1
Department of Control, Expertise and Services, Faculty of Food and Animal Sciences, “Ion Ionescu de la Brad” University of Life Sciences, 8 Mihail Sadoveanu Alley, 700489 Iasi, Romania
2
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Chemistry, “Alexandru Ioan Cuza” University of Iasi, 11 Carol I Blvd, 700506 Iasi, Romania
†
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Agriculture 2023, 13(1), 75; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13010075 - 27 Dec 2022
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 3652
Abstract
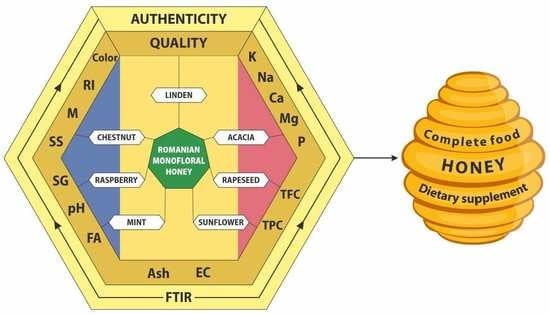
The objective of this research was to evaluate some quality-defining physicochemical parameters (moisture, specific gravity, pH, free acidity, ash, electrical conductivity, total phenols, and total flavonoids content, K, Ca, Mg, Na, and P) of seven Romanian monofloral honeys (linden, acacia, rapeseed, sunflower, mint,
[...] Read more.
The objective of this research was to evaluate some quality-defining physicochemical parameters (moisture, specific gravity, pH, free acidity, ash, electrical conductivity, total phenols, and total flavonoids content, K, Ca, Mg, Na, and P) of seven Romanian monofloral honeys (linden, acacia, rapeseed, sunflower, mint, raspberry, and chestnut) collected in 2017. The investigated quality parameters are mainly within the recommended limits set by standards for honey. Sample analyses indicate the presence of antioxidants, such as TPC (17.9–73.2 mg GAE/100 g) and TFC (0.84–4.81 mg QE/100 g), and high amounts of K (101–1462 mg kg−1), Ca (58.3–167.5 mg kg−1), Mg (24.8–330.6 mg kg−1), Na (94.5–233.3 mg kg−1), and P (34.1–137.2 mg kg−1). The Pearson’s correlations between some parameters (such as color/TFC, color/Mg, color/P, EC/Ash, mm Pfund/TFC, TPC/TFC, K/Ash, P/Mg), together with PCA, HCA, and ANOVA statistics, highlight three main factors that explain the variability in the dataset and could be attributed to stability, mineral, and color/antioxidant contributions. FTIR spectra confirm the authenticity of all the monofloral honeys. The results and data processing confirm the influence of environmental elements (soil, water, air) on the honey composition and highlight the quality of honey, as a complete food and a therapeutic product.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Animal Nutrition and Productions)
▼
Show Figures