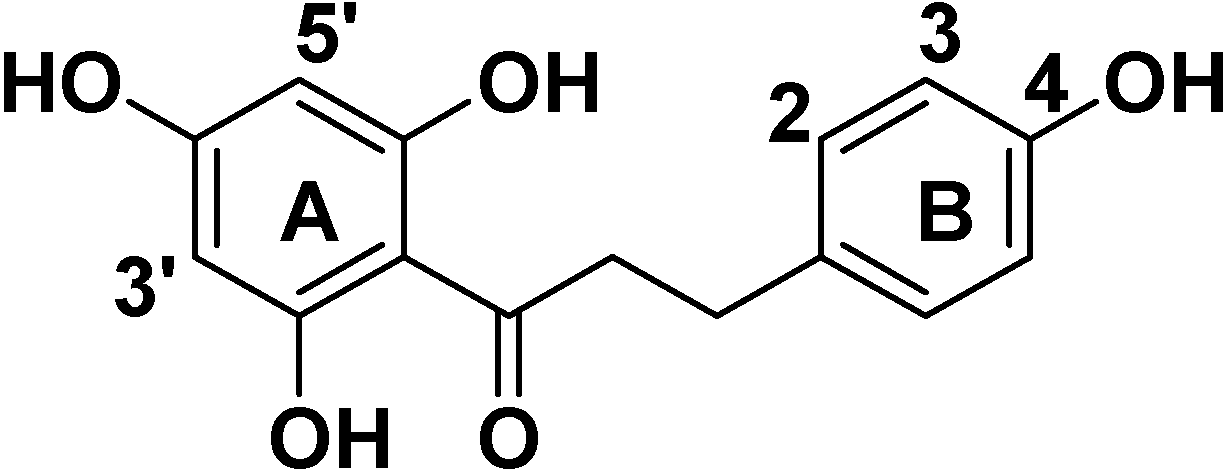
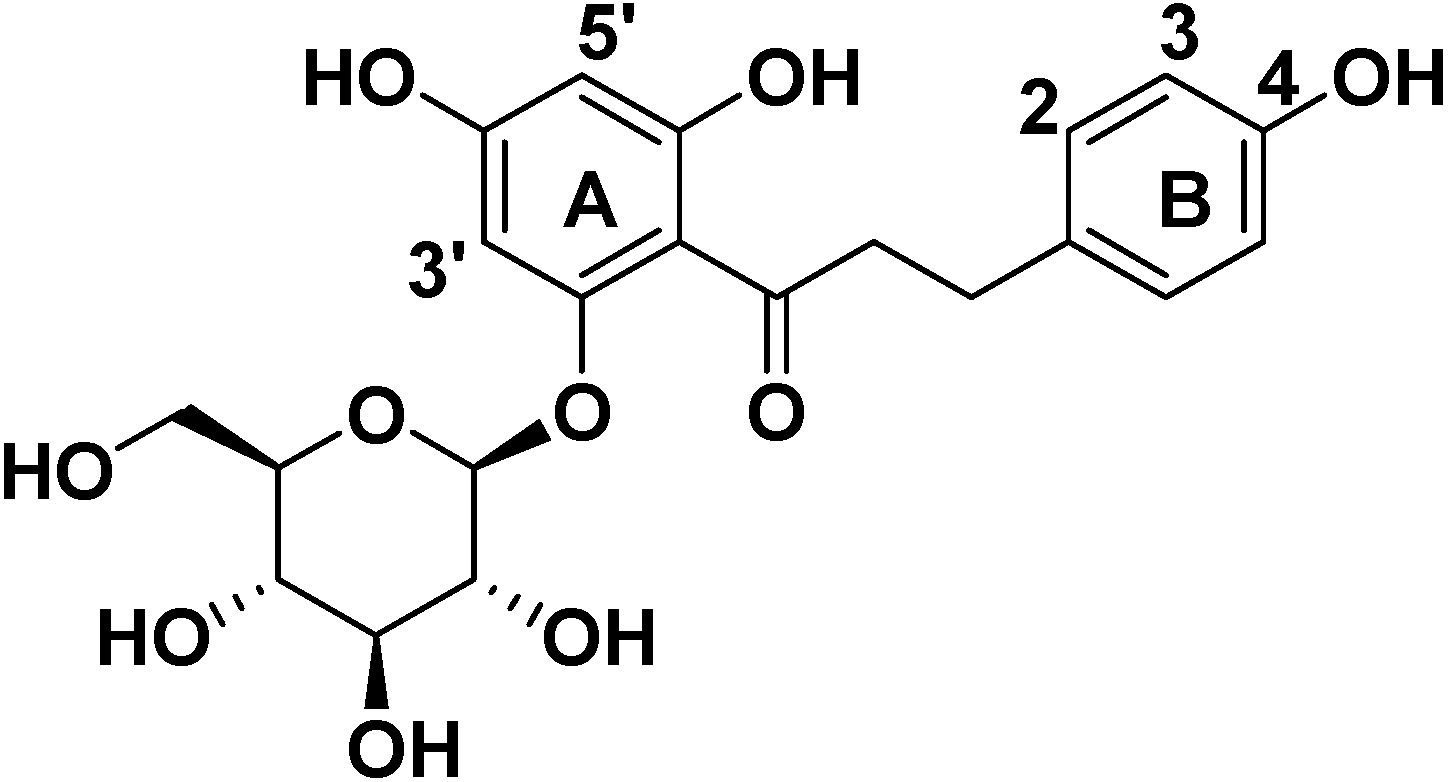
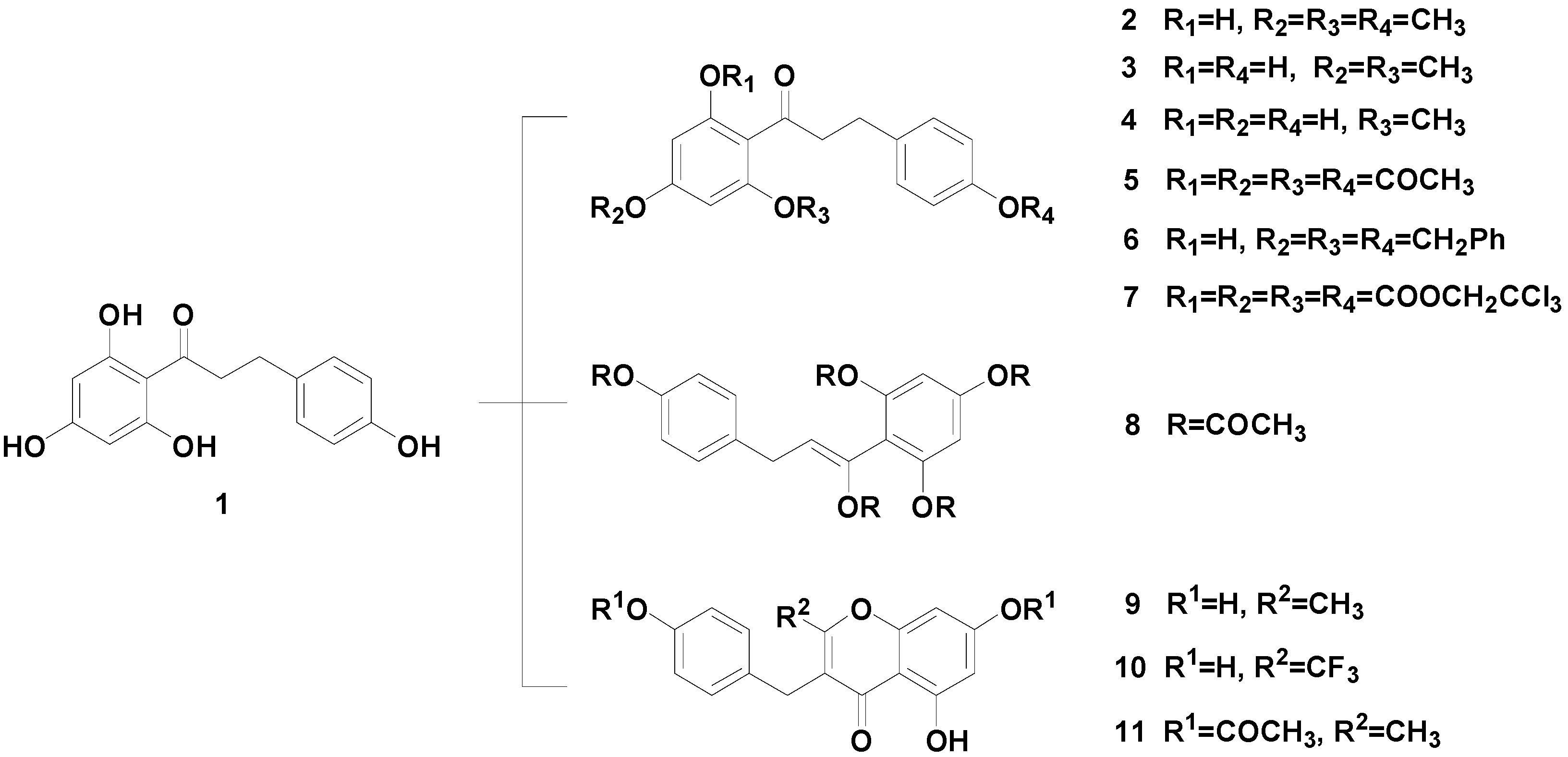
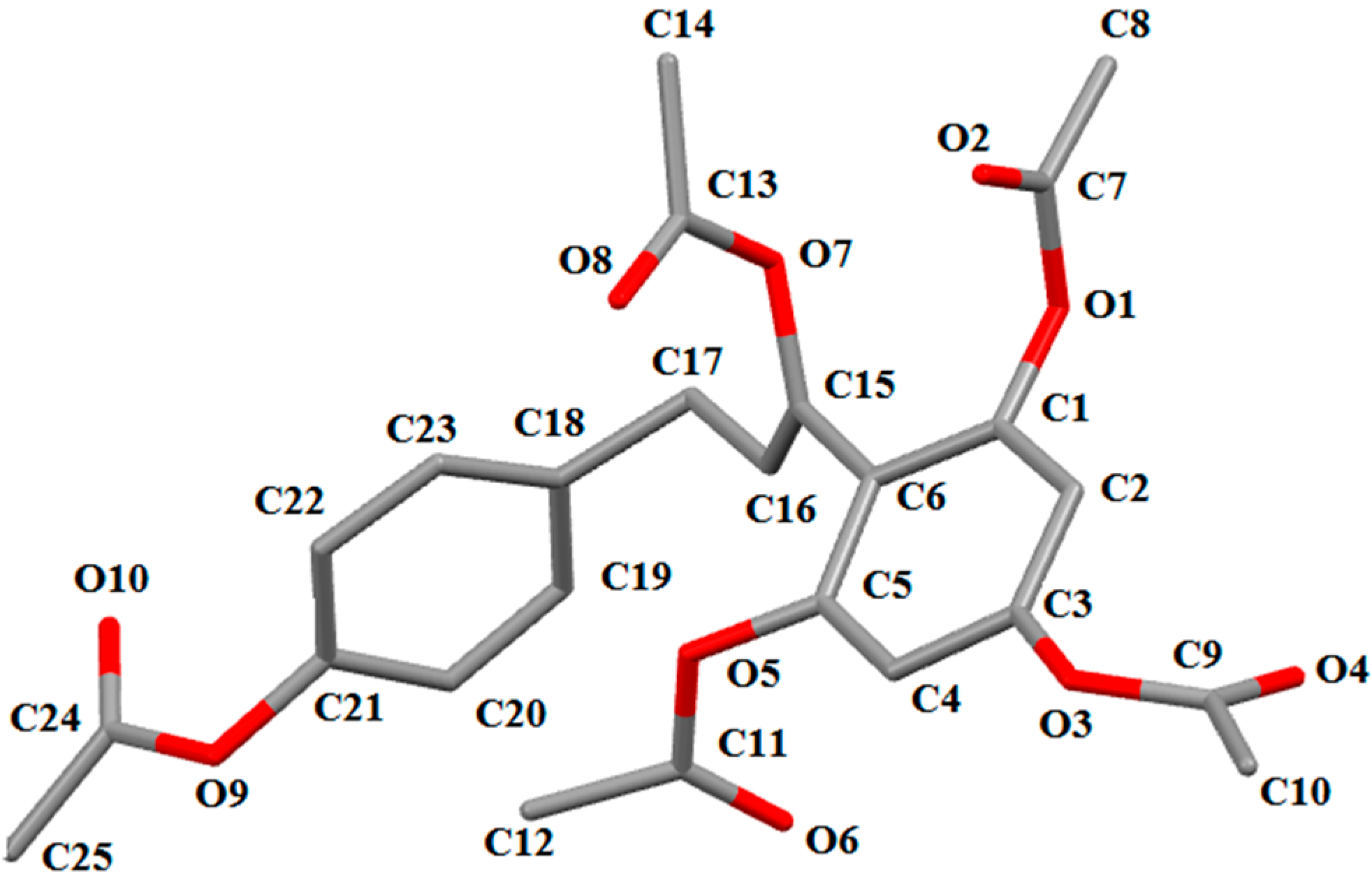
2. Results and Discussion


| Compound | IC50 (μM) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDA-MB-231 | A549 | SPC-A1 | EC109 | MCF-7 | |
| 1 | 30.54 ± 1.95 | 133 ˃ 100 | 147 ˃ 100 | 148 ˃ 100 | 78.64 ± 0.86 |
| 2 | 14.73 ± 1.28 | 132 ˃ 100 | 131 ˃ 100 | 138 ˃ 100 | 117 ˃ 100 |
| 3 | 14.43 ± 0.99 | 18.79 ± 0.54 | 32.90 ± 1.13 | 30.35 ± 0.76 | 8.42 ± 0.74 |
| 4 | 6.93 ± 0.78 | 23.15 ± 0.92 | 39.29 ± 0.78 | 31.79 ± 1.09 | 137 ˃ 100 |
| 5 | 40.886 ± 1.94 | 103 ˃ 100 | 94.35 ± 1.25 | 109 ˃ 100 | 104 ˃ 100 |
| 6 | 37.615 ± 1.15 | 105 ˃ 100 | 96.40 ± 0.38 | 82.48 ± 1.18 | 66.21 ± 1.22 |
| 7 | 0.839 ± 0.83 | 50.81 ± 0.66 | 47.25 ± 0.93 | 42.14 ± 0.88 | 10.16 ± 1.04 |
| 8 | 33.593 ± 0.67 | 95.43 ± 0.83 | 101 ˃ 100 | 95.41 ± 1.39 | 12.49 ± 0.89 |
| 9 | 31.69 ± 1.64 | 62.80 ± 0.96 | 91.5 ± 1.63 | 87.26 ± 0.91 | 88.73 ± 1.62 |
| 10 | 21.27 ± 1.36 | 113 ˃ 100 | 94.50 ± 1.36 | 103 ˃ 100 | 111 ˃ 100 |
| 11 | 92.168 ± 0.86 | 110 ˃ 100 | 97.20 ± 1.45 | 107 ˃ 100 | 108 ˃ 100 |
| Phlorizin | 3.649 ± 1.19 | 120 ˃ 100 | 133 ˃ 100 | 116 ˃ 100 | 15.99 ± 0.67 |
| Docetaxel | 0.998 ± 1.04 | 70.30 ± 1.06 | 149 ˃ 100 | 56.44 ± 1.62 | 1.46 ± 1.52 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Information
3.2. MTT Assay
3.3. Synthesis
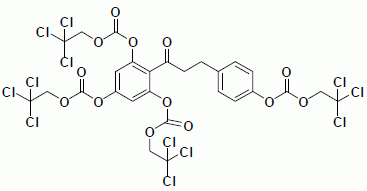
3.3.1. Carbonic Acid 3,5-bis-(2,2,2-Trichloroethoxycarbonyloxy)-2-{3-[4-(2,2,2-trichloroethoxy-carbonyloxy) phenyl] propionyl}phenyl Ester 2,2,2-Trichloroethyl Ester (7)
3.3.2. 5,7-Dihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-2-trifluoromethylchromen-4-one (10)
3.4. X-ray Crystallographic Data
3.5. Characterization of Compounds 2–6, 8, 9 and 11
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Le Marchand, L.; Murphy, S.P.; Hankin, J.H.; Wilkens, L.R.; Kolonel, L.N. Intake of flavonoids and lung cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, J.; Liu, R.H. Apple phytochemicals and their health benefits. Nutr. J. 2004, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosch, C.; Halbwirth, H.; Stich, K. Phloridzin: Biosynthesis, distribution and physiological relevance in plants. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setala, K.M.E. Composition and Method for Rational Treatment of Cancer. U.S. Patent 4,555,806, 21 January 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Forman, S.A.; Verkman, A.S.; Dix, J.A.; Solomon, A.K. Interaction of phloretin with the anion transport protein of the red blood cell membrane. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1982, 689, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, S.; Kombrabail, M.H.; Prabhananda, B.S. Effect of phloretin on ionophore mediated electroneutral transmembrane translocations of H(+), K(+) and Na(+) in phospholipid vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1510, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oresajo, C.; Stephens, T.; Hino, P.D.; Law, R.M.; Yatskayer, M.; Foltis, P.; Pillai, S.; Pinnell, S.R. Protective effects of a topical antioxidant mixture containing vitamin C, ferulic acid, and phloretin against ultraviolet-induced photodamage in human skin. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2008, 7, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobori, M.; Shinmoto, H.; Tsushida, T.; Shinohara, K. Phloretin-induced apoptosis in B16 melanoma 4A5 cells by inhibition of glucose transmembrane transport. Cancer Lett. 1997, 119, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.A.; Falk, R.E. The efficacy of phloridzin and phloretin on tumor cell growth. Anticancer Res. 1993, 13, 2287–2292. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, W.; Dianjun, W.; Yabin, P.; Dengkui, P.; Weijun, G.; Yuehui, M. Phloretin induced apoptosis of human hepatoma cells SMMC-7721 and its correlative biological mechanisms. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2012, 6, 648–659. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, E.J.; Shin, H.K.; Kwon, D.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Surh, Y.J.; Park, J.H. Induction of apoptosis in HT-29 colon cancer cells by phloretin. J. Med. Food 2007, 10, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H.; Ho, Y.S.; Tsai, C.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Tseng, H.; Wei, P.L.; Lee, C.H.; Liu, R.S.; Lin, S.Y. In vitro and in vivo study of phloretin-induced apoptosis in human liver cancer cells involving inhibition of type II glucose transporter. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 2210–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenkranz, J.R.; Lewis, N.G.; Kahn, C.R.; Roth, J. Phlorizin: A review. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2005, 21, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhorukov, V.L.; Kurschner, M.; Dilsky, S.; Lisec, T.; Wagner, B.; Schenk, W.A.; Benz, R.; Zimmermann, U. Phloretin-induced changes of lipophilic ion transport across the plasma membrane of mammalian cells. Biophys. J. 2001, 81, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezk, B.M.; Haenen, G.R.; van der Vijgh, W.J.; Bast, A. The antioxidant activity of phloretin: The disclosure of a new antioxidant pharmacophore in flavonoids. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 295, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenta, C.; Cladera, J.; O’Shea, P.; Hadgraft, J. Effect of phloretin on the percutaneous absorption of lignocaine across human skin. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 90, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, G.; Heidi, H.; Bernd, S.; Dirk, H.; Karl, S. Opinion on the possible role of flavonoids as energy escape valves: Novel tools for nature’s Swiss army knife? Plant Sci. 2010, 178, 297–301. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; Wu, C.H.; Chou, H.M.; Wang, Y.J.; Tseng, H.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, L.C.; Lee, C.H.; Lin, S.Y. Molecular mechanisms of econazole-induced toxicity on human colon cancer cells: G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and caspase-8 independent apoptotic signaling pathways. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2005, 43, 1483–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holla, B.S.; Poojary, K.N.; Bhat, K.S.; Ashok, M.; Poojary, B. Synthesis and anticancer activity studies on some 2-chloro-1,4-bis-(5-substituted-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-ylmethyleneoxy)phenylene derivatives. Indian J. Chem. 2005, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Li, Z.-W.; Zhang, W.; Xu, R.; Gao, F.; Liu, Y.-F.; Li, Y.-J. Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Biological Evaluation of a Series of Phloretin Derivatives. Molecules 2014, 19, 16447-16457. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191016447
Wang L, Li Z-W, Zhang W, Xu R, Gao F, Liu Y-F, Li Y-J. Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Biological Evaluation of a Series of Phloretin Derivatives. Molecules. 2014; 19(10):16447-16457. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191016447
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Li, Zheng-Wei Li, Wei Zhang, Rui Xu, Fei Gao, Yang-Feng Liu, and Ya-Jun Li. 2014. "Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Biological Evaluation of a Series of Phloretin Derivatives" Molecules 19, no. 10: 16447-16457. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191016447