Electronics 2022, 11(19), 3109; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11193109 - 28 Sep 2022
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 3090
Abstract
Network intrusion, such as denial of service, probing attacks, and phishing, comprises some of the complex threats that have put the online community at risk. The increase in the number of these attacks has given rise to a serious interest in the research
[...] Read more.
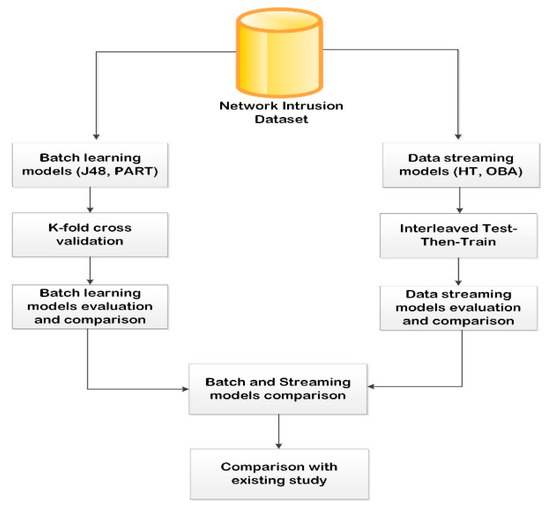
Network intrusion, such as denial of service, probing attacks, and phishing, comprises some of the complex threats that have put the online community at risk. The increase in the number of these attacks has given rise to a serious interest in the research community to curb the menace. One of the research efforts is to have an intrusion detection mechanism in place. Batch learning and data streaming are approaches used for processing the huge amount of data required for proper intrusion detection. Batch learning, despite its advantages, has been faulted for poor scalability due to the constant re-training of new training instances. Hence, this paper seeks to conduct a comparative study using selected batch learning and data streaming algorithms. The batch learning and data streaming algorithms considered are J48, projective adaptive resonance theory (PART), Hoeffding tree (HT) and OzaBagAdwin (OBA). Furthermore, binary and multiclass classification problems are considered for the tested algorithms. Experimental results show that data streaming algorithms achieved considerably higher performance in binary classification problems when compared with batch learning algorithms. Specifically, binary classification produced J48 (94.73), PART (92.83), HT (98.38), and OBA (99.67), and multiclass classification produced J48 (87.66), PART (87.05), HT (71.98), OBA (82.80) based on accuracy. Hence, the use of data streaming algorithms to solve the scalability issue and allow real-time detection of network intrusion is highly recommended.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in "Networks" Section)
►
Show Figures